Unit 4 Master Disease List: Review
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Microbial agents that cause diseases of the skin and eyes include:
Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Variola virus, Rubeola virus, Varicella Zoster virus, Human Papillomavirus, Herpes simplex virus, Candida albicans
Microbial agents that cause diseases of the Nervous system include:
Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae type B, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium leprae, Clostidriium tetani, Clostridium botulinum, Poliovirus, Lyssavirus, Arbovirus
Microbial agents that cause diseases of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic system include:
Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Bacillus anthracis, Francisella tularensis, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia pestis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Rickettsia ricketsii, Toxoplasma gondii
Microbial agents that cause diseases of the Respiratory system include:
Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Cornynebacterium diphtheria, rhinovirus/coronavirus, Bordetella pertussis, Legionella pneumophila, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Orthomyxovirus, Coccidioides immitis
Microbial agents that cause diseases of the (oral and) Digestive system include:
Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli (O157:H7), Taenia, Giardia lamblia
What can cause necrotizing fasciitis?
Streptococcus pyogenes
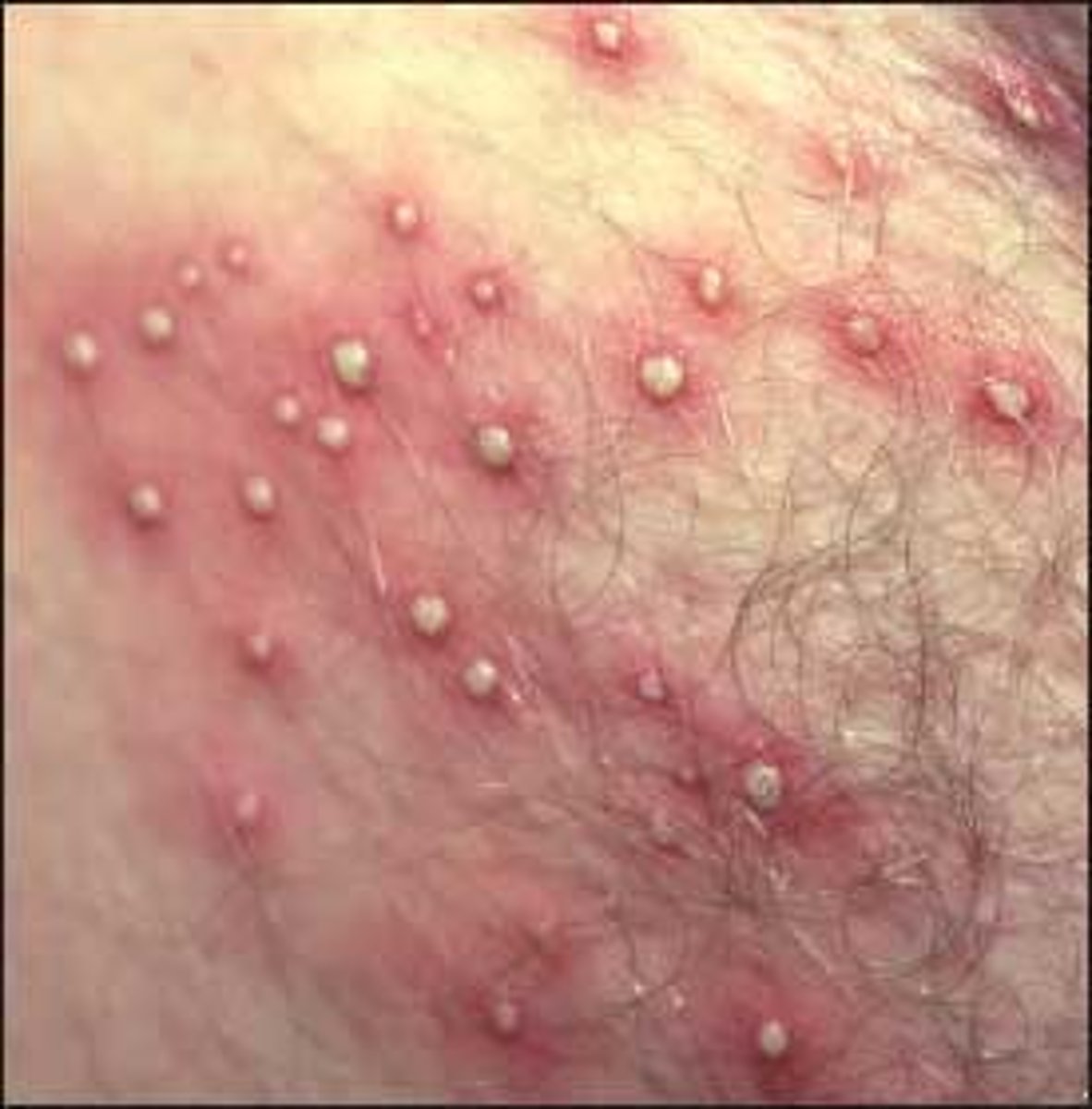
What can cause folliculitis?
Staphylococcus aureus
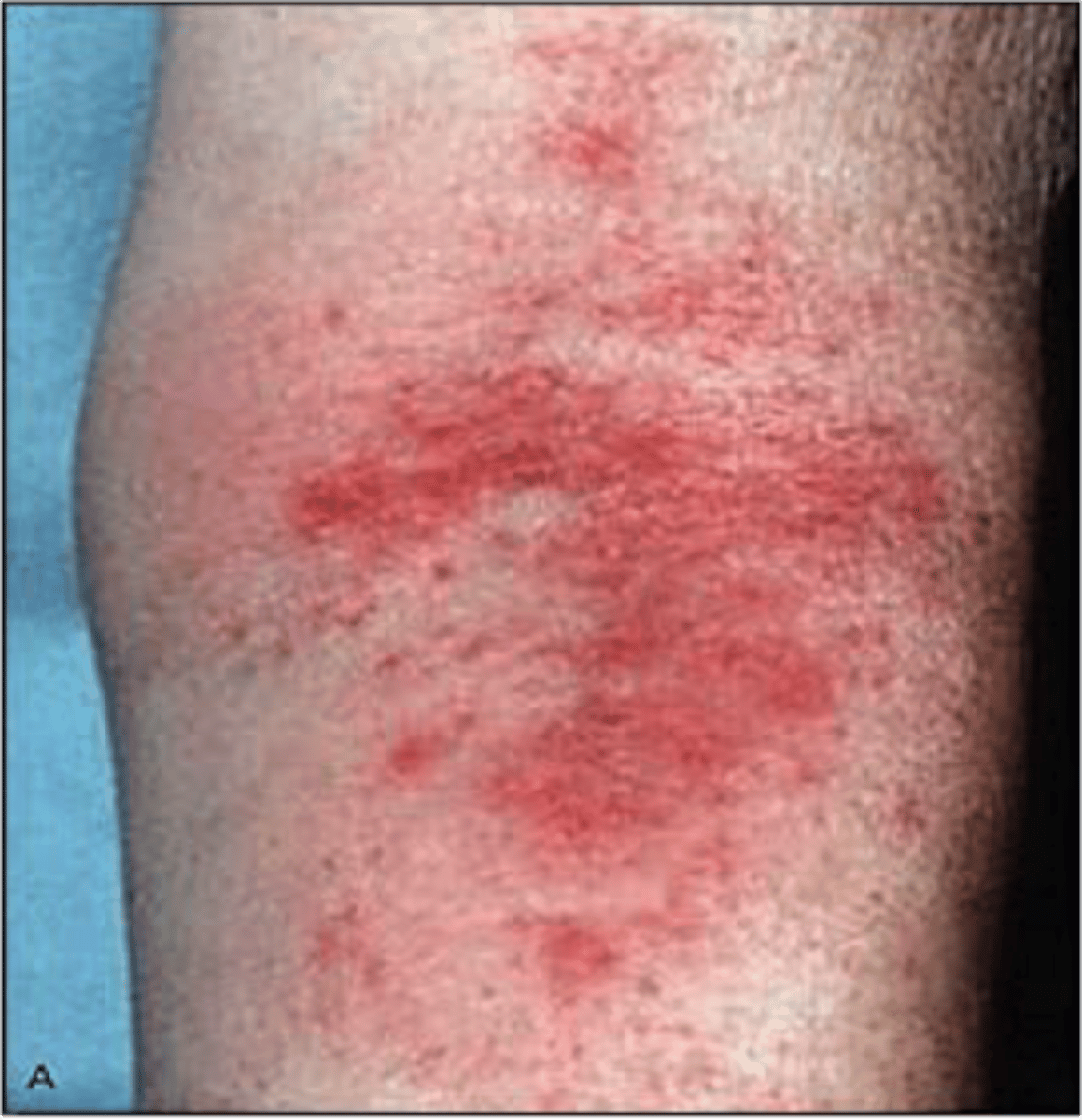
What can cause dermatitis?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
________________________ is considered an opportunistic pathogen and can invade the skin in burn patients and/or the lungs in Cystic Fibrosis patients
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What causes smallpox?
Variola virus
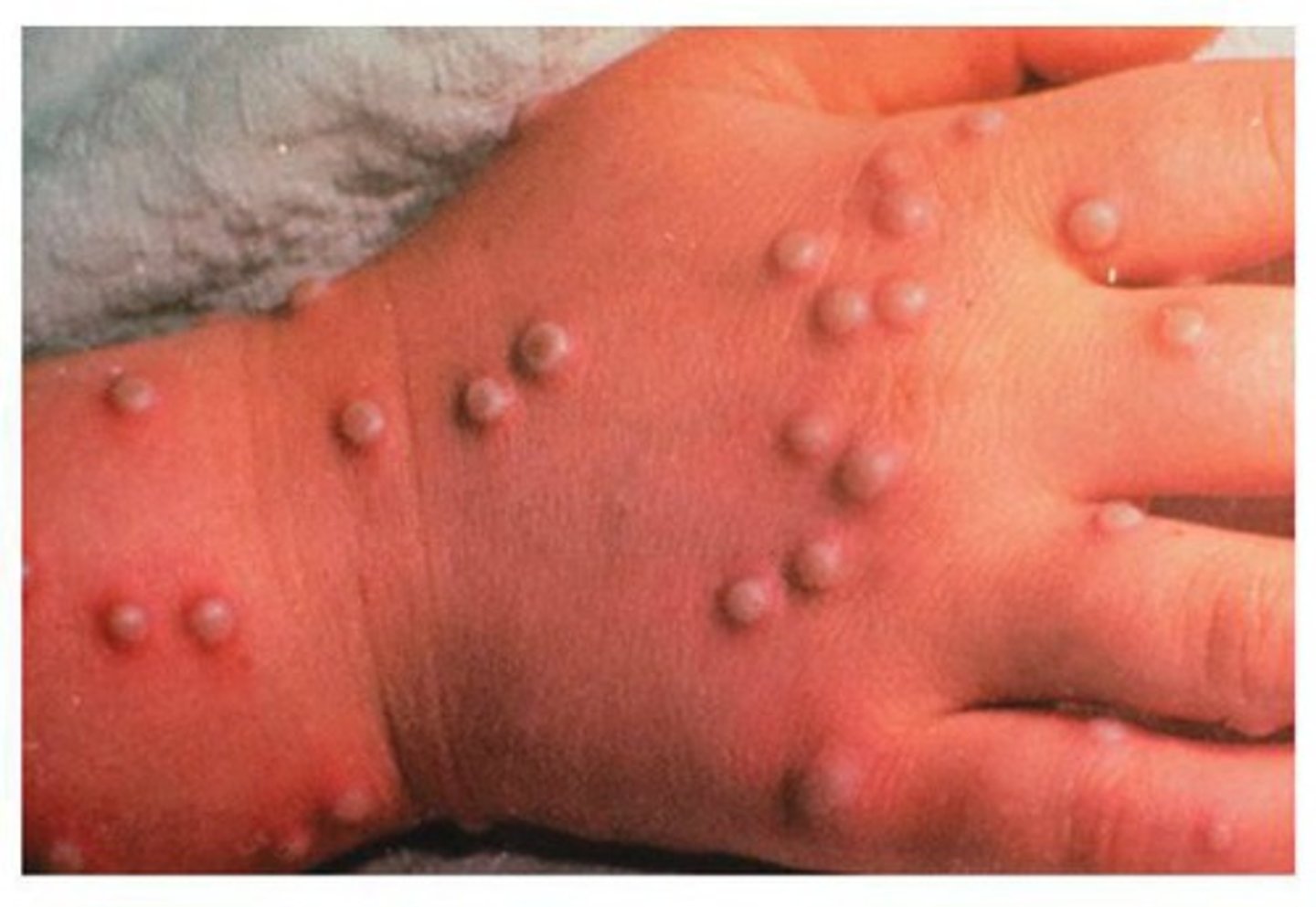
Identify the Agent:
DNA Orthopoxvirus, characterized by pox lesions on the skin and organs
Variola Virus
What causes measles?
Rubeola virus
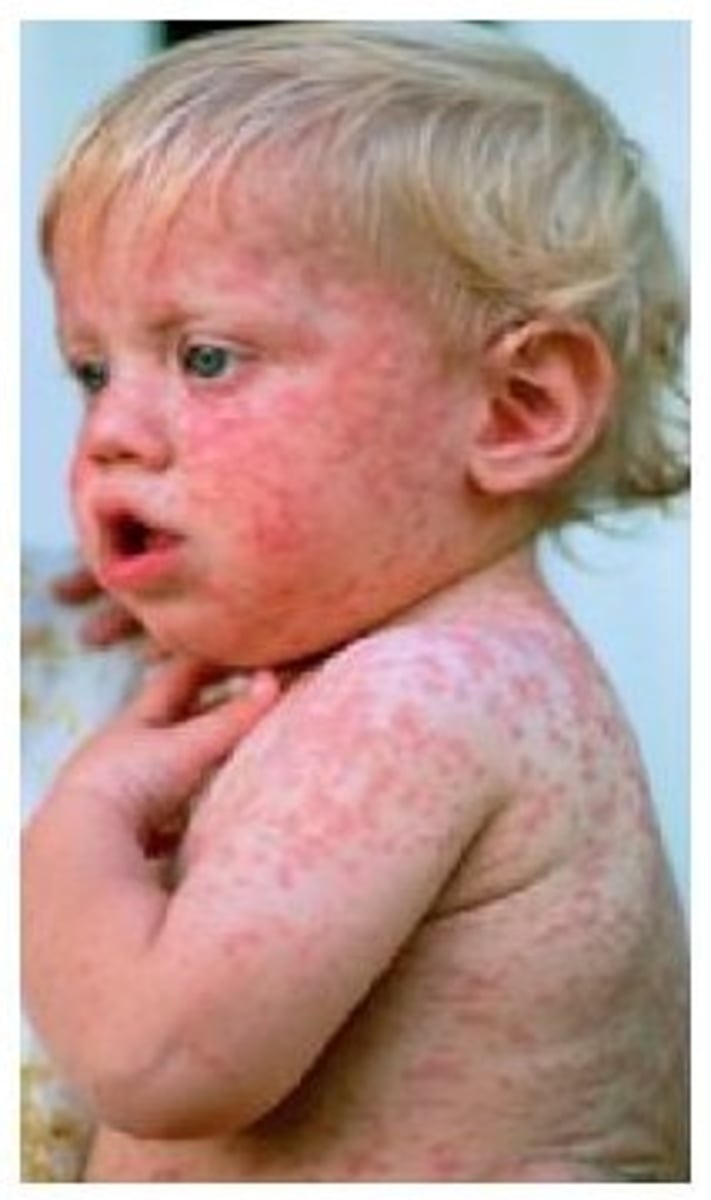
Identify the Agent:
RNA Paramyxovirus characterized by fever, inflammation of the mucous membranes, and rose-colored spots on the skin; also called measles
Rubeola virus
What causes chickenpox?
Varicella zoster virus
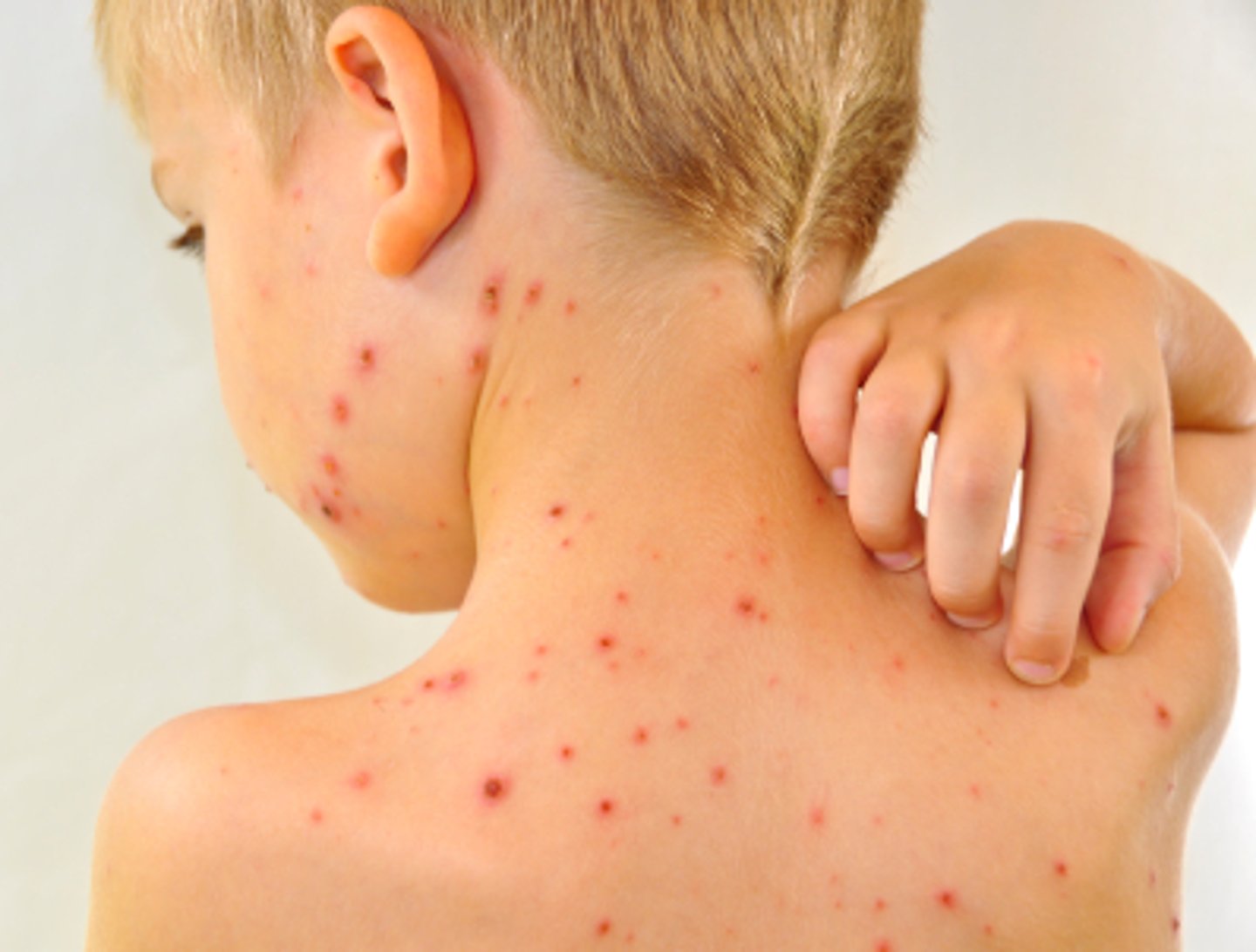
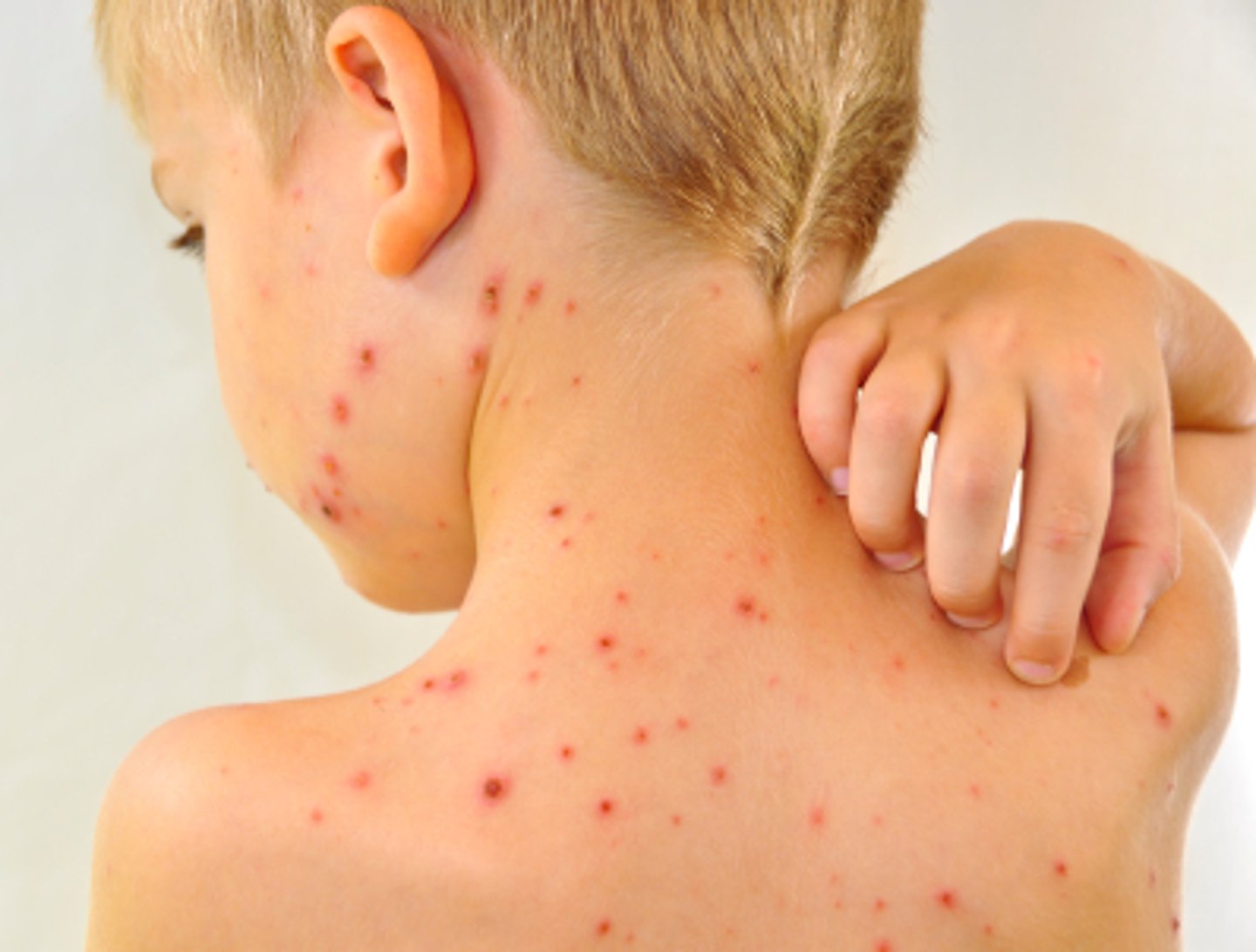
Identify the Agent:
DNA Herpes virus characterized by a fever, headache, malaise, then red itchy lesions on the back and trunk that spread across body
Varicella zoster virus
What causes HPV?
Human papillomavirus
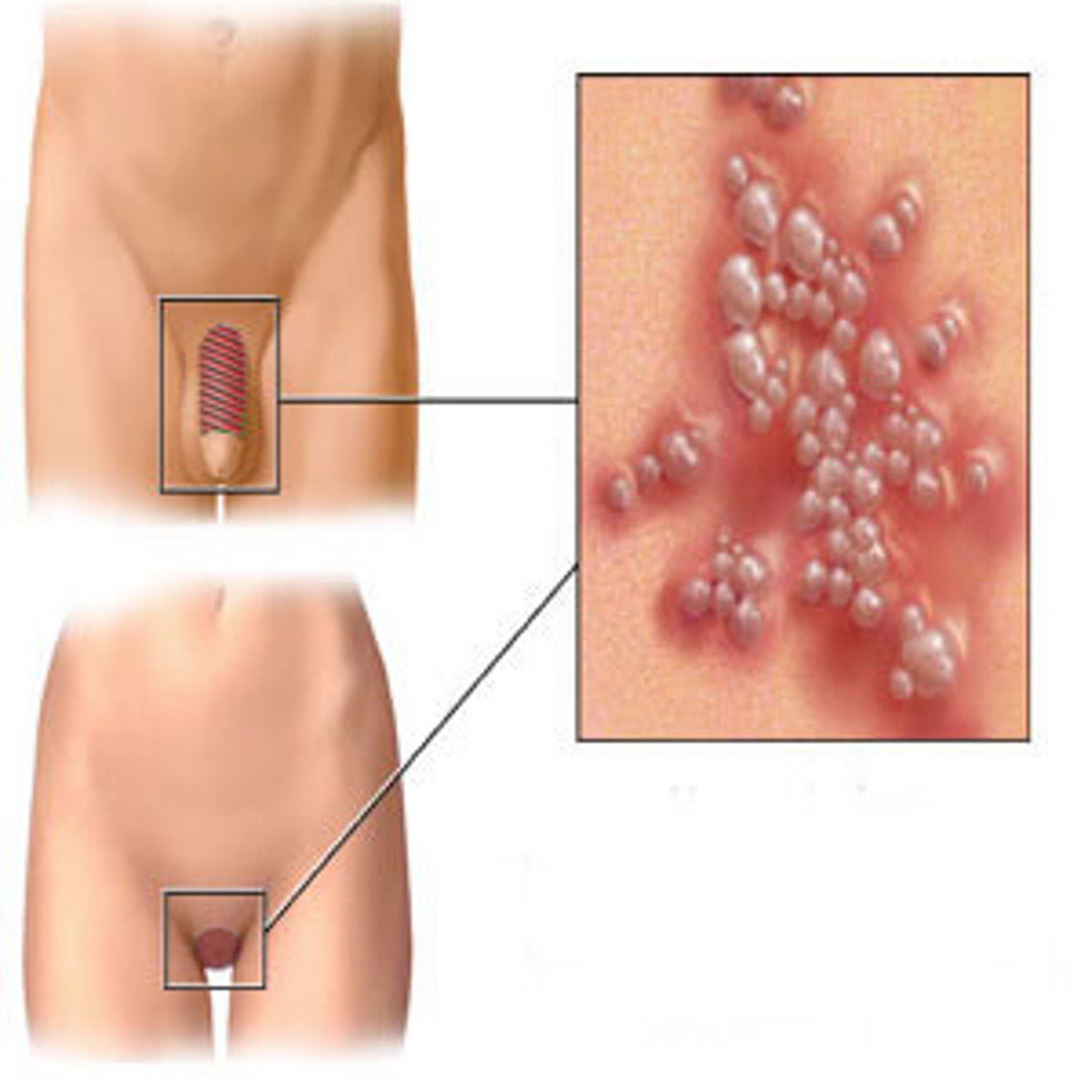
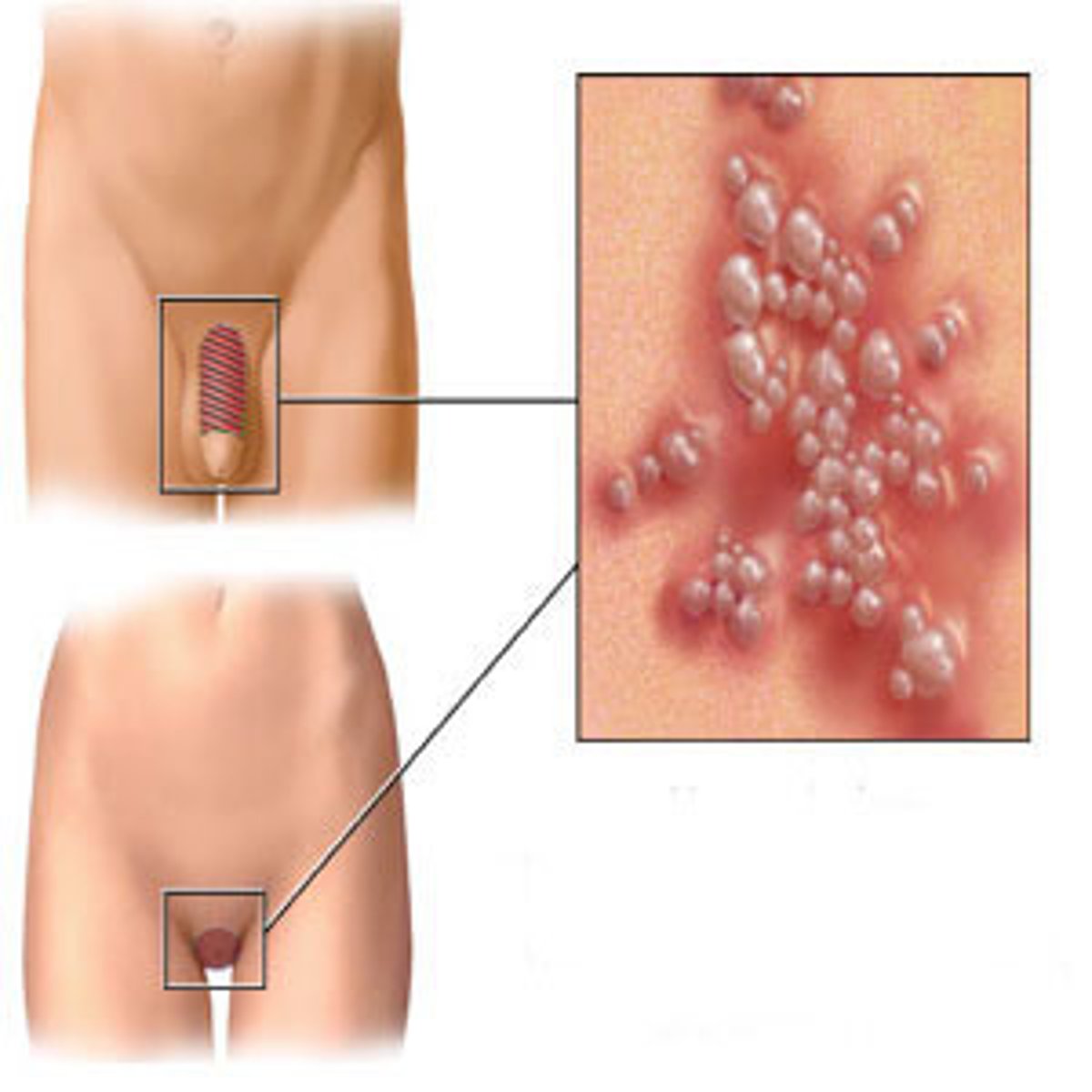
Identify the Agent:
DNA Papovavirus charaterized by (genital) warts
Human papillomavirus
What causes cold sores?
Herpes simplex virus
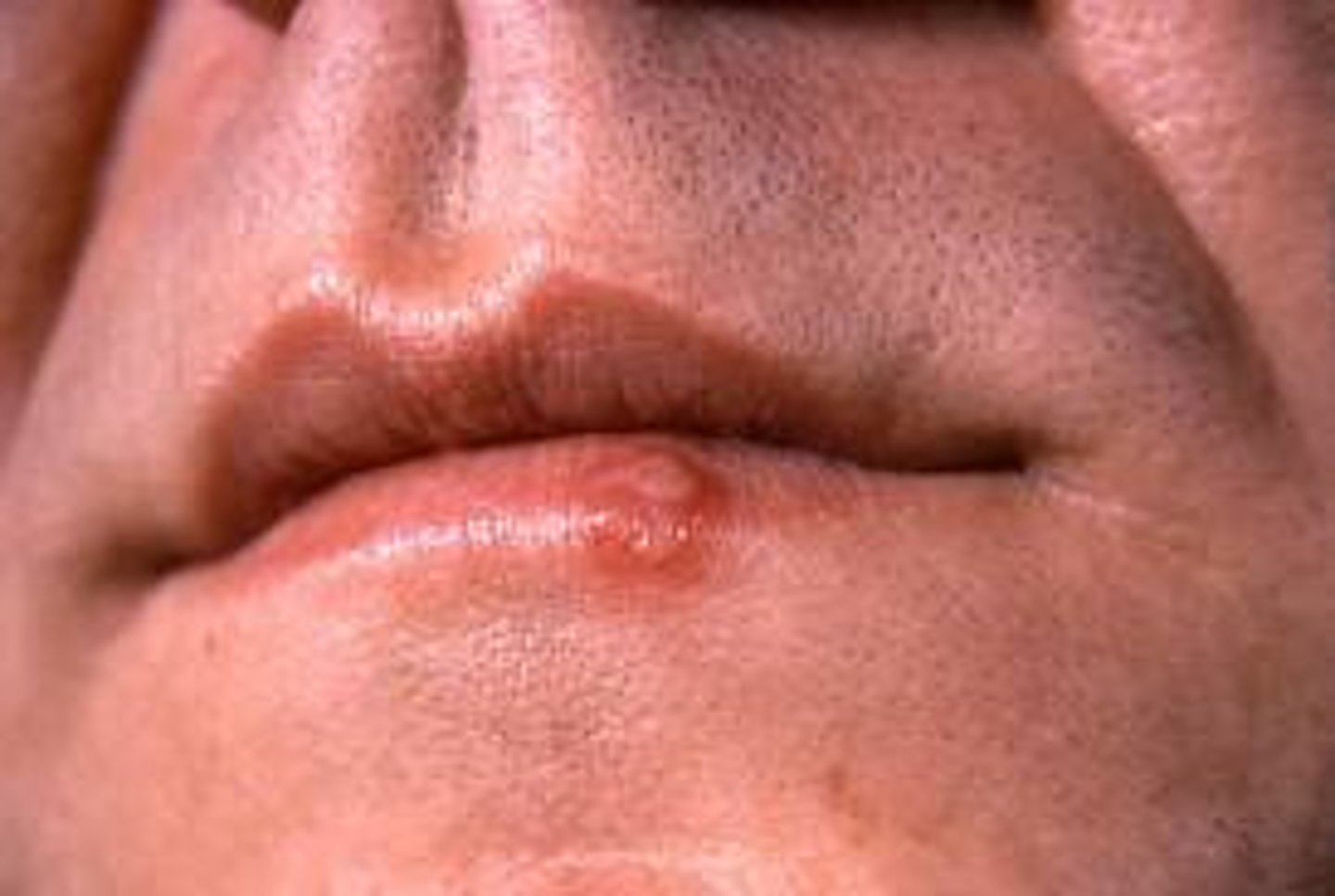
Identify the Agent:
DNA Herpes virus characterized by cold sores or fever blisters
Herpes simplex virus
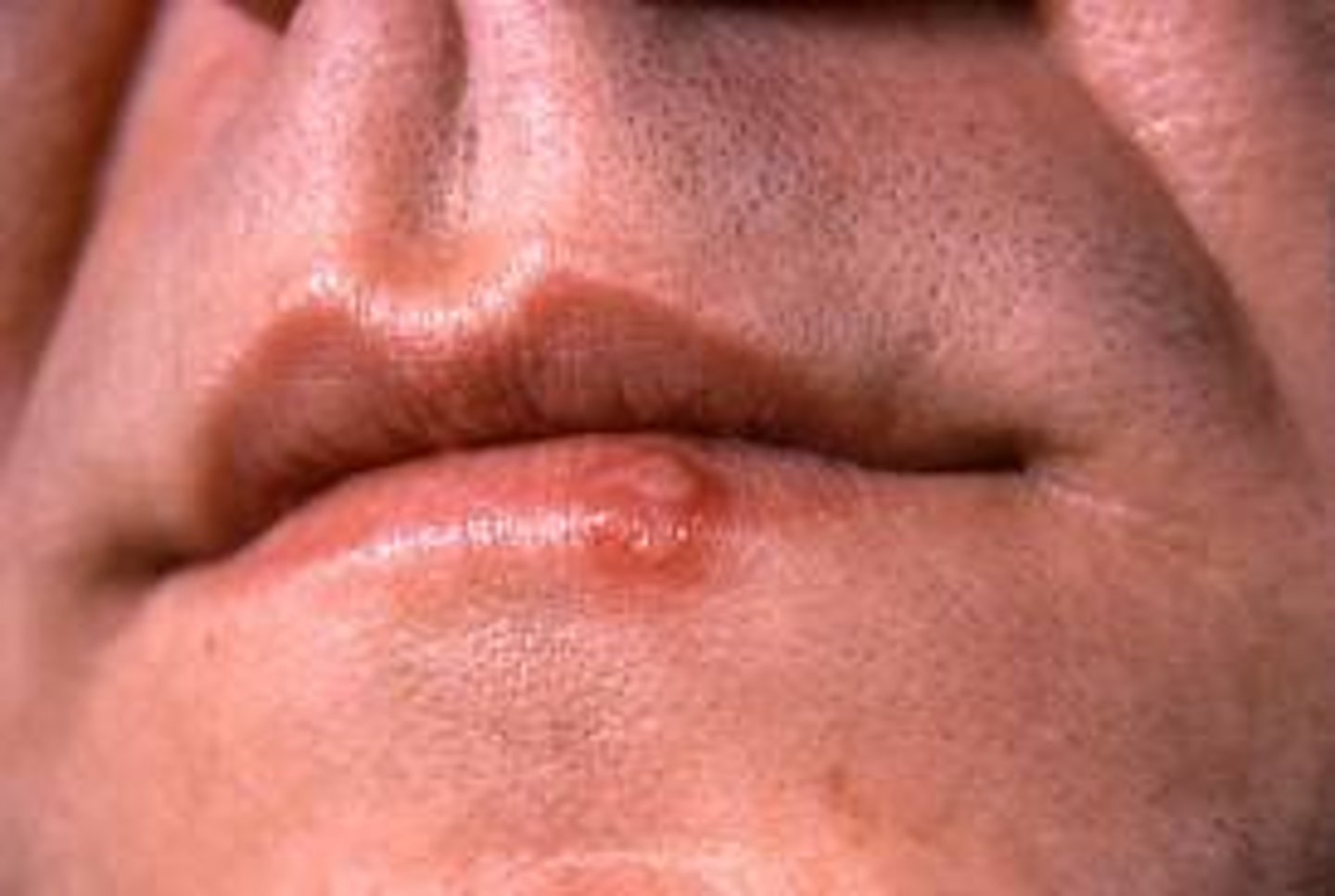
What is HSV-2 associated with?
Genital herpes/infections, perinatal infections
What causes candidiasis?
Candida albicans
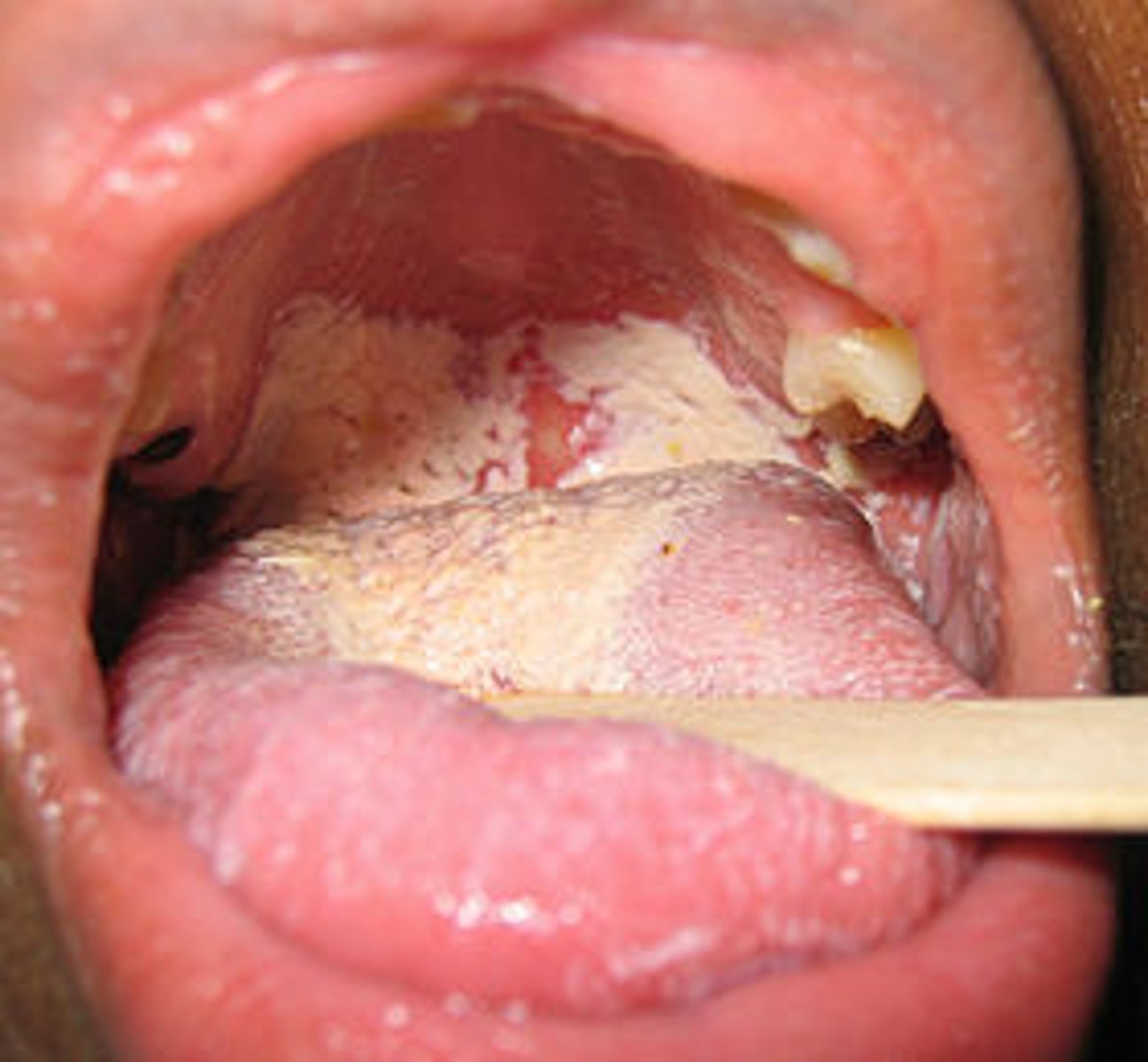
Identify the Agent:
Dimorphic yeast-like fungus (usually kept in check by bacterial microbiota) characterized by oral thrush
Candida albicans
What 3 microbes can cause meningitis?
Hint: Sweets Never Hurt Me (Me = Meningitis)
S. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, H. Influenzae Type B

What causes meningococcal meningitis?
Neisseria meningitidis
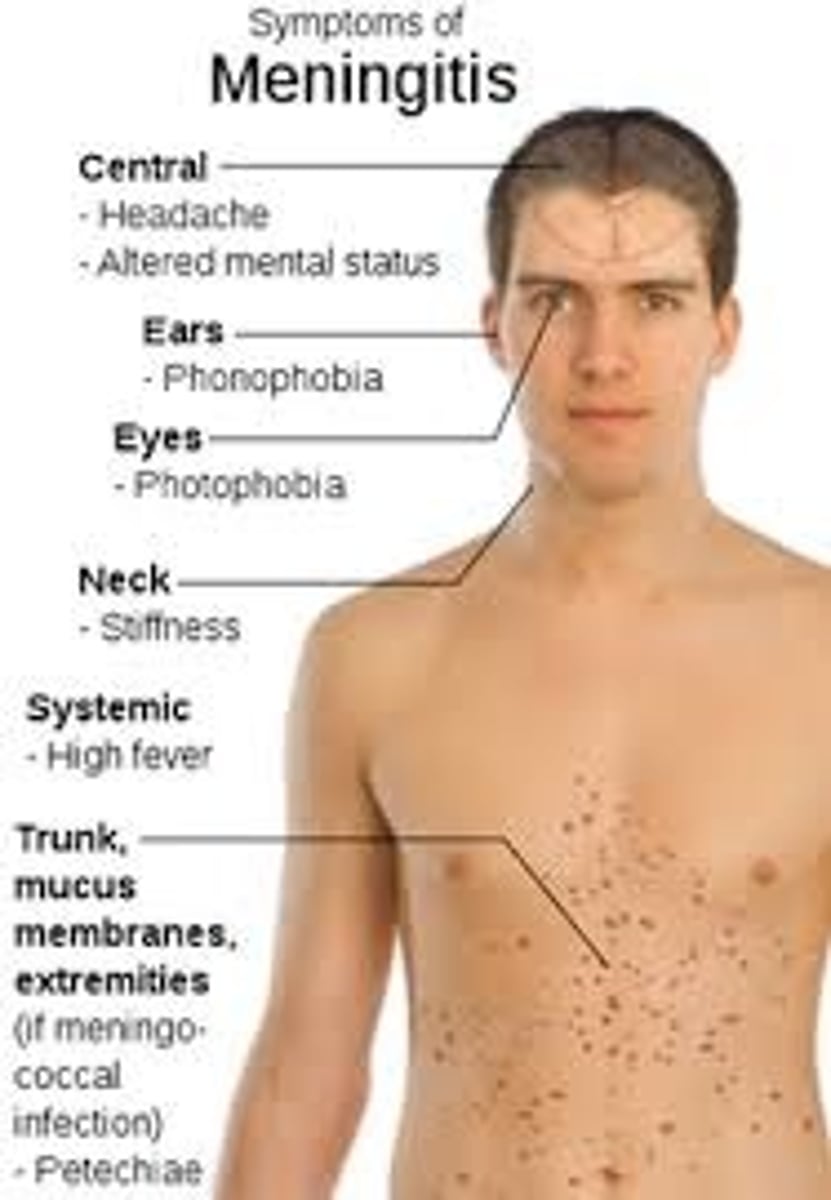
Identify the Agent:
Gram negative diploocci bacterium that is typically found in human nasopharynx characterized by stiff neck, fever, headache and inflamed meninges
Neisseria meningitidis
What causes Haemophilus meningitis?
Haemophilus influenzae

Identify the Agent:
Also known as Hib, gram-negative, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic; characterized by shortness of breath, cough, fever, chills
Haemophilus influenzae

What causes Streptococcal meningitis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
What causes Listeriosis?
Listeria monocytogenes
What causes Hansen's disease/Leprosy
Mycobacterium leprae
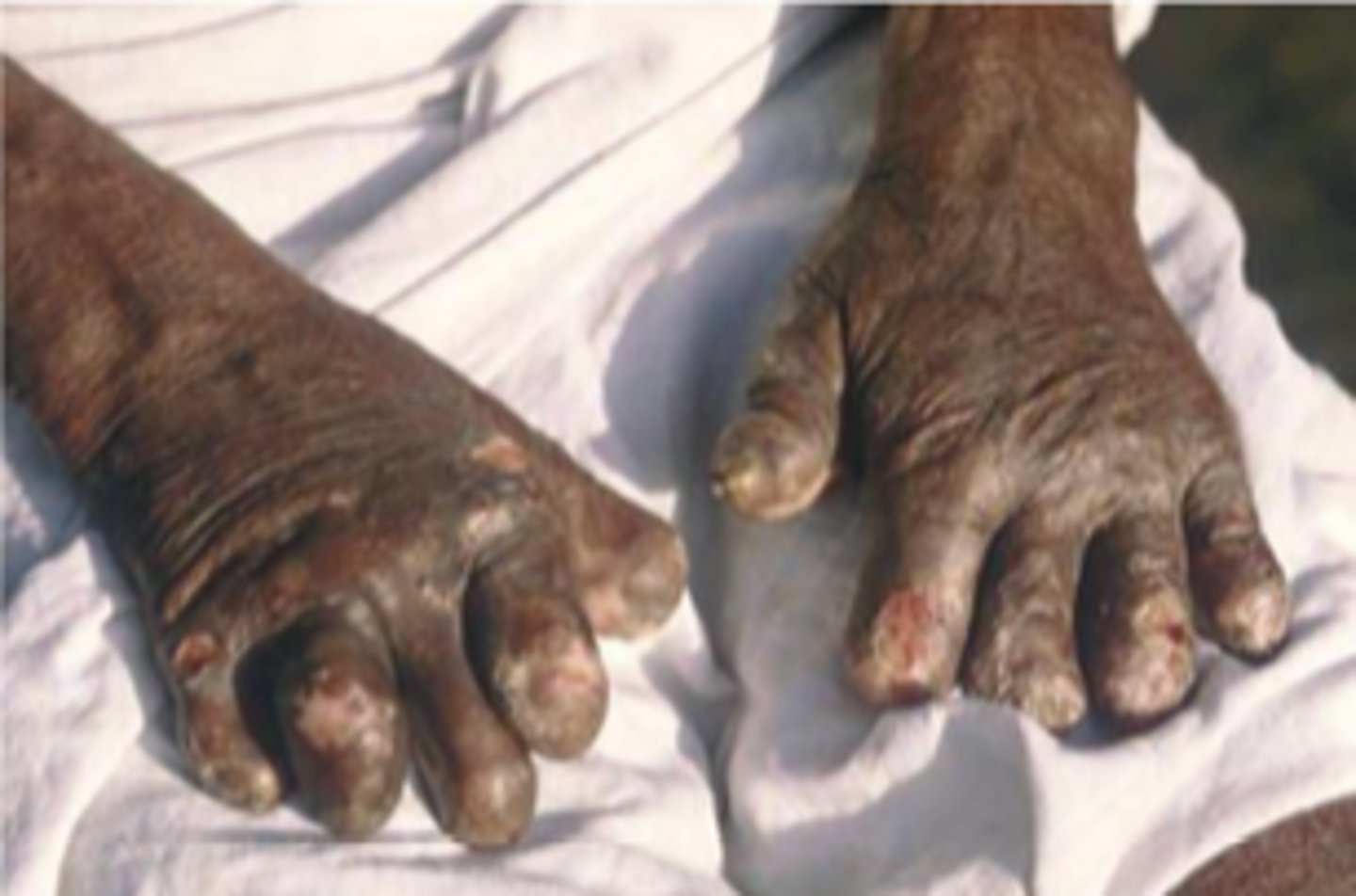
What test might help diagnose Mycobacterium (leprae/tuberculosis)?
Acid Fast
What causes tetanus?
Clostridium tetani
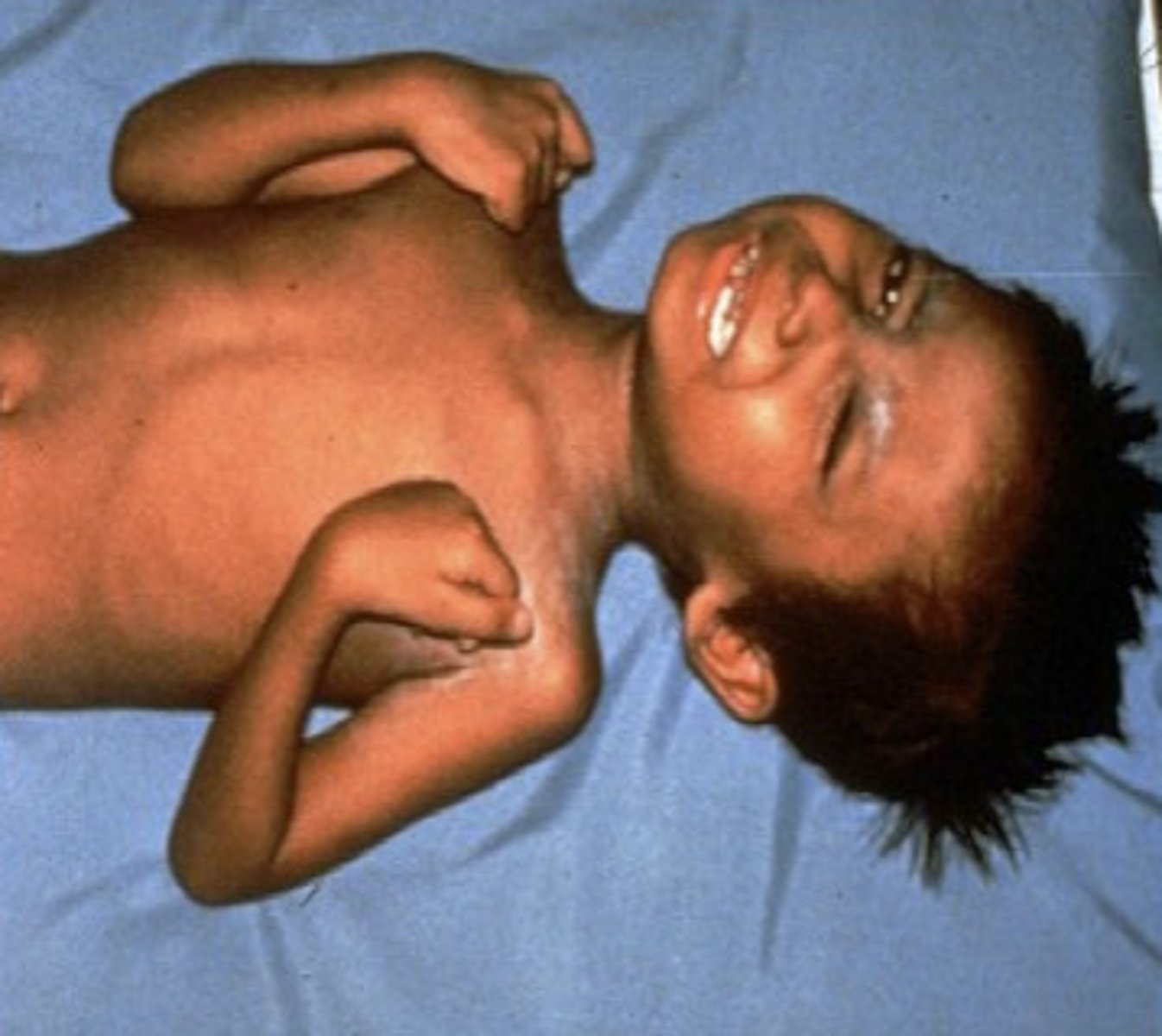
What is the tetanus vaccine made of specifically?
Tetanosplasmin toxins
What does prophylaxis mean?
Treatment given or action taken to prevent disease.
A patient is diagnosed with a disease that could be passed to the family, what should the family do to prevent obtaining it?
Prophylaxis
What causes botulism?
Clostridium botulinum
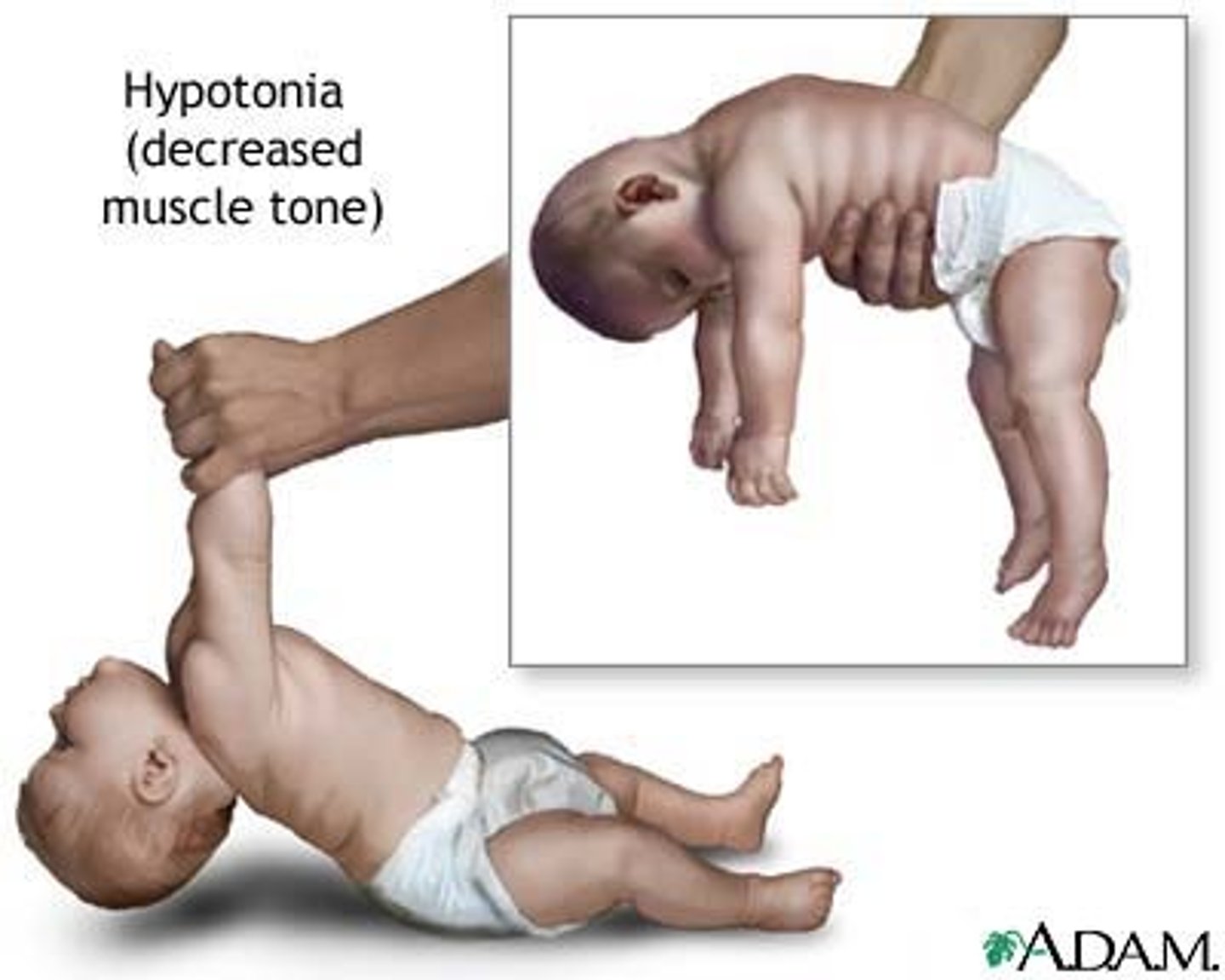
Wat causes Polio?
Poliovirus
Identify the Agent:
RNA Poliovirus; contagious viral illness that in its most severe form causes nerve injury leading to paralysis, difficulty breathing and sometimes deat
Poliovirus
What causes rabies?
Rhabdovirus

Identify the Agent:
RNA Lyssavirus bullet shaped virus; Characterized by flu-like symptoms, malaise in the first stages but can develop into delirium and abnormal rabid behavior if left untreated
Rhabdovirus

What causes West Nile Virus/Encephalitis?
Flavivirus
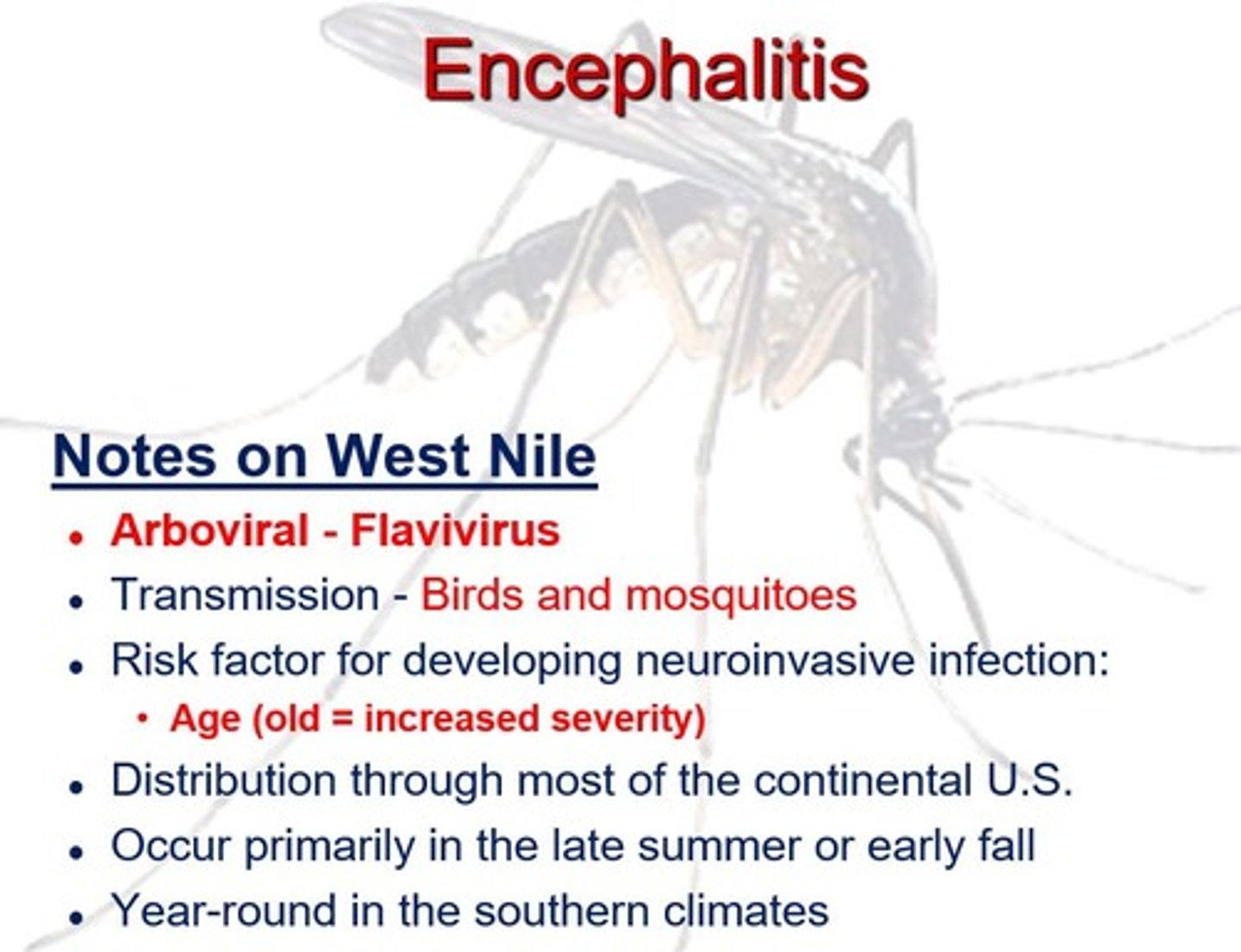
Identify the Agent:
RNA Arbovirus typically transmitted via mosquitoes and characterized by fever, headache, and stiff neck; can lead to encephilitis
Flavivirus

S. aureus and S. pneumoniae are the two most common, gram positive isolates from cultures in __________________
Sepsis
What causes Rheumatic fever?
Streptococcus pyogenes
Subacute endocarditis is most commonly caused by what organism?
Streptococcus viridians

Acute endocarditis is most commonly caused by what organism?
Staphylococcus aureus

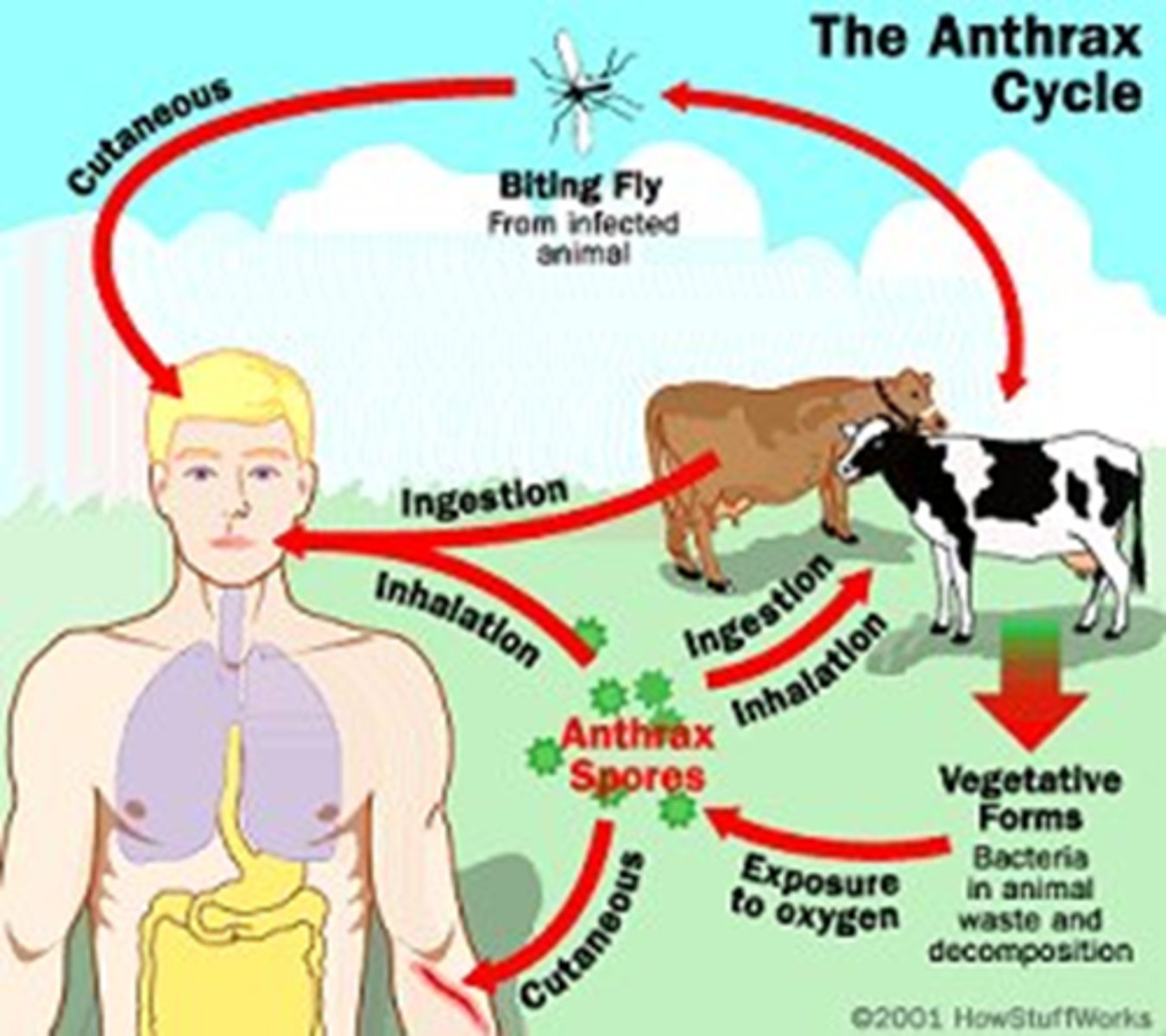
What causes anthrax?
Bacillus anthracis
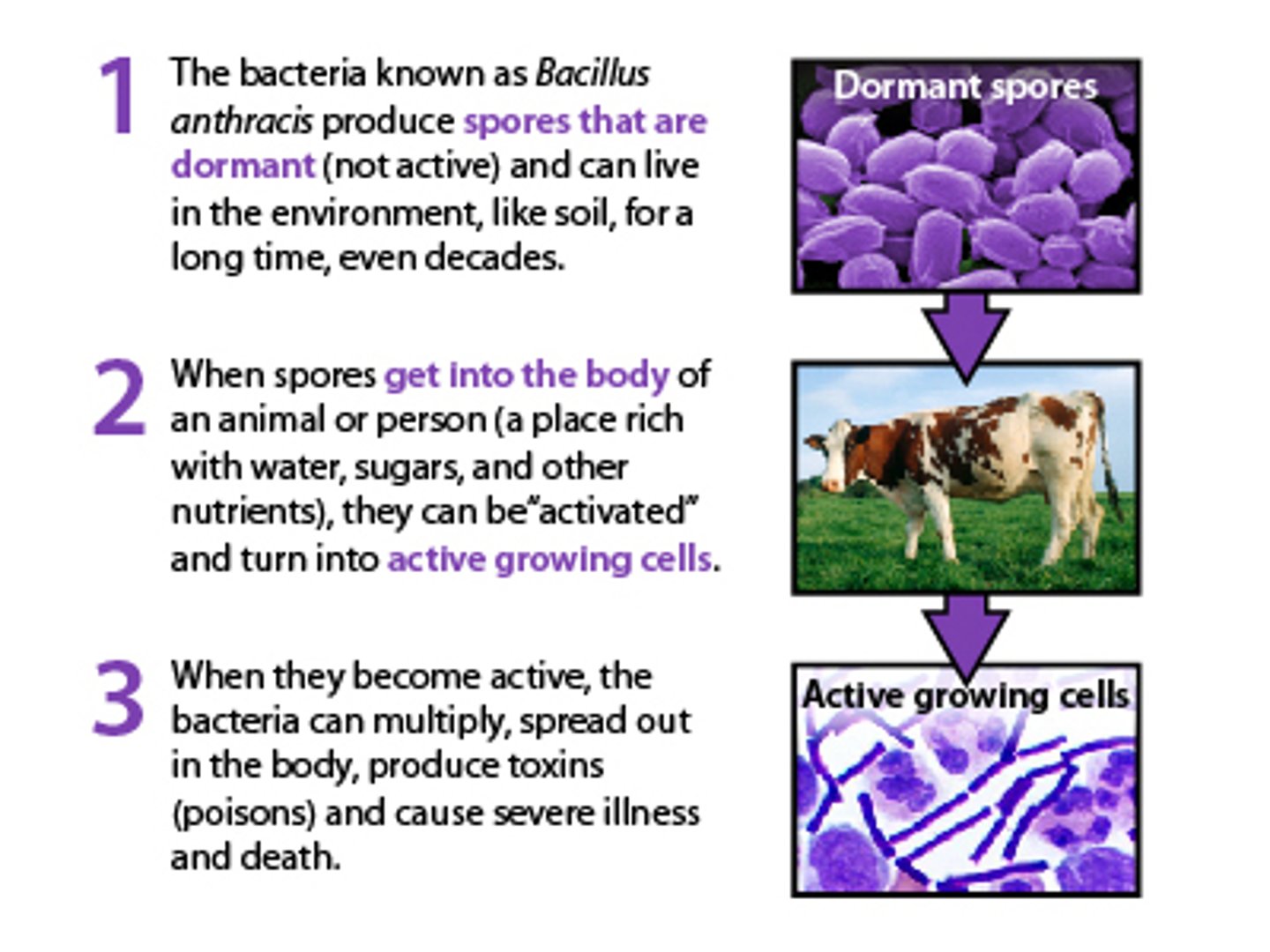
What are the three types of anthrax?
~ Cutaneous (most common)
~ Gastrointestinal (least common)
~ Inhalation (most deadly)
What causes Tularemia?
Francisella tularensis
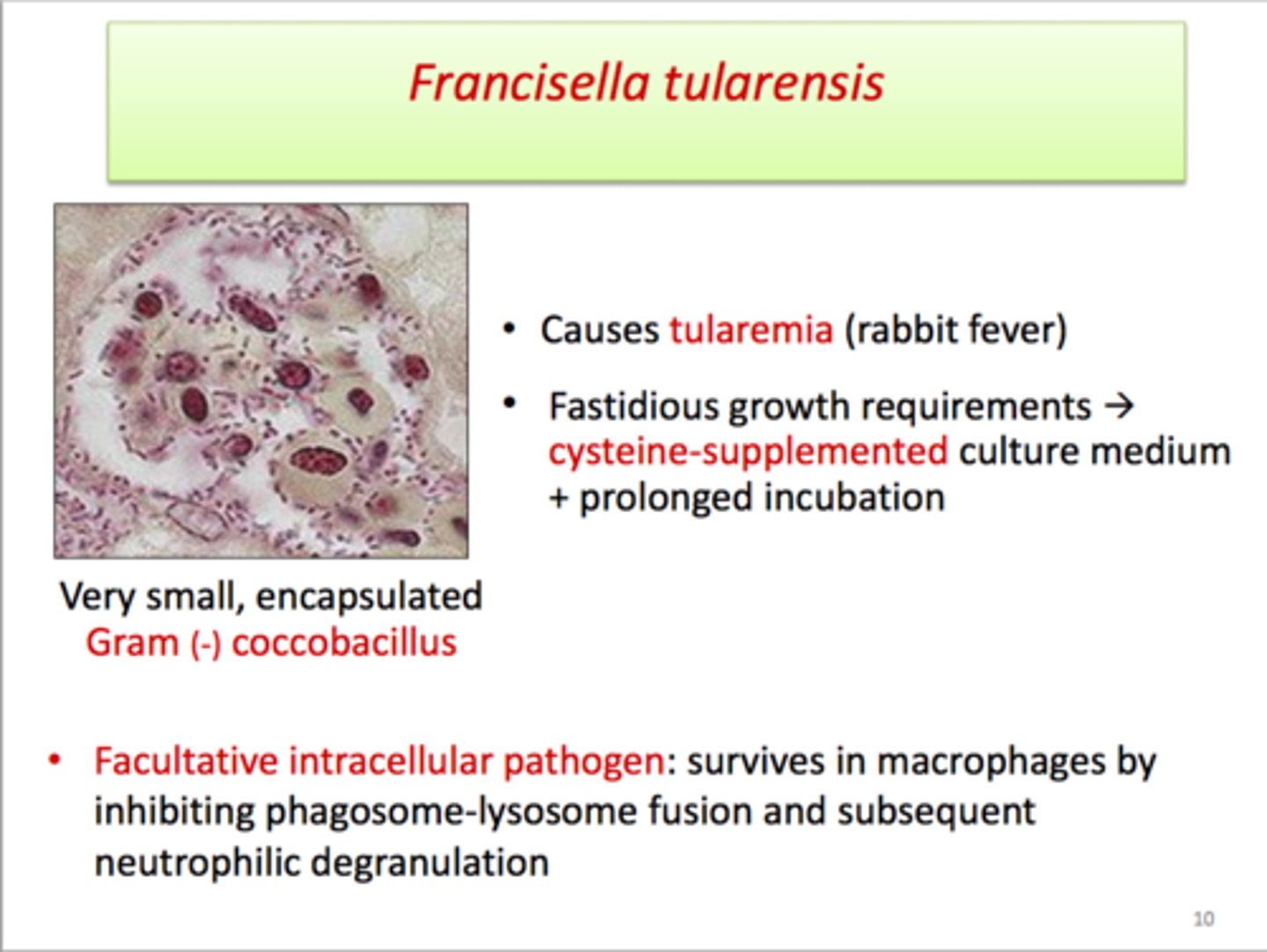
What is another name for tularemia?
Rabbit fever

What can cause gas gangrene?
Clostridium perfringens

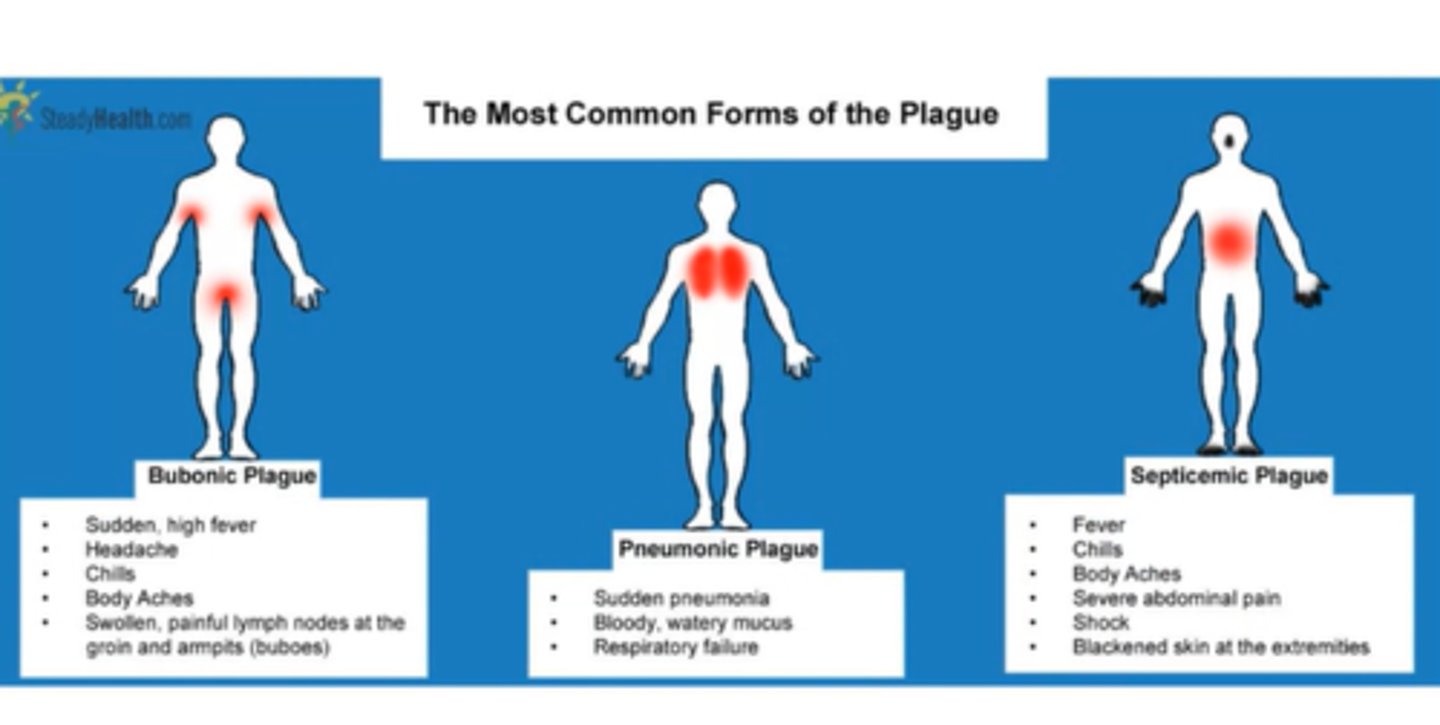
What causes plague?
Yersinia pestis
What are the 3 types of plague?
Bubonic, septicemic, pneumonic
What causes lyme disease?
Borrelia burgdorferi
A fungus like microbe spread through the dusty soil would most likely be?
Coccidioidmycosis
What causes toxoplasmosis?
Toxoplasma gondii
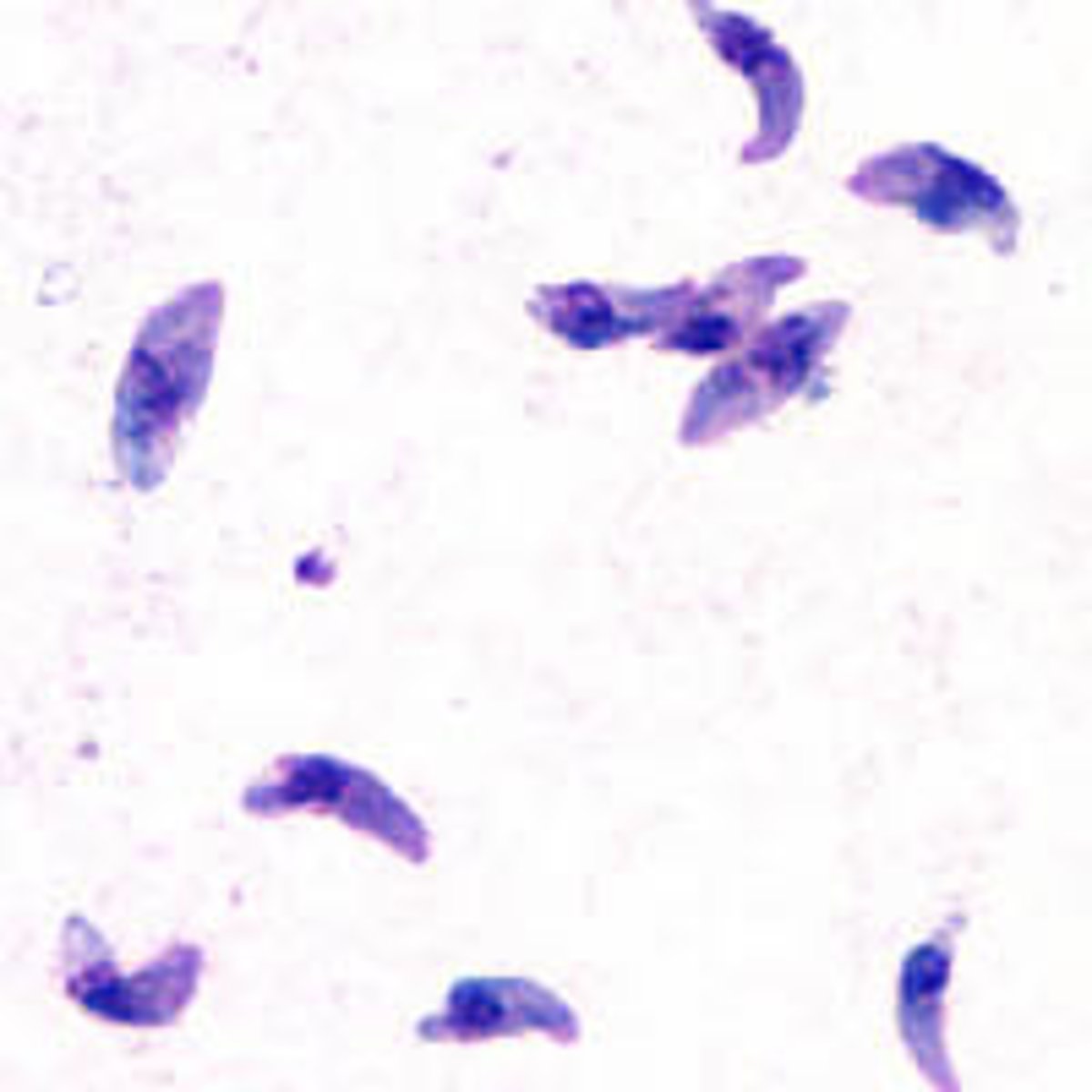
Is Coccidioidmycosis anaerobic or aerobic?
Aerobic
What causes Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
Rickettsia rickettsii
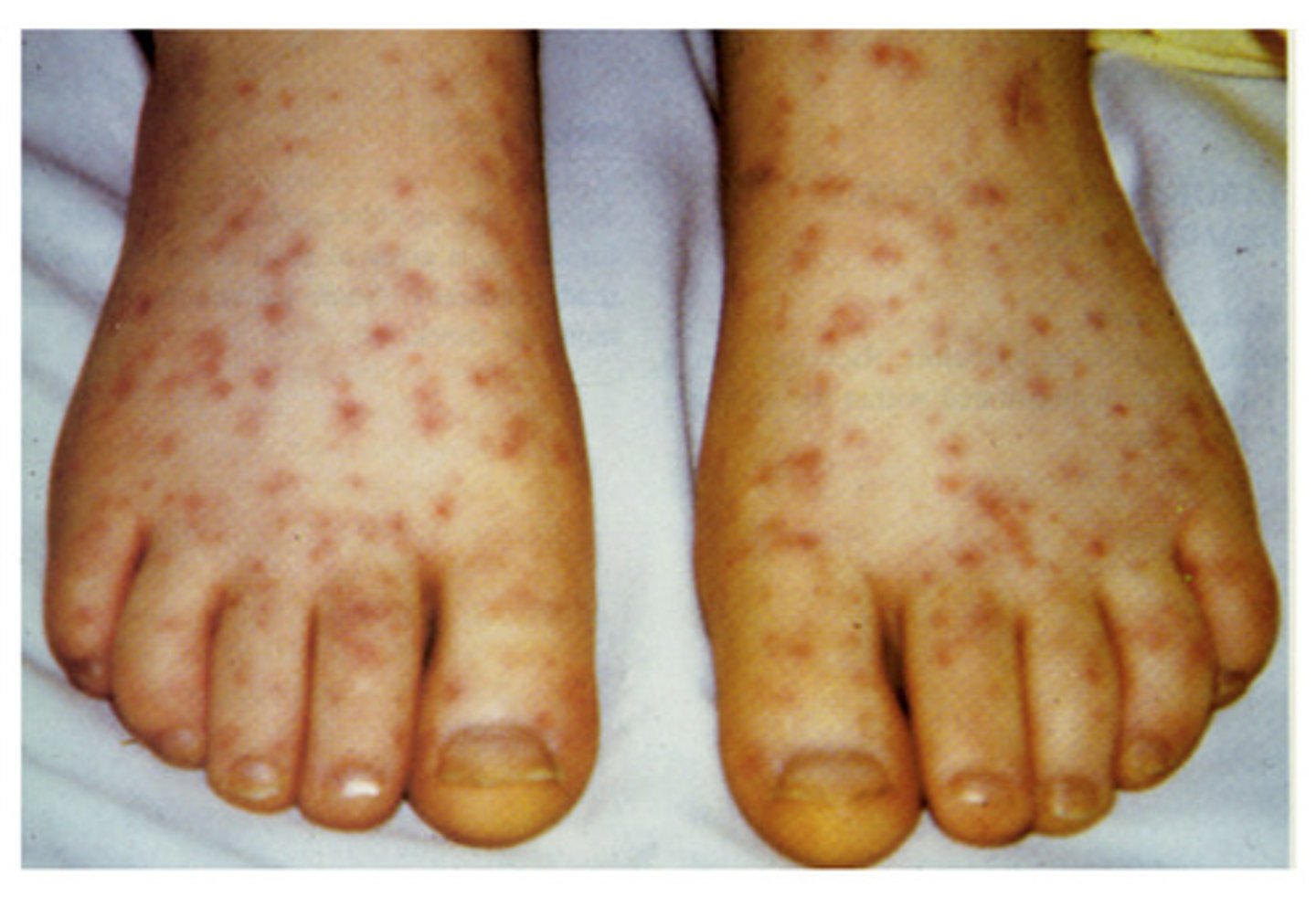
What causes Strep Pharyngitis?
Group A Streptococcus pyogenes
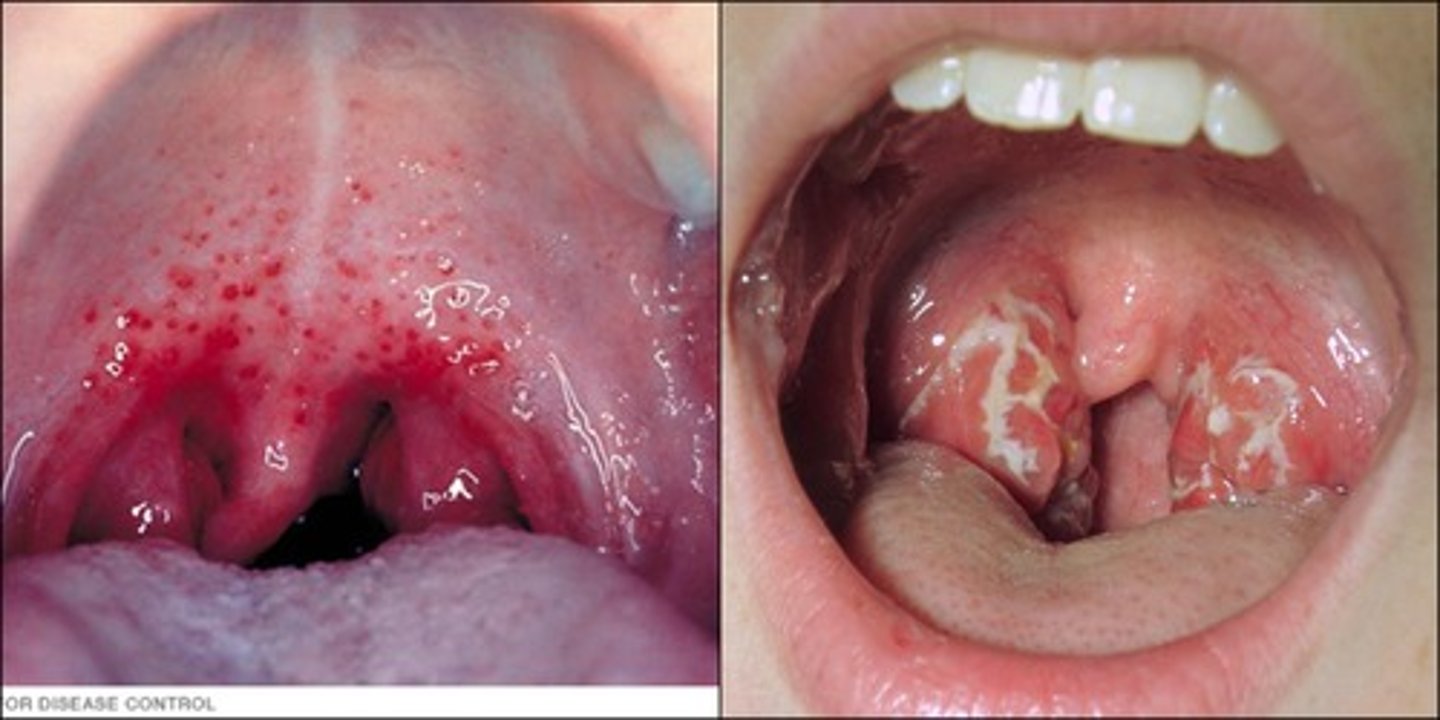
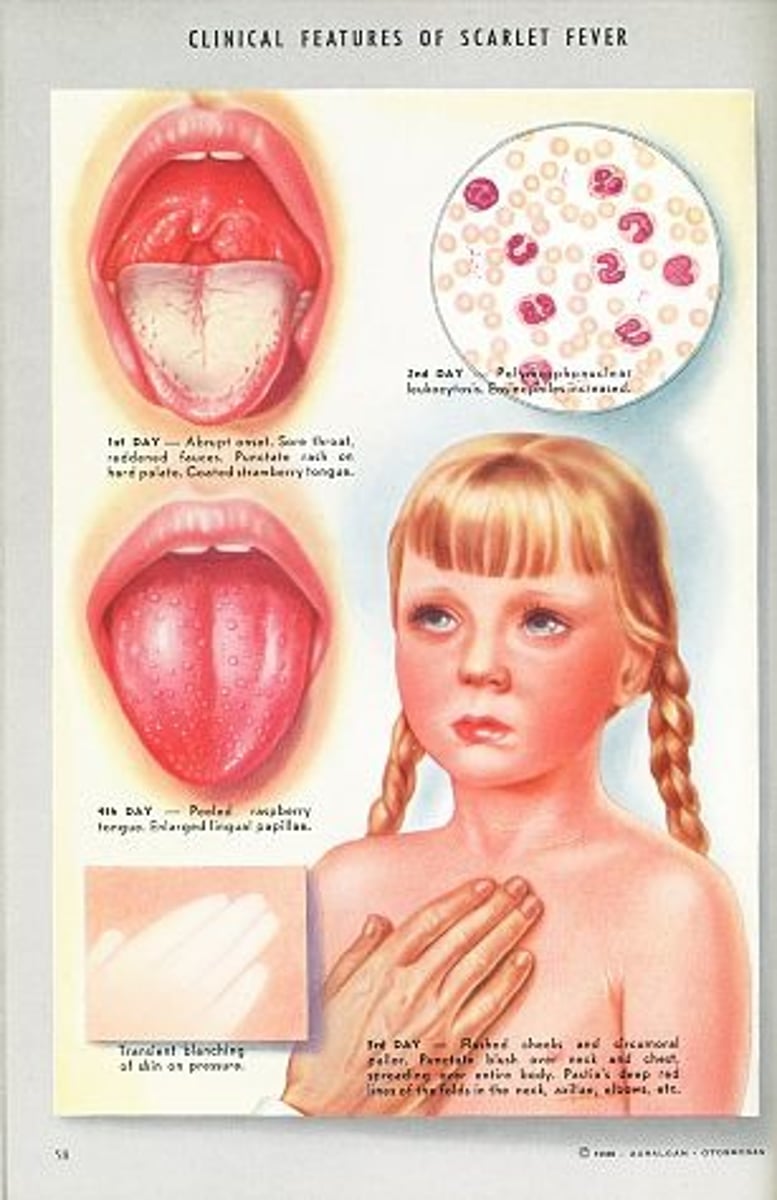
What causes scarlet fever?
Streptococcus pyogenes; usually after a strep throat diagnosis
What can cause laryngitis/epiglottitis?
H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, viruses
What causes sinusitis?
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, S. aureus, S. pyogenes
What causes diphtheria?
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
What can cause otitis media?
S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, H. influenzae
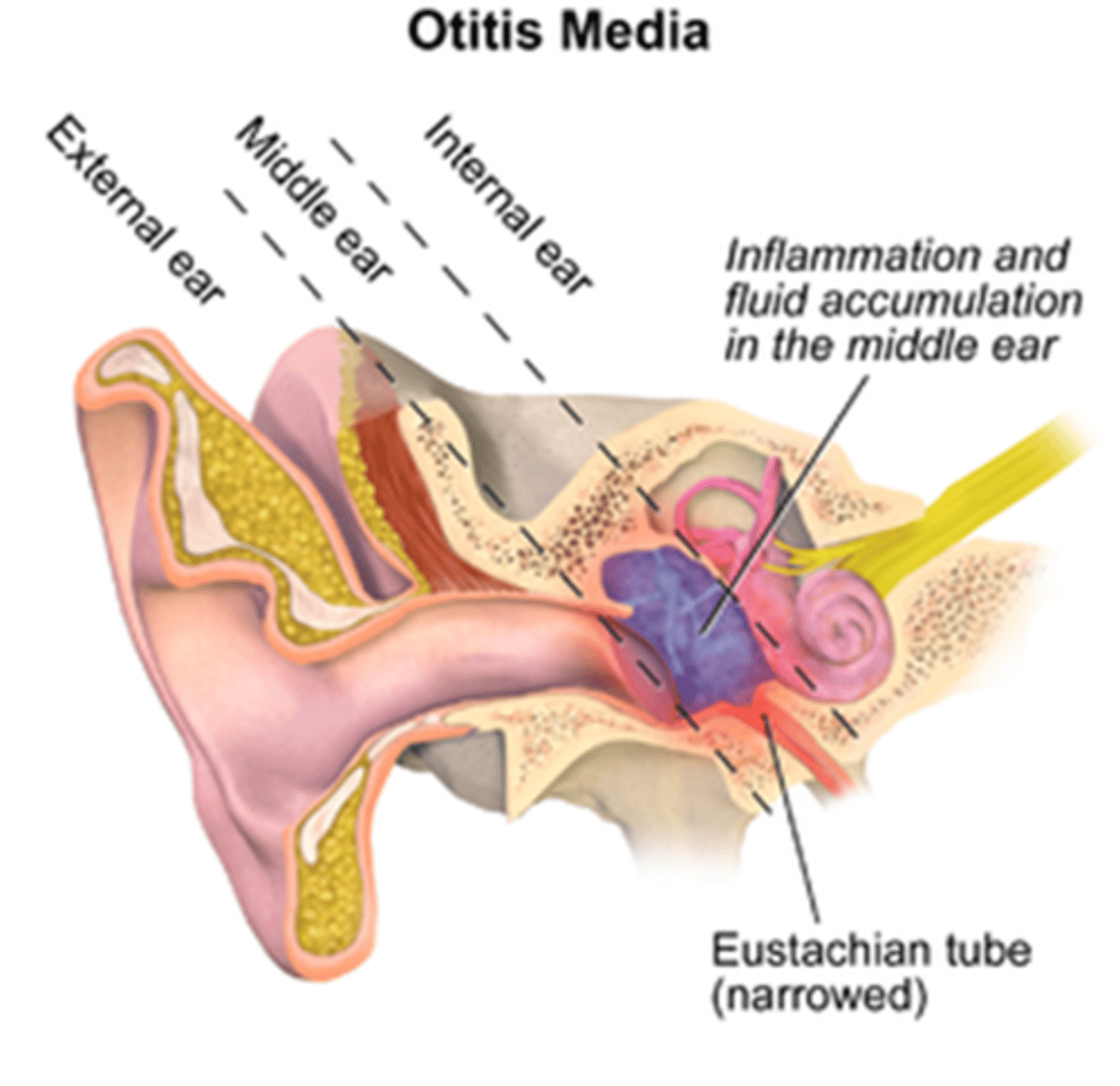
What is the most common etiological agent of otitis media out of the following: S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, H. influenzae
S. pneumoniae
What causes the common cold?
Rhinovirus/Coronavirus

What can cause bronchitis?
S. pneumoniae, M. pneumoniae, Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, some Haemophilus
What causes Whooping Cough?
Bordetella pertussis
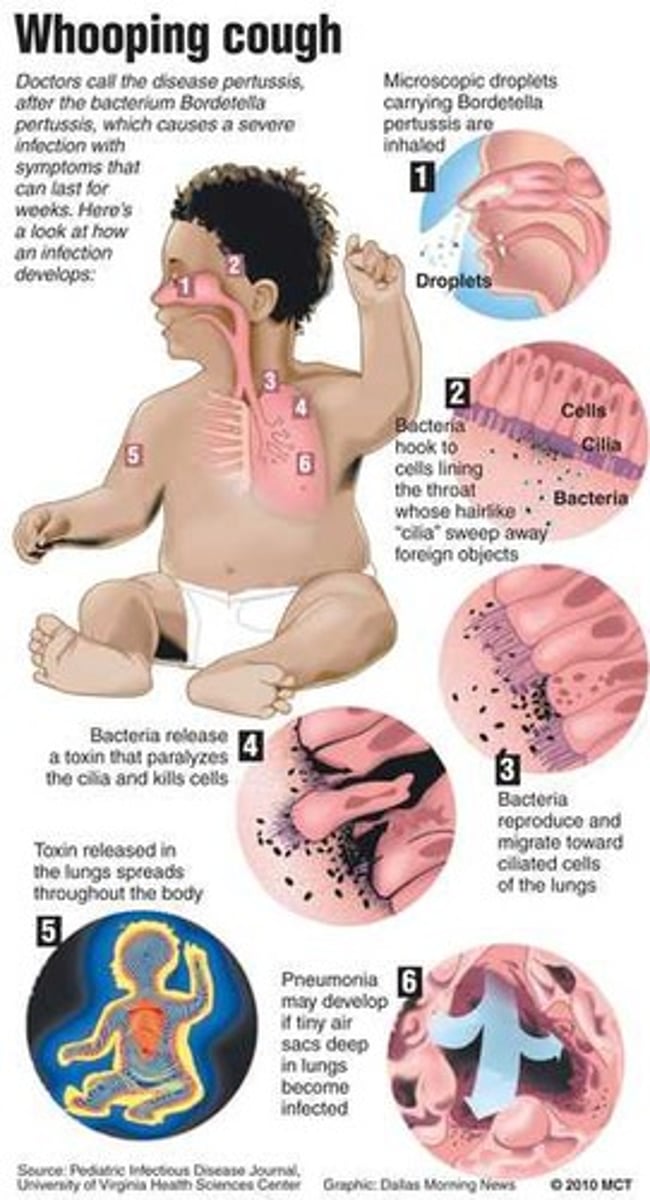
S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, M. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, fungi and viruses all have the potential to cause ______________________ ___________________
Bacterial pneumonia
What causes Legionnaire's disease/legionellosis?
Legionella pneumophila
What causes TB?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
What causes the flu?
Influenza RNA orthomyxovirus
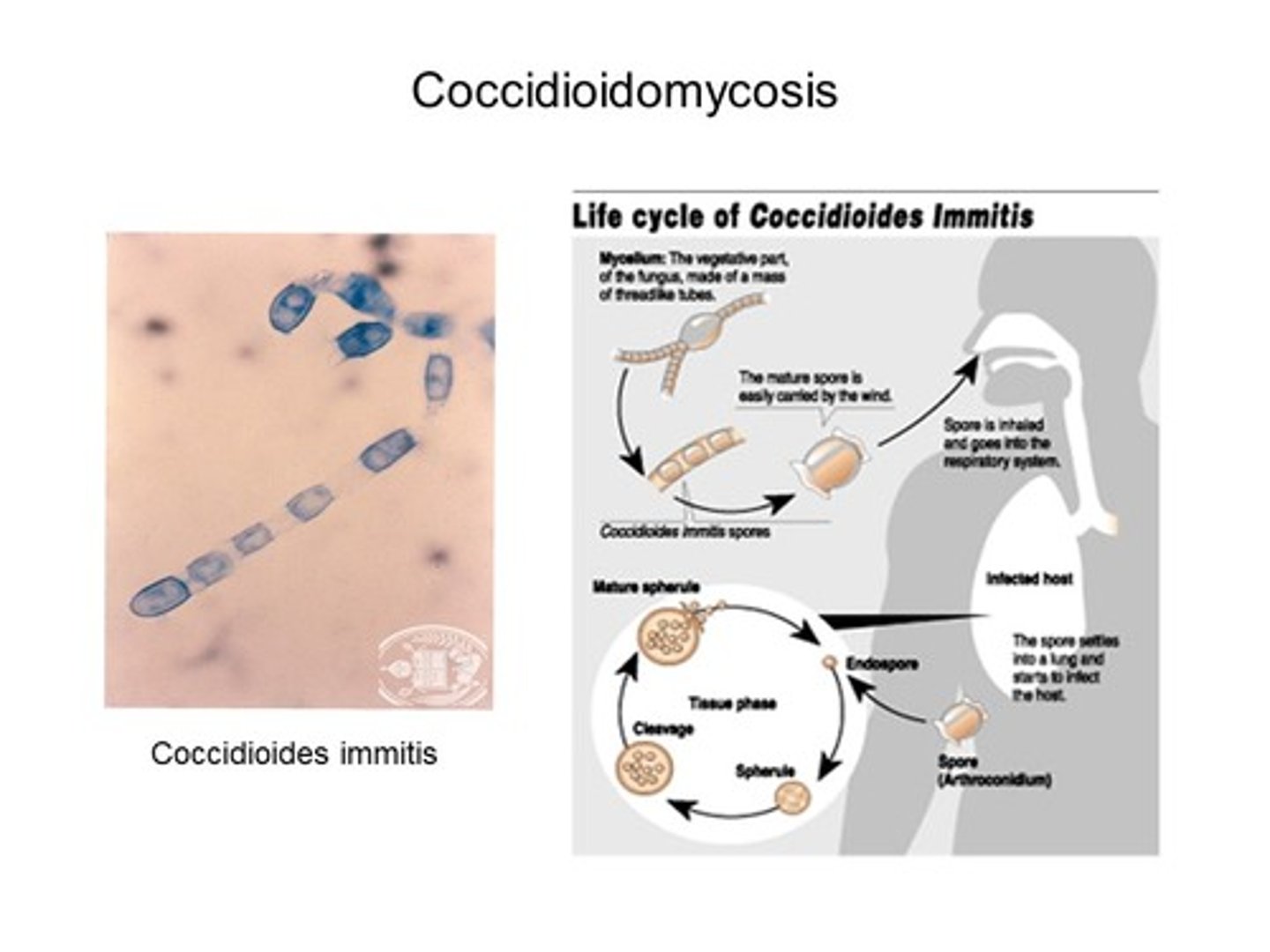
What causes Coccidioidomycosis?
Coccidioides immitis
What can causes Staph food intoxication?
Staphylococcus aureus
What causes Enterohemorrhagic E. coli? (Be specific!)`
E. coli O157:H7
What causes Taeniasis?
Taenia genus of tapeworms
What causes Giardiasis?
Giardia lamblia
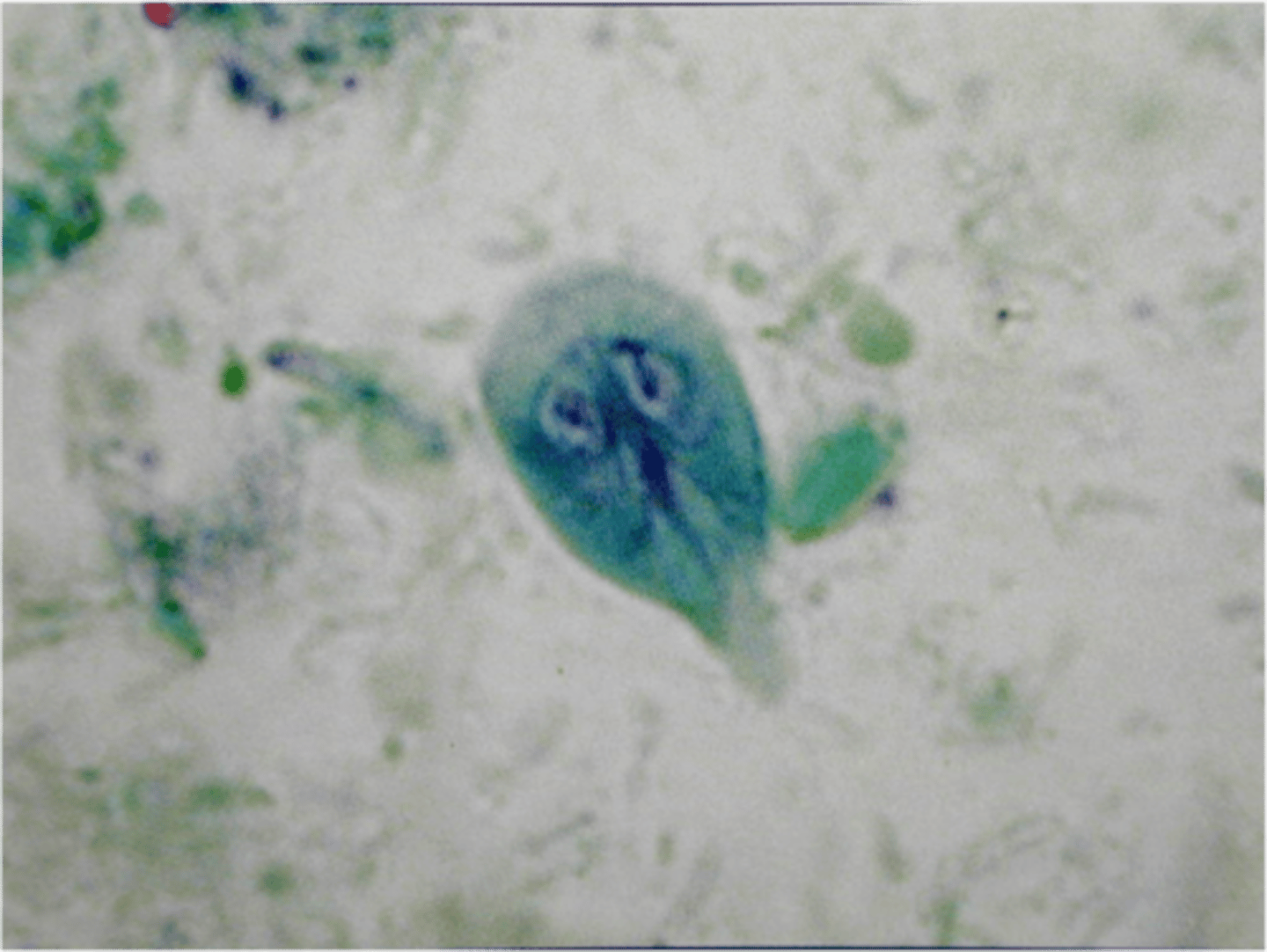
Is Giardia lamblia a protozoa or bacteria?
Protozoa
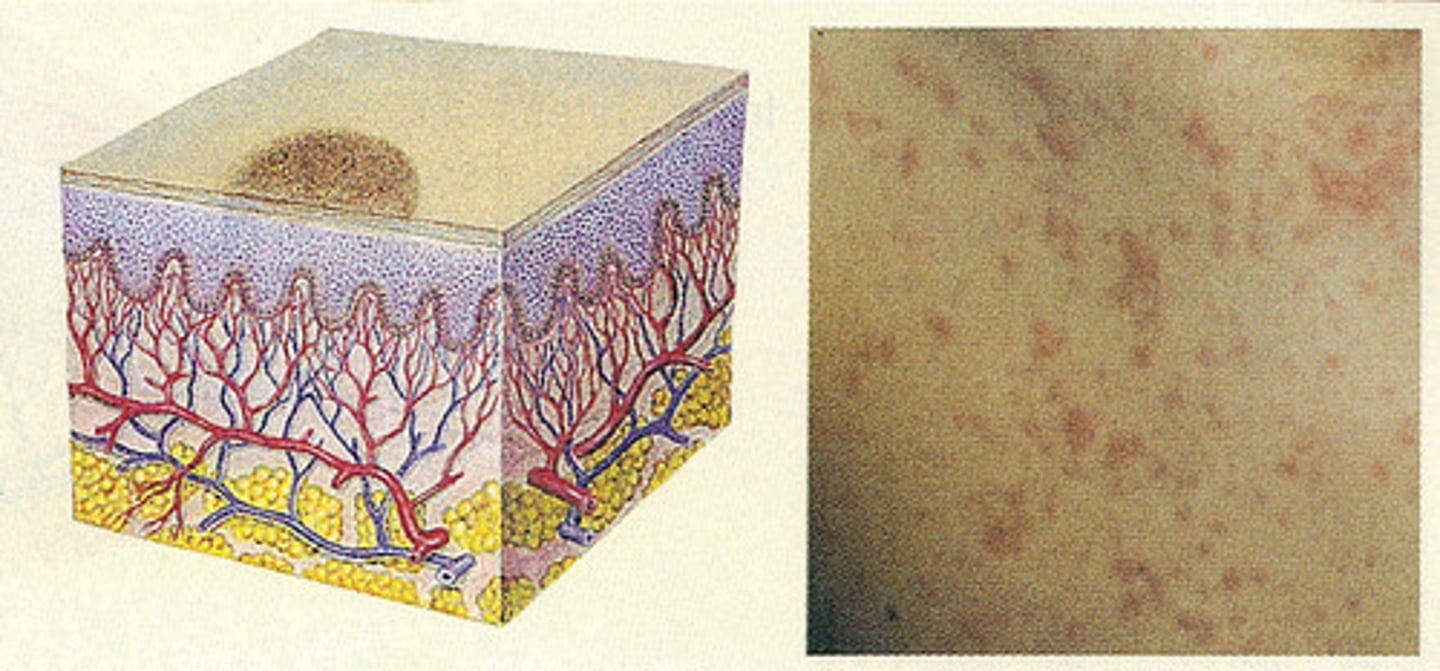
A flat lesion that differs in color from the surrounding skin is known as a what?
Macule
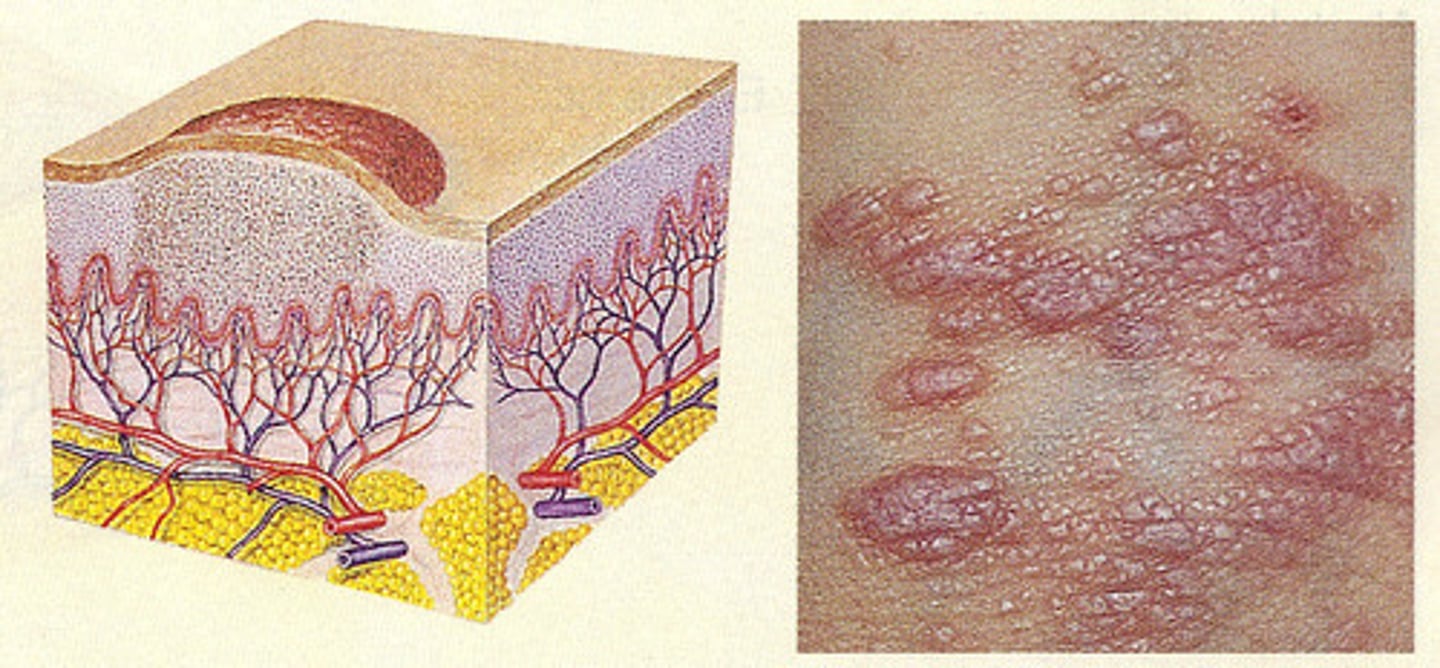
A generally small, elevated solid lesion of the skin that contains no fluid and may develop pus is known as a what?
Papule
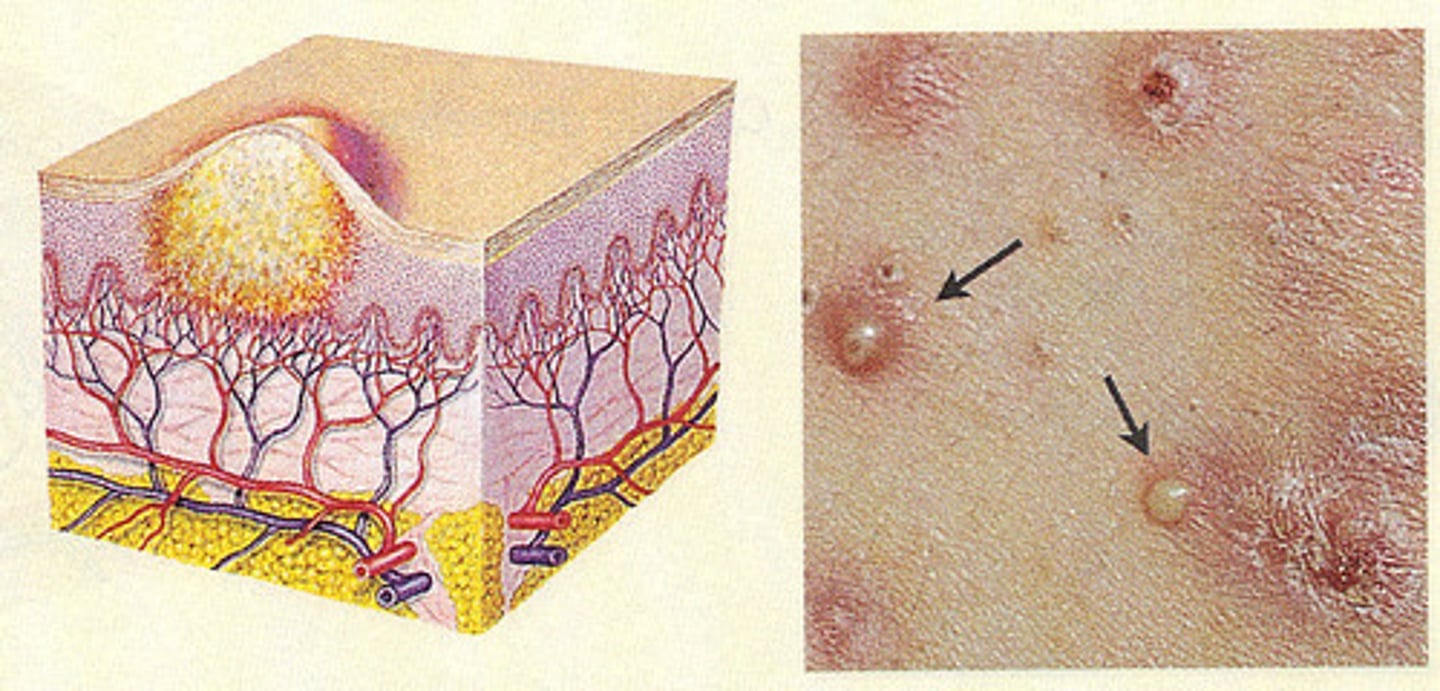
An infected, pus-filled papule is known as what?
Pustule
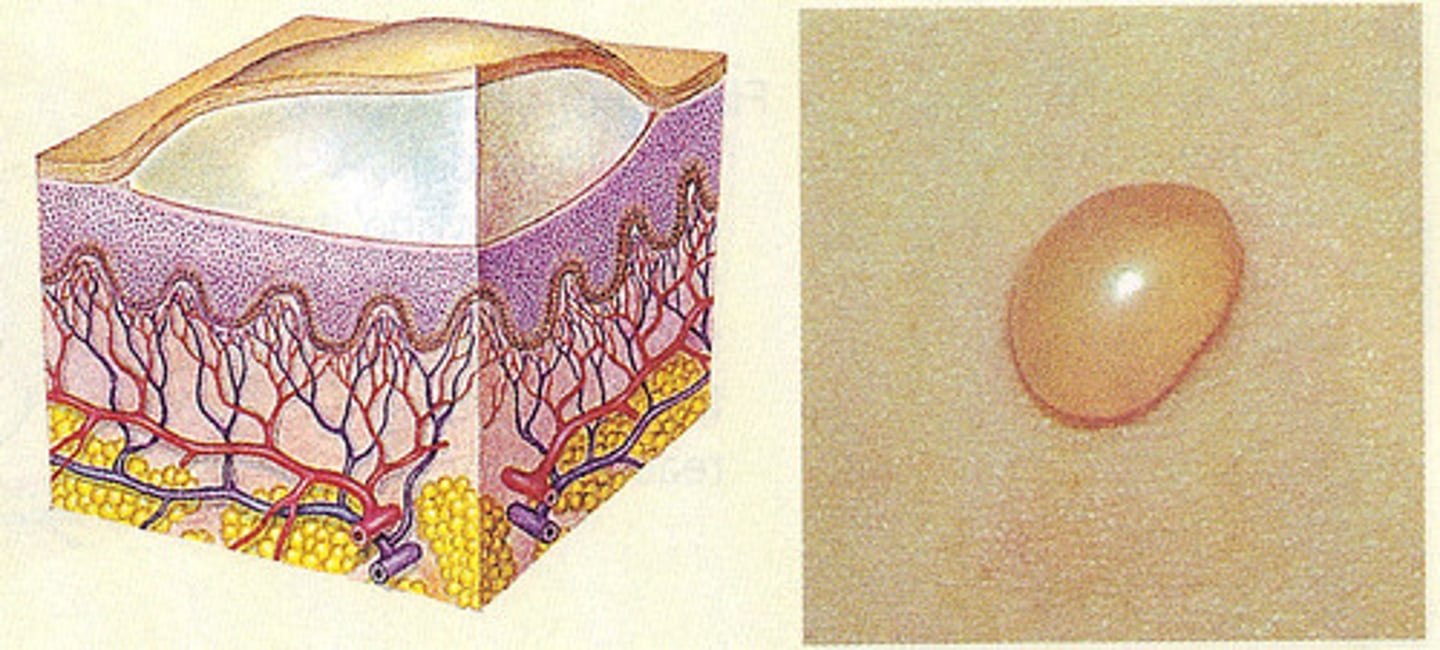
A fluid-filled, very small elevated lesion is known as what?
Vesicle
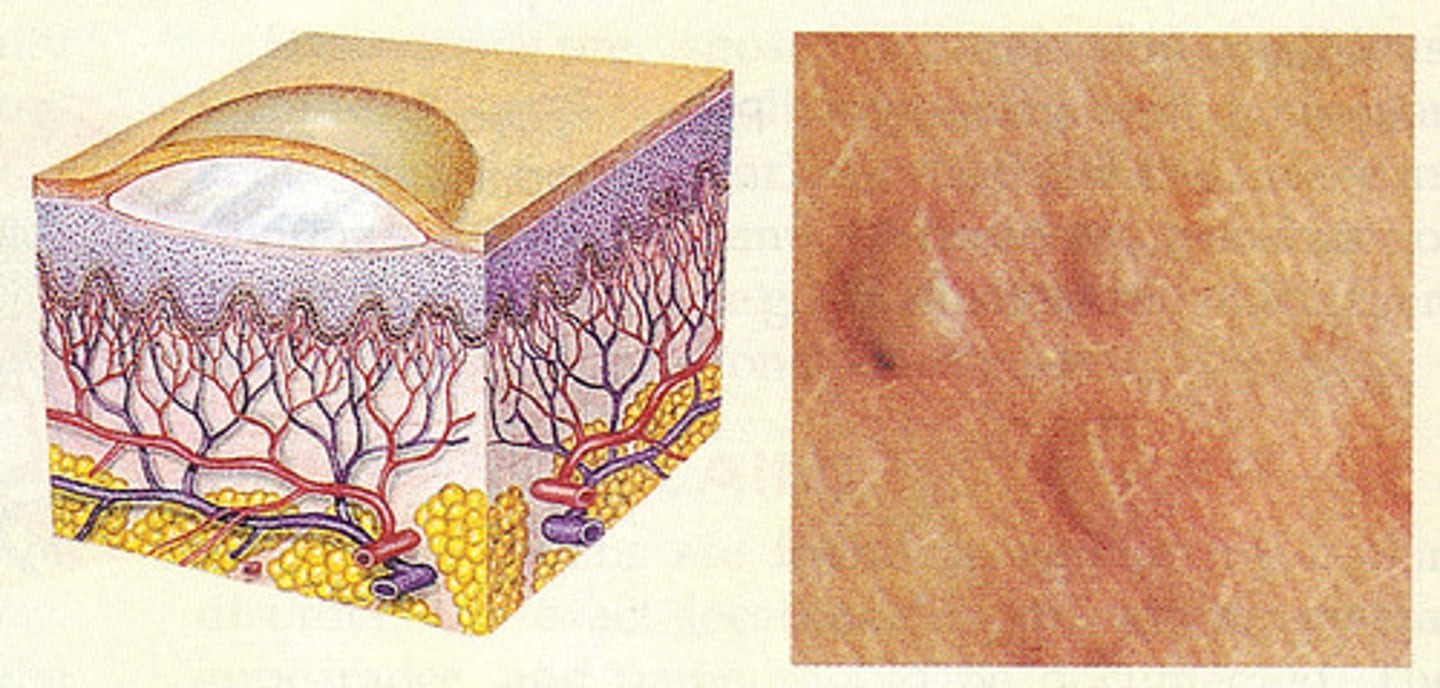
A large blister containing a watery fluid that is similar to, but larger than, a vesicle is known as what?
Bulla
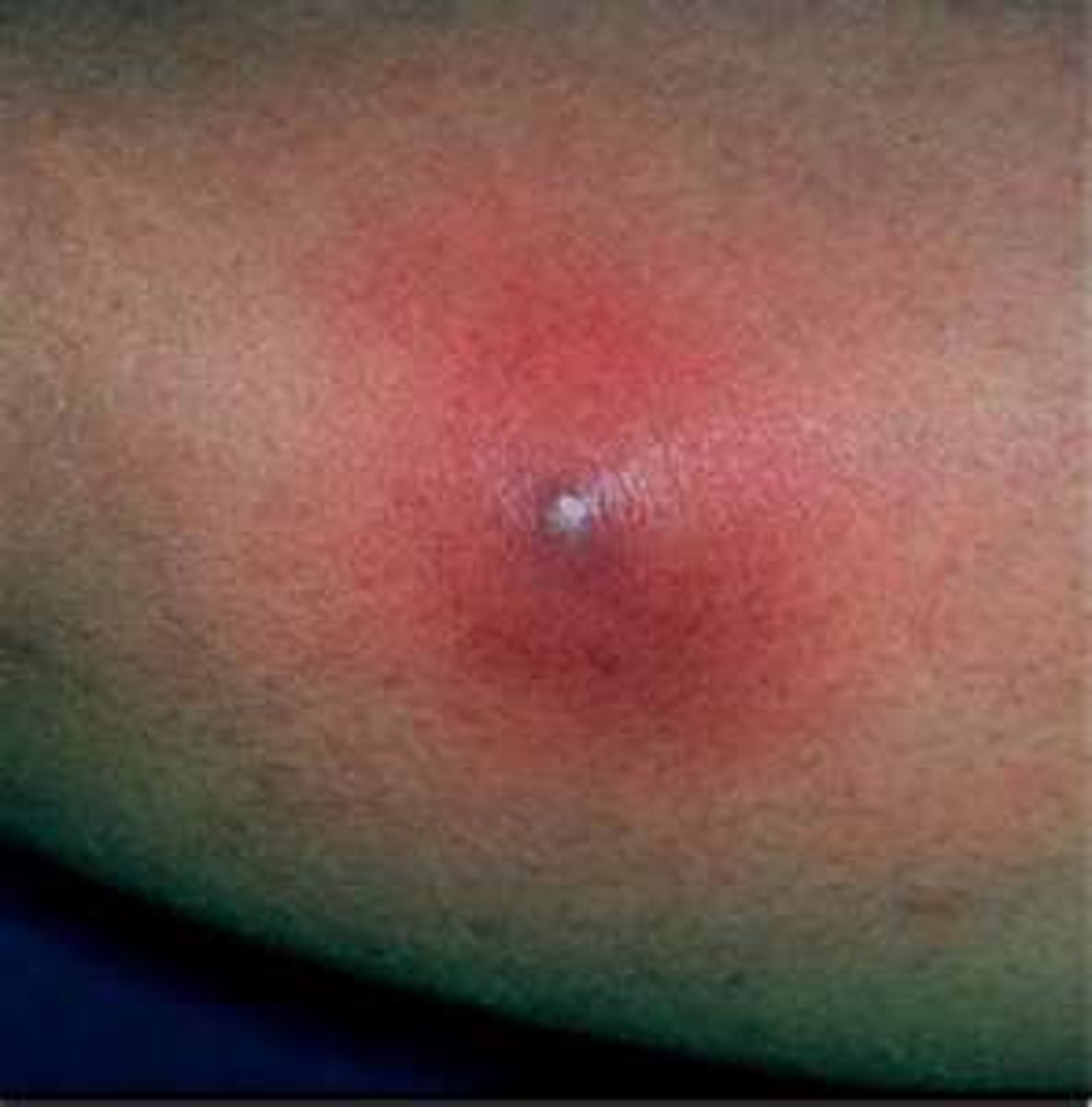
A boil, or hair follicle abscess is known as what?
Furuncle
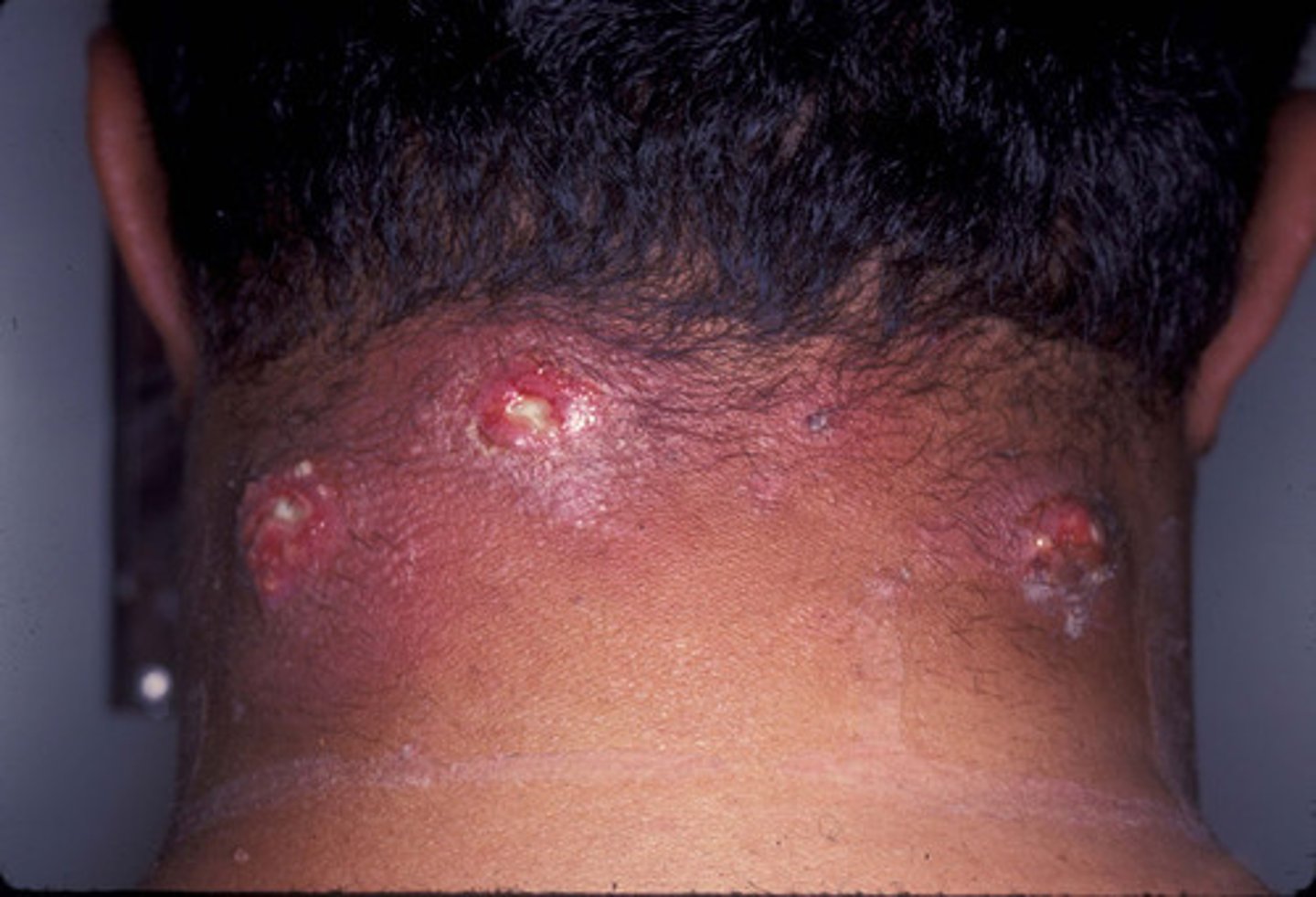
A cluster of furuncles is known as what?
Carbuncle
Of the following, which lesion is typically flat and red?
- Macule
- Papule
- Pustule
- Vesicle
Macule
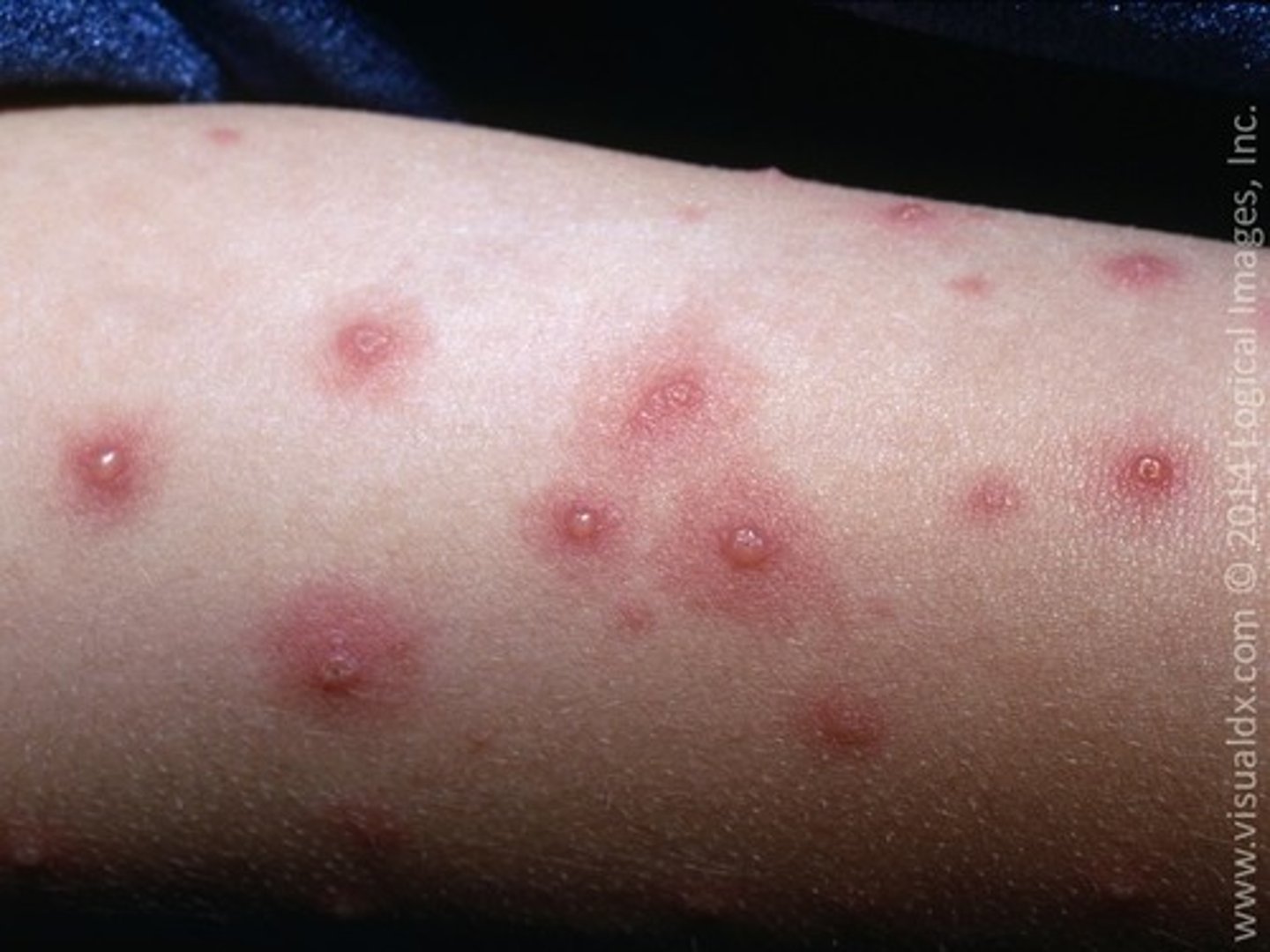
What kind of skin lesions are presented by chickenpox?
Vesicles
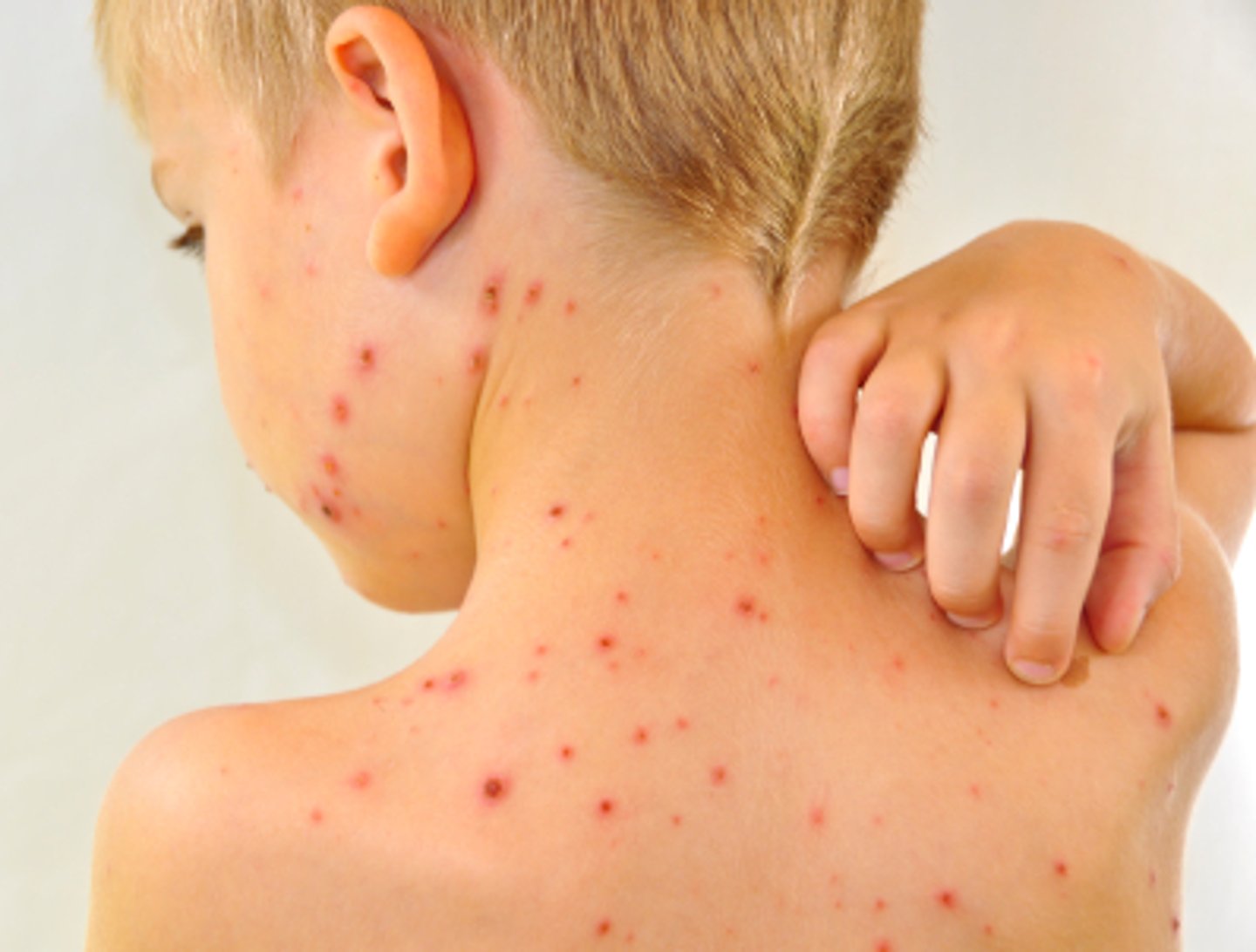
Identify the Agent/Diagnosis:
A red blister-like rash, itching, tiredness, and fever. The rash appears first on the stomach, back and face and can spread over the entire body causing between 250 and 500 itchy blisters. Can be serious, especially in babies, adults, and people with weakened immune systems. Preventable by vaccine.
Chickenpox caused by Varicella Zoster Virus
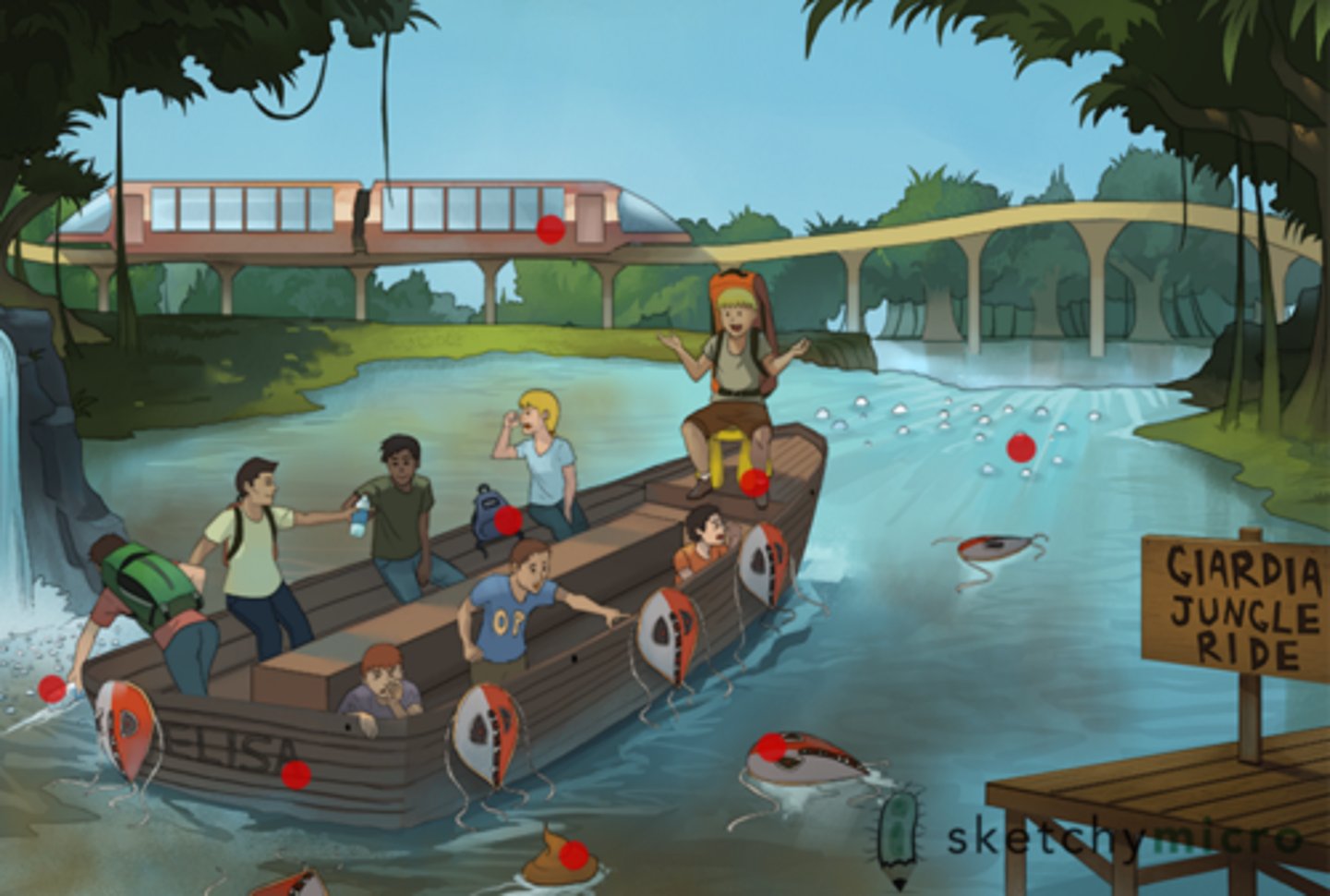
Identify the Agent/Diagnosis:
A patient presents to the hospital after just having spent a weekend at the lake. Her symptoms include greasy, foul-smelling diarrhea and flatulence, loss of appetite and fatigue. What could this possibly be?
Giardiasis caused by Giardia lamblia

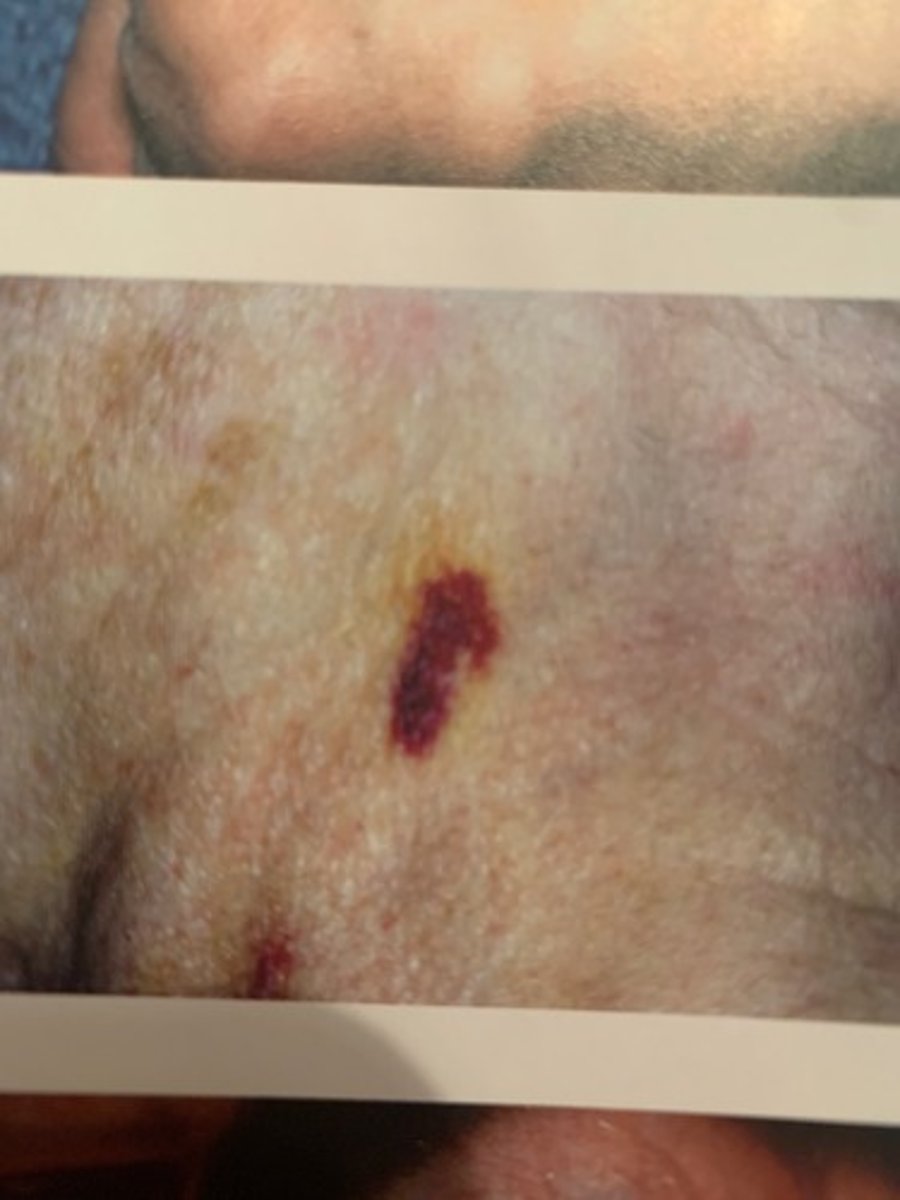
Identify the Agent/Diagnosis:
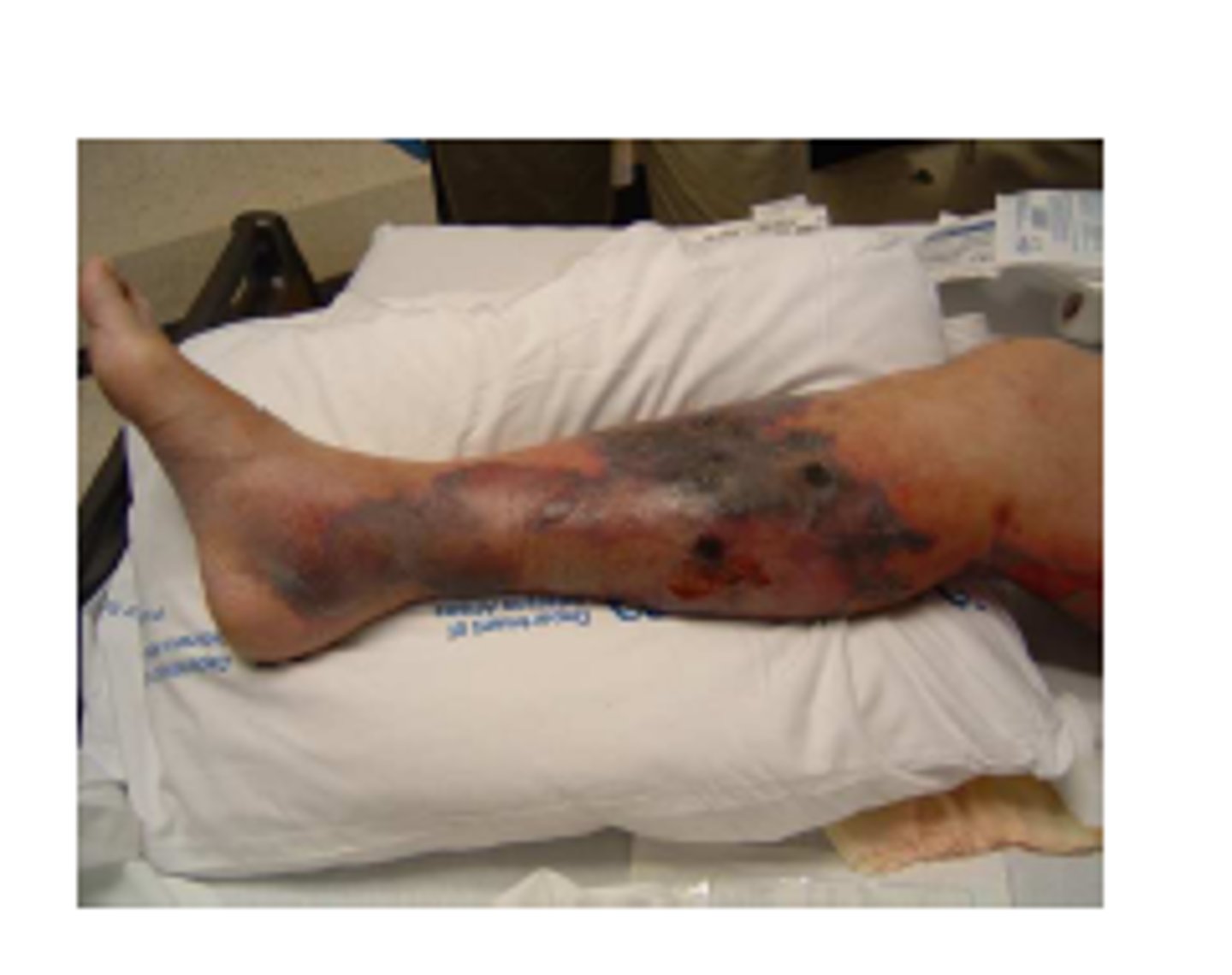
A man presents to the emergency room a few days after falling off of his bicycle to which he scraped his legs along the pavement. He notices that the scrapes have begun to turn redish-purple in the affected area and he has been experiencing severe pain, fever, and vomiting. A hemolysis test of the skin scraping shows to be beta-hemolytic. What is this patient experiencing and what is its cause?
Necrotizing fasciitis by group A Streptococcus (GAS) bacteria
Identify the Agent/Diagnosis:
A patient presents with large red raised lumps on the skin, with what look to be white spots on the inner area. The patient states that it did not always look this way and began as a few, small red raised bumps that looked like whiteheads. They then progressed to this and spread further out. What are the names of these lumps? What could have caused this?
Folliculitis to furuncles to carbuncles caused by Staphylococcus aureus that began as local and began to spread systemically
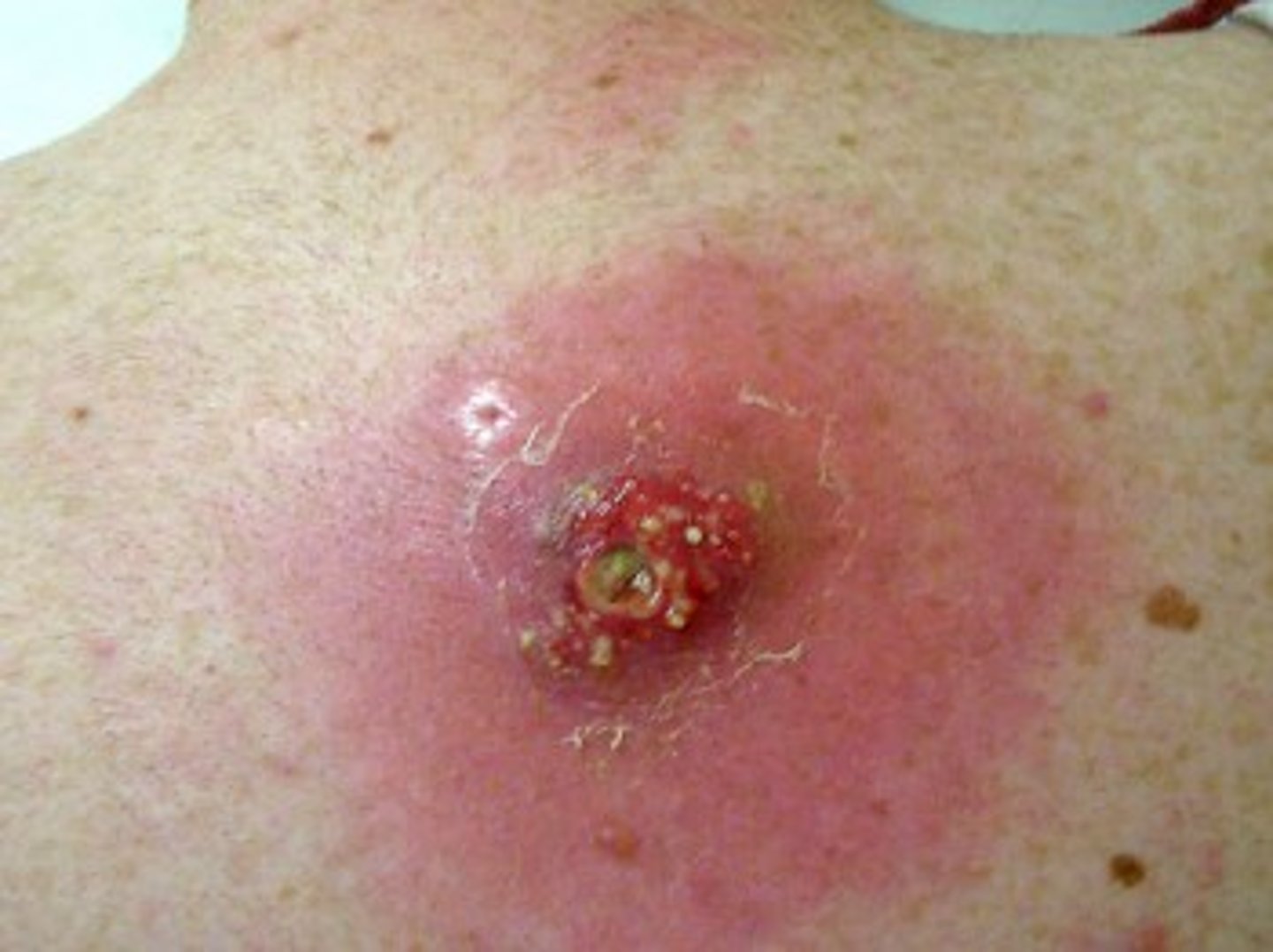
Identify the Agent/Diagnosis:
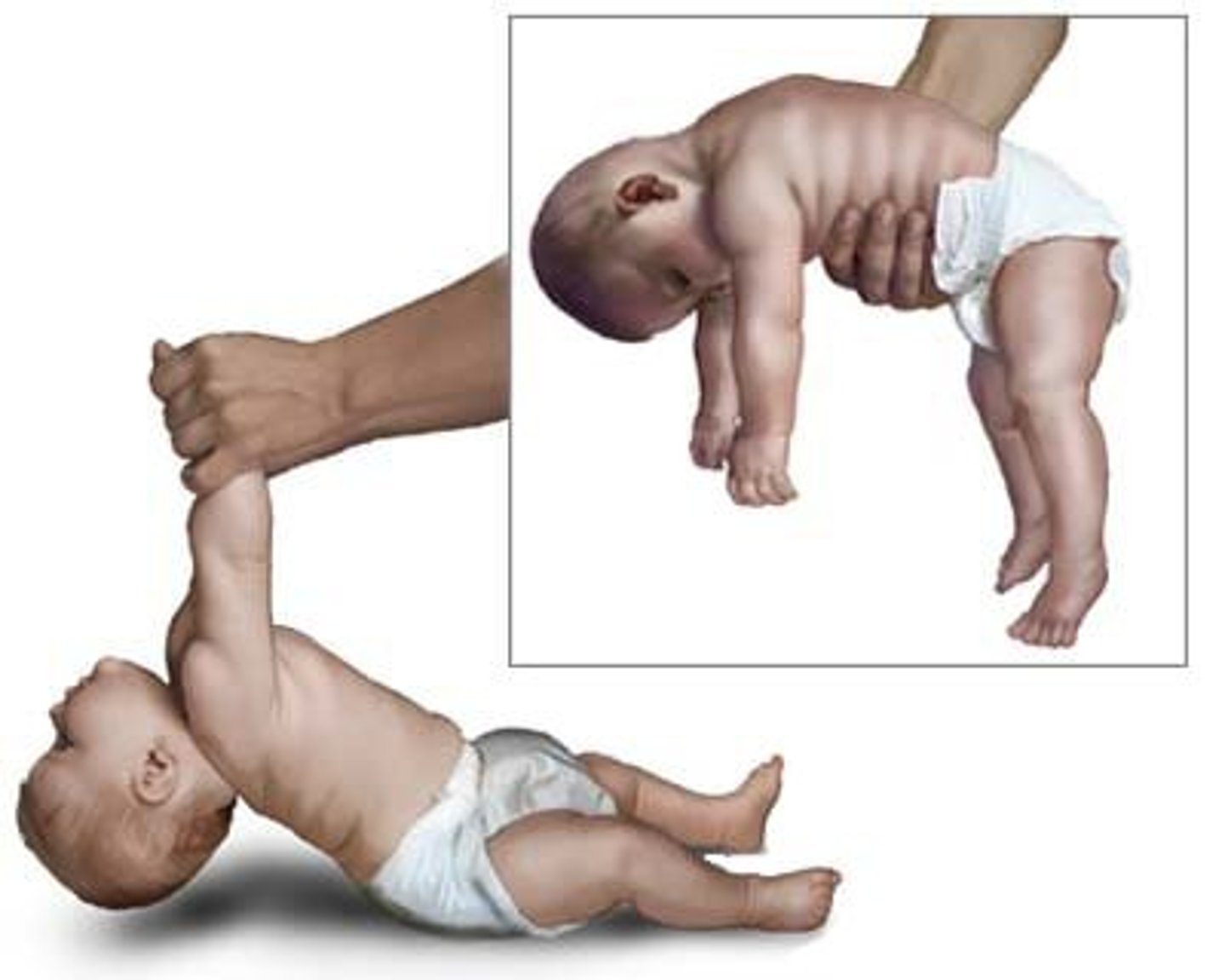
A mother brings her 5 month old into the ER stating that her child has not been mobile the last few days and refuses to eat or drink. The mother reports that they have not done anything out of the ordinary but had a picnic over the weekend where they tried some local berries and honey from the farmers market. What is this baby experiencing? What is the cause of this paralysis?
Botulism by Clostridium botulinum