AP Hug Vocab/Concepts
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
Reference Maps
Designed for people to refer to for general info about places. Political and Physical
Thematic Maps
Used as a communications tool, tells how human activities are distributed
Cartogram
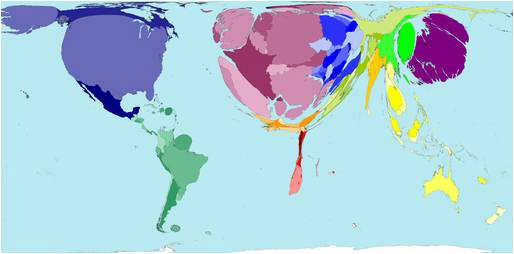
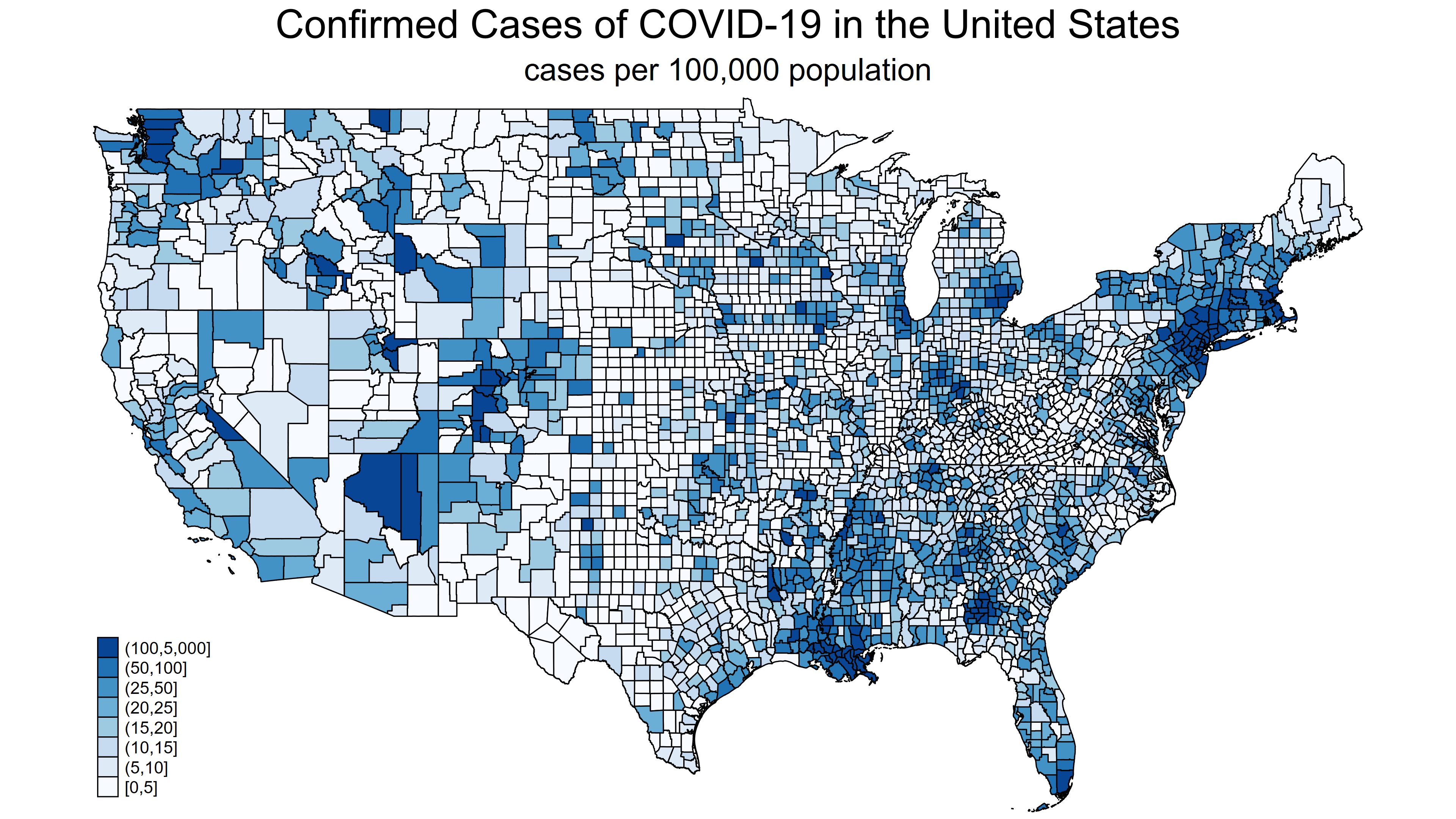
Choropleth
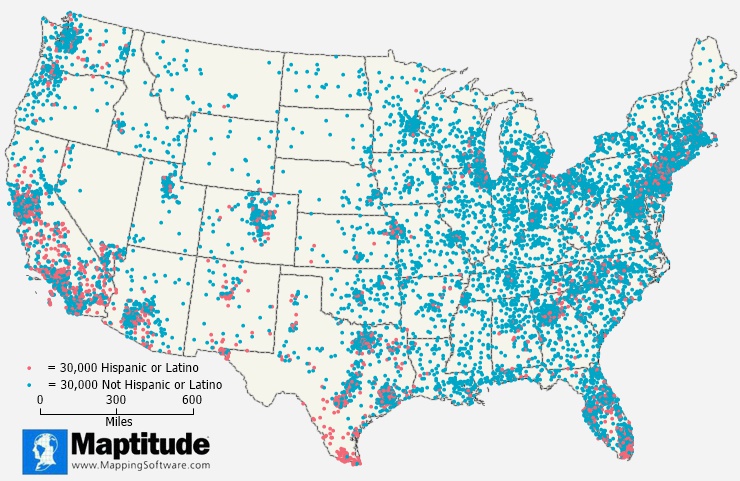
Dot Density
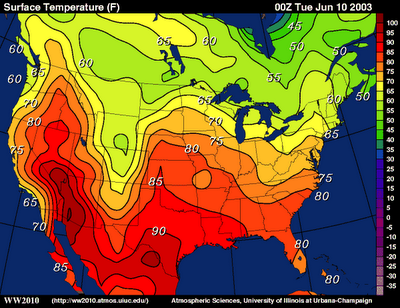
Isoline
Graduated Symbol
Mercator Map
Shape and Directions are fairly accurate, Distorted toward poles
Robinson Map
Everything is distorted a little
Goode Map
Continent sizes are accurate, directions/distances aren’t accurate
Gall Peters Projection
Shape of countries mainly near the equator are distorted
Geospatial Data
All information including physical features and human activity
GIS
Geographic Information System, computer system that captures, stores, checks, and displays data related to positions of Earth’s surface
GPS
Geographic Positioning System, system which uses data from satellites to pin-point a location on Earth and helps find ways to destination
Remote Sensing
Process of taking pictures of Earths surface from satellites/airplanes to provide understanding of Earths geography over large distances
Spatial Information
May come from field observations, media reports, travel narratives, policy documents, interviews, landscape analysis, and photographic interpretation
Census Data
Official count of individuals in a population (US - happens every 10 years)
Absolute Location
Precise spot where something is located
Relative Location
Where something is located in relation to other things
Space
Extent of area, can be relative/absolute
Place
Specific human/physical characteristics of a location
Distance Decay
Describes effects of distance on cultural/spatial interactions
Time-Space Compression
Increasing sense of connection that seems to bring people closer together even when distances are the same (ex. Internet)
Sustainability
Goal of humans reaching equilibrium with environment, meeting needs of current but leaving resources for future generations
Environmental Determinism
How physical environment caused social development
Possibilism
Physical environment may limit some human actions but people can adjust to environment
Global SoA
World at one level of data
Regional SoA
Continents of world regions data
National SoA
One or more countries data
Local SoA
Subnational level (ex. Counties, Zipcodes in the US)
Arithmetic Density
Total number of objects in an area
Physiological Density
Number of people by unit area of arable land
Agricultural Density
Ratio of farmers to amount of arable land
Carrying Capacity
Maximum population size the environment can sustain
CBR
Crude Birth Rate, number of live births per one thousand people in population
CDR
Crude Death Rate, number of deaths per one thousand people in population
Doubling Time
Time period it takes for population to double in size
IMR
Infant mortality rate, number of babies that die during first year per 1000 live births
RNI/NIR
Rate of Natural Increase, positive means population is growing, negative means population is decreasing
TFR
Total fertility rate, average number of children a woman is predicted to have in her child bearing ages
Epidemiological Model
Stage 1 - Pestilence/Famine (high CDR), Stage 2 - Receding Pandemics, Stage 3 - Degenerative/Human Created Disease (ex. Polio, Heart attack), Stage 4 - Delayed Degenerative (ex. Cancer)
Malthusian Theory
Population increase geometrically, food supply increases arithmetically (Population > Food Supply growth)
Neo Malthusian Theory
Earths resources only supports finite population, pressure on scarce resources = war and famine, family planning/contraceptives = low population and protection of resources to prevent war/famine
Antinatalist policies
When country provides incentives for people to have less children
Pronatalist Policies
When country provides incentives for people to have more children
Dependency Ratio
Ratio of number of people not in workforce to those who are in workforce (dependents may be 13 yo or younger/65 and older)
Transhumance
Moving herds of animals to highlands in summer, lowlands in winter
Brain Drain
When majority of educated/skilled workers leave areas to better opportunities elsewhere
Ethnocentrism
Judging other cultures based on rules of your own
Cultural Landscapes
Forms superimposed on physical environment by activity of humans (ex. Rice fields, street lights, churches, etc)
Ethnic Neighborhoods
Neighborhood, district/suburb which retains some cultural distinction from larger surrounding areas
Stimulus Diffusion
Diffusion in which cultural adaptation is created as result of introduction of cultural trait from another place.
Hierarchical Diffusion
Idea spread by passing along urban to rural
Contagious Diffusion
Transmission through close contact (ex. Disease)
Reverse Hierarchical
Diffusion from rural to urban
Creolization
Language that began as combination of two other languages, spoken as primary language of a group of people
Lingua Franca
Mutually understood and commonly used language by people who have different native language
Colonialism
Effort by one country to settle in territory to impose political, economic, and cultural principles
Imperialism
Policy of extending countries influence through political/military force to already developed areas by indigenous people
Time-Space Convergence
Decline in travel time between locations as result of transportation, communication, and technology/social innovations
Ethnic Religion
Religion that focuses on one ethnic group (ex. Hinduism, Judaism)
Universalizing Religion
Religion that attempts to appeal to all people, worldwide focus (ex. Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism)
Acculturation
Adoption of cultural traits of another culture
Assimilation
Process of person/group losing cultural traits and adopting traits from another culture
Multiculturalism
When various ethnic groups coexist with one another without sacrificing particular identities
Syncretism
Blending traits from two different cultures to form a new trait
State
Political unit with permanent population and boundaries recognized by other states (ex. USA, Australia)
Nation
People who think of themselves as one based on shared sense of culture and history, desires political autonomy (ex, French, German, Indian)
Nation-states
State with a single nation (ex. Japan, Iceland, Armenia)
Stateless Nations
Nation without their own independent state (ex. The Kurds, Palestinians, Hmong)
Multinational States
State with two or more nations (ex. France, USA, Mexico, China, Russia)
Multistate Nation
Nation living across states (ex. Korea, Russia, Kurds)
Autonomous Regions
Area which governs itself but not independent country (ex. Greenland, Hong Kong)
Semi-autonomous Regions
Area which can govern itself in certain areas, but does not have complete power to govern (ex. Nunavut, Canada, Indian Reservations, US)
Sovereignty
Final authority over a territory and right to defend territorial integrity against incursion
Neocolonialism
Gaining indirect control of another country through economic/political pressure
Shatterbelts
Region caught between stronger colliding external forces, under persistent stress, often fragmented by aggressive rivals (ex. Israel/Palestine, Ukraine/Russia, Balkans)
Territoriality
Perceived connection of people, culture, and economic systems to land
Relic Boundary
Boundary that no longer exists as international border but remnants of its existence remain (ex. Berlin Wall)
Superimposed Boundary
Boundary drawn by powerful outsiders and ignores existing cultural groups (Ex. Berlin Conference)
Subsequent Boundary
Boundary that evolves as cultural landscape of an area takes shape and changes as cultural landscape changes (Ex. Ireland and Northern Ireland, Sudan and South Sudan)
Antecedent Boundary
Boundary in natural landscape that existed before cultural landscape emerged and stayed in place as people moved in (ex. Mountains between France and Spain, Lakes between US and Canada)
Geometric Boundary
Boundary that follows a straight line (ex. US and Canada, North and South Korea)
Consequent Boundary
Boundary that coincides with cultural groups (ex. India Hinduism and Pakistan Islam)
EEZ
Exclusive Economic Zone, Zone of water adjacent to contiguous zone (200 miles) in which state has right to explore, exploit, conserve, and manage resources.
Gerrymandering
Redrawing voting district boundaries to give advantage to a political party
Ethnic Seperatism
Mainly religion, language, or ethnicity related differences (ex. Quebec)
Ethnic Cleansing
Mass expulsion/killing members of an unwanted ethnic or religious group in society
Irredentism
When a state wants to annex a territory whose population is ethically similar
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages gained by increased level of production. Countries agree to produce more of a good, revenue received from selling that good increases.
Centripetal Forces
Force that tends to unify people and enhance support for state (Petal - Pull)
Centrifugal Forces
Force that divides the state (Fugal - Fatal)
Mediterranean Climate
Hot/dry summer climate, mild winter, defined rainy season, produces grapes, olives, figs, dates, tomatoes, zucchini, wheat, barley. (Found in Mediterranean, California/Oregon, Central Chile, South Africa’s Cape, Parts of Australia)
Tropical Climate
Hot/Humid climate, produces cassava, bananas, sugar cane, sweet potato, papaya, rice, maize
Extensive Agriculture
Agriculture which sues small amounts of labor on large area of land
Intensive Agriculture
Agriculture that uses lots of labor on small area of land
Market Gardening
Intensive, fruits and vegetables sold fresh to consumers but most are sold to large processors for canning/freeze, found in southeast US, California, Southeast Australia, warm
Plantation Agriculture
Intensive, specializes in one crop and transported for sale on global market, tropical, commodity and speciality crops
Mixed Crop/Livestock
Intensive, commercial arming characterized by crops and livestock being on the same farm, cold/warm
Shifting Cultivation
Extensive, farmers move from one farm to another (ex. Slash-and-Burn Agriculture)