1.1 A SIMPLE MODEL OF THE ATOM, SYMBOLS, RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS, ELECTRONIC CHARGE AND ISOTOPES
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms

Dalton’s atomic model
John Dalton proposed that atoms were tiny, indivisible spheres that made up all matter.
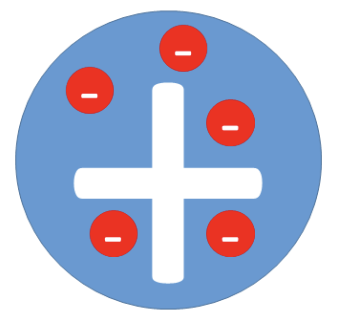
Plum Pudding Model
J.J. Thomson discovered electrons and suggested atoms were a ball of positive charge with negative electrons scattered through it.
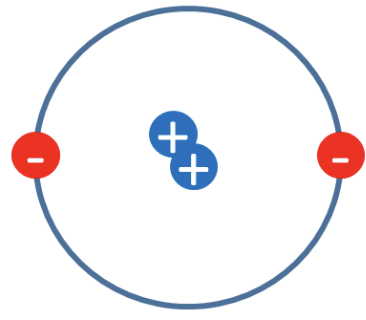
Rutherford’s Nuclear Model
After the alpha particle scattering experiment, Rutherford concluded that atoms have a small, dense, positively charged nucleus with electrons around it.
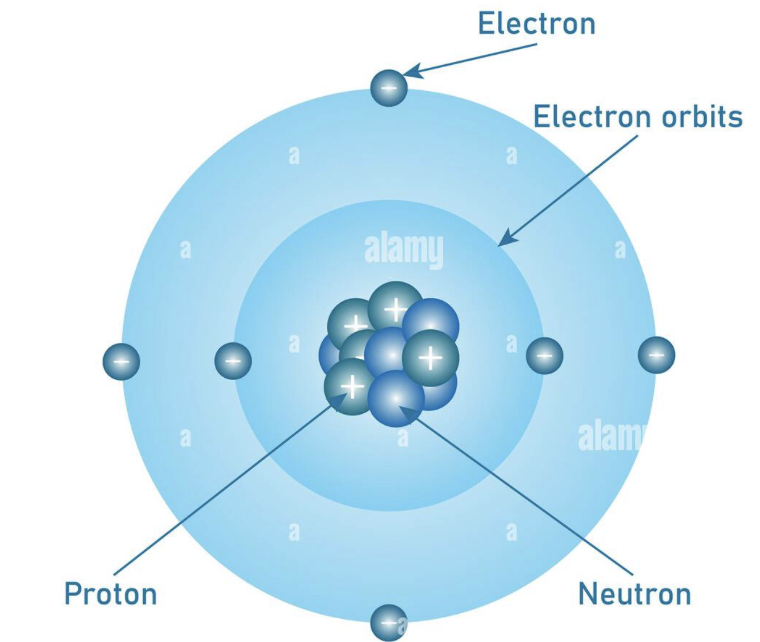
Bohr Model
Niels Bohr suggested electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels or shells.
Chadwick’s discovery
James Chadwick discovered the neutron, explaining the missing mass and charge in the nucleus.
Subatomic particles
Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Proton charge and mass
Protons have a charge of +1 and a relative mass of 1.
Neutron charge and mass
no charge and mass of 1
Electron charge and mass
charge is -1 and mass is very small
Atomic number
The number of protons in an atom (equals number of electrons in a neutral atom).
Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
Overall charge of an atom
Atoms are neutral because the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
Electron arrangement
Electrons occupy the lowest energy levels first, with a maximum of 2, 8, and 8 electrons in the first three shells.
Electronic configuration example
Nitrogen (atomic number 7) has the configuration 2, 5.
Importance of electron arrangement
Electron configuration determines how atoms react and what bonds they form.
Atom
The smallest part of an element that can exist.
Element
A substance made up of only one type of atom with the same atomic number.
Compound
A substance made of two or more elements chemically bonded together.
Formation of compounds
Compounds form through chemical reactions between elements.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Relative atomic mass (Ar)
The weighted average mass of an element’s isotopes, taking into account their abundance.
Mixture
Two or more elements or compounds not chemically bonded together.
Properties of mixtures
Each substance in a mixture keeps its own chemical properties and can be easily separated.
Filtration
Used to separate insoluble solids from liquids.
Crystallisation
Used to obtain crystals from a solution by evaporating the solvent.
Distillation
Used to separate liquids with different boiling points (simple or fractional distillation).
Chromatography
Used to separate substances based on how they move through a medium.