Normal Newborn Transitions (week 12)
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Demonstrate knowledge of newborn transition respiration, circulation, thermoregulation, immune system, digestion, and elimination.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What does the fetal lung fluid do?
expands the alveoli and aids in lung development
What is a key component of initiating respiratrion?
The fetal lung fluid that is produced in the lung tissue
Surfactant
What does surfactant do?
decreases the surface tension of the fluid remaining in the alveoli after birth
so that within the first inspiration, the sacs can fill and open up with air
Before birth which organ in the maternal was responsibly for gas exchange for the fetus?
The placenta
What mechanical factors can stimulate the baby’s first breath (respiration)?
fetal chest being compressed during vaginal birth
recoiling of the chest which draws a small amount of air into the lungs
What chemical factors can help stimulate the baby’s first breath?
the increased pressure of CO2 and decreased pH
What thermal factors can help stimulate the baby’s first breath?
temperature changes from inutero to room temp
What sensory factors can help stimulate the baby’s first breath?
sound, light, smells, touch, pain
What are key changes that are happening in respiration after birth?
pulmonary blood flow resistance decreases which allows for increases pulmonary blood flow
lungs take over as site of gas exchange
What are key changes that happen in the circulatory system after birth?
fetal shunts gradually close (4-6 weeks) as pulmonary vascular resistance drops
may hear heart murmurs
The umbilical vein carries
oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus
The umbilical arteries carry
deoxygenated blood from the fetal heart to the placenta
What does the Ductus Venosus (DV) do in fetal circulation?
allows oxygenated blood from the fetus (via the umbilical vein) to bypass the liver and flow directly into the inferior vena cava which carries it back to the heart
What does the Foramen Ovale (FO) do in fetal circulation?
now the fetal blood and IVC blood is coming back to the heart, the right atrium, and instead of draining into the right ventricle and to the pulmonary artery (to get oxygenated) since the lungs is not the site of gas exchange for the fetus (it’s the placenta), it bypasses pulmonary perfusion and goes straight to the Left Atrium (although* not all blood goes here some still go to right ventricle and pulmonary artery, but now we move to next shunt; Ductus Arteriosus)
What does the Ductus Arteriosus (DO) do in fetal circulation?
connects the pulmonary artery directly to the aorta
helps to optimize oxygen rich blood to the lower peripheral tissues
Lungs in fetus in fetal circulation have high or low vascular resistance
high vascular resistance
they are vasoconstricted
low CO2
What happens to the Ductus Venosus (DV) in newborn circulation?
no longer needed and closes
since the placenta is gone, the umbilical vein is no longer bringing oxygen rich blood back to the body, so the ductus venosus isn’t needed (what it previously did was combine umbilical vein blood with IVC)
What happens to vascular resistance in newborn circulation?
drops
so lungs in the newborn circulation have lower vascular resistance and blood flow increases through the pulmonary vessels
What happens to the Foramen Ovale (FO) and the Ductus Arteriosus in newborn circulation?
they close
since vascular resistance drops, there isn’t pressure anymore for blood to go from right to left atrium or for pulmonary artery to directly link to aorta cause of increased pressure/resistance (there’s no more of that resistance)
What are the 3 shunts in fetal circulation that optimize delivery of oxygen rich blood to the brain and periphery?
Ductus Venosus
Foramen Ovale
Ductus Arteriorsus
In fetal circulation the lungs have high/low pulmonary vascular resistance?
High pulmonary vascular resistance
In fetal circulation, the lung have low/high pulmonary blood flow?
Low pulmonary blood flow
In the newborn/neonatal circulation, what shunts are open to optimize oxygen rich blood flow?
None — all shunts in fetal circulation are now closed
no more mixing of oxygen rich and oxygen not-rich blood
In newborn circulation, the pulmnoary vascular resistance is high/low?
Low pulmonary vascular resistance
In newborn circulation, the pulmonary blood flow is high/low compared to fetal circulation?
higher
pulmonary blood flow approx. equal to systemic blood flow
In Utero what regulates the fetal body temp?
maternal body temp
In post natal what regulates the baby’s body temp?
newborn must now maintain their own body temp
How are newborns predisposed to heat loss?
thin skin
little subcutaneous (white) fat
newborns have 3x greater surface area to body volume compared to adults
rate of health loss is 4x greater for newborns compared to adults
What are protective factors newborns have against heat loss?
flexed fetal position (extrmeities closing around self)
brown fat formed in fetal development (body burns this to generate heat)
What is non-shivering thermogenesis (NST)?
way newborns burn brown fat to get heat
What is the primary source of body heat production for the newborn?`
non-shivering thermogenesis (NST)
**What are the 4 main ways newborns lose body heat (all passive heat loss methods)?**
conduction
convection
evaporation
radiation
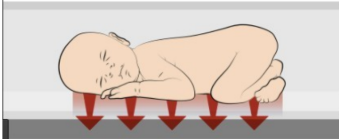
**What is conduction heat loss?**
heat loss through contact with solid surfaces
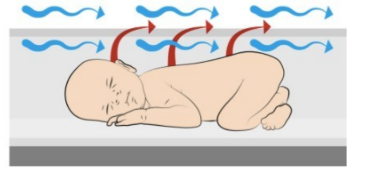
**What is convection heat loss?**
heat loss through local air currents (so air moving across the body surface)
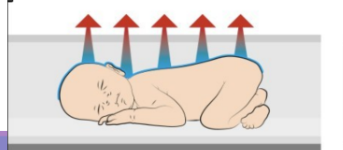
**What is evaporation heat loss?**
heat loss through evaporation of moisture on skin (like how when we sweat) (newborn skin wet at birth and that makes them cold)
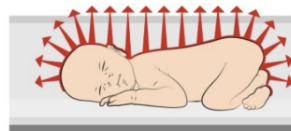
**What is radiation heat loss?**
heat loss from body to the surrounding atmosphere (ie; like radiator?)
What are the 2 main types of immunity the newborn has?
Passive Immunity
Active Immunity
How does passive immunity happen?
passive immunity is given from the mom’s IgG antibodies that cross the placenta (usually happens in 3rd trimester) (plus from breastmilk)
How does the newborn get Active Immunity?
produce IgM antibodies right after birth, to protect against gram negative bacteria
IgA usually produced in ~2 weeks of age, used to protect GI and respiratory systems (little bit also comes from breastmilk)
What are 3 key functions of the newborn liver?
energy source (since baby’s liver has been storing glycogen since the 3rd trimester)
site of bilirubin conjugation (which is byproduct of RBC breakdown)
storage of iron, metabolism of drugs, production of coagulation factors
Do breastfed infants need an iron supplement? How about non-breastfed newborns?
no, breastfed infants do not need an iron supplement (get enough iron from breastmilk) until they start transitioning to solid foods (~4-6 months)
non breastfed newborns should be given iron fortified formula
Unconjugated bilirubin is ______ soluble
fat soluble (do not want this, so liver helps make it conjugated so it can be excreted in stool)
Conjugated bilirubin is _____ soluble
water soluble (yes we want this)
Unconjugated/conjugated is toxic to the brain (pick one)?
Unconjugated bilirubin is toxic to the brain in high levels (which is why you want to conjugate it) cause it can cross the blood brain barrier
What are the 3 digestive enzymes that help breakdown food for newborns?
pancreatic amylase
produced ~4-6 months
needed to digest complex carbs
amylase
gets in breastmilk
also produced in saliva until 3 months
lipase
needed for fat metabolism and absorption
get this enzyme from breastmilk
Gastric emptying is quicker for babies who are breastfed or formula fed (pick one)?
breastfed
When is stool typically passed for a newborn?
first 24-48 hours of life
What is the name of the first stool a baby passes? And how does it look like?
called Meconium
thick, dark/black substance
What is the progression of newborn stool?
Meconium (dark, black, thick, gooey)
Transitional stool (brown → green)
Breastfed babies (yellow/gold, mild sweet/sour odor)
Formula fed (pale yellow to light brown, much more odorous)
Who passes more stool, breastfed or formula fed babies?
breastfed babies
What colors of stool are concerning?
white
bright red
dark black
blood streaked
When do you expect to see voiding (urine output) in a newborn?
first 24 hours of birth (must be seen by 48 hours)
Day 1-2 void how many times?
2-6 times
Day 3-4 void how many times
6-8 times
Day 5+ void how many times?
6-8 times