plant fibres - cotton, linen etc
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
different origins of plant fibres
seminal hair (flower, fruit)
stem
fruit enveloppe
leaves
sap
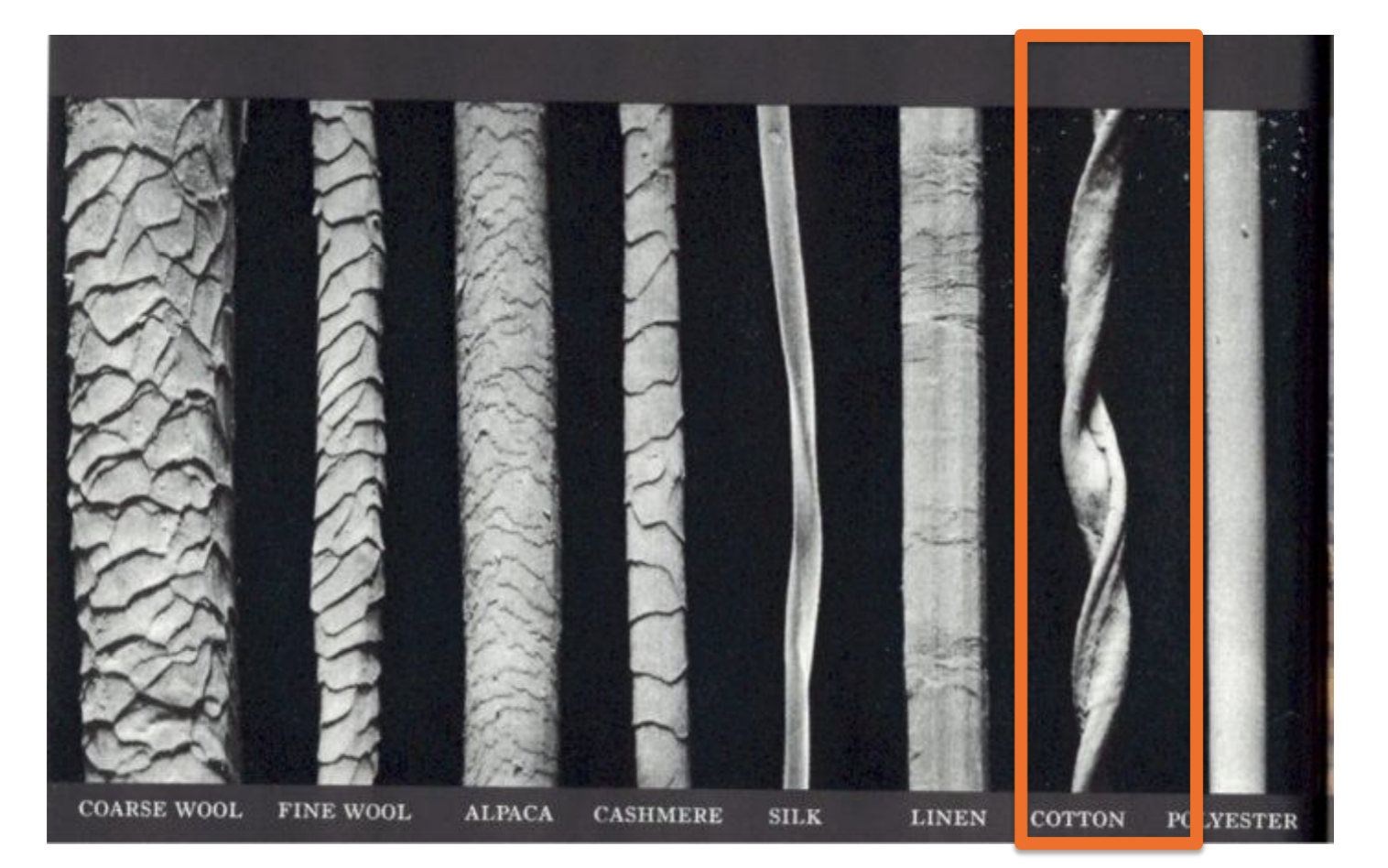
characteristics of cotton
herbaceous plant of 1-1.5m or shrub/bush of 5-6m
soft filaments protecting the cotton seed
30 seeds per flower
length of filament is 12-60mm
white, yellow, red
production in China and India
also US and Brazil
evidence of growth in South America and India as early as 5000BC
in Middle East and North Africa as early as 3000BC
grows in tropical and subtropical climates
needs a lot of water - Aral Sea dried out
has many enemies like virus, bacteria, fungi, insects so needs treatments

garments made with cotton
casual: workwear, sportswear, military, underwear
formal: shirts
utility: household linen, cleaning, towels
cotton - casual clothes
workwear:
jeans, docker pants, overalls, tank top
denim:
de Nîmes
originally for tents then trousers during California Gold Rush
twill weave 3×1, coloured warp, off white weft
thick, dense, robust
raw denim is very stiff
special finishes like stone washing and bleaching
selvedge denim is woven in small width with red selvedge visible at side of leg, expensive and rare
military:
garbadine which is thick, dense, neat diagonals
trench coats, safari jacket, cargo pants, chinos
cotton - sportswear & underwear
t-shirts, polo shirts, tank tops
sports shorts
sweaters and jogging pants
underwear
socks
PJs
comfort wear
sweatshirts
fleece fabric
invented in 1920s on American campuses
1934: Hoodie by Champion
1950s: Russel Athletic: grey heathered fabric so white cotton and black polyester for better resistance
cotton - formal
soft, easy care, thin (8 layers at collar point)
poplin: thin, dense, sleek
Oxford: thicker, grainy look
twill: diagonals
piqué, Bobby: small patterns
chambray: blue & ecru, irregular look, plushy surface
flannelette: brushed shirting
seersucker: cloqué fabric
cotton - different qualities
length of fibres are 12-60mm
best varieties have fibres longer than 32mm (long and extra long)
for high end luxury
combing: sorting the longest fibres, eliminating short ones
extra long: Giza (Egyptian), pima and supime (southwest US), Sea Island (South US and Caribbean)
mercerised cotton:
chemical treatment causing swelling, untwisting and surface modification of fiber
more resistant, better to dye, shinier, less shrinkage
used for shirts and socks (Fil d’Ecosse)
properties of cotton
thin and soft
resistant
breathable
absorption, takes up dye
easy care
hygienic
not expensive
BUT
dries slowly
odours
shrinks
wrinkles
not insular
vulnerable to mildew
ethical considerations
cotton quality labels
pure cotton label
international logo
organic cotton
1-2% cotton production
no GMO, organically approved pesticides
… but more water, more surface bc reduced yield, harmful pesticides (copper sulfate), more frequent treatments
labels: GOTS, BIORE, EKO, FAIR TRADE
Better Cotton Initiative
crop protection, water, soil health, biodiversity, fibre quality, decent work, management system
linen - general characteristics
fiber extracted from stem of flax plant (80-120 cm)
grows easily
best linen from Caen to Amsterdam + Ireland
processing:
retting - getting rid of bark and releasing fibers
scrutching - removing debris, sorting fibers
Masters of Linen label guarantees quality
linen general properties
cool to the touch
regulates heat
mechanical resistance
low elasticity so stiffer, more springy
absorbent
rot resistant
BUT
wrinkles easily
costly
used for summer wear, furnishing fabrics, bed linen
2 qualities:
- dry spun: rough, irregular, stiffer
- wet spun: finer, softer, more regular
pineapple fiber
Piñatex by Ananas Anam
marketed as alternative to leather
fibers transformed into felt
plant fibre identification codes
cotton CO
linen LI
ramie RA
jute JU
hemp HA
sisal SI
coco CC
abaca AB (banana leaf)