MGMT 311 Exam 2 w/ Jia Han
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Marketing Research
Systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to specific marketing situation of organization
Includes new products and modes of distribution
Market Research
Narrower concept of research into specific market
Why use Marketing Research
Focuses and organizes marketing information, permitting…
Spotting current + upcoming problems
Reducing business risks
Identifying sales opportunities
Developing plans of action
Measures effectiveness of 4 Ps
Measures Market Potential, Share, and Extension
Measures Consumer motivation, purchase behavior, and satisfaction
Marketing Research Process
Defining the problem + research objectives
Developing research plan
Implementing research plan
Interpreting and reporting findings
Market Research Process Step 1: Define marketing problems + research objectives
Exploratory Research
Preliminary information
Define the problem and suggest hypothesis
“Please describe current level of your satisfaction to the restaurant”
Descriptive Research
Describe marketing problems
“What do you think of the restaurant”
Causal Research
Test hypothesis about cause-and-effect relationships
“What is the relationship between coffee price and customer repurchase price”
Market Research Process Step 2: Developing Research Plan
Outlines sources of existing data to spell out…
Research approaches
Contact methods
Sampling plans
Instruments
Management problem
Research Objectives
Information Needed ←
How the results will help management decisions
Budget
Market Research Process Step 3: Collecting and Analyzing the Data (Implementing the Research Plan)
Primary Data
Research Approaches
Contact Methods
Sampling Plan
Research Instruments
Secondary Data
Secondary Data (Advantages and Disadvantages)
Advantages:
Lower Cost
Obtained quickly
Cannot otherwise be collected
Disadvantages: Lack of…
Relevance
Accuracy
Current-ness
Impartiality
Examples:
Government data
Research institution reports and journals
News; Magazines
Primary Research
Research Approaches
Contact Methods
Sampling Plan
Research Instruments
Examples":
Direct-mail questionnaires
Online or Telephone surveys
Experiments; Panel Studies; Test Marketing; Behavior Observation
Step 3: Research Plan Implementation → Primary Research → Research Approaches (#1)
Observational research (Watching people in their natural environment)
Survey research
Experimental research
Step 3: Research Plan Implementation → Primary Research → Contact Methods (#2)
Mail
Telephone
Personal
Online
Focus Group Interviewing
Online Marketing Research:
Online Survey
Online behavioral tracking
Online behavior targeting (ad targeting)
Online focus group
Step 3: Research Plan Implementation → Primary Research → Sampling Plan (#3)
Sample: Segment of population selected for marketing research to represent population as a whole
Probability Samples:
Simple random samples
Stratified samples (represents equal % of each demographic)
Nonprobability Samples:
Judgment samples
Convenience Samples (Most convenient group to sample)
Quota Samples (Hit Target # of sample size)
Step 3: Research Plan Implementation → Primary Research → Research Instruments (#4)
Questionnaires
Most common
In person, telephone, online
Flexible
Researchers must be careful with wording
Useful in exploratory research
Use different formatting: scales, rankings, open/closed-ended questions
Mechanical Instruments
People meters
Checkout scanners
Neuro-marketing
Market Research Process Step 4: Interpreting and Reporting the Findings
Clean data: Edit, code, tabulate
Present: Organized manner;
Brand
Capitalized value of trust between company and consumer
Adds value
Role of Brand Image: Company Perspective
Extension of feelings to new products
Upcharging
Customer loyalty
More frequent purchases
Positive word-of-mouth
Greater channel power
Attracts higher quality employees
More favorable ratings
Brand Equity
Differential effect of know brand name for customer response to product and marketing
Counters/opposite of brand parity
Measured by…
Financial value
Stock value
Revenue premium
Consumer value
Steps to Brand Strategy
Brand Positioning
Attributes
Benefits
Beliefs + Values
Brand Name Selection
Brand Sponsorship
Licensing
Co-Branding
Brand Development
Line extensions
Brand extensions
Multi-brands
New brands
Branding vs Positioning
Branding: What experience can I expect; Proof of successful positioning; Promises good user experiences; Owns a word/phrase
Positioning: Why buy me?; Comes before Branding; Establishes preference for brand relative to competitive offerings based on perception of unique + important difference
Brand Loyalty
Ultimate Objective of Branding
Only brand a consumer purchases
Drivers:
Emotion
Value
Levels of Brand Loyalty
Brand Recognition
Awareness
Identification
Brand Preference
Previous Experience
Brand Choice
Brand Insistence
Refuse Alternatives
Ultimate Stage (Where Brand wants to be)
Types of Brands
Generic Products
Manufacturer’s Brand
Private Brand
Captive Brands
Family Brand
Individual Brand
Type of Brand: Generic Products
Absence of brand
Plain label
Type of Brand: Manufacturer’s Brand
Manufacturer = Brand
HP
Sony
Dell
Type of Brand: Private Brand
Wegman’s
Member’s Mark
Weiss
Popularity of this has fluctuated
Connotation of low price & quality w/ few differences
→
Value purchase with improved quality + higher loyalty toward retail outlets (low loyalty to specific brands); Differentiate private outlets + increased advertising of private brands + increased in-store display & packaging quality
Higher gross margins and lower prices for retailers of private labels, with greater loyalty and differentiation from national brands
Type of Brand: Captive Brands
Spinoff or Private label
Exclusivity
Type of Brand: Family Brand
Single name for related products (eg. Amazon)
Type of Brand: Individual Brand
PepsiCo
Frito Lay
Unilever
P&G
Co-Branding
Partnership of two brands for something
Licensing
Product that purchases licensing to use/display brand name of other company
Brand Strategies
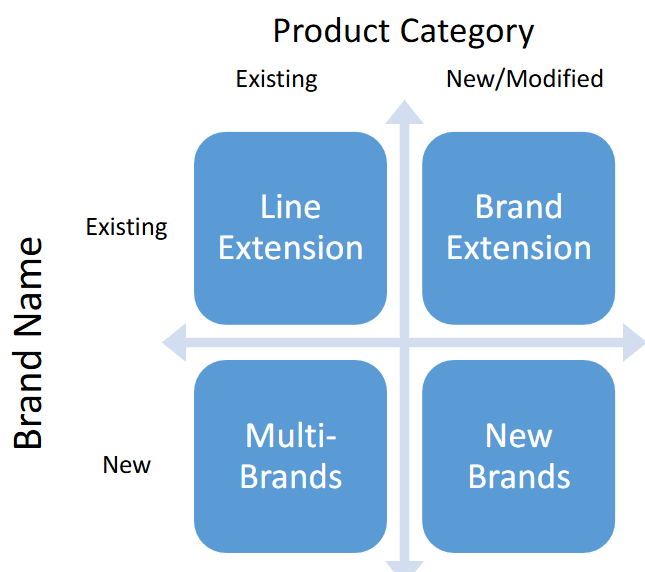
Brand Dilution
Brand weakening from overuse, price-cutting, and ill-judged brand extensions
Promotion Mix
Specific blend of promotion tools used persuasively to communicate customer value + build customer relationships

The Promotional Mix: Advertising
Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by identified sponsor
The Promotional Mix: Sales Promotion
Short-term incentive to encourage purchase/sale of product/service
The Promotional Mix: Personal Selling
Personal interaction by firm’s sales force for purpose of engaging customers, making sales, and building customer relationships
The Promotional Mix: Public Relations
Building good relations with company’s various publics by obtaining favorable publicity, building corporate image, and killing rumors
The Promotional Mix: Direct Marketing
Engaging Directly with carefully targeted individual consumers and customer communities for immediate response and lasting relationships
How Marketing Comms Environment is changing
Mass markets have fragmentation → shift from mass to target marketing
Information technology facilitates segmentation
Less broadcasting, more narrowcasting
IMC Integrated Marketing Communications
Integrating + Coordinating comms. channels to deliver clear + consistent + compelling message about org. + products
The Comms Process: Encoding and Decoding messages (image)
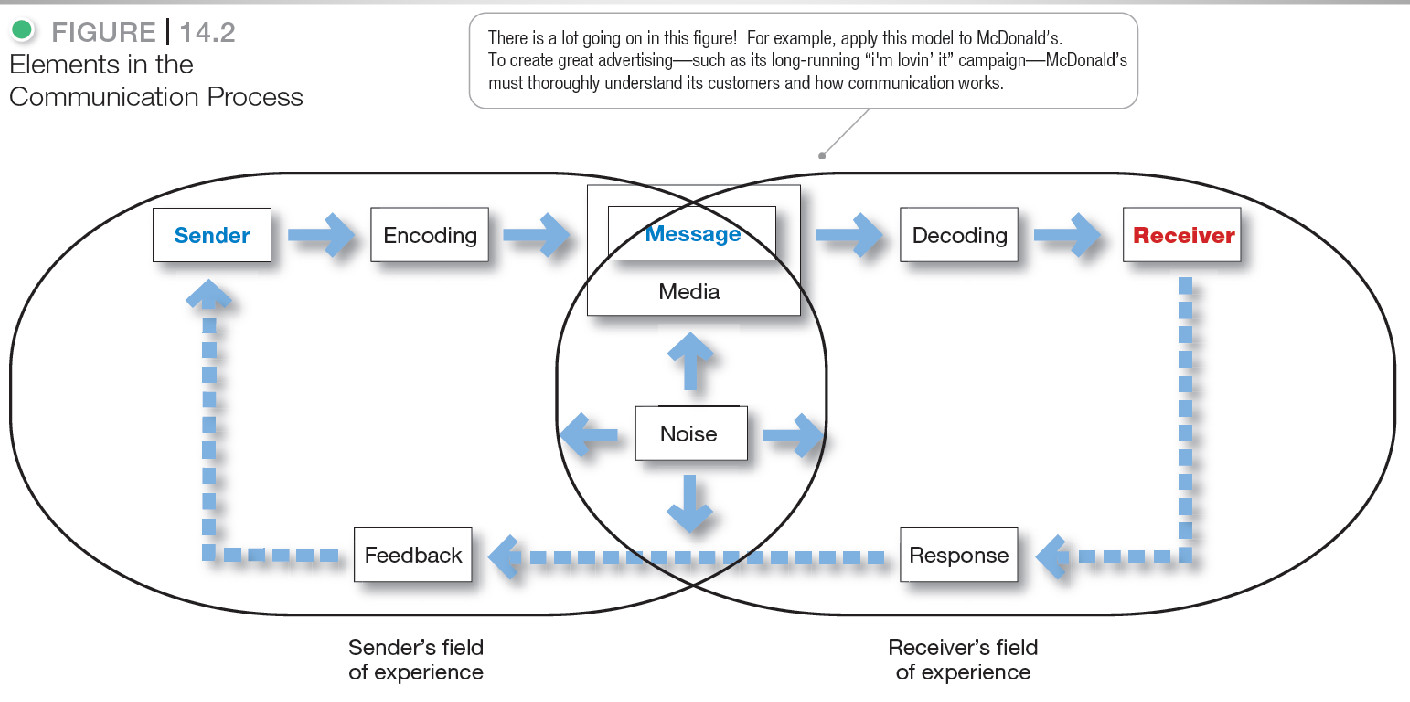
Steps in Effective Marketing Comms.
ID Target Audience
Determine Comms. Objectives
Design Message
Choose Media
Select Message Source
Collect Feedback (sometimes step 5, for some reason smh)
Effective Marketing Comms. Step 2: Determining Comms. Objectives
Use 6 Buyer Readiness Stages
Awareness
Knowledge
Liking
Preference
Conviction
Purchase
Example: Domino’s “AnyWare” campaign to order on anything for delivery anywhere
New CEO reworks crust
New order tracking
New easy means of order (one click, AnyWare, etc)
Drones and new deliveries
Scanning pizza for points
No third-party delivery to avoid fees
2000+ stores (which steal profits from current ones) to achieve <30 mins delivery
Effective Marketing Comms. Step 3: Designing Message
AIDA Framework
Message content contains appeals/themes to produce desired results…
Rational Appeals — Statistics; facts
Emotional Appeals — Love, price, joy, humor, fear, guilt, shame
Moral Appeals — Moralty
Message Content: What to Say
Message Structure + Format: How to Say It
3 Message Structure Options:
Whether to draw a conclusion (Throw a fact out with no direction)
One vs Two Sided Arguments (Only favorable arguments vs both downs and ups)
Order of Argument presentation (Clear order of eg. challenge, solution, result)
Message Format
Design, layout, copy, color, shape, movement, words, sounds, voice, body language, dress, etc
AIDA Model
Describes consumer engagement with article, advertisement, offer, or product
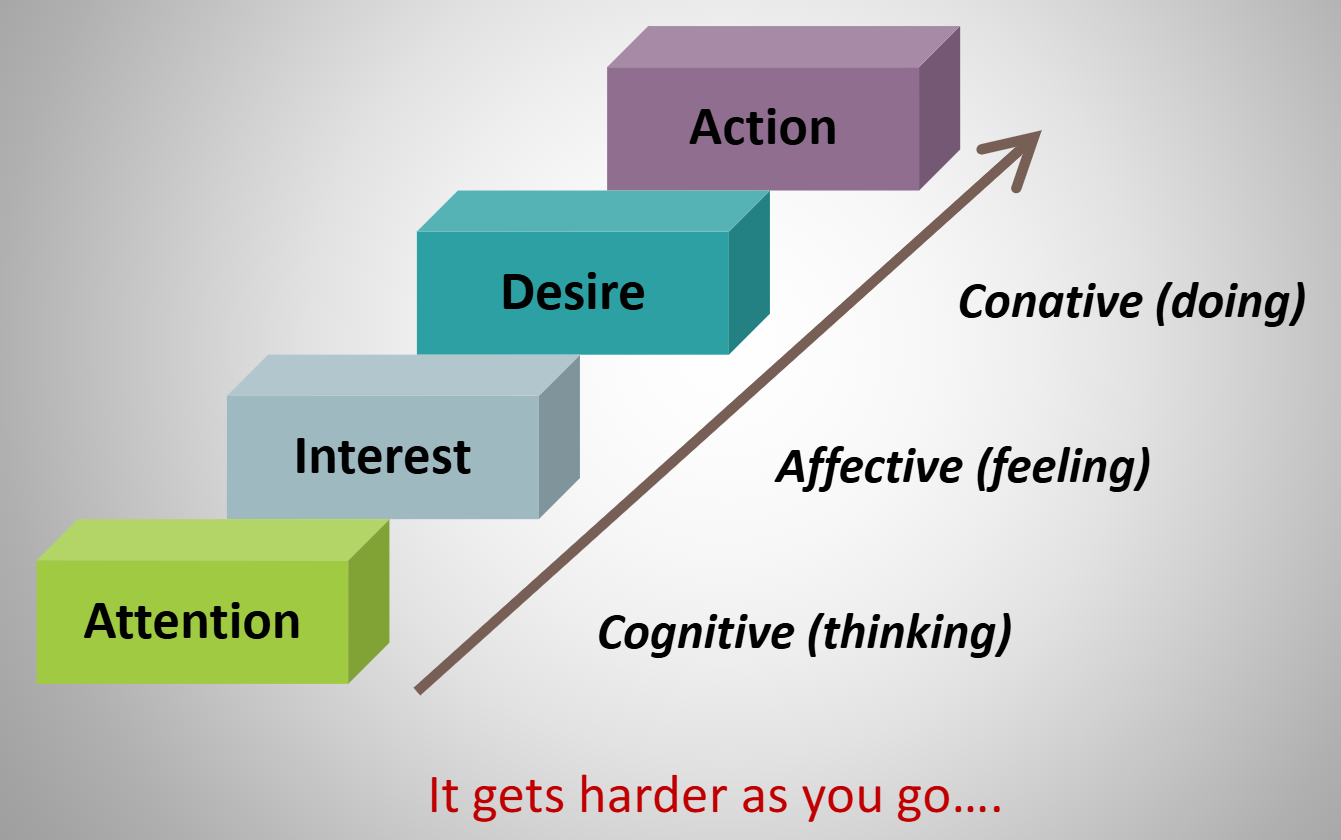
AIDA: Attention
Headline
Visuals
Layout
Colors
Size
Electronic; Sound; Music; Animation
AIDA: Interest
Drama/Story (Dos Equiss)
Cartoons (M&Ms)
Dialogue (“It’s a Diet Coke Thing)
AIDA: Desire
Arouse desire
Unique selling proposition
Rationale
Convenience persuasion
AIDA: Action
Ask consumers to do something
Imperative: ‘drink coke’
Facilitate: ‘1-800…’
Direct Competitive: “supplies are limited”
Message Strategies
Primary tactic/approach to deliver message theme
Cognitive
Affective
Conative
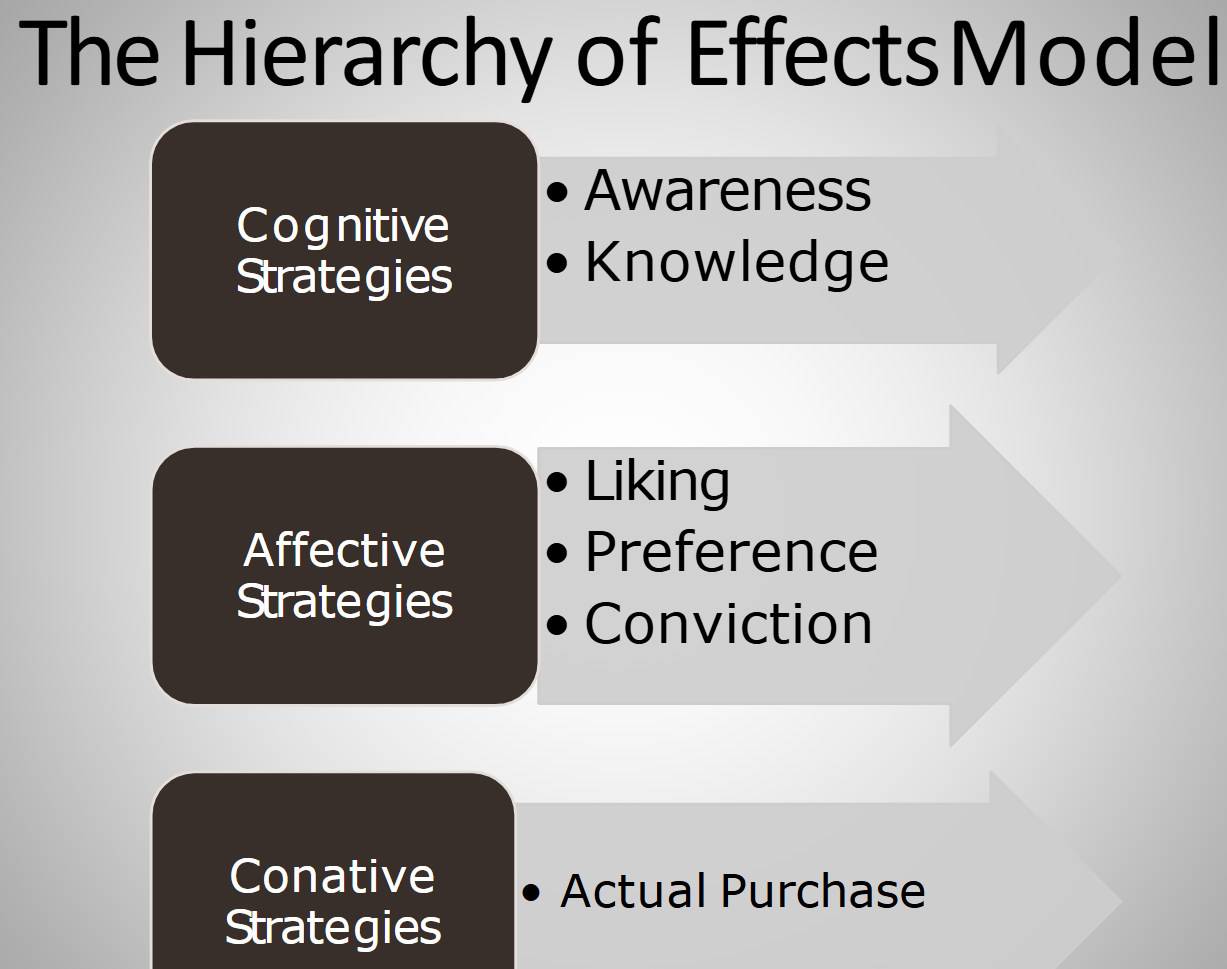
Messaging Strategies: Cognitive
Generic Messages
No claim of superiority (PepsiCo)
Preemptive Messages
Superiority by attribute before competition
Unique Selling Proposition
Explicit, testable claim of uniqueness/superiority (Can be proven)
Hyperbole
Untestable exaggeration
Comparative Advertising
Compare against competition; use with care, can work against you
Messaging Strategies: Affective
Invoke feelings/emotions matched to product/service/company
Messaging Strategies: Conative
Support promotional efforts with…
Coupons
Phone-in promotions
Sweepstakes
Internet Promotions/coupons
Developing Effective Comms. Step 4: Choosing Media
Personal Comms. Channels
Face-to-face, phone, mail, Internet
Word-of-mouth influence is critical
Buzz marketing cultivates opinion leaders
Nonpersonal Comms. Channels
Media, atmosphere, events
Developing Effective Comms. Step 5: Selecting Message Source
Celebrities, athletes, entertainers, professionals, health care providers
Highly credible sources are more persuasive
Poor spokespersons can tarnish brand
Developing Effective Comms. Step 6: Collecting Feedback
Recognition, recall, and behavioral measures assessed
May suggest changes in product/promotion
Digital Marketing
Promoting products/services with digital distribution channels
Clutter
Major problem; cost of selling tripled in past decades
Traditional media has broken trust with consumers
Digital Marketing Strategies
Internet Marketing
Mobile Marketing
Social Marketing
Viral Marketing
Digital Marketing Strategies: Internet Marketing
Gives consumers a voice, publishing platform, and forum to be heard, shared, and researched
Supports…
Product Sales
Sponsorship sales
Service sales
Additional revenue streams (banner ads)
Community relations
Brand-customer connection (blogs, chats, etc)
General promotion
Digital Marketing Strategies: Mobile Marketing
Marketing on/with mobile device (text promos, push notifications, etc);
Massive potential growth
Mobile Apps:
Engage consumers with brand
Streamline business use
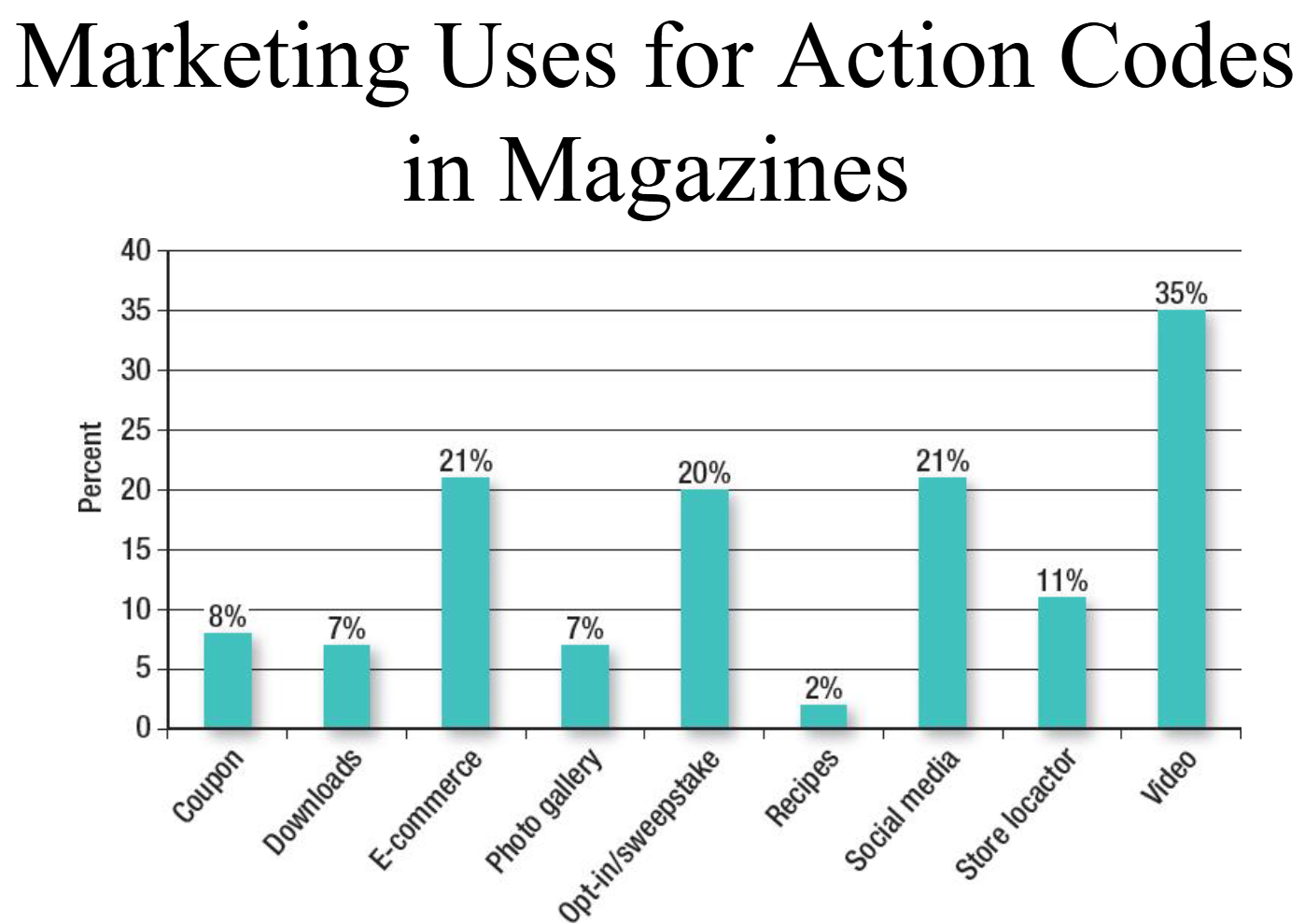
Action Codes:
QR, watermarks, 2D Barcodes
Engagement
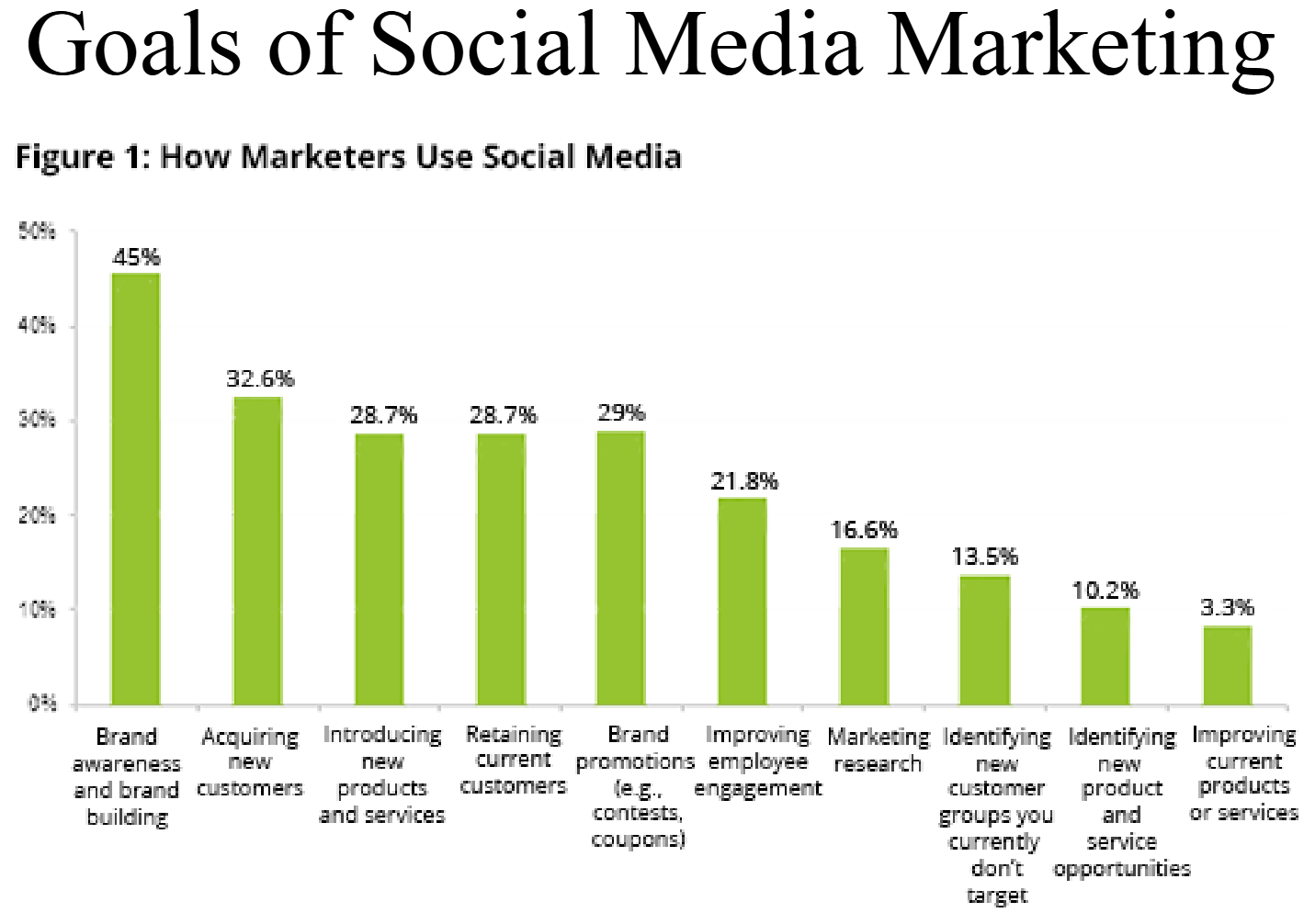
Digital Marketing Strategies: Social Media
Online communities exchanging information, ideas, messages, other content (vids, music, etc); Social media platforms share messages quickly, and can cause…
Purchase
Subscription
Registration to online community
Participation in event
Social Media Platform: Software or tech allowing users to build, integrate, or facility community, interaction with users, and user-generated content
Social Networking Sites (Insta)
Bookmarking Sites (Pinterest)
Social News Sites (Sites linking other news/articles)
Online Forums: Message boards (quora)
Blogging Sites: Blogs
Microblogs (Twitter)
Social Media Marketing Plan
Executive Summary
Brief Overview
Analysis of Competition
Body of Plan
Phases:
Set goals
Target audience
Develop strategies
Produce content
Implement plan
Monitor
Measure
Viral Marketing
Encourages individuals to pass on marketing message to others for exponential growth by word-of-mouth (ALS, Duolingo, Eyes, Lips Face song, etc)
Dell: Early Adopter of Social Media
Leader in online frictionless commerce
One of first to launch online discussion forum
First company to hit $1M in one day in online revenue
One of first to launch online support
Also #DellLove Personally thanking customers

Dell’s Social Media Services Group (SMSG)
Advisor in…
Understanding what is being said about brand, industry, competitors, products, etc
Improving customer relationships via social media
Building their social media strategy
Public Policy Issues in Direct and Digital Marketing
Irritation: Annoying + Offending Customers
Unfairness: Taking unfair advantage of impulsive or less-sophisticated buyers
Staples pricing by geography down to a few miles
Deception: “Heat merchants” design ads to mislead consumers
Fraud: Identity theft + financial scams
Consumer Privacy: Concerns marketers have too much information and use it for unfair advantages
The (New) Promotional Mix: Social Media
Two Interrelated promotional roles:
Enables companies to talk to customers
Enables customers to talk to one another
New Comms. Paradigm:
Information on products/services communicated by individual customers
Customer behavior influenced by social media
Customers reduce reliance on advertising as source of information
Marketers must learn to talk to customers instead of at them, with…
Networking platforms (#MyBeautyMySay)
Provide Customer Engagement
Provide Information
Provide Exclusivity
Use Stories (Salvatore Ferragamo)

Inbound vs Outbound marketing
Outbound: Traditional Advertising Methods
Inbound: Marketing strategies focusing on pulling audiences in instead of going to get prospects’ attentions
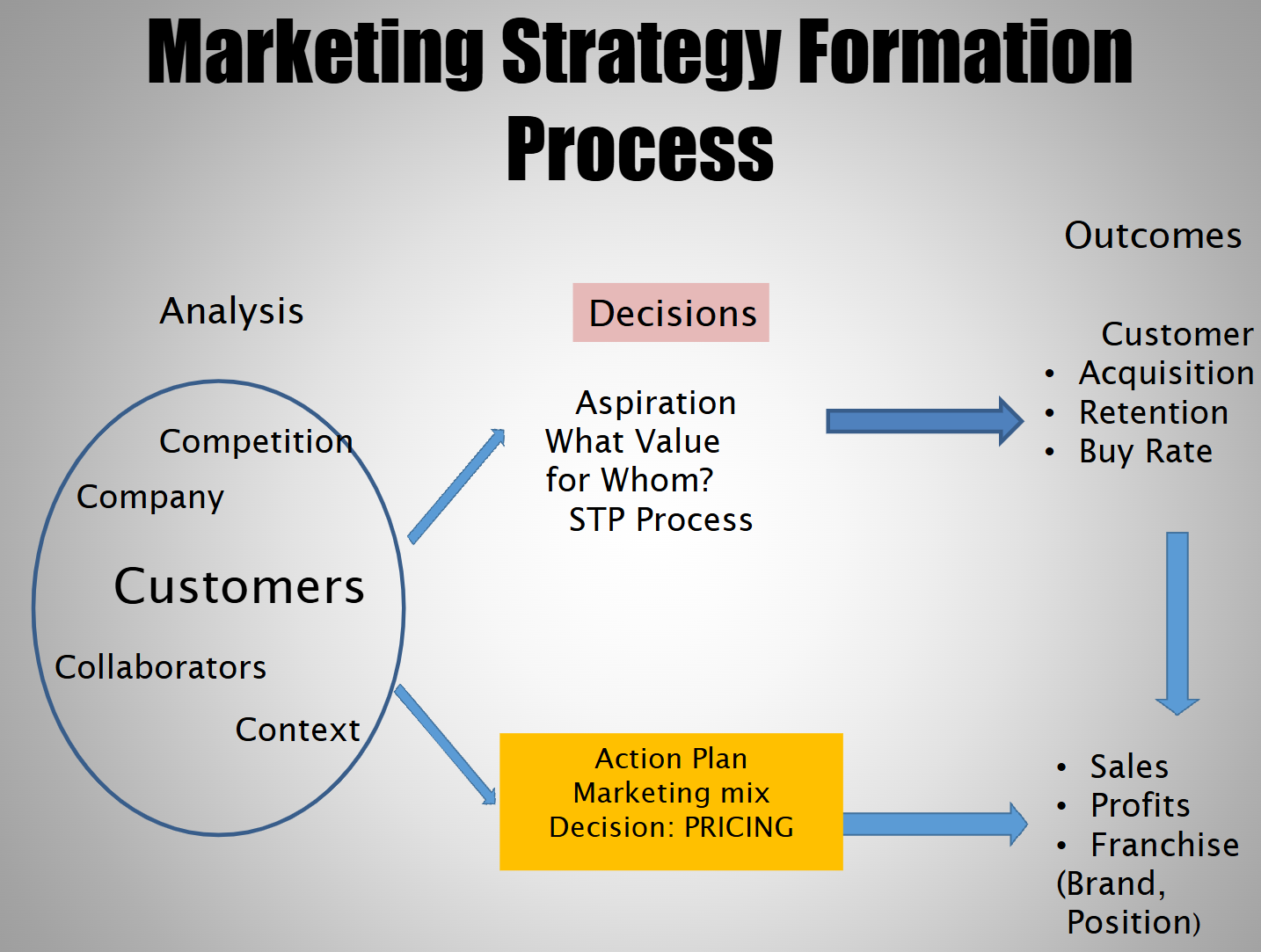
Marketing Strategies Formation Process (Image)
Price
Amount of money charged for product/service, or sum of all values customers exchange for benefits of having/using product/service
One of most flexible marketing mix elements
Key strategic tool for creating customer value + building relationships
Focus on customers, costs, and competitors to set prices
Major Pricing Strategies
“Cost-Based Pricing” — Sets prices based on costs of product + fair rate of return for effort + risk (Price-Floor Strategy)
“Value Based Pricing” — Using buyer's’ perceptions of value instead of sellers’ cost (eg. services, art, superior goods, etc) (Price-Ceiling Strategy); No demand above this price
Competition-Based Pricing: Setting prices based on competitors’ strategies, costs, prices, and market offerings
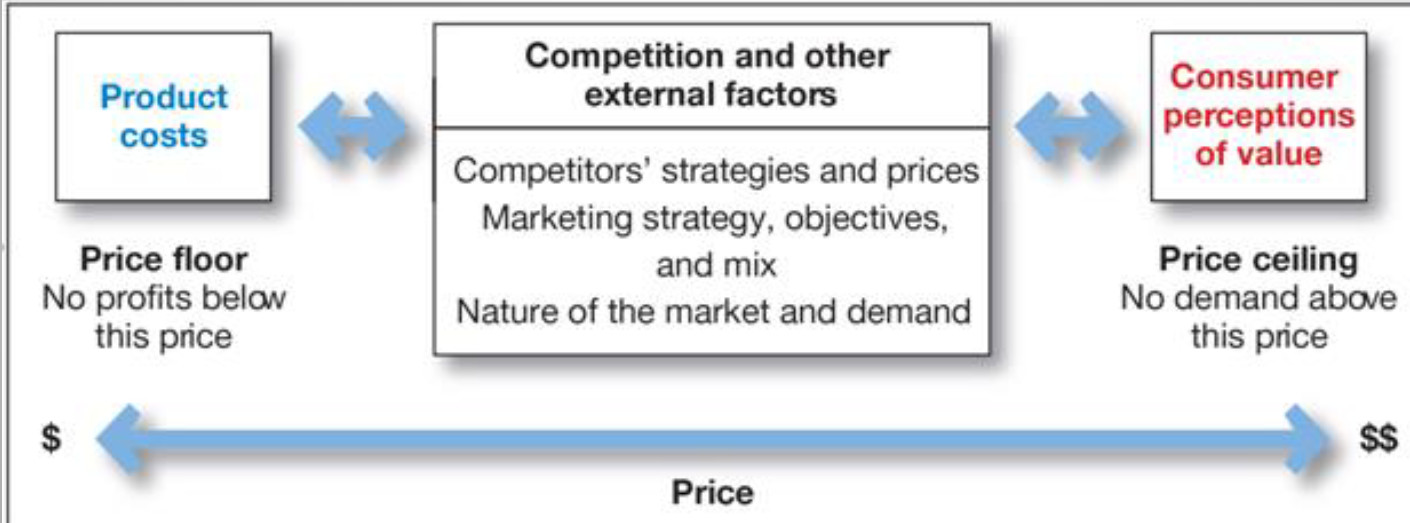
Two Types of Customer “Value-Based Pricing”
Good-Value Pricing: Offering right combo of quality + service @ fair price
Everyday Low Pricing
High-Low Pricing: High everyday prices with frequent promotions for temporarily lower prices
Value-Added Pricing: Use value-added features/services to differentiate offerings to justify higher prices
Cost-Based Pricing Aspects
Cost-Plus Pricing: Adds standard markup to costs of product
Benefits:
Sellers certain of costs
Price competition minimized
Buyers feel it is fair
Disadvantages: Ignores demand and competitor prices; thereby doesn’t make a lot of sense (not the best price)
Break-Even Pricing (Target Return Pricing): Setting price to break even on costs or make target return
Fixed Costs: Nonvaried with production/sales levels (Rent, heat, interest, executive salaries, etc)
Variable Costs: Vary with production levels (Raw materials, packaging, etc)
Total Costs = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs
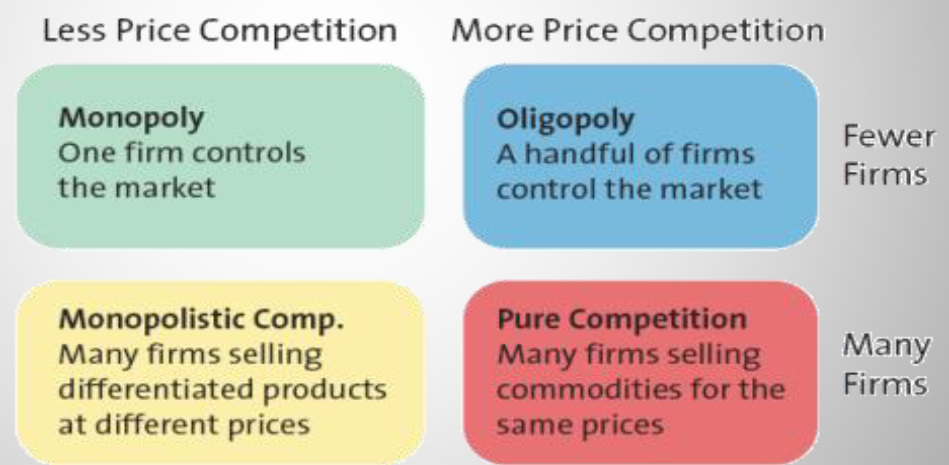
Types of Markets
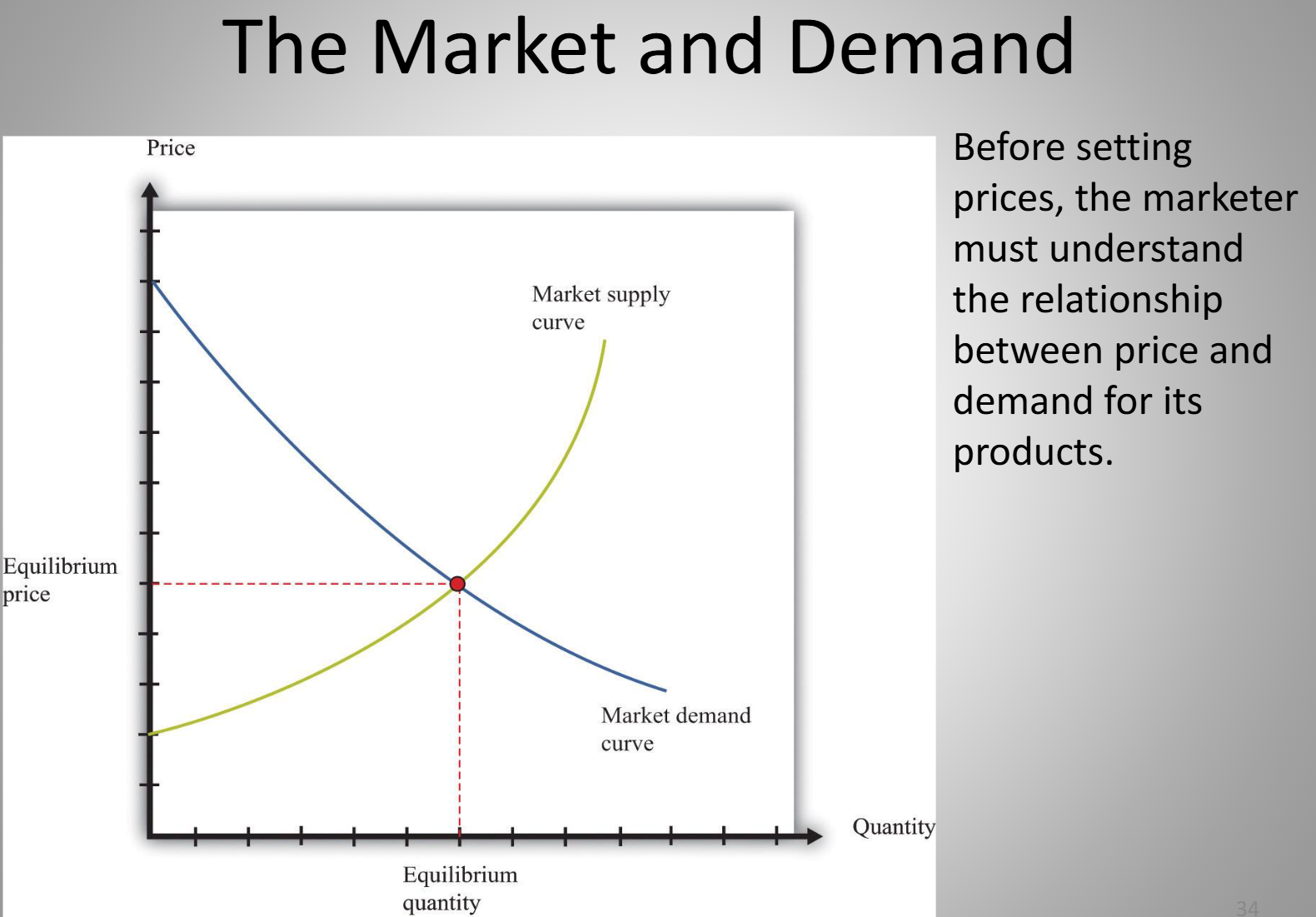
Supply and Demand Curves
Inversely related 😀
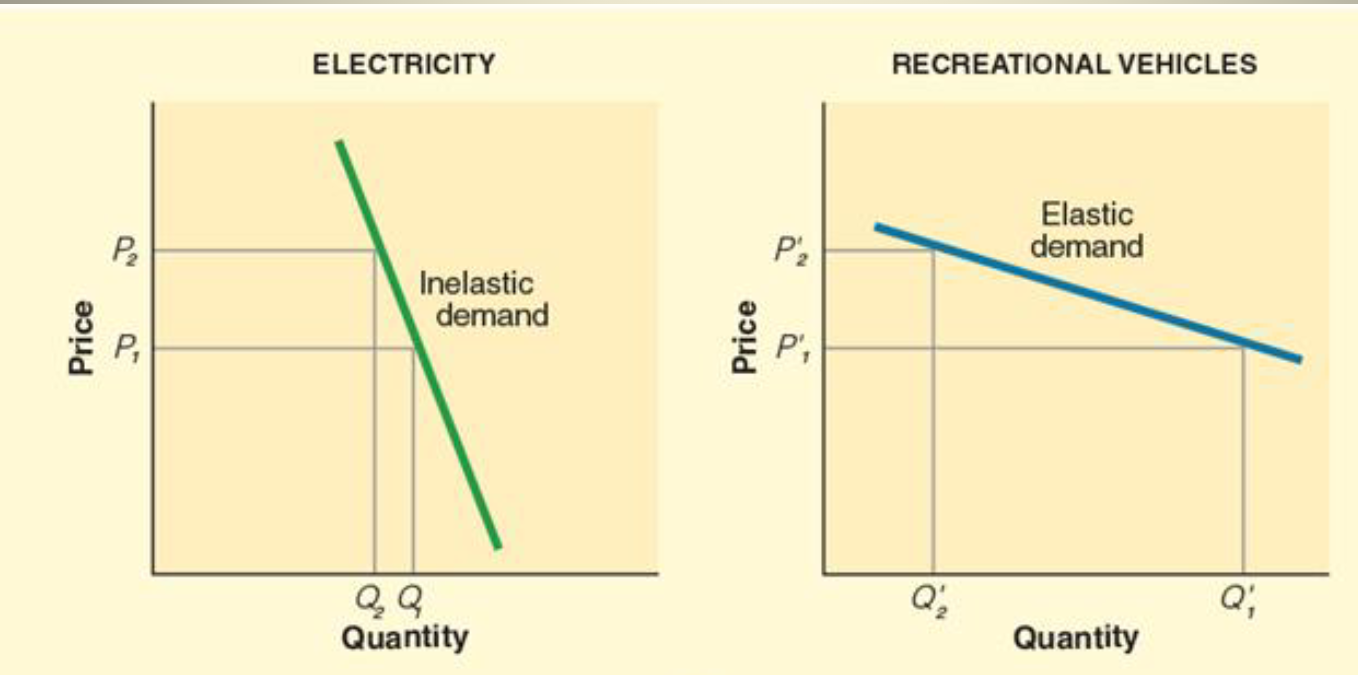
Price Elasticity of Demand
Measure of sensitivity of demand to changes in price
Inelastic Demand: Change in price → Barely changing demand (eg. necessities) E < 1
Elastic Demand: Change in price → Significant change in demand; E > 1
Unit Elastic Demand: Elasticity = 1
PED = %▲ in Quantity Demanded / %▲ In Price (WE USE ABSOLUTE VALUE)
Marginal Analysis
Examines change in one unit on costs and revenues
Marginal Cost: Extra cost of producing one more unit
Marginal Revenue: Extra revenue from sale of one more unit
MR > MC units add to profits; MR < MC units subtract from profits
Optimal Quantity: MR = MC
Product Mix Pricing Strategies
Product Line Pricing: Price based on cost, differences, customer evaluations, and competitors’ prices between items in product line
Optional Product Pricing: Considers optional/accessory products along with main product (automobiles)
Captive Product Pricing: Set prices of products that are needed for main products (printer ink,
Product Bundle Pricing: Combines several products at reduced total price (full makeup kit)
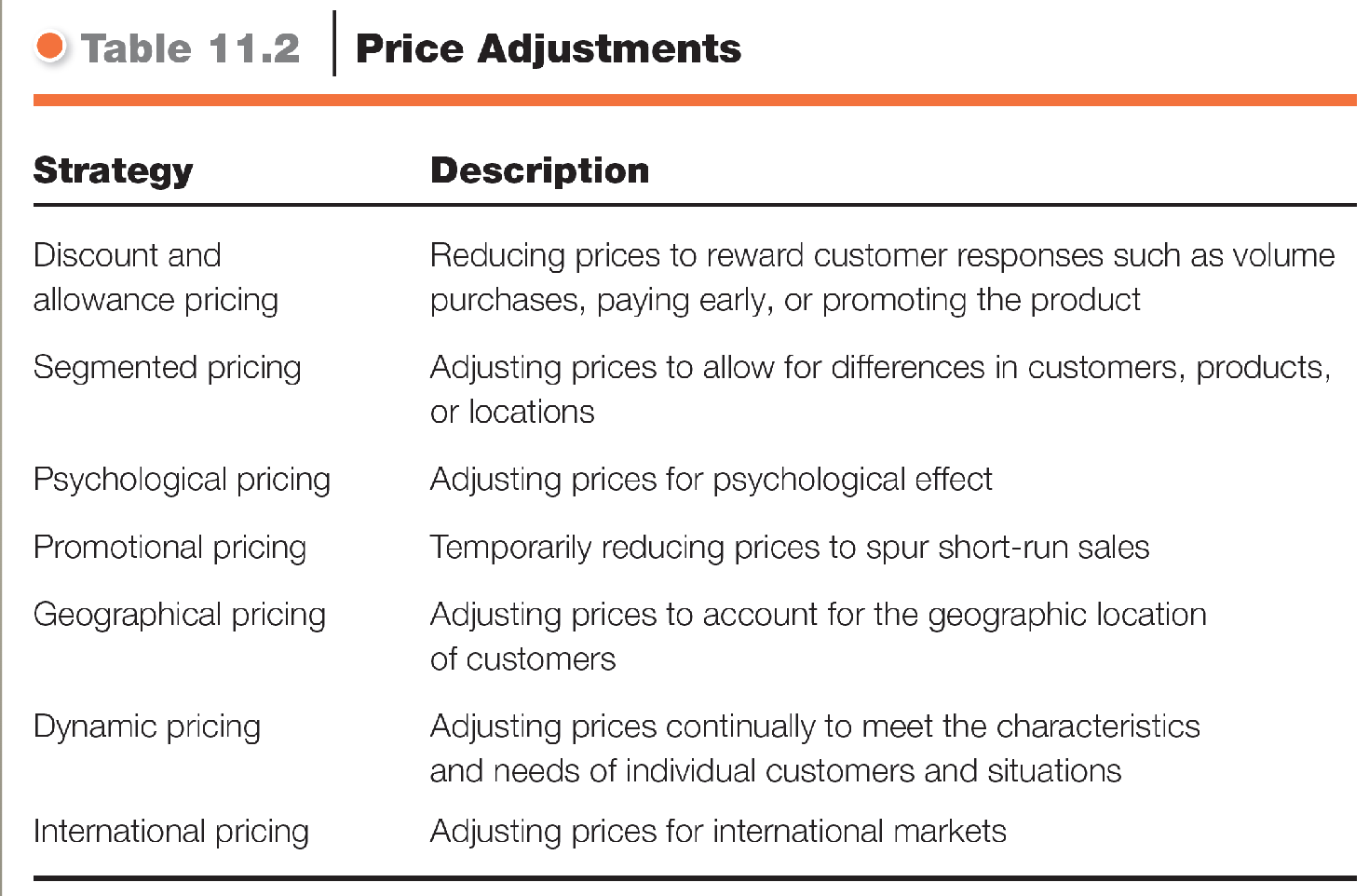
Price Adjustment Strategies
Discount and Allowance pricing: Reduce prices to reward customer responses (volume purchases, early payments, engaging promotions)
Segmented Pricing: Selling at multiple prices w/o difference in production costs
Markets must be legally segmentable, with different degrees of demand,
Customer-segment
Product-form
Location-based
Time-Based
Promotional Pricing: Characterized by temporarily lower pricing (below listing and/or cost)
Special-event pricing
Limited-Time Offers
Cash Rebates
Low-interest financing, extended warranties, free maintenance
Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices continually (airports)