Anatomy and Physiology Lab 4: Skeletal System of Torso
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Axial Skeleton location
skeletal system composed of the bones down the middle of the body
ex. skull, vertebral column, sternum, ribs
Appendicular skeleton location
upper and lower limbs and the girdles that attach them to the axial skeleton
What does articulation mean?
joint or connection between bones
What is a condyle look like on a bone?
large-ish bony nub on the end of a bone. The nub on animations of bone that make them look like bones
What does a facet look like on a bone?
only on vertebra, the projections on the top and bottom (superior and inferior)
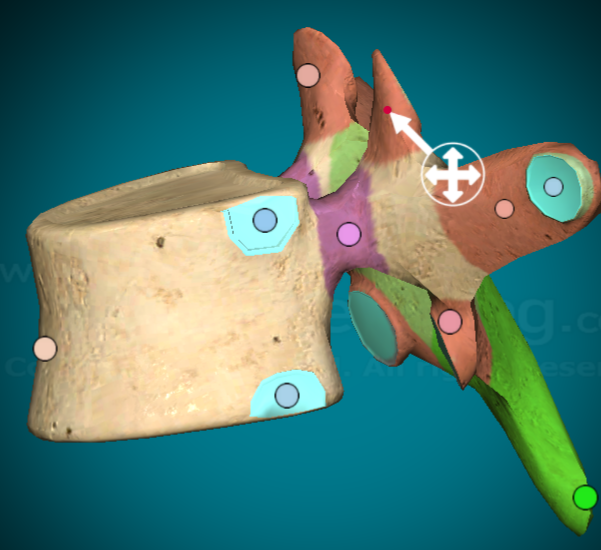
What does the head of a bone look like?
prominent, rounded epiphysis
What does a trochlea on a bone look like?
like a sideways hour glass on the distal end of the humerus. It attaches to the ulna and allows for joint movement.
What is fossa look like on a bone?
a fingerprint-like depression

What does a sulcus look like on a bone?
a shallow grove (can be between two tubercles like on the humerous?)
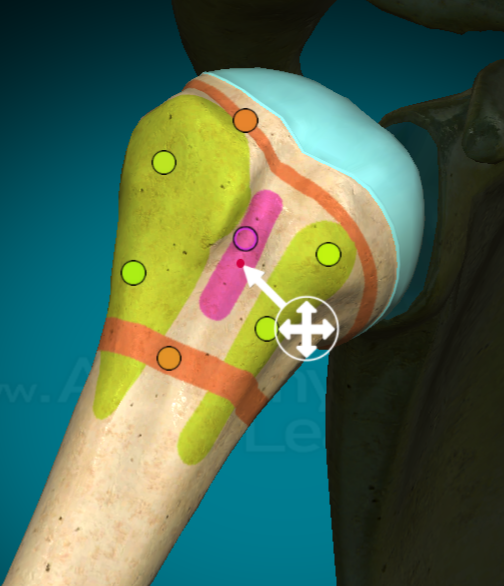
What does a crest look like on a bone?
a narrow, raised ridge along the long edge of a bone
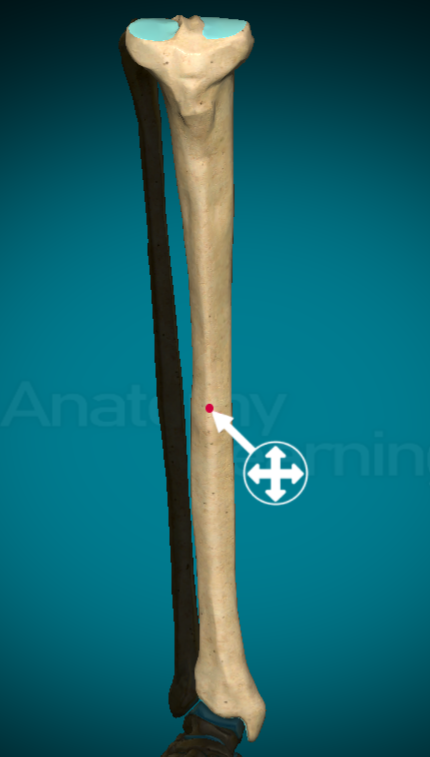
What is an epicondyle on a bone?
less prominent nub right near the condyle
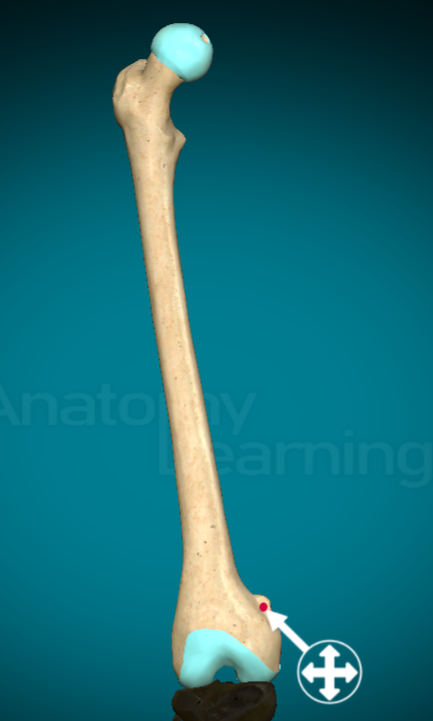

What does a line look like on a bone?
less prominent raised ridge on a bone (?)
What is a “process” on a bone?
bone projection that attached tendon, ligament, or muscle (varies in size)
What does a “spine” on a bone look like?
sharp, slender ridge
What is a trochanter on a bone?
FEMUR ONLY
massive rough projection near the hip
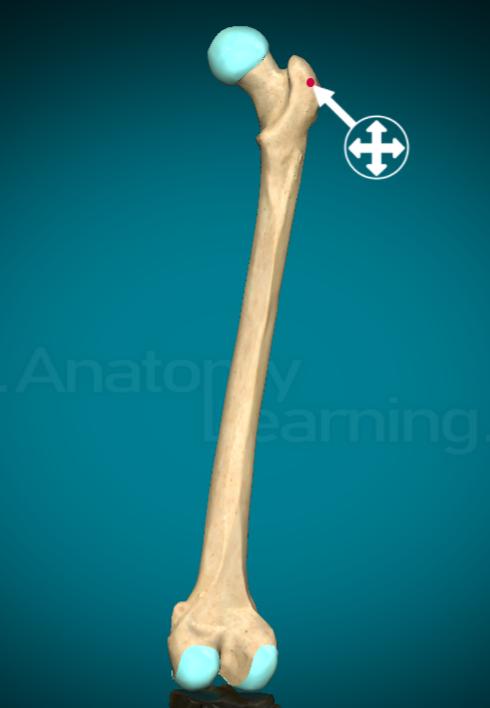
What is a tubercle on a bone?
small, round projection that connects muscles, ligaments, and tendons
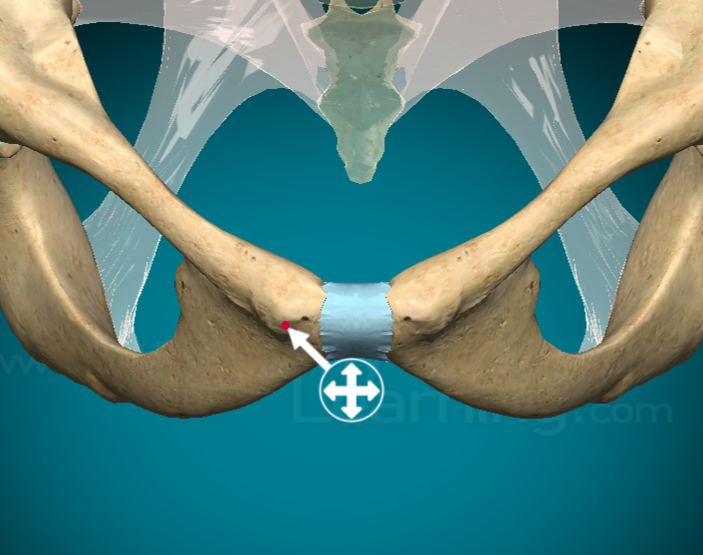
What is a tuberosity on a bone?
slightly larger, round projection that connects muscles, ligaments, and tendons
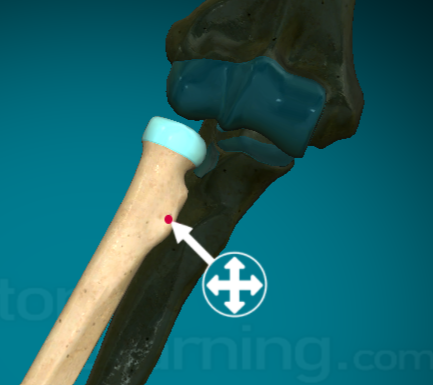
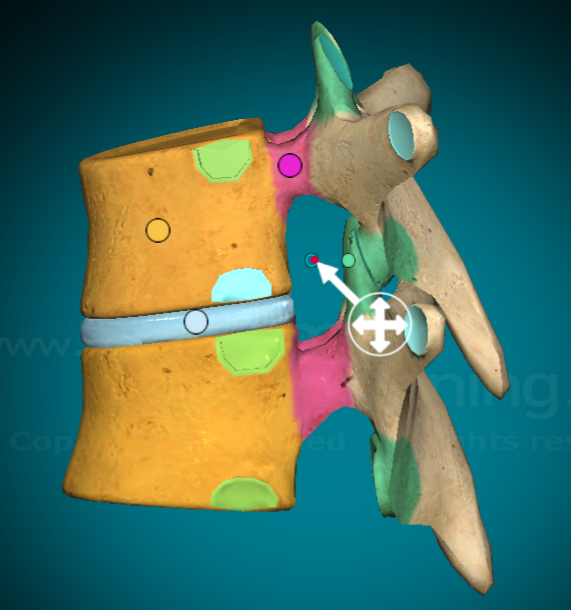
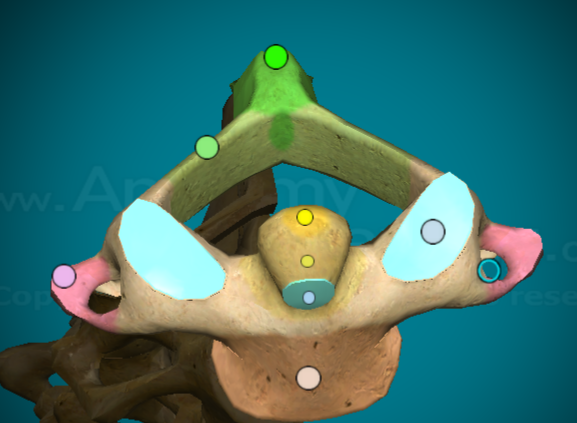
What is the “body” on a typical vertebra?
the largest, fattest portion of the vertebra (main portion)
Where is the vertebral arch on a typical vertebra?
the top curve of the vertebral foramen
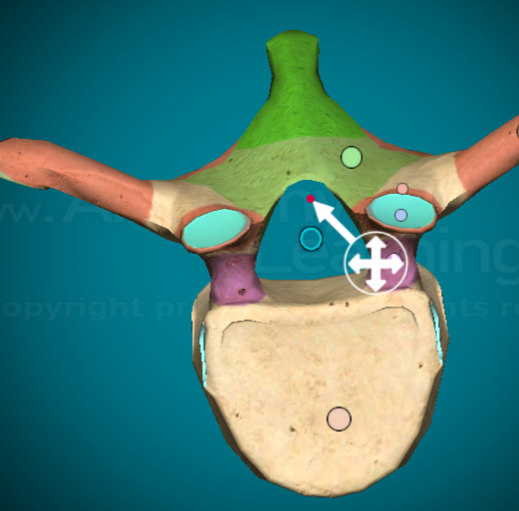
Where is the pedicle on a typical vertebra?
the bit of bone that connects the transverse process to the body of the vertebra
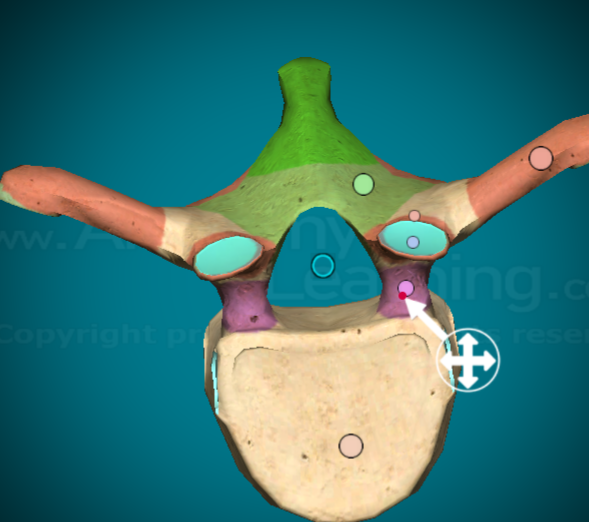
Where is the lamina on a typical vertebra?
the bit of bone that connects the spinus process to the transverse process of the vertebra
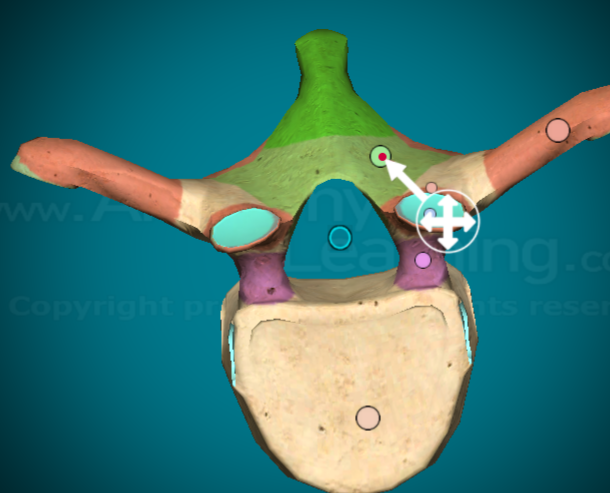
Where is the vertebral foramen on a typical vertebra?
the hole in the center where the spinal column goes
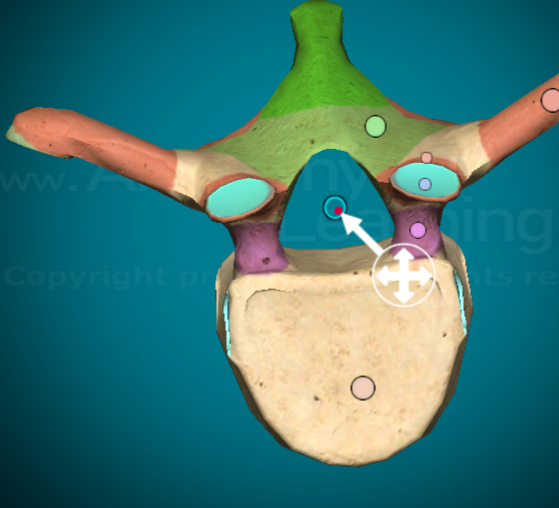
Where is the vertebral canal on a typical vertebra?
the tunnel that is created from the vertebral foramen when multiple vertebra are stacked on top of one another
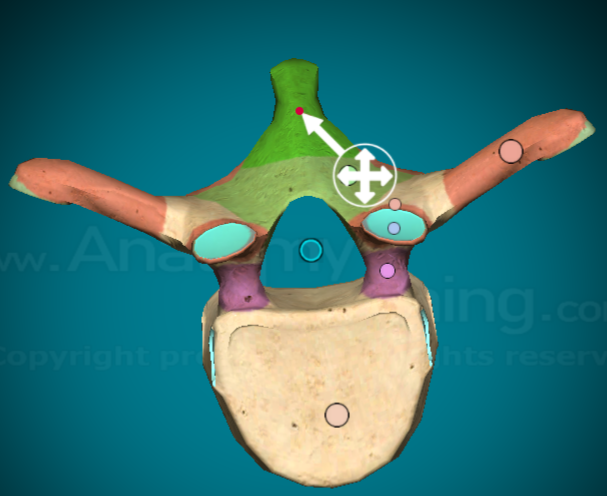
Where is the spinous process on a typical vertebra?
the large, slender, most posterior projection that comes out of the vertebra
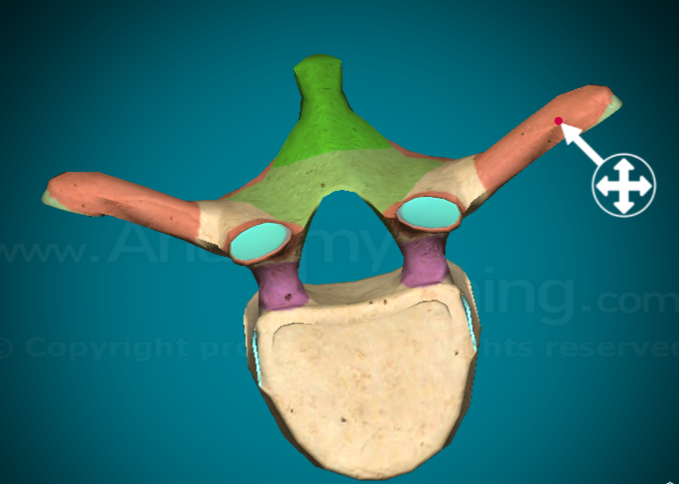
Where are the transverse processes on a typical vertebra?
the large, bilateral projections that come out at an angle
Where are the superior articular facets on a typical vertebra?
when looking at the vertebra from the top, the projections that come out towards you (when two vertebra are connected, the inferior facet and the superior facet connect to form the intervetebral foramen)
Where are the inferior articular facets on a typical vertebra?
When looking at the vertebra from the bottom, the projections that come out towards you (when two vertebrae are connected, the inferior facet and the superior facet connect to form the intervertebral foramen)
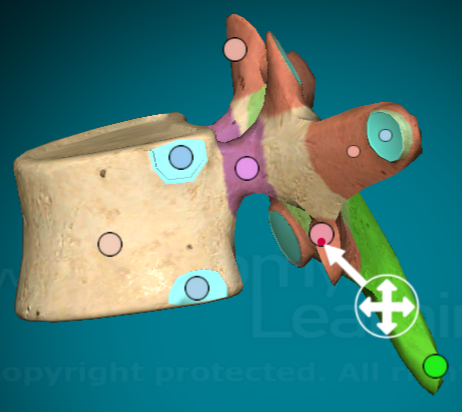
Where is the intervertebral foramen on a typical vertebra?
the hole created when inferior facet and superior facets connect
What and where are the concave curves of our spine?
thoracic and sacral
What and where are the convex curves of our spine?
cervical and lumbar
What are the 4 regions of our spine?
Cervical vertebrae
thoracic vertebrae
lumbar vertebrae
sacrum
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
What are the distinctive features of the cervical vertebrae?
considerably smaller than the other vertebrae
all have transverse foramen (bilateral holes where the transverse processes are on the other vertebrae
Distinctive features of C1 (Atlas)
NO BODY
v thin
have transverse foramen instead of transverse processes
has a nub of a spinus process
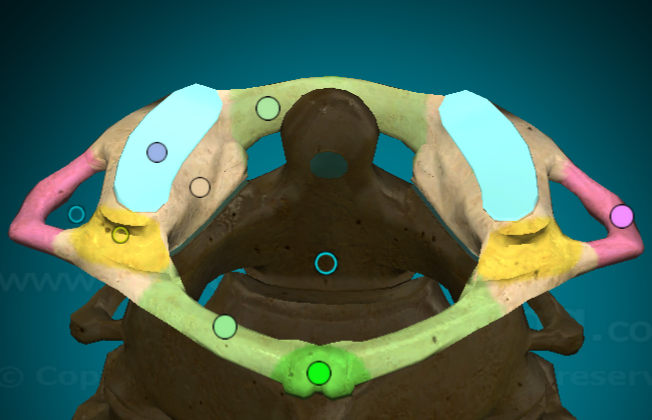
Distinctive features of C2 (Axis)
dens
transverse processes

How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
Distinctive features of thoracic vertebrae
all have ribs attached
a heart-shaped body
downward tilting spinus processes
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
Distinctive features of lumbar vertebrae
very chunky
kidney bean-shaped body
blunt spinus process
some people have 6 of them, but it doesn’t cause issues
How many fused vertebrae make up the sacrum?
5
What are the ala on the sacrum?
The bilateral wing-like protrusions on near the top of the bone
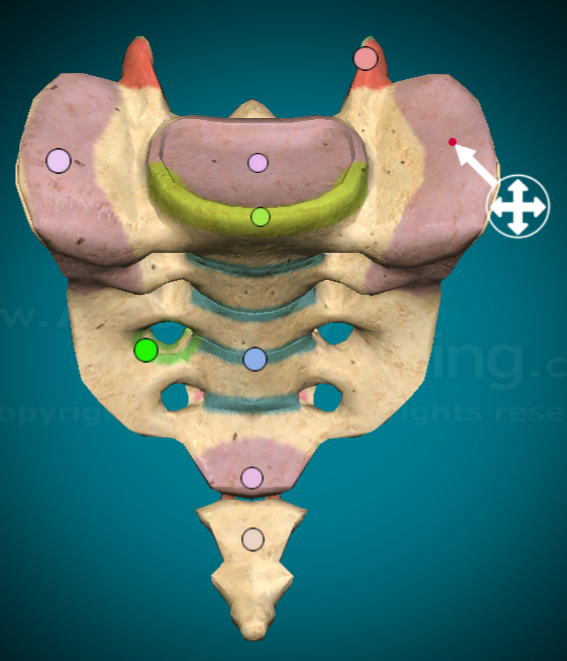
What does the body of the sacrum look like?
a fused strip between the pairs of foramina
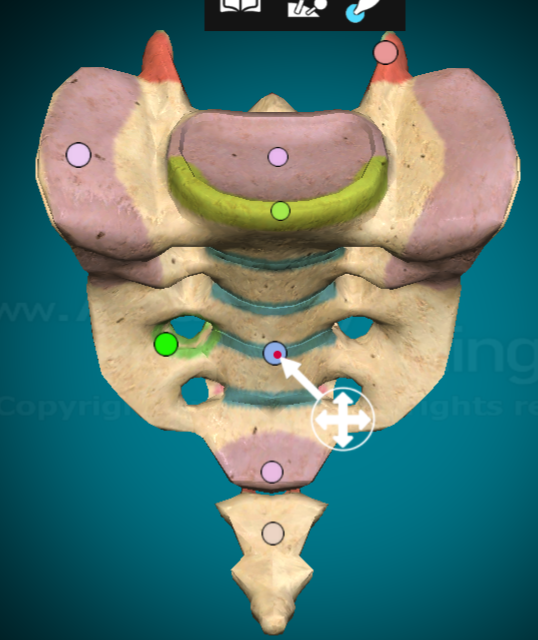
What are the anterior sacral foramina?
the 4 pairs of bilateral holes when looking at the sacrum from the front
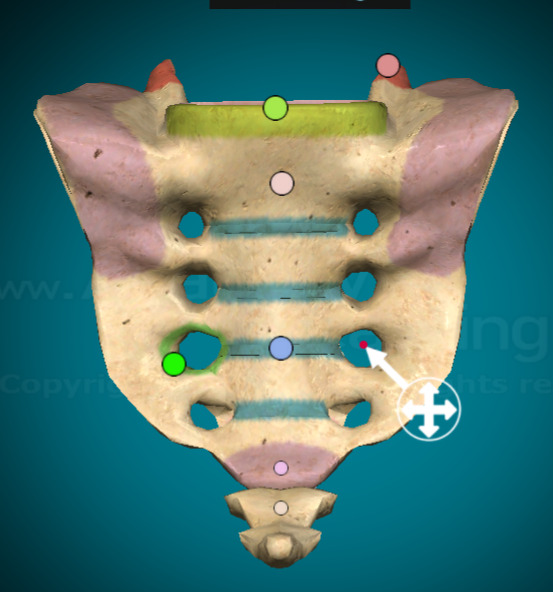
What are the posterior sacral foramina?
the 4 pairs of bilateral holes when looking at the sacrum from the back
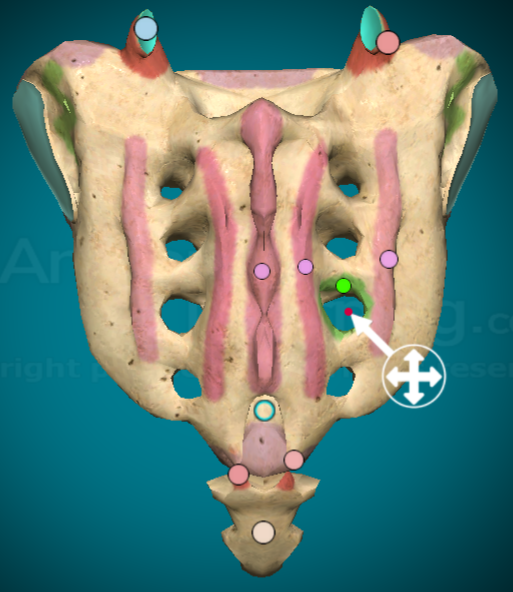
What is the median sacral crest?
ridge down the midline (posterior view) of the sacrum
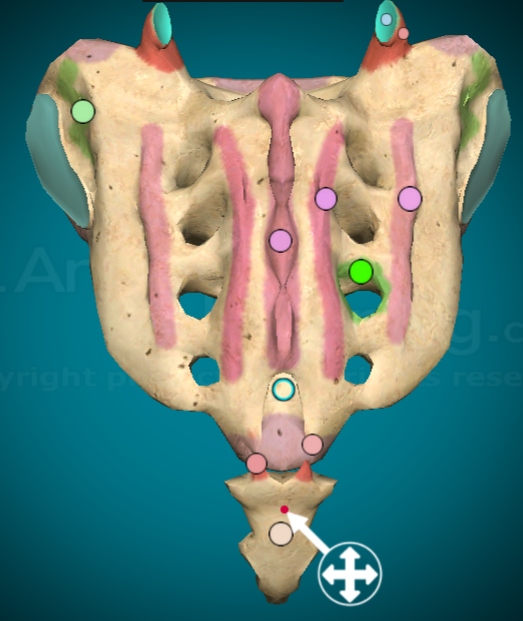
What and where is the coccyx?
the tiny little bone at the base of the sacrum that’s an upside down triangle shape
What are the parts of the sternum?
manubrium (sternal/jugular notch and sternal angle)
body
xiphoid process
Where is the sternal/jugular notch on the manubrium?
the top little curve
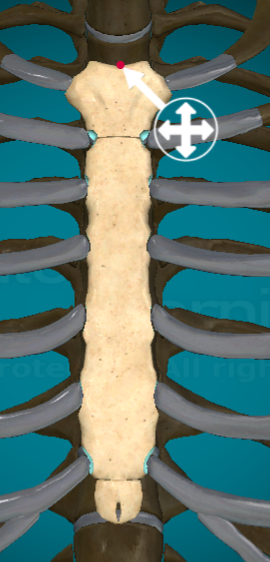
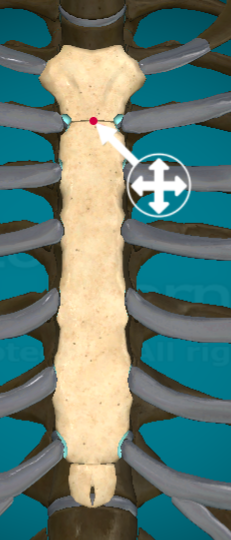
Where is the sternal angle on the manubrium?
the bottom line that connects the manubrium to the body of the sternum
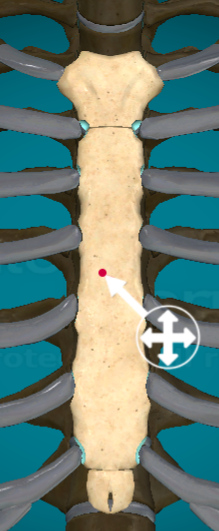
What and where is the body of the sternum?
where? between the manubrium and the xiphoid process
what? the main section of the sternum that attaches ribs 2-7
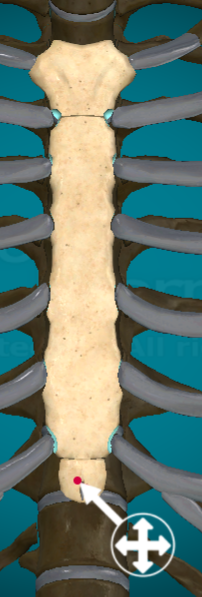
What and where is the xiphoid process on the sternum?
What? the tiny little upside down triangle bone
Where? below the body of the sternum
How many ribs does a human have?
24 (12 pairs)
What are true ribs? Which ribs are true ribs?
True ribs attach to the sternum directly
ribs 1-7 are true ribs
What are false ribs? What are floating ribs? Which ribs are false ribs?
False ribs don’t connect directly to the sternum. They either connect to rib 7 or they aren’t connected to anything at all; floating ribs. ribs 8-10 are false ribs, and ribs 11 and 12 are specifically floating ribs
How do ribs connect to sternum?
They are connected to cartilage which is connected to the sternum. The more flexible cartilage allows for rib expansion and breating.
How do ribs connect to the vertebral column?
transverses processes on vertebra connect to articular facet on rib
the ends of the rib also attach to the side of the vertebral body
What is costal cartilage?
the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum