GODBLESS SA EXAM
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
ASEPSIS
absence of microorganism that cause disease
aseptic technique
methods by which contamination with microorganisms is prevented
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTION
an ideal agent would have a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity against pathogenic organisms
PERSISTENT ACTIVITY
an agent offering persistent activity keeps the bacterial count low under the gloves
SAFETY
an ideal agent would be non-irritating and non-sensitizing
ACCEPTANCE
probably most important to achieving compliance in using a new product is its acceptance by the healthcare worker
SURGICAL SITE INFECTION
is an infection that occurs after surgery in the part of the body where the surgery took place
Preoperative
education given to families from surgeon's clinic about proper hygiene before surgery and bathing instructions for night before or day of surgery
Intraoperative
appropriate antibiotic dosing
environmental controls
maintain a clean environment
wear clean surgical attire
surgical skin prep and wound classification
hand hygiene
minimize traffic
adequate sterilization of instruments
Post-operative
discontinuing antibiotics after 24 hrs
maintain blood sugar (if diabetic), normothermia (36°c or better) and tissue perfusion with supplemental oxygen
hand hygiene for dressing changes and sterile supplies
education of preventing Surgical Site Infection upon discharge with patient and families
CLEANING
physical removal or organic material or soil from objects and is usually done by using water with or without detergents
STERILIZATION
destruction of all forms of microbial life; it is carried out in the hospital with steam under pressure, liquid or gaseous chemicals, or dry heat
DISINFECTION
defined as the intermediate measures between physical cleaning and sterilization, is carried out with pasteurization or chemical germicides
HIGH-LEVEL DISINFECTION
can be expected to destroy all microorganisms, with the exception of large numbers of bacterial spores
INTERMEDIATE DISINFECTION
inactivates mycobacterium tuberculosis, vegetative bacteria, most viruses, and most fungi; does not necessarily kill bacterial spores
LOW-LEVEL DISINFECTION
can kill most bacteria, some viruses, and some fungi; cannot be relied on to kill resistant microorganisms such as tubercle bacilli or bacterial spores
CRITICAL ITEMS
are instruments or objects that are introduced directly into the bloodstream or into other normally sterile areas of the body
SEMICRITICAL ITEMS
items that come in contact with intact mucous membranes, but they do not ordinarily penetrate body surfaces
NONCRITICAL ITEMS
items that either do not ordinarily touch the patient or touch only intact skin
Steam Sterilization
most inexpensive and effective method for sterilization
Ethylene Oxide Gas Sterilization
it is a more complex and expensive process than steam sterilization
it is usually restricted to objects that might be damaged by heat or excessive moisture
Rinsing
Cleaning
Drying
Inspection and assembly
Packaging
Labeling
Sterilization
Storage
Distribution
Role of CSSD
ensure delivery room T° is between 25-28 °
Ensure that there are no air drafts
Discuss maternal and NB care in the immediate postpartum period
Perform HANDWASHING
Arrange instrument and other needs + 0.5 chlorine solution for decontamination
Prepare equipment and NB resuscitation
Prepare for the Birth
HAND HYGIENE
single most important method of controlling spread of infection
HANDWASHING
visibly dirty or visibly soiled with blood or fluids
40 – 60 seconds
HAND RUB
hands are not visibly soiled
access to handwashing facilities is not available
Gloving
To reduce the risk of contamination of hands with blood and other body fluids
Sterile gloves
what gloves to use in surgical procedures, vaginal delivery
Non sterile/clean gloves
what gloves to use in potential for touching blood, body fluids, secretions, stool/urine and items visibly soiled by above:
direct patient exposure— examination, handling of patients
indirect patient exposure— emptying basins, handling instruments, handling waste, cleaning up spills of body fluids
SUPINE HYPOSENSITIVE SYNDROME
When a pregnant woman is lying flat on her back, the weight of her uterus and its contents compresses the large blood vessel (vena cava) leading from her lower body to the heart.
MCDONALD RULE
used to determine the age of gestation by measuring the fundus
BARTHOLOMEW RULE
fundal height is determined by relating to the different landmarks in the abdomen
JOHNSONS RULES
used to estimate the weight of the fetus in grams
Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) Monitoring
measuring of the fetus’ heart rate during labor by using special instruments
Tachycardia
Baseline FHR above 160 bpm
Bradycardia
Baseline FHR less than 120 bpm
Electronic Fetal Heart Monitoring (EFM)
an electronic monitor used to continuously measure the fetus's heart rate and using a pressure sensor to monitor the mother's contractions at the same time.
Internal Monitoring
Measure the heart rate through a wire called (electrode) contains a needle, inserted through the vagina and cervix, and placed under the baby's scalp.
Baseline Variability
Refer to fluctuation caused by balancing acts of sympathetic (increase FHT) and parasympathetic branches (decreases FHT) of the autonomic nervous system.
Accelerations
Non Periodic accelerations are temporary normal increases in FHR caused by fetal movement, a change in maternal position, or administration of an analgesic.
Prolonged Decelerations
are decelerations that decrease from the FHR baseline of 15 beats/min or more and last longer than 2 to 3 minutes but less than 10 minutes. They generally reflect an isolated occurrence, but they may signify a significant rent, such as cord compression or maternal hypotension. For this reason they must be reported and documented
Decelerations
Rate of FHT decreases at the onset of uterine contraction but return to normal before the end of contraction this is normal response of the fetus to head compression caused by umbilical
Variable Decelerations
The pattern of variable decelerations refers to decelerations that occur at unpredictable times in relation to contractions. They may indicate compression of the cord, which can be an ominous development in terms of fetal well-being (Fig. 15.20). Cord compression may be occurring because of a prolapsed cord, but it most often occurs because the fetus is simply lying on the cord. It tends to occur more frequently after rupture of the membranes than when membranes are intact, or with oligohydramnios (the presence of less than a normal amount of amniotic fluid), such as occurs in postterm pregnancy or with intrauterine growth restriction. As a first step, change the woman's position from supine to lateral if she is not already lying on her side. If a prolapsed cord is diagnosed as the cause of the variable decelerations, oxygen will be prescribed as well as changing her position to a knee-to-chest one to help relieve pressure on the cord.
FUNDAL GRIP
palpate the upper abdomen of women in a lie down position.
LATERAL GRIP
This process is done to identify the location of a fetal back.
PAWLICK'S GRIP
Palpate the lower part of the abdomen which is just above the symphysis portion.
PELVIC GRIP
Palpation of the pelvis is performed.
PARTURITION
correct term for the process of childbirth
Labor
Birth of the Baby
Birth of the Placenta
3 Stages of Childbirth
crowning
when the head is first visible
Cephalic
head first
breech
feet or buttocks first
cesarean section
also known as c-section where fetus is delivered through a horizontal incision in abdominal and uterine walls, advisable when fetus is improperly aligned (transverse position), multiple fetuses, fetal distress, mother is worn out, or mother has a transferrable genital condition of infection
EPISIOTOMY
incision through the skin and muscles in the perineum, made during a vaginal delivery
“BEING BORN IN THE CAUL”
when the amniotic sac has not ruptured during labor or pushing; infant is born with intact membranes
SUTURES
anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together
diamond shaped spaces on top, top back, and sides of the skull
Lactation
the hormone oxytocin that started the process of childbirth has several other effects on the body
passage
(a woman's pelvis)
passenger
(the fetus)
powers
(uterine factors)
psyche,
a woman's psychological state
SUTURE LINES
The fetal skull is not yet completely ossified at birth and its bones are joined only by membranes so that spaces actually exist between them.
VERTEX
The area between the two fontanelles
SINCIPUT
The area over the frontal bone
OCCIPUT
the area over the occipital bone
VERTEX POSITION
Occurs when the head is completely flexed so that the chin touches the chest. It is the most ideal type of presentation because the smallest diameter of the fetal head, occipito bregmatic (9.5 cm), is presented with the posterior fontanel as the presenting part.
SINCIPUT POSITION
Occurs when the head is partially flexed and the anterior fontanel is the presenting part. The occipitofrontal diameter (12.5 cm) is presented for delivery Also called military position because it gives the appearance of a military person at attention.
BROW PRESENTATION
Occurs when the head is extended or bent backward causing the occipitomental diameter (13.5 cm) to be presented for delivery
FACE PRESENTATION
Occurs when the head is sharply extended causing the occiput to come in contact with the back of the fetus. During the course of labor, resistance by the pelvic floor can cause the head to extend further causing neck fracture and damage to the cervical cord.
Shoulder Presentation
In a transverse lie, a fetus lies horizontally in the pelvis so the longest fetal axis is perpendicular to that of the mother.
Chin Presentation
Occurs when the head is hyperextended with the chin as the presenting part.
Compound Presentation
This presentation occurs when there is prolapsed of the fetal hand alongside the vertex, breech or shoulder
Longitudinal Lie
The long axis of the fetus is parallel to the long axis of the mother, meaning, the fetus is lying lengthwise in the mother's abdomen
Oblique Lie
This lie is the most unstable. The fetus assuming this lie usually rotates to transverse or longitudinal lie in the course of labor.
Transverse Lie
The long axis of the fetus forms a right angle with the long axis of the mother, which means that the fetus is lying crosswise in the mother's abdomen
FETAL POSITION
refers to the relationship of the presenting part to one of the quadrant of the mother's pelvis
Pelvic Landmarks
The pelvis is divided into several areas in order to locate accurately the position of the presenting part.
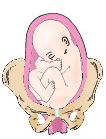
Right occiput anterior
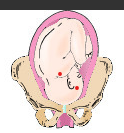
Right occiput transverse
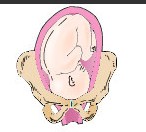
Right occiput transverse

Left occiput anterior
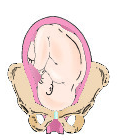
left occiput transverse
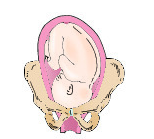
Left occiput posterior
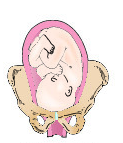
Right mentum anterior
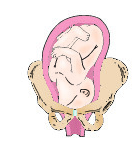
Right mentum posterior
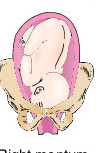
Left mentum anterior
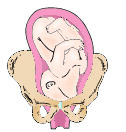
Left sacrum anterior
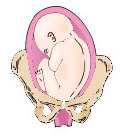
Left sacrum posterior