Bio Term Test 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:18 PM on 1/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
How old is Earth?
4\.6 billion years old
2
New cards
When did the First Life Forms Appear on Earth?
3\.8 billion years ago
3
New cards
How did Life Arise?
1. Abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules
2. Joining of these small molecules
3. Packing of the molecules into protocells
4. Origin of self replicating molecules (RNA)
4
New cards
What were the First Catalysts?
Ribozymes (RNA)
RNA both helped in self replicating and catalyzing
RNA both helped in self replicating and catalyzing
5
New cards
Early Atmosphere
It was a reducing environment (as opposed to an oxidizing atmosphere)
These conditions favored a synthesis of organic compounds
These conditions favored a synthesis of organic compounds
6
New cards
Soup Analogy
Ingredients = Oparin and Haldane
Oven = Energy such as lightning and UV radiation
Oven = Energy such as lightning and UV radiation
7
New cards
Miller and Urey
They provided conditions similar to earths early atmosphere and tested the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis
Simulated conditions in a lab
Produced amin acids
Simulated conditions in a lab
Produced amin acids
8
New cards
What does the Fossil Record Reveal?
It reveals the changes in history of life on earth and it shows the kinds of organisms on Earth overtime
9
New cards
Sedimentary Rocks
Deposited into layers called strata and are the richest source of fossils
10
New cards
Where are Older Fossils?
Older fossils are farther down in the earth
Newer ones are nearer the top
Newer ones are nearer the top
11
New cards
Stromatolites
The oldest known fossils
They are rocks formed by the accumulation of sedimentary layers on bacterial mats
They are layers of single cell organisms on top of each other
They are rocks formed by the accumulation of sedimentary layers on bacterial mats
They are layers of single cell organisms on top of each other
12
New cards
When do Stromatolites date back to?
3\.5 billion years ago
13
New cards
How long were Prokaryotes the only Inhabitants of Earth?
1\.5 billion years
14
New cards
Oxygen Revolution
O2 accumulated gradually in the atmosphere from about
2\.7 to 2.4 billion years ago
2\.7 to 2.4 billion years ago
15
New cards
Proof of Oxygenic Revolution
Branded iron formation of rocks
The iron reacted with the oxygen to rust
The iron reacted with the oxygen to rust
16
New cards
Consequences of the Oxygenic Revolution
Many prokaryotic groups could not adapt to increased atmospheric O2 levels
Some groups survived and adapted using cellular respiration to harvest energy
Some groups survived and adapted using cellular respiration to harvest energy
17
New cards
When do the Oldest fossils of Eukaryotes Date back to?
1\.8 billion years ago
18
New cards
Endosymbiont Theory
The theory proposes that mitochondria and plastids (chloroplasts and related organelles) were formerly small prokaryotes living with in larger host cells
19
New cards
Endosymbiont
A cell that lives within a host cell
20
New cards
Serial Endosymbiosis
Mitochondria evolved before plastids through sequence of endosymbiotic events
ATP for the host cell was the rent that the mitochondria paid
ATP for the host cell was the rent that the mitochondria paid
21
New cards
Evidence of the Endosymbiotic Theory
Have two membranes
Utilize electron transport enzyme
Has its own DNA
Have ribosomes
Utilize electron transport enzyme
Has its own DNA
Have ribosomes
22
New cards
Prokaryotic Ribosome
50S subunit
30S subunit
70S ribosome
30S subunit
70S ribosome
23
New cards
Eukaryotic Ribosome
60S subunit
40S subunit
80S ribosome
40S subunit
80S ribosome
24
New cards
When did the Second Wave of diversification Occur?
When the multicellularity evolved and gave rise to algae, plants, fungi, and animals
25
New cards
Cambrian Explosion
The sudden appearance of fossils resembling modern animal phyla in the Cambrian period (535-535 millions years ago)
26
New cards
When was the Land Colonized?
Fungi, plants and animals began to colonize land about 500 million years ago
27
New cards
What Evolved from lobe-finned Fish and When?
Tetrapod’s about 365 millions years ago
28
New cards
What Evolved from Tetrapod’s and When?
The human lineage evolved around 6-7 million years ago
29
New cards
When did Modern Humans Originate?
195,000 years ago
30
New cards
What does the Rise and Fall of Groups of Organisms Reflect?
It reflects the differences in speciation and extinction rates
31
New cards
What can Extinction be Caused by?
Can be caused by changes to a species biotic and abiotic environment
32
New cards
Mass Extinction
The rate of extinction is increased dramatically
33
New cards
Adaptive Radiation
The rapid evolution of diversity adapted species from a common ancestor
34
New cards
What May Adaptive Radiation Follow?
Mass extinctions
The evolution of novel characteristics
The colonization of new regions
The evolution of novel characteristics
The colonization of new regions
35
New cards
Taxonomy
Ordered division and naming of organisms
36
New cards
Linnaeus (18th Century)
Published a system of taxonomy based on resemblances
37
New cards
2 Key Features of Linnaeus’s System
1. Utilize binomial nomenclature: Genus + Specific epithet
2. Utilizes Hierarchal classification
38
New cards
Taxonomic Groups from Broad to Narrow
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
39
New cards
Taxon
A taxonomic unit at any level
40
New cards
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
41
New cards
Systematics
Classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships
Use fossil, molecular, and genetic data to infer evolutionary relationships
Use fossil, molecular, and genetic data to infer evolutionary relationships
42
New cards
What does Phylogenetic Tree Represent?
It represents a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships
43
New cards
Branch Point (Node)
Divergence of two species from a common ancestor
44
New cards
Sister Taxa
Groups that share an immediate common ancestor that is not shared by any other group
Sisters not cousins
Sisters not cousins
45
New cards
Rooted Tree
Includes a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree
46
New cards
Basal Taxon
Diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group
47
New cards
Polytomy
A branch from which more than two groups emerge
48
New cards
What do Phylogenetic Trees Show?
Pattern of descent
49
New cards
What do Phylogenetic Trees not Show?
When or how much genetic change has occurred in a lineage
50
New cards
Can Taxa be Rotated Around Nodes and still Depict the same Relationships?
Yes
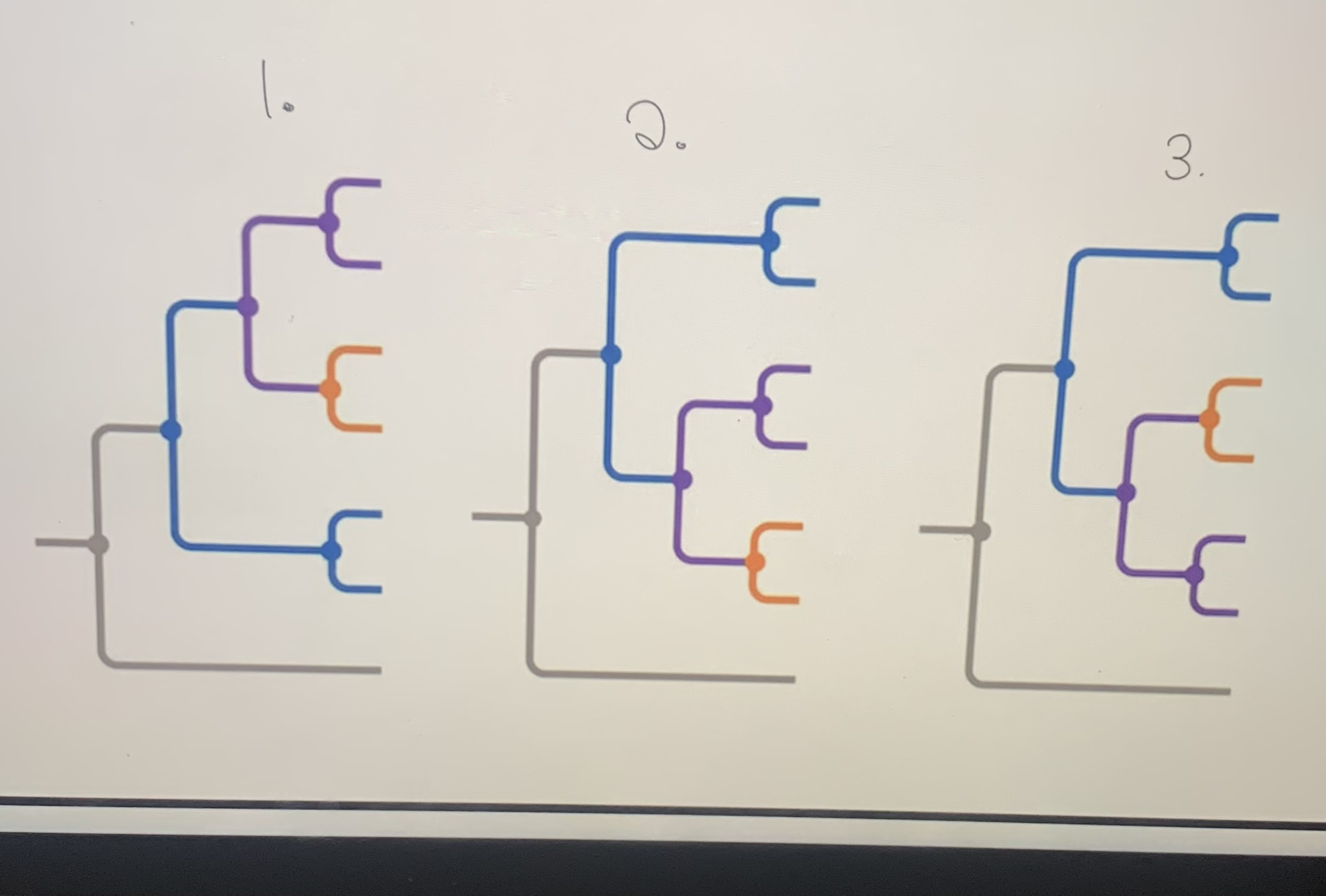
51
New cards
Monophyletic Group
Consists of all the descents of a single common ancestor
52
New cards
Paraphyletic Group
Consists of some, but not all descendants of a single common ancestor
53
New cards
Polyphyletic Group
Does not include the common ancestor of all descendants (excludes at least one monophyletic group)
54
New cards
3 Ways of Making a Phylogeny
1. Character Table
2. Phylogenetic tree
3. DNA
55
New cards
How to Make a DNA Phylogeny?
Start with the first hypothesis
Map all the changes onto the tree and count the number of events
Do the same for other Phylogenetic hypothesis
The tree with the fewest number of events is the best tree
The first tree is the most parsimonious
Map all the changes onto the tree and count the number of events
Do the same for other Phylogenetic hypothesis
The tree with the fewest number of events is the best tree
The first tree is the most parsimonious
56
New cards
Parsimony
The fewest number of evolutionary steps
57
New cards
Phylogenetic Bracketing
Allows for us to predict features of an ancestor from features of its descendants
58
New cards
What are the Best Hypotheses for Phylogenetic Trees?
The trees that fit the most data:
Morphological, molecular, and fossil
Morphological, molecular, and fossil
59
New cards
How Many Kingdoms did Early Taxonomists Have?
2
Plants or animals
Plants or animals
60
New cards
The 5 Kingdoms
Monera (prokaryotes)
Protista
Fungi
Plantar, and Animalia
Protista
Fungi
Plantar, and Animalia
61
New cards
Monera
Archaea and bacteria prokaryotes
Small
Lack internal Organelles
Simple genetic information
Important in nutrient cycling, agents of disease
Small
Lack internal Organelles
Simple genetic information
Important in nutrient cycling, agents of disease
62
New cards
Protista
Single celled eukaryotes
Most artificial of kingdoms
Have flagella and cilia
Have true organelles
Range from algae to animal- and fungal-like heterotrophs
Almost all are aquatic and aerobic
Most artificial of kingdoms
Have flagella and cilia
Have true organelles
Range from algae to animal- and fungal-like heterotrophs
Almost all are aquatic and aerobic
63
New cards
Plantae
Multicellular photosynthetic autotrophs
All terrestrial, secondary specialization -Adapts to prevent dying
All terrestrial, secondary specialization -Adapts to prevent dying
64
New cards
Fungi
Multicellular
Heterotrophic - Obtain nutrients by absorptions
Degrade organic matter majority of lifecycle spent in haploid state
Heterotrophic - Obtain nutrients by absorptions
Degrade organic matter majority of lifecycle spent in haploid state
65
New cards
Animalia
No cell walls
Separate tissues
Cell fate is determined
Most complex organisms with many feedback and control systems
Separate tissues
Cell fate is determined
Most complex organisms with many feedback and control systems
66
New cards
3 Domain System
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Archaea
Eukarya
67
New cards
Which of the 3 Domains are more Closely related to Each other?
Eukaryotes and Archaea
68
New cards
What does a typical Prokaryotic Cell Contain
Fimbriae
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Bacterial chromosome
Cell wall
Capsule
Flagella
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Bacterial chromosome
Cell wall
Capsule
Flagella
69
New cards
Most Common Shapes of Prokaryotic Cells
Coccus
Bacillus
Spiral
Bacillus
Spiral
70
New cards
Prokaryote Cell Wall
Peptidoglycan
71
New cards
Are Eukaryotes or Prokaryotes Bigger?
Eukaryotes
72
New cards
Capsule
A polysaccharide and/or polypeptide layer covers many prokaryotes
Sits on top of the cell wall
Viscous and gelatinous
Sits on top of the cell wall
Viscous and gelatinous
73
New cards
Functions of the Capsule
Contribute to virulence
Resists drying
Resists engulfment
Enables adhesion
Resists drying
Resists engulfment
Enables adhesion
74
New cards
Streptococcus Mutans
Plaque develop and produce acid, which dissolves tooth enamel
75
New cards
Fimbriae
Hair like appendages that allow prokaryotes to stick to their substrate or other individuals in a colony
All over the cell
Small and thin
Solid structure
All over the cell
Small and thin
Solid structure
76
New cards
Pili
Involved in motility (gliding and twitching motility)
Conjugation pili involved in DNA transfer from one cell to another
Conjugation pili involved in DNA transfer from one cell to another
77
New cards
Function of Cell Wall (Prokaryote)
Maintain cell shape
Physical protection
Prevents the cell from bursting in a hypotonic environment
Physical protection
Prevents the cell from bursting in a hypotonic environment
78
New cards
Gram Positive Characteristics
Thicker peptidoglycan
No outer membrane
Purple circle
No outer membrane
Purple circle
79
New cards
Gram Negative Characteristics
Thinner peptidoglycan
Outer membrane
Pink rod
Outer membrane
Pink rod
80
New cards
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Alcohol dehydrates peptidoglycan
CV-I crystals do not leave
CV-I crystals do not leave
81
New cards
Gram Negative Bacteria
Alcohol dissolves outer membrane and leaves holes in peptidoglycan
CV-l washes out; cells are colorless
Safranin added to stain cells
CV-l washes out; cells are colorless
Safranin added to stain cells
82
New cards
Cell Wall in Eukaryotes (Plants)
Plant cells walls made of different polymers
Cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, lignin
Cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, lignin
83
New cards
Cell Wall in Eukaryotes (Fungi)
Fungal cell walls made of chitin, glucans
84
New cards
Internal Organization in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic cell usually lack complex compartmentalization
However some prokaryotes do have specialized membranes that perform metabolic functions
However some prokaryotes do have specialized membranes that perform metabolic functions
85
New cards
Prokaryotic Flagella
Flagellin
Used for propulsion
Have a motor (4 rings) and a hook
Allow bacteria to move toward or away from stimuli by “running and tumbling”
Fluid structure
Used for propulsion
Have a motor (4 rings) and a hook
Allow bacteria to move toward or away from stimuli by “running and tumbling”
Fluid structure

86
New cards
3 Types of Taxis (Stimuli)
Chemotaxis
Phototaxis
Magnetotaxis
Phototaxis
Magnetotaxis
87
New cards
Monotrichous
1 flagella on 1 end
88
New cards
Amphitrichous
2 flagella 1 per each end
89
New cards
Lopotrichous
4 flagella at 1 end
90
New cards
Peritrichous
Flagella surrounding everywhere
91
New cards
Amphilophotrichous
Tuft of flagella at both ends
92
New cards
Magnetotaxis
Small magnets inside of bacteria used to move around
93
New cards
Eukaryotic Flagella
Tubulin based
9 microtubules around and 2 in the middle
Whip like motions
9 microtubules around and 2 in the middle
Whip like motions
94
New cards
Prokaryotic Chromosome
DNA is in a nucleoid region
Usually a circular chromosome
Less DNA than the eukaryotic genome
DNA is supercoiled
Usually a circular chromosome
Less DNA than the eukaryotic genome
DNA is supercoiled
95
New cards
Eukaryotic Chromosome
Large linear with several copies
96
New cards
Why is DNA Packaged into Chromosomes
1. Compact the DNA to fit into the cell
2. Protect the DNA from damage
3. Transmit all DNA to daughter cell when the cell divides
97
New cards
Extra chromosomal DNA in Prokaryotes
Bacteria can carry smaller rings of DNA called plasmids
They replicate independently and carry genes that are useful in stressful condition
They replicate independently and carry genes that are useful in stressful condition
98
New cards
Plasmid
Small circular, independent double-stranded DNA molecule
They can be frequently transmitted from one bacterium to another
They can be frequently transmitted from one bacterium to another
99
New cards
Extra Chromosomal DNA in Eukaryotes
Mitochondria or the chloroplast (have their own DNA)
Endosymbiosis
Endosymbiosis
100
New cards
Cell Division in Prokaryotes
Reproduce quickly by binary fission
Ranges from 20 minutes to 24 hours
Can have multiple copies of the plasmid in the cell
May be divided into 2 offspring by chance
Ranges from 20 minutes to 24 hours
Can have multiple copies of the plasmid in the cell
May be divided into 2 offspring by chance