Slope Stability and Mass Movement
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards to help study the key terms and concepts related to slope stability and mass movement.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Slope
A sloped surface on the landscape, which can be rock slopes or soil-covered slopes. (Crozier, 1986)
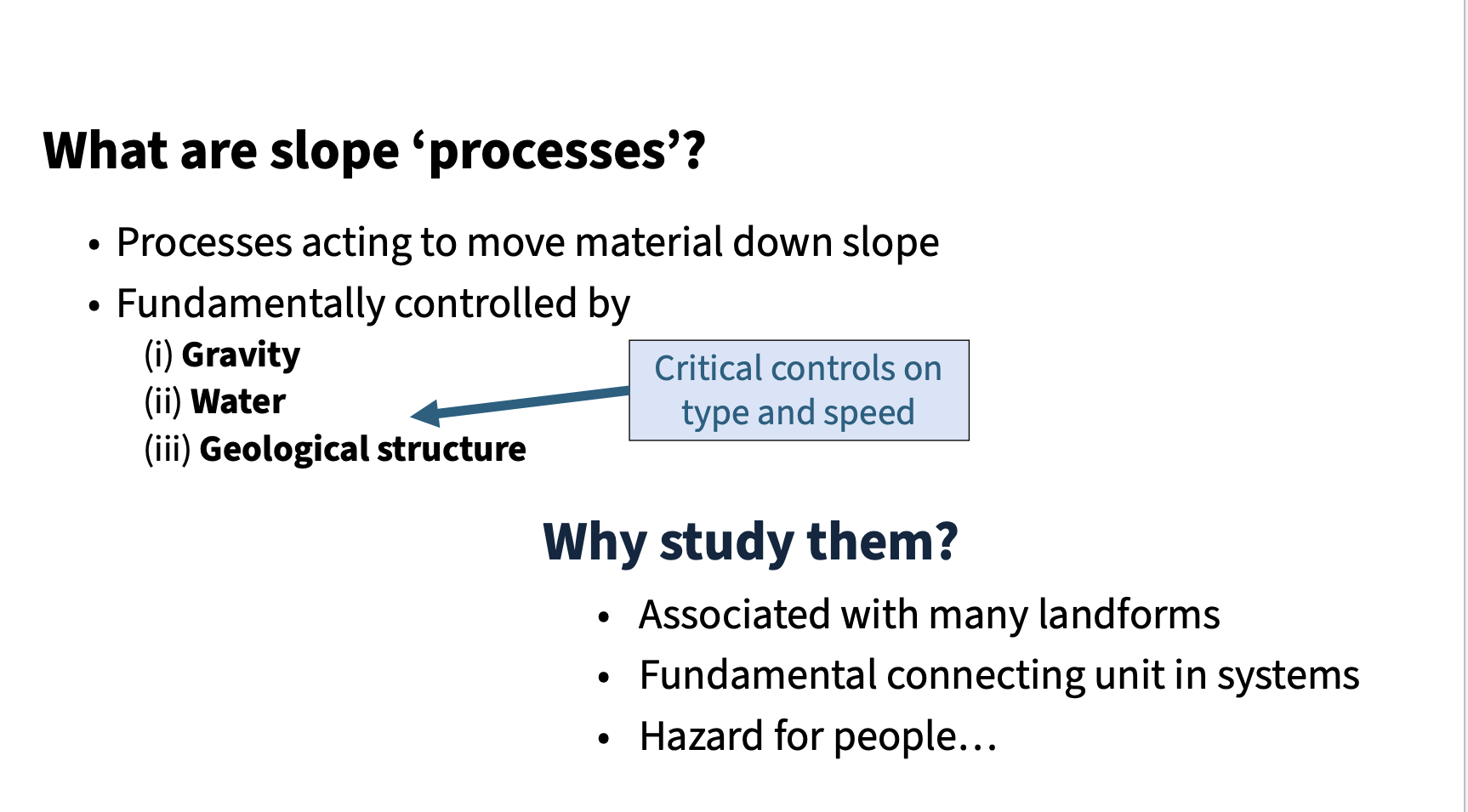
Mass movement
The movement of soil and rock material down a slope due to gravity. (Crozier, 1986) - catastrophic
Shear stress
The stress component that acts parallel to the surface of a material. (Crozier, 1986)
slope falls because of stress or strength
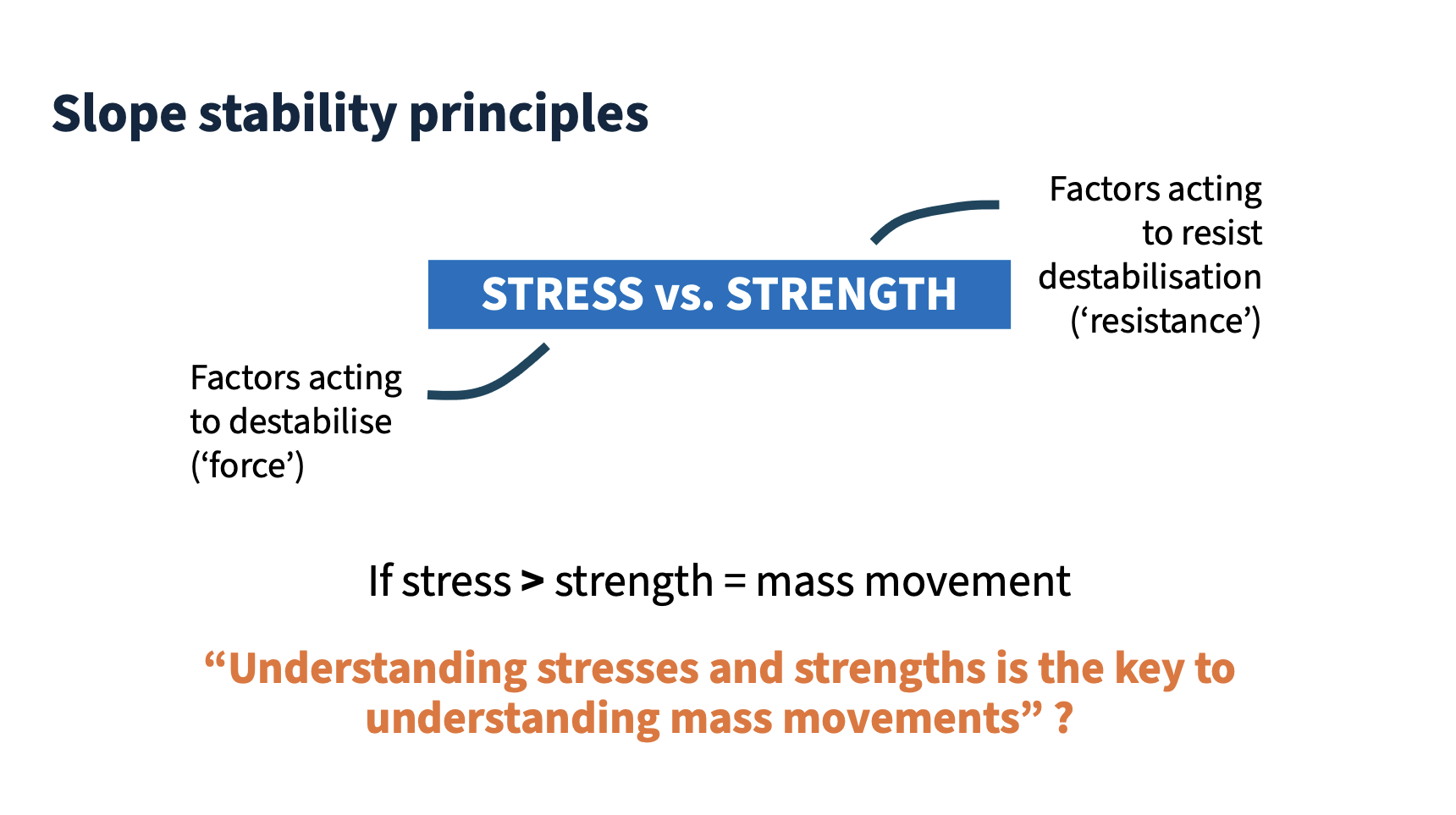
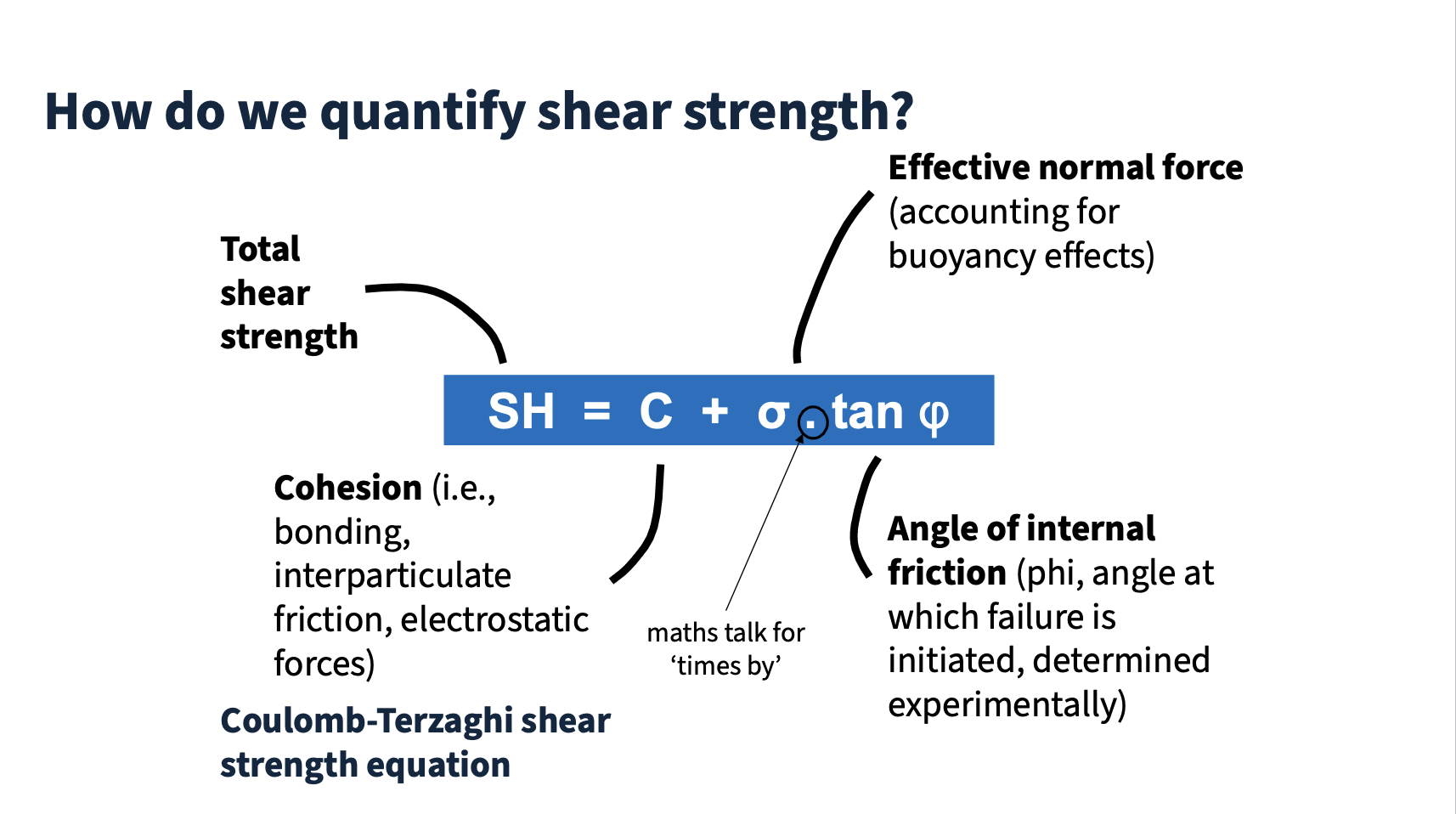
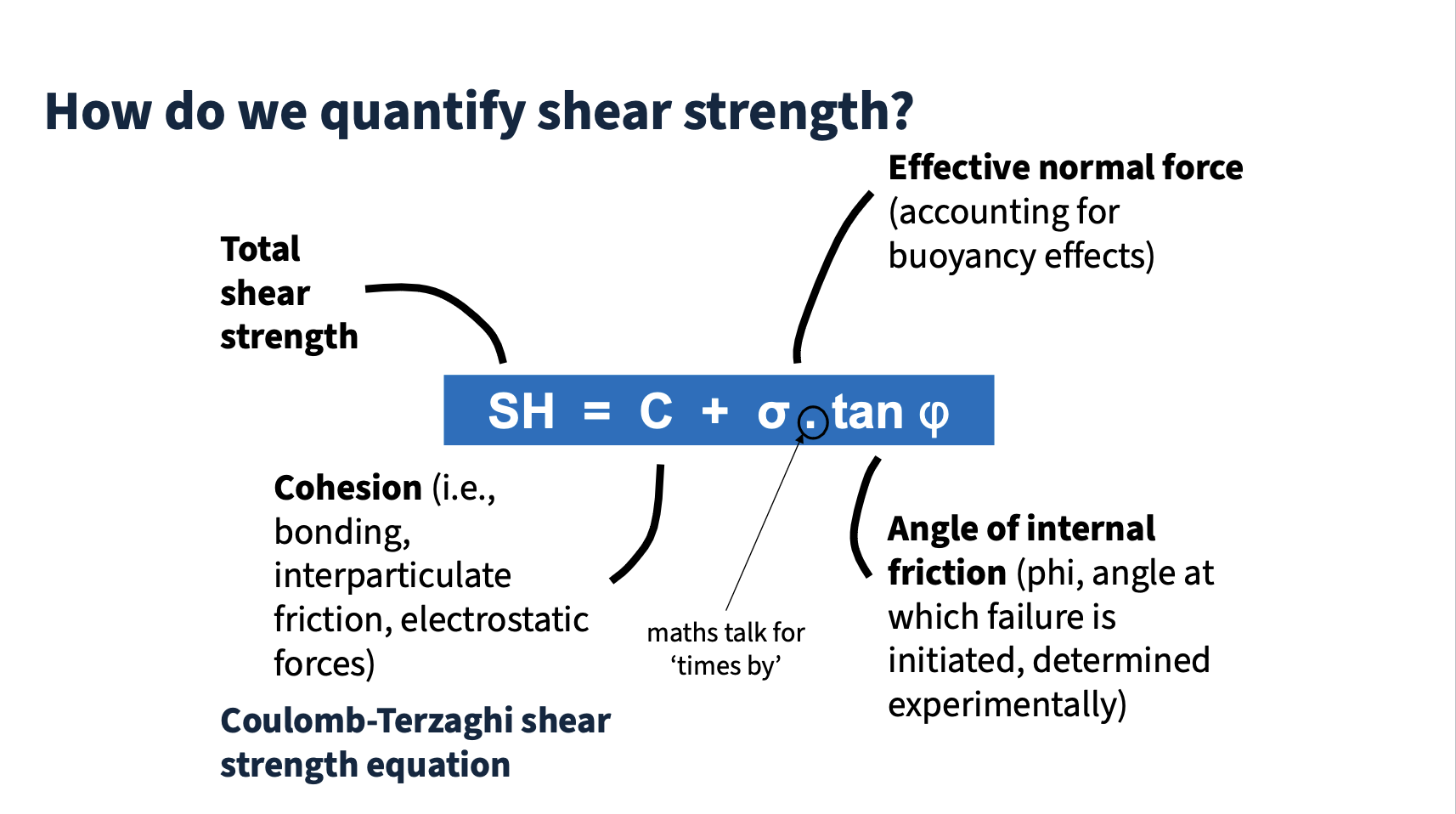
Shear strength
The internal resistance of a material to shear stress, determined by effective normal stress and cohesion. (Crozier, 1986)
Landslide
A sudden and fast movement of a large amount of earth material down a slope. (Crozier, 1986)

Triggers of landslides
Factors such as heavy rainfall, earthquakes, or human activities that can initiate a landslide. (Crozier, 1986)
Tectonic activity
Geological processes associated with the movement of the Earth's lithosphere, often associated with landslides in active regions.
Creep
The slow, gradual movement of soil or rock down a slope. (Crozier, 1986)
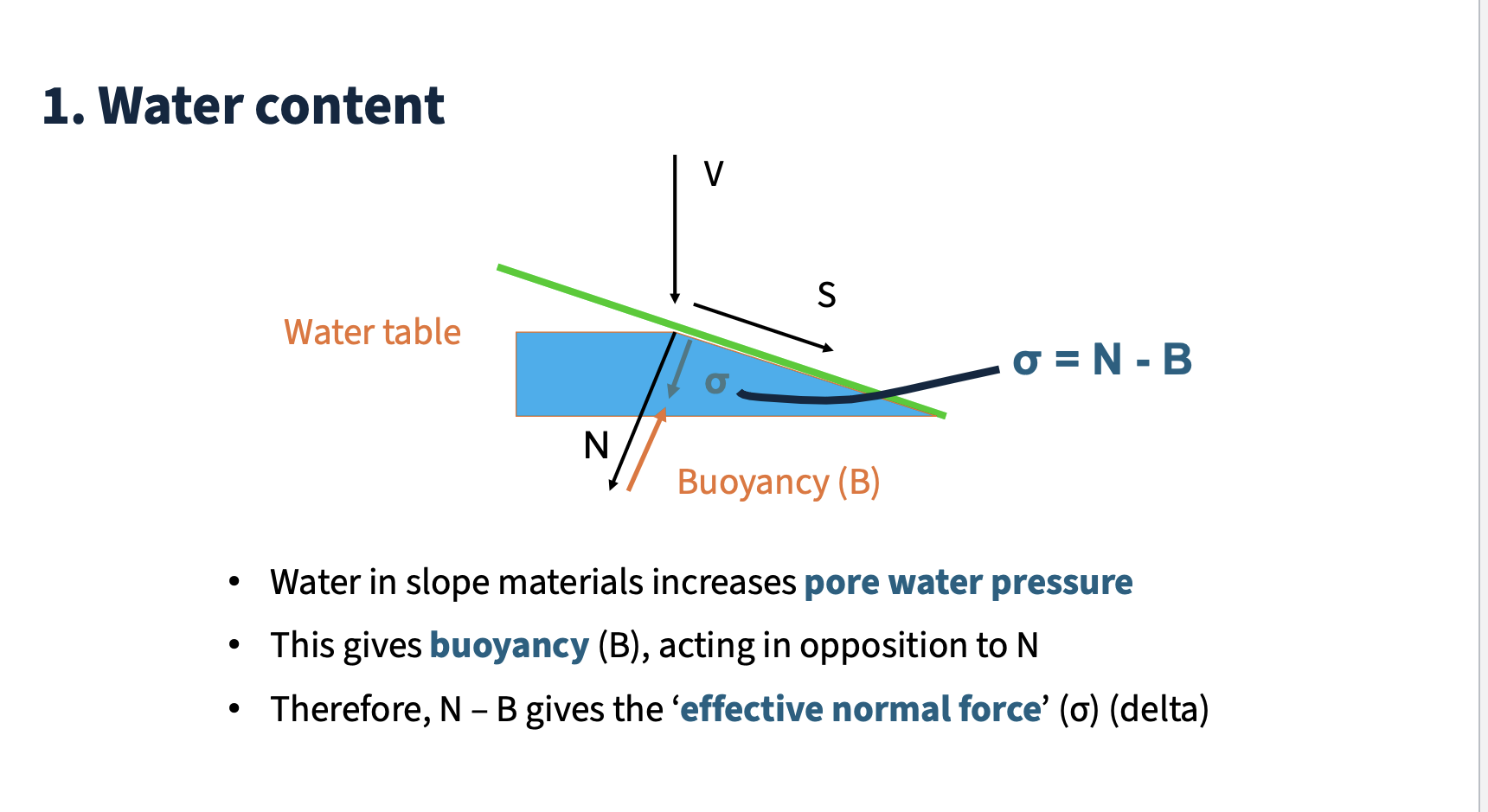
Pore pressure
Pressure exerted by water within the pores of soil or rock, affecting slope stability. (Crozier, 1986)
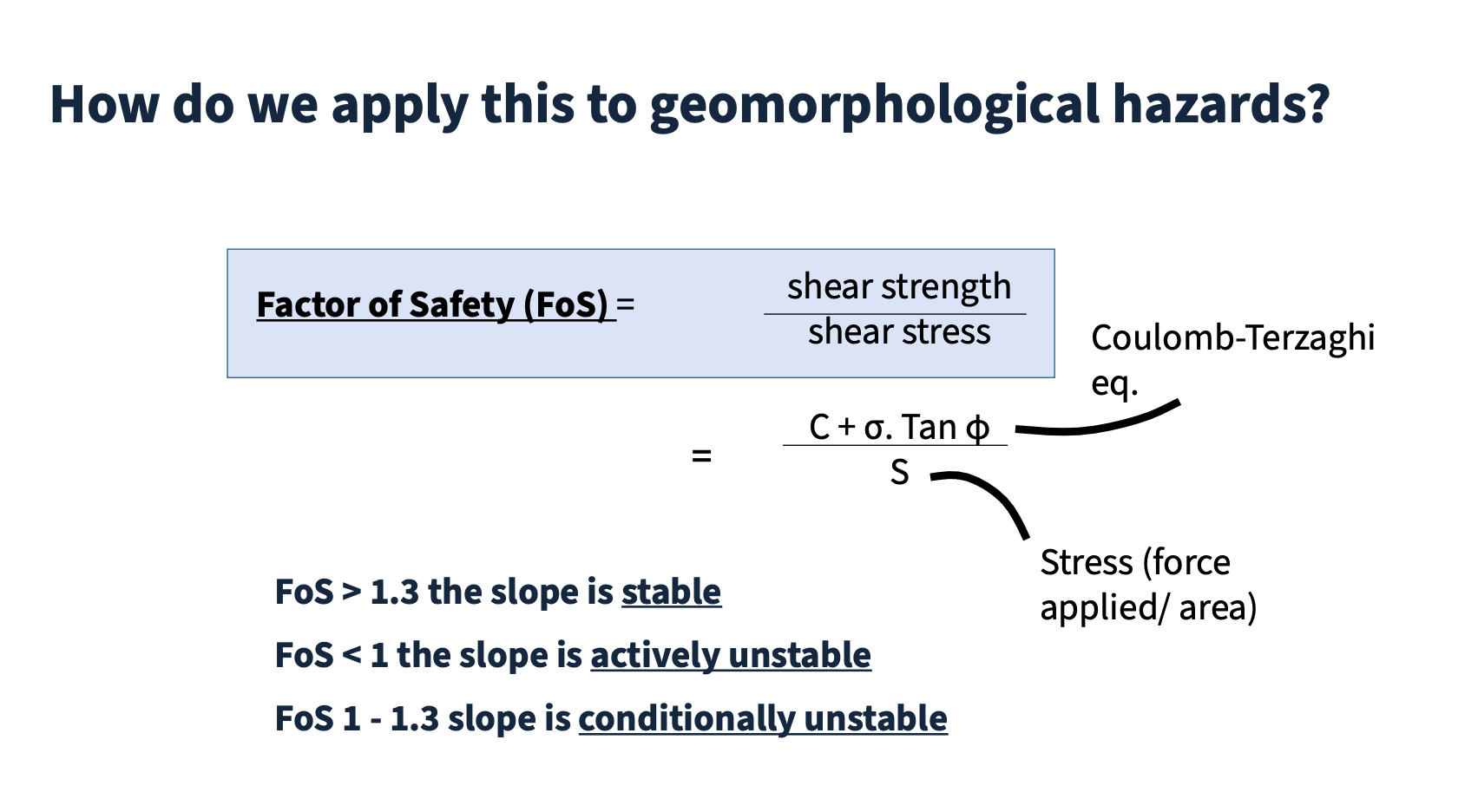
Coulomb-Terzaghi equation
An equation used to calculate shear strength of a slope based on normal stress and cohesion. (Crozier, 1986)
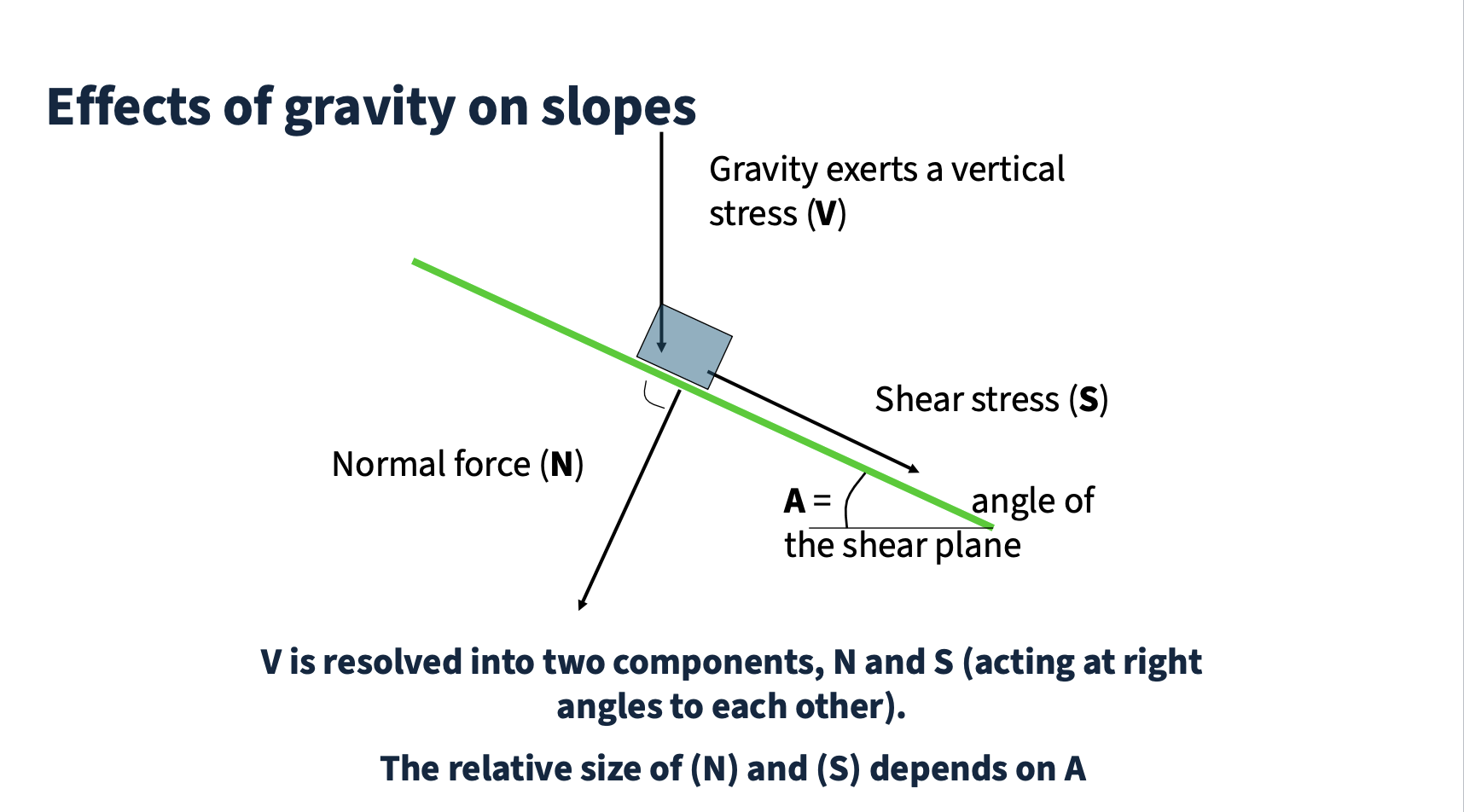
Effects of gravity on slopes
Gravity pushing down on an object
when balance changes between forces - land moves
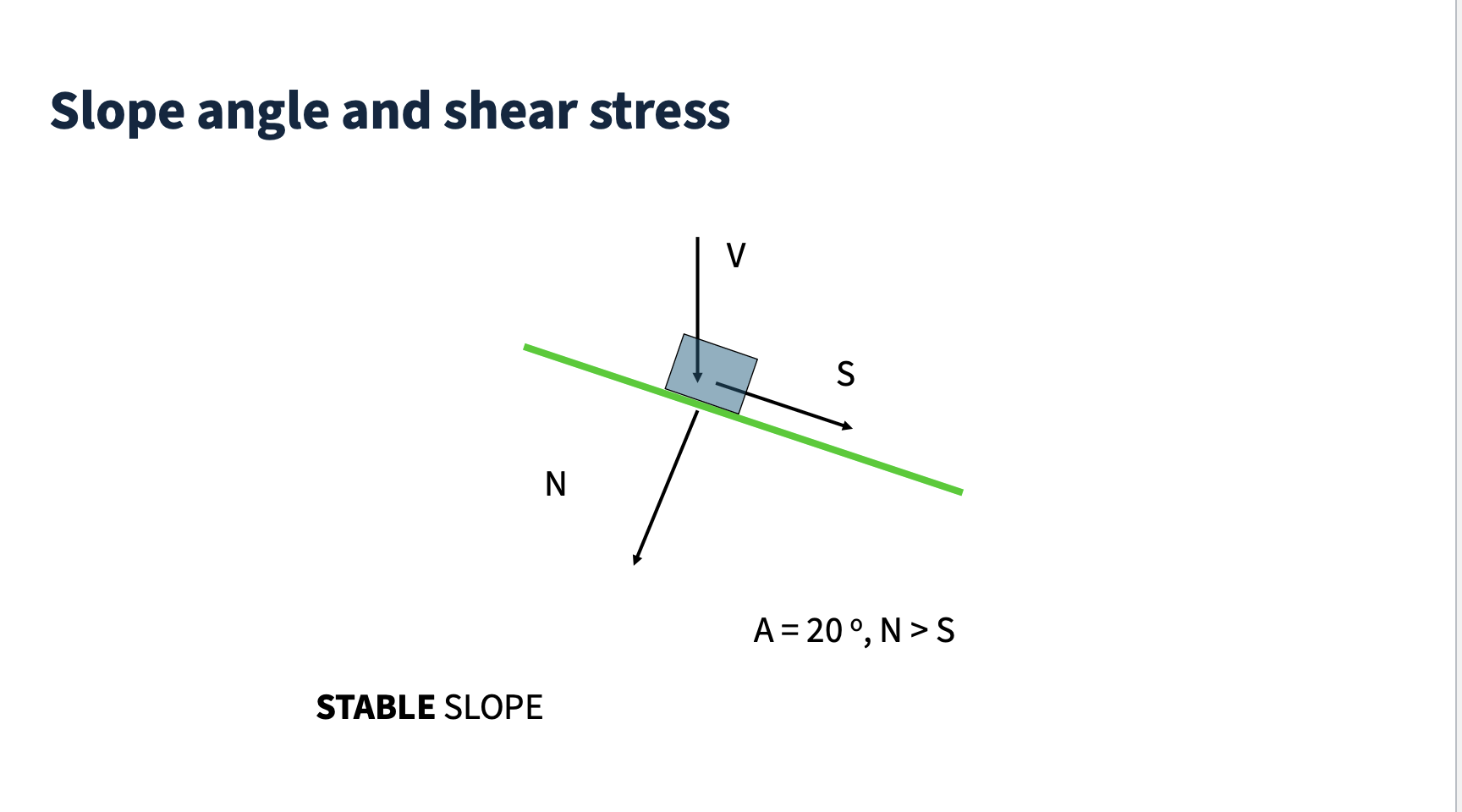
Stable slope
Normal force is greater than shear stress
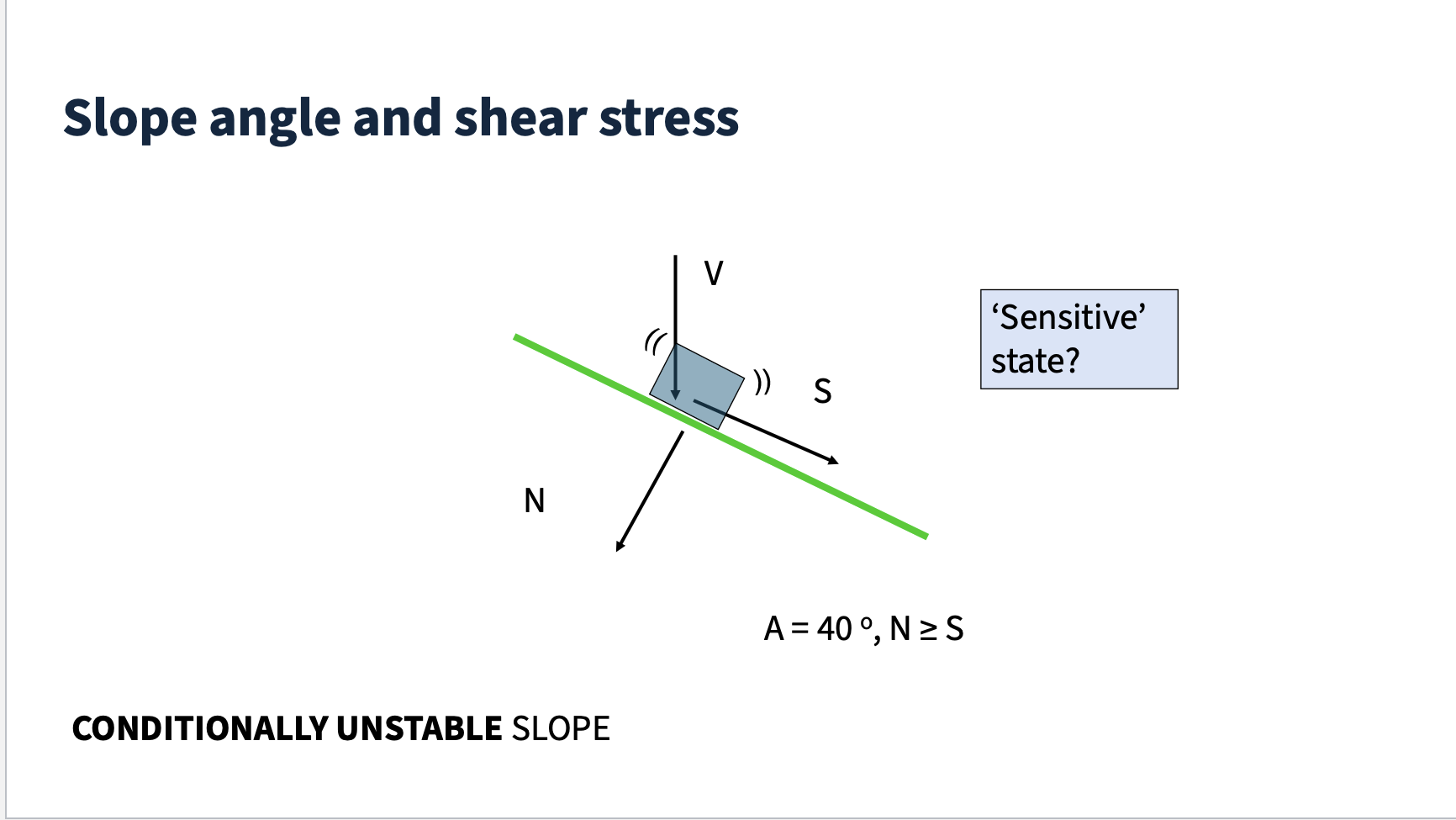
Conditionally unstable slope
Normal force is equal to or greater than shear stress
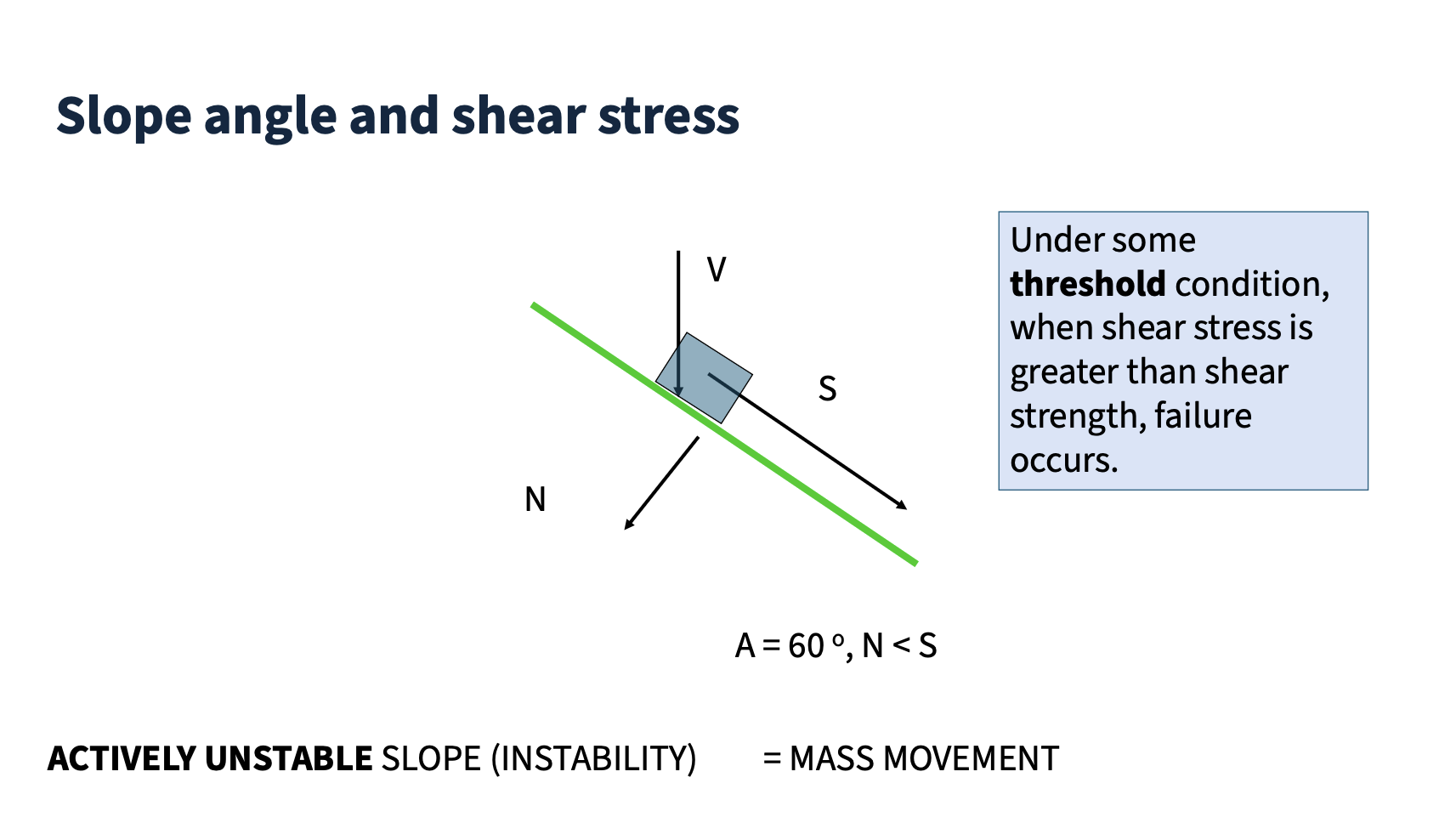
Actively unstable slope
slope is failing
threshold provides a set of conditions
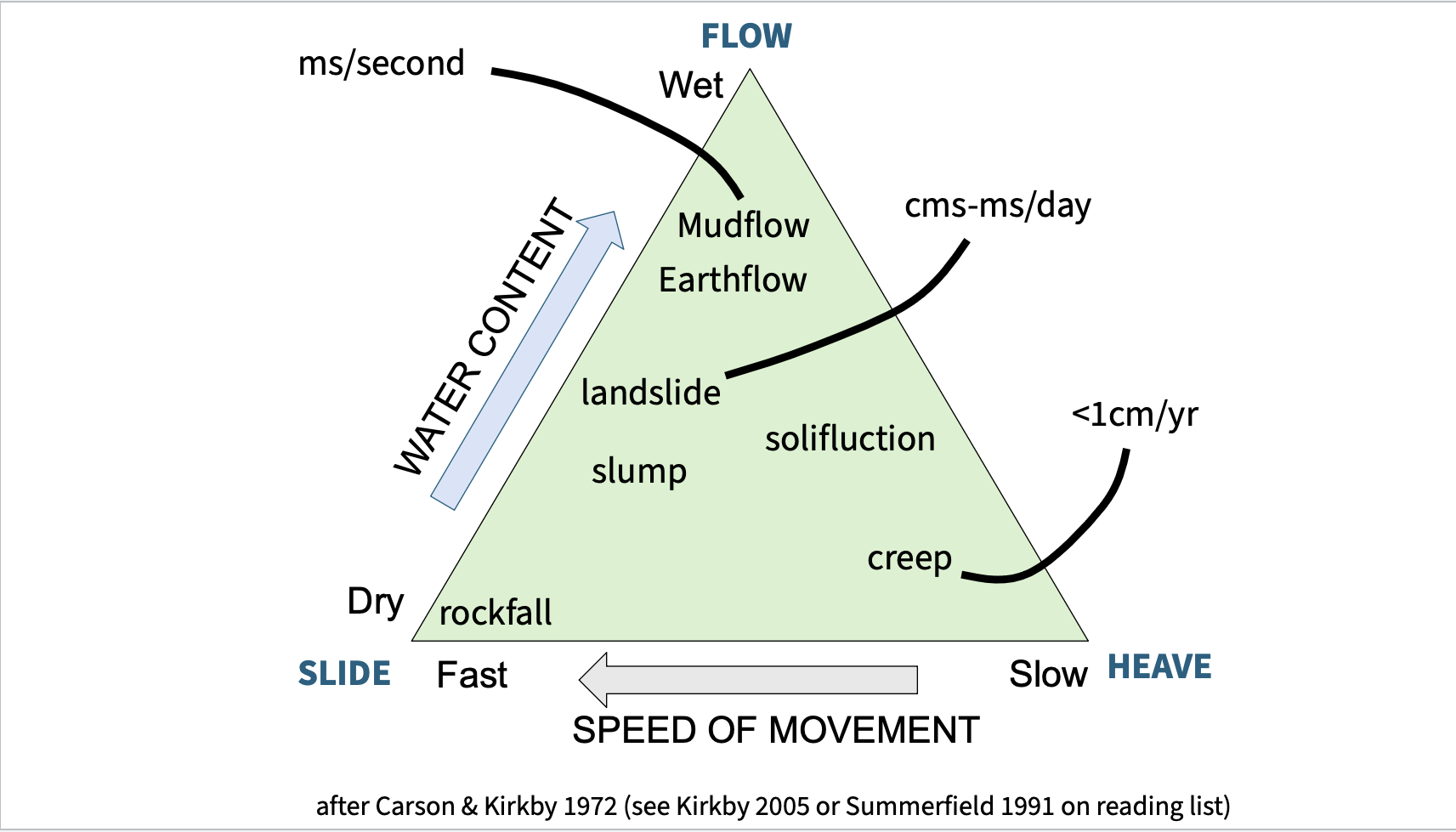
Water content
particles stick together
more water - slope falls more quickly
Slope materials and structure
(Kirkby, 2005)

application to geomorphological hazards

Measuring shear stress

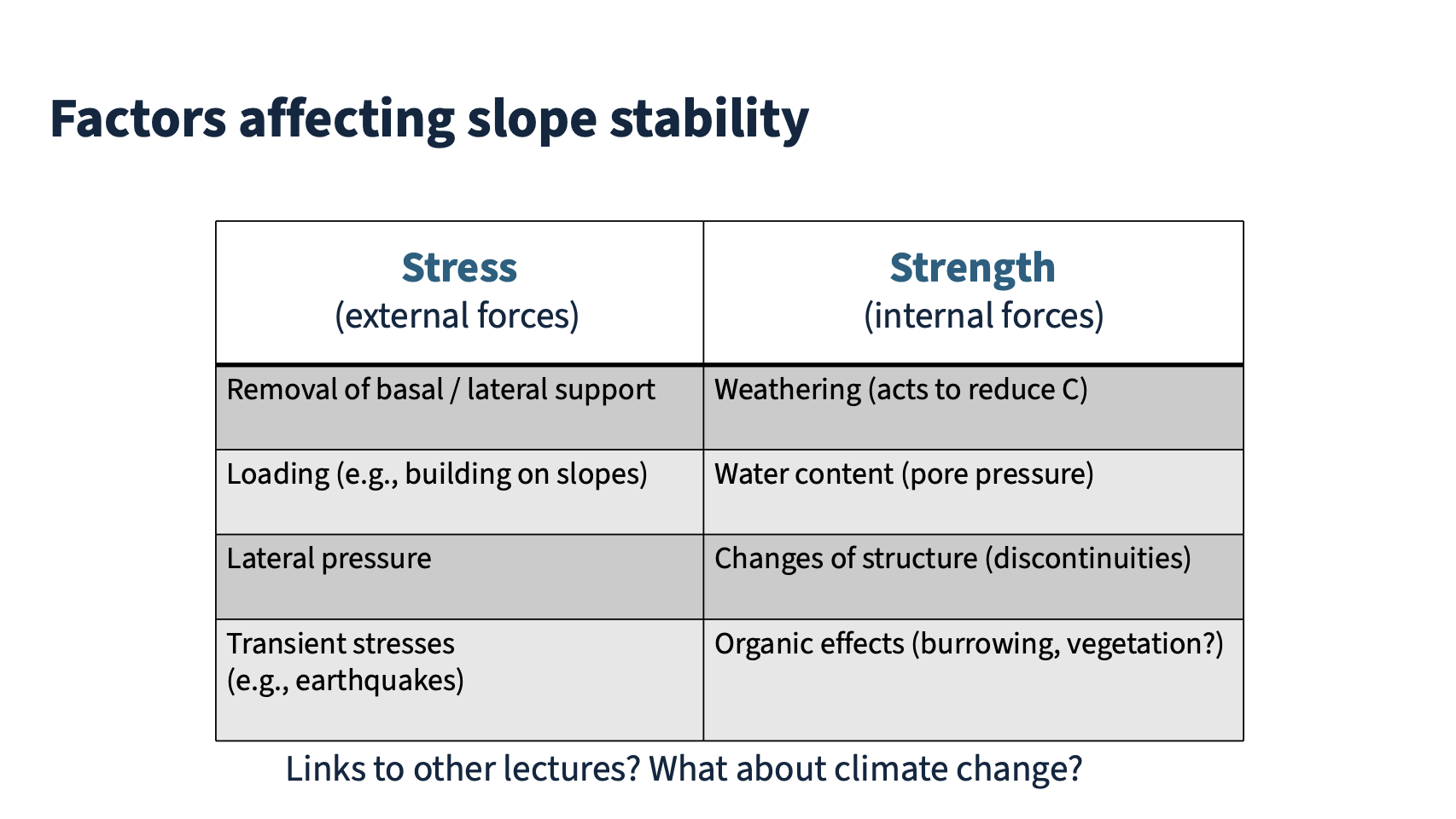
Factors affecting slope stability
(Kirkby, 2005)
Factors to consider

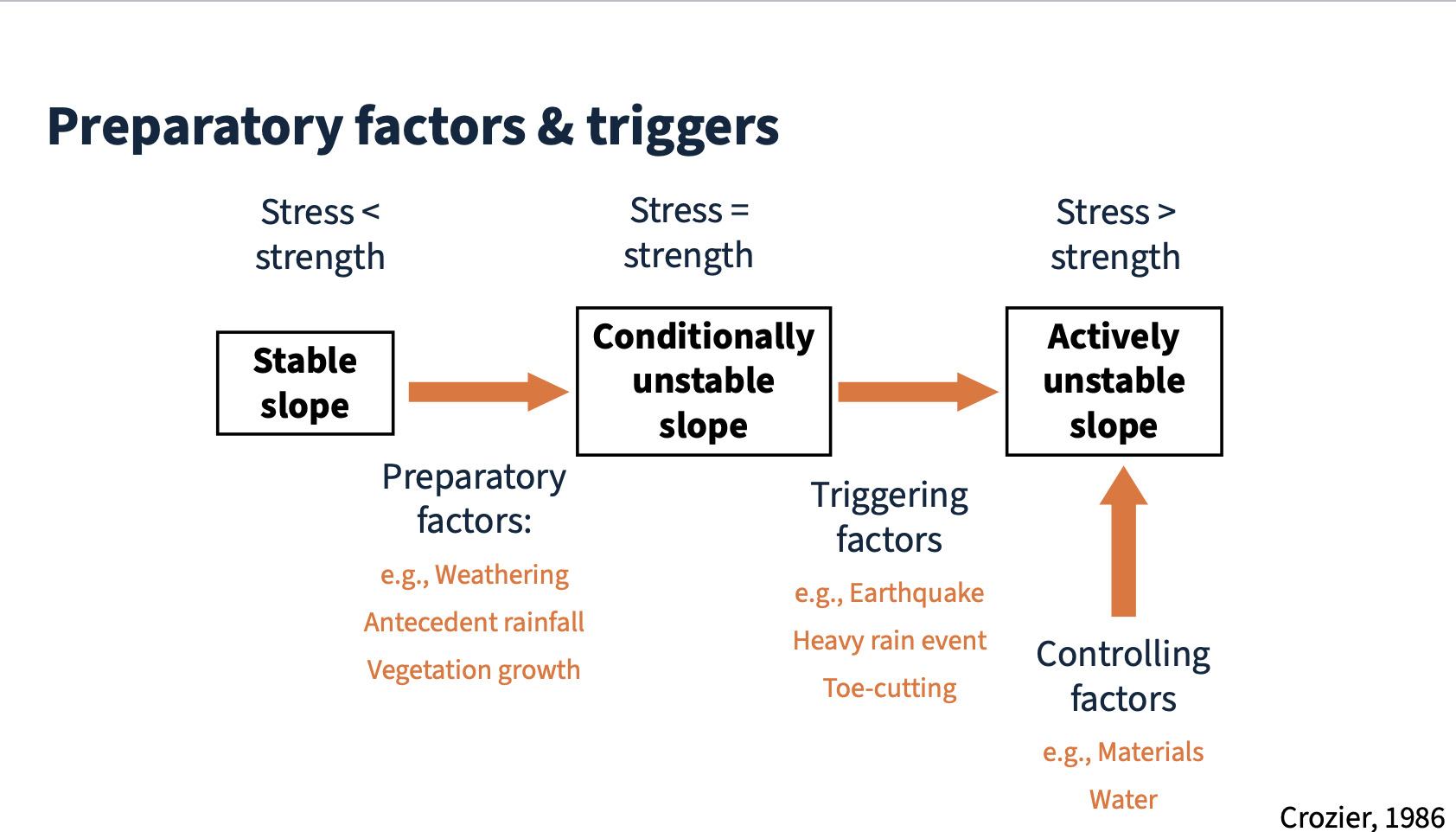
Preparatory factors and triggers
Continued
Case study: North Norfolk Coast

Geographic clues to mass movement
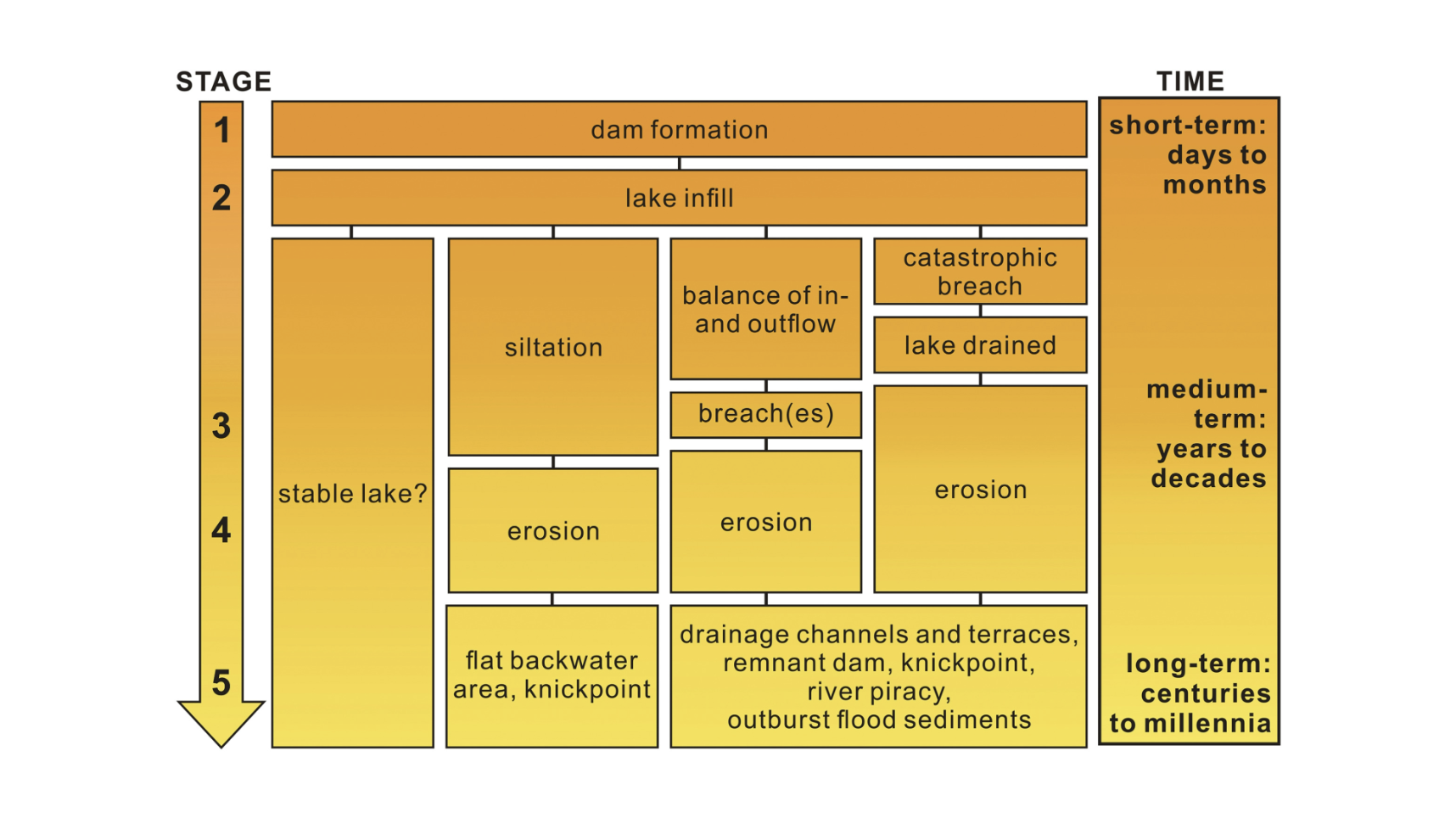
Case study: Nepal



