IB Biology SL - ALL UNIT QUESTIONS
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
{pink highlight} or ** - extra info; [] - marks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
data for a sample population that exhibits a large standard deviation:
a. must have a few samples in the population
b. has sample data points that are all close the the mean value
c. has sample data points that are spread out far from the mean
d. does not exhibit variation
c. has sample data points that are spread out far from the mean
the level of significance (probability value, p) used for t-test is always: _____
p = 0.05
finding the sum of a set of values and dividing it by the number of values is used to calculate the ____
mean
the average leaf length of one plant is 2.5 cm with a standard deviation of 0.5cm. what does this indicate?
a. 95% of all leaves fall within the ranges of 2.0 to 3.0cm
b. 68% of all leaves fall within the ranges of 1.5 to 3.5 cm
c. 68% of all leaves fall within the ranges of 2.5 to 3.0cm
d. 95% of all leaves fall within the ranges of 1.5 to 3.5cm
d: 95% of all leaves fall within the ranges of 1.5 to 3.5cm
an error bar is a graphical representation of the ______
standard deviation
which is a density-independent limiting factor for a kangaroo?
a. forest fire
b. predation
c. climate change
d. eutrophication
a. a forest fire
outline the changes in elk population between the years 1930 and 2004
between 1930-1968, numbers reduce, 1968-1970 increases, 1990’s (~1996) numbers go down, lowest in 1990 and highest in 1990.
![<p>list <strong>two </strong>biotic factors, other than wolf predation or culling, that could affect the elk population [2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c90b0783-215b-4d1b-8114-da7de0d345a0.png)
list two biotic factors, other than wolf predation or culling, that could affect the elk population [2]
competition
disease
lack of food
emigration / migration / immigration
![<p>label two phases on the nutrient-rich medium and sewage water [2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/69bc28e4-70b8-4d88-9928-6cf026245f66.png)
label two phases on the nutrient-rich medium and sewage water [2]
plateau (carrying capacity)
exponential growth
![<p><strong>compare </strong>(similarities) the population growth curve in nutrient-rich medium and sewage water [2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f20976c4-72a7-49f4-aefe-4d887a39fe21.png)
compare (similarities) the population growth curve in nutrient-rich medium and sewage water [2]
similarities:
both growth curves are sigmoid
both curves reach carrying capacity / plateau at same time
both start exponential growth at the same time

state two factors that limit the duckweed population size in 24 days
competition
overpopulation
lack of food
lack of light
lack of space
lack of food/nutrients/minerals/resources
lack of oxygen / carbon dioxide
disease
(herbivore) predation
pH
temperature
describe a method to determine the population size of motile organisms [3]
capture-mark-release-recapture method
this method determines population size by capturing organisms and marking them, noting how many were marked, releasing, after some time they capture organisms randomly then note how many were marked.
then they use the lincoln index to estimate population size
state one example of mutualism [1]
clown fish & anemone (think nemo)
zooxanthellae and hard corals
bacteria & plant root nodules
mycorrhizae in orchidaceae
for data that shows normal distribution, what percentage of data will fall outside of 2 standard deviations?
around 5%
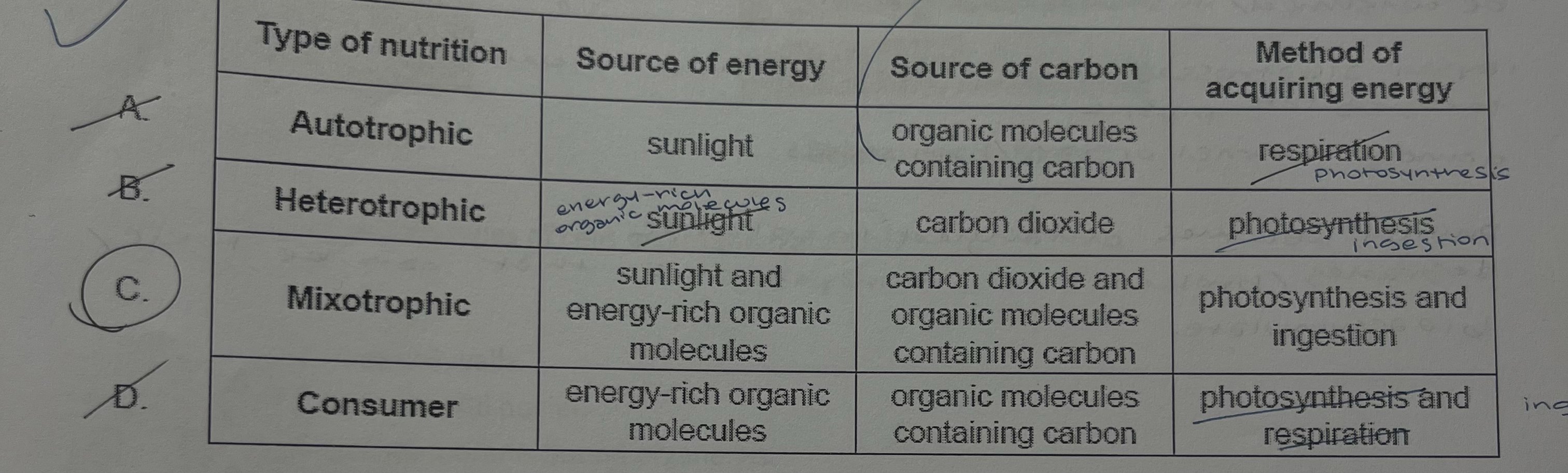
what are common features of holozoic nutrition and saprotrophic nutrition?
a. are mostly fungi & bacteria; secrete enzymes to digest food; do NOT ingest food particles
b. are mostly fungi & bacteria; do NOT secrete enzymes to digest food; ingest food particles
c. are NOT mostly fungi & bacteria; do NOT secrete enzymes to digest food; ingest food particles
d. are NOT mostly fungi & bacteria; do NOT secrete enzymes to digest food; do NOT ingest food particles
c. are NOT mostly fungi & bacteria; do NOT secrete enzymes to digest food; ingest food particles
distinguish between obligate and facultative anaerobes [1]
obligate anaerobes can ONLY use anaerobic systems to survive and thrive
facultative don’t necessarily need both systems but uses the other as a supplement
dentition can help scientists identify the diet of a species but this can be misleading. state one example of how dentition may not accurately represent a species’s diet. [2]
dentition suggests that sharp teeth and big canines can be for intimidation or for a carnivorous diet to cut through meat
however, this can be misleading
for example, the evening bat has sharp and prominent canines. according to dentition, this organism would be considered a carnivore but in actuality they are strictly frugivores (fruit only-diet)
for example, gorillas have sharp and prominent canines. according to dentition, this organism would be considered a carnivore but in actuality they are primarily herbivores.
sketch a labeled diagram of the layers of a rainforest [3]
canopy
shrub layer
forest floor
thick layers of peat found under dipterocarp forest soils are being lost by rapid decomposition and combustion. explain how this may contribute to the current biodiversity crisis [3]
decrease biodiversity because the dipterocarp trees will reduce in number due to habitat loss
loss of nutrients for dipterocarp
animals and plants which inhabit that ecosystem will be lost, furthering the lack of biodiversity
less biodiversity, less adaptations…
destabilizes ecosystem
pollution → the burning of peat specifically can also increase greenhouse gases
accelerates climate change - affects CO2 cycle
contributing more to global warming
species may go extinct due to global warming as they can’t adapt fast enough to the changing environment which results in biodiversity loss
which further contributes to the biodiversity crisis
** anthropodgenic (human activity)
identify the trophic level of sea lions [1]
secondary consumer, 3rd trophic level
outline the additional information that would be required to convert the food web into a pyramid of energy [2]
size of study area
energy content in each trophic level
energy released/wasted/lost to heat
why? because all of these effect the relative amount of energy that will be moving to the next trophic level
![<p>outline a reason that the orca whale would be difficult to represent in a pyramid of energy [1]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1a7774f1-2cec-4bfc-9dbd-565fc66534e2.png)
outline a reason that the orca whale would be difficult to represent in a pyramid of energy [1]
orca whale eats from multitudes of secondary consumers, pyramid would be very large
therefore the orca whale would be on different trophic levels, making the energy pyramid hard to draw
describe how communities rely on each other for supplies of energy [7]
autotrophs/producers/plants provide energy for consumers/heterotrophs/the community;
autotrophs convert light to chemical energy / photosynthesis;
energy flows along food chains/through food webs;
example of food chain with at least three named organisms and arrows to show energy flow;
heterotrophs rely on carbon compounds/food from other organisms (for their energy);
consumers ingest food/digest food internally;
primary consumers/herbivores feed on/rely on producers/plants/autotrophs;
secondary consumers feed on primary consumers/predators feed on prey;
detritivores ingest/eat dead organic matter/digest dead organic matter internally;
saprotrophs/decomposers feed on dead organic matter (produced by other organisms);
saprotrophs digest externally / secrete/release digestive enzymes;
energy not recycled/energy lost as heat/lost due to respiration/energy lost between trophic levels;
explain how energy and nutrients are transferred in ecosystems [1]
energy enters from sun (continuous energy)
light energy is converted to chemical energy by plants through photosynthesis
energy is lost through heat and movement through food chain (10% each level)
nutrients are recycled by detritivores & saprotrophs
nutrients aren’t lost, energy is transformed/changed
nutrients / carbon composition / energy flows through means of feeding
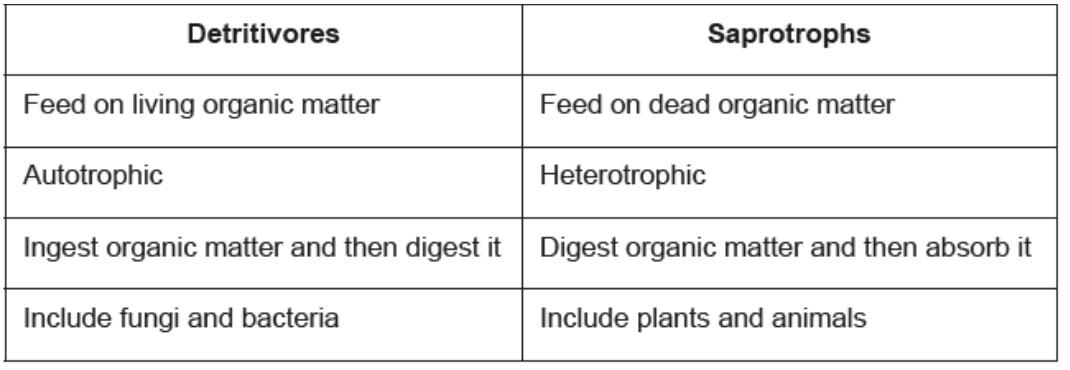
what is a difference between detrivores and saprotrophs?
c. detrivores ingest organic matter and then digest it; saprotrophs digest organic matter and then absorb it
what is a community?
a. a group of individuals of the same species in a given area
b. a group of animals that interact socially
c. a group of organisms interacting with the abiotic environment
d. a group of populations interacting with each other within a given area
c. a group of organisms interacting with the abiotic environment
explain the reasons for food chains rarely containing more than 4-5 trophic levels
energy is lost between the trophic levels;
transfer between levels is only usually 10% efficient OR energy transformations take place in living organisms / the process is never 100% efficient;
energy is lost by the organism/used in respiration / released as heat/movement;
energy is lost as waste/feces/urine/undigested food/uneaten parts;
as energy is lost between trophic levels and so (higher ones) have less biomass / less biomass available for next level;
describe how increased concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide may change coral reef ecosystems [4]
increased concentration of CO2 in solutions produce carbonic acid, which releases H+
makes water more acidic
zooxanthellae start to die as the pH is non-optimal
coral bleaching due to lack of food (bc zooxanthellae dies)
other organisms like fish can be harmed as they rely on coral for habitat
increased algae growth, more photosynthesis occurs, more dissolved CO2
shells of mollusks can’t form due to high acidity
outline an adaptation of an organism for the hot desert biome [3]
saguro cactus
waxy waterproof skin
shallow roots for efficient water uptake
fennec fox
large ears to dispel heat
nocturnal hunters (cool @ night)
obtain water from food → adapted kidneys
from the data, identify the depth along the transect where the greatest species richness is observed

6.5 meters
outline the relationship between zooxanthellae and reef-building coral reef species [2]
coral → food + energy from zooxanthellae
zooxanthellae → obtain habitat, shelter, + exposure to light
suggest one way in which depth may be a limiting factor for coral [1]
low light levels result in less photosynthesis, lower metabolize; zooxanthellae leave or die; coral dies due to lack of food
low temperature slows down enzymatic function of photosynthesis, lowers metabolism, zooxanthellae die or leave, no food for coral, coral bleaching, coral dies
describe how toxins such as DDT might concentrate in the bodies of birds
birds are secondary consumers, they eat a lot of insects who eat grass
distribution of energy - eat more, greater concentration of DDT
DDT is accumulated in fat tissue which is transferred when eaten
airplanes are sprayed with DDT, both in the air, contact
high concentrations of DDT in the water
biomagnification / bioaccumulation
which factor(s) would be expected to vary in a closed terrestrial mesocosm?
i. carbon content
ii. temperature
iii. biomass
a. i only
b. i and ii only
c. ii and iii only
d. i, ii, and iii
b. i and ii only
discuss the health consequences and environmental consequences of the use of DDT
weakens bird’s eggshells - reduces biodiversity
reduced reproductive success in birds of prey
affects phytoplanktons, the basis of the food web
due to biomagnification, the concentration increases throughout the trophic levels
kills bird populations
kills insects other than intended mosquitoes
negative impact on health for top predactor
![<p>identify the main source of energy of <em>thais</em> [1]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/21765ee2-d2f5-4fed-b6ee-131bd7dd5c22.png)
identify the main source of energy of thais [1]
acorn barnacles
![<p>limpets feed on photosynthetic algae. identify the trophic level of limpets [1]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a1f43738-5a4c-446f-a37c-b193a4b8f2e2.png)
limpets feed on photosynthetic algae. identify the trophic level of limpets [1]
2nd trophic level, primary consumer, herbivore

predict what would happen to this community if the following organisms were removed from the ecosystem:
i. mytilus
ii. acorn barnacles
i. not much change, starfish have 5 other sources of food, only 0.03
ii. population of thais decrease, population of bivalves increase, population of starfish increase a bit
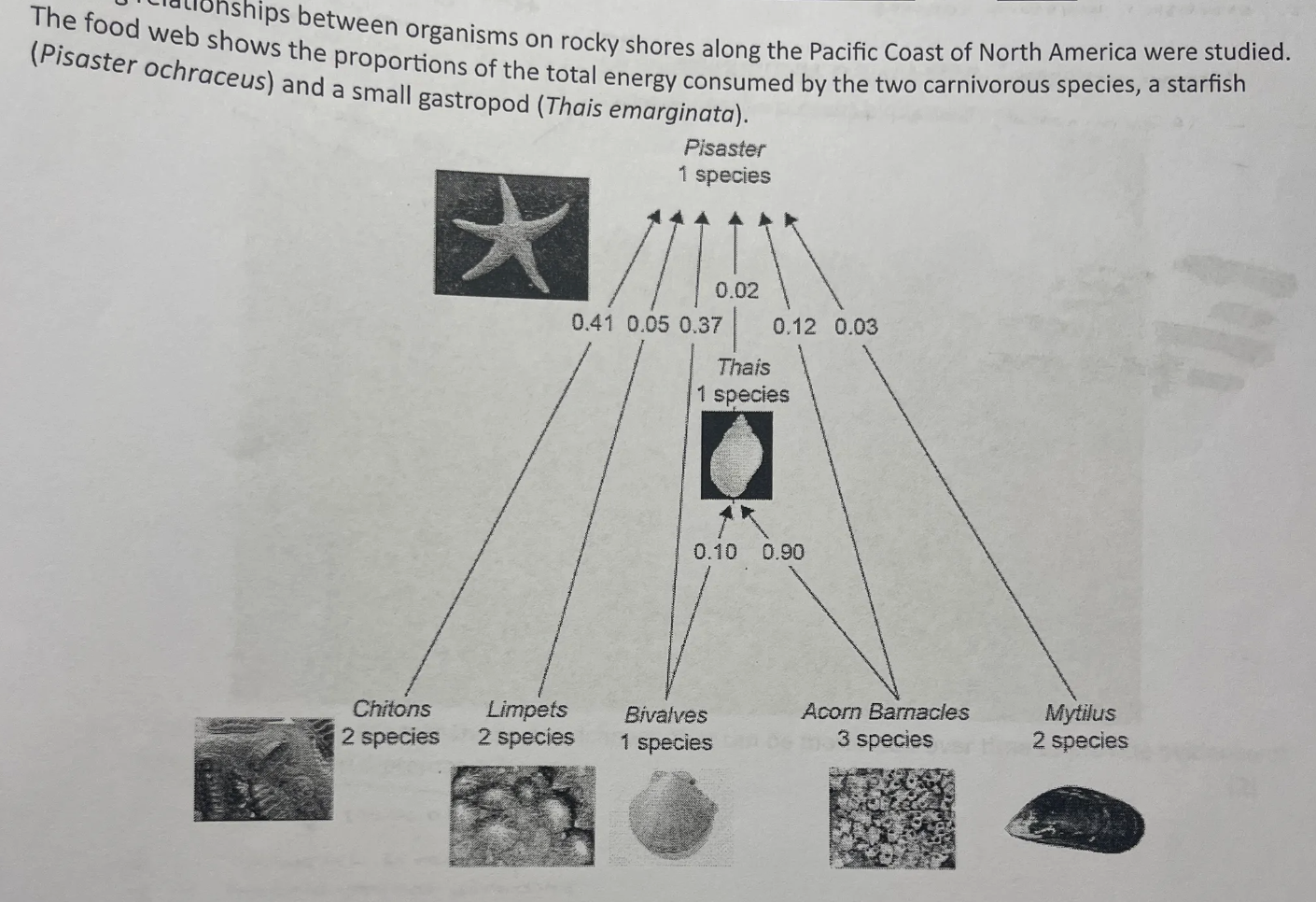
piaster is considered a keystone species. explain the effects of piaster on this community
organisms could overpopulate and producers would be close to extinction
ecosystem will collapse if eliminated, as it has a disproportionate effect on the community - feeds on all organisms, maintains population of all other species / autotrophs
eliminated species, biodiversity/diversity decreases
list two variables, other than species richness, that can be monitored over time to provide evidence of biodiversity loss in dipterocarp forests [2]
lack of habitat
genetic diversity
functional diversity
population of different species
lifespan of different species
keystone species
outline the reason for the loss of dipterocarp forest ecosystems in south asia [2]
logging for farmers
agricultural use of land
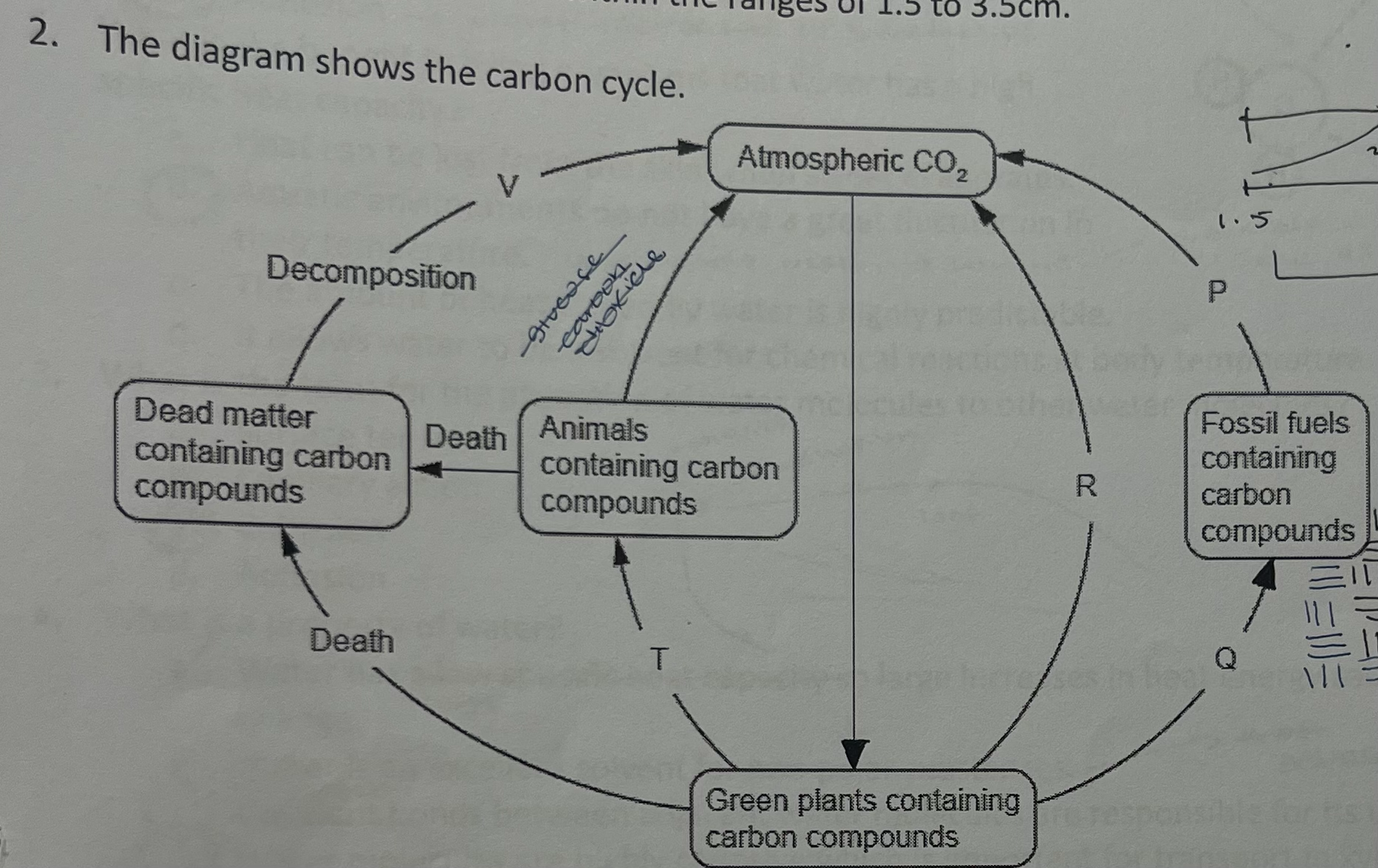
which letters represent respiration
a. r and t
b. p and v
c. q and r
d. r and v
a. r and t
describe how plants affect the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
plants reduce CO2 through photosynthesis
glucose → plants → cellular respiration
plants → decompose
carbon in dead plants is trapped / stored in fossil fuels
combustion of plants/animals adds to CO2 in atmosphere
detritivores decomposing dead organic matter (plants) release CO2 through cellular respiration
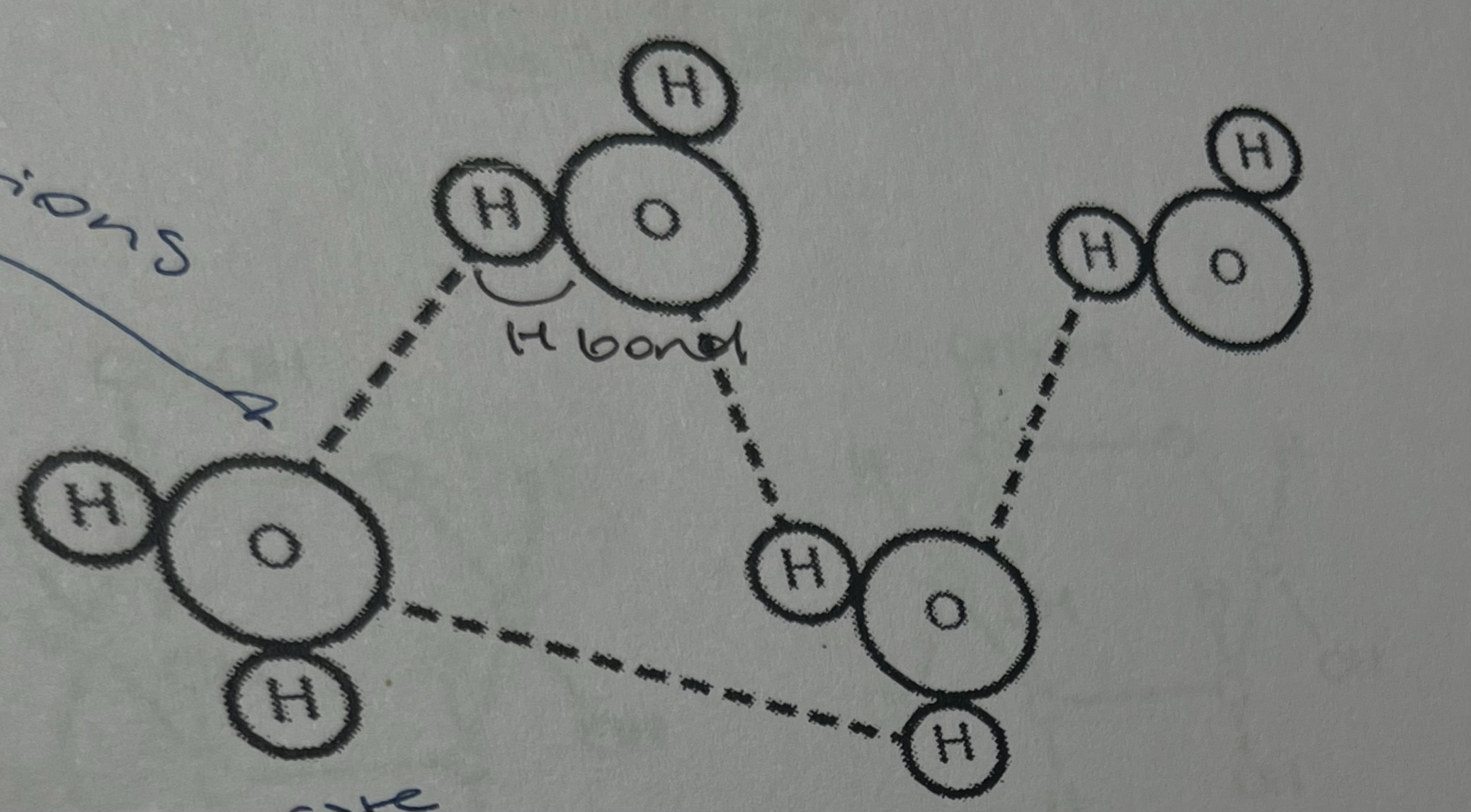
the diagram shows water molecules. which property of water is not illustrated?
a. cohesion
b. dipolarity
c. hydrogen bonding
d. adhesion
d. adhesion
what is the benefit to living organisms that water has a high specific heat capacity?
a. heat can be lost from the skin when sweat evaporates
b. aquatic environments don’t have a great fluctuation in their temperature
c. the amount of heat stored by water is highly predictable
d. it allows water to be a solvent for chemical reactions to other water molecules
b. aquatic environments don’t have a great fluctuation in their temperature
what is the term for the attraction of water molecules to other water molecules?
a. surface tension
b. capillary action
c. cohesion
d. adhesion
c. cohesion
what is a property of water?
a. water has a low specific heat capacity so large increases in heat energy cause a small temperature change
b. water is an excellent solvent for non-polar substances
c. covalent bonds between adjacent water molecules are responsible for its unique properties
d. water molecules are highly cohesive which is important for transport in xylem
d. water molecules are highly cohesive which is important for transport in xylem
what distinguishes cellulose from glycogen and starch?
a. only cellulose is found in plants
b. only cellulose is made up of glucose monomers
c. cellulose is far more branched than starch and glycogen
d. cellulose has a structural role whereas starch and glycogen function in energy storage
d. cellulose has a structural role whereas starch and glycogen function in energy storage
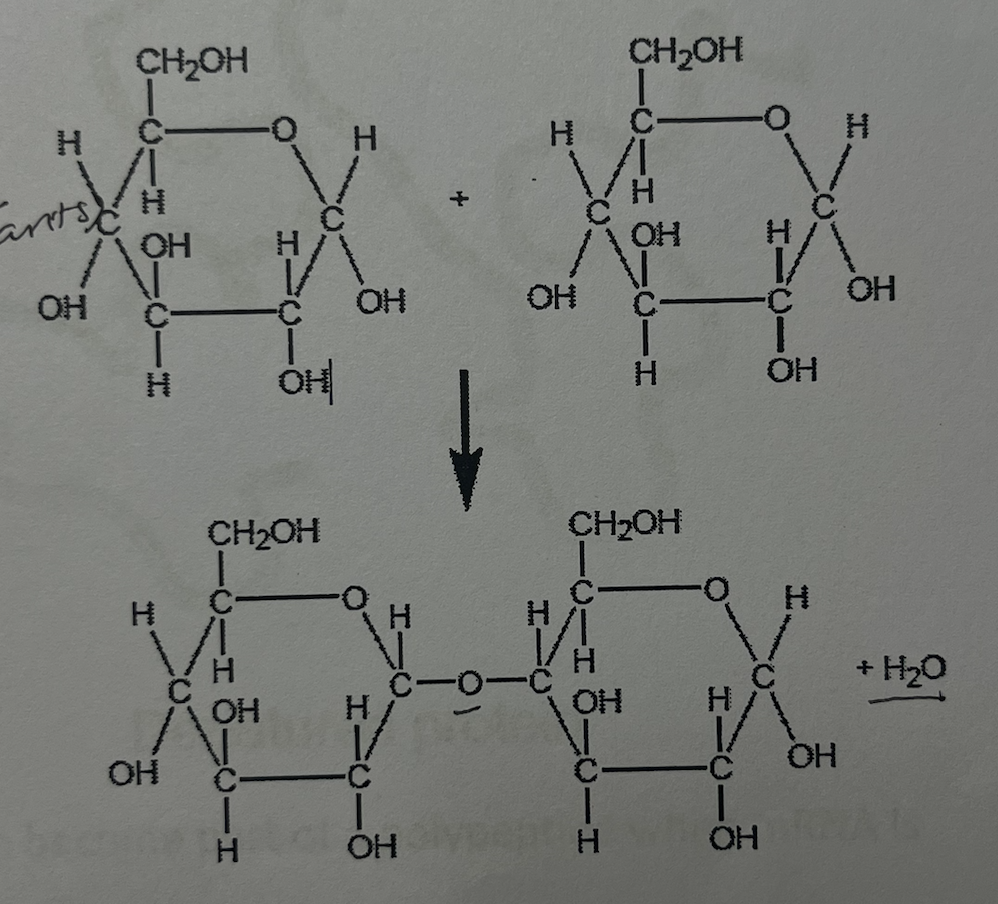
what type of molecule is formed by chemical reaction shown in the diagram
a. dipeptide
b. disaccharide
c. diglyceride
d. cellulose
b. disaccaride
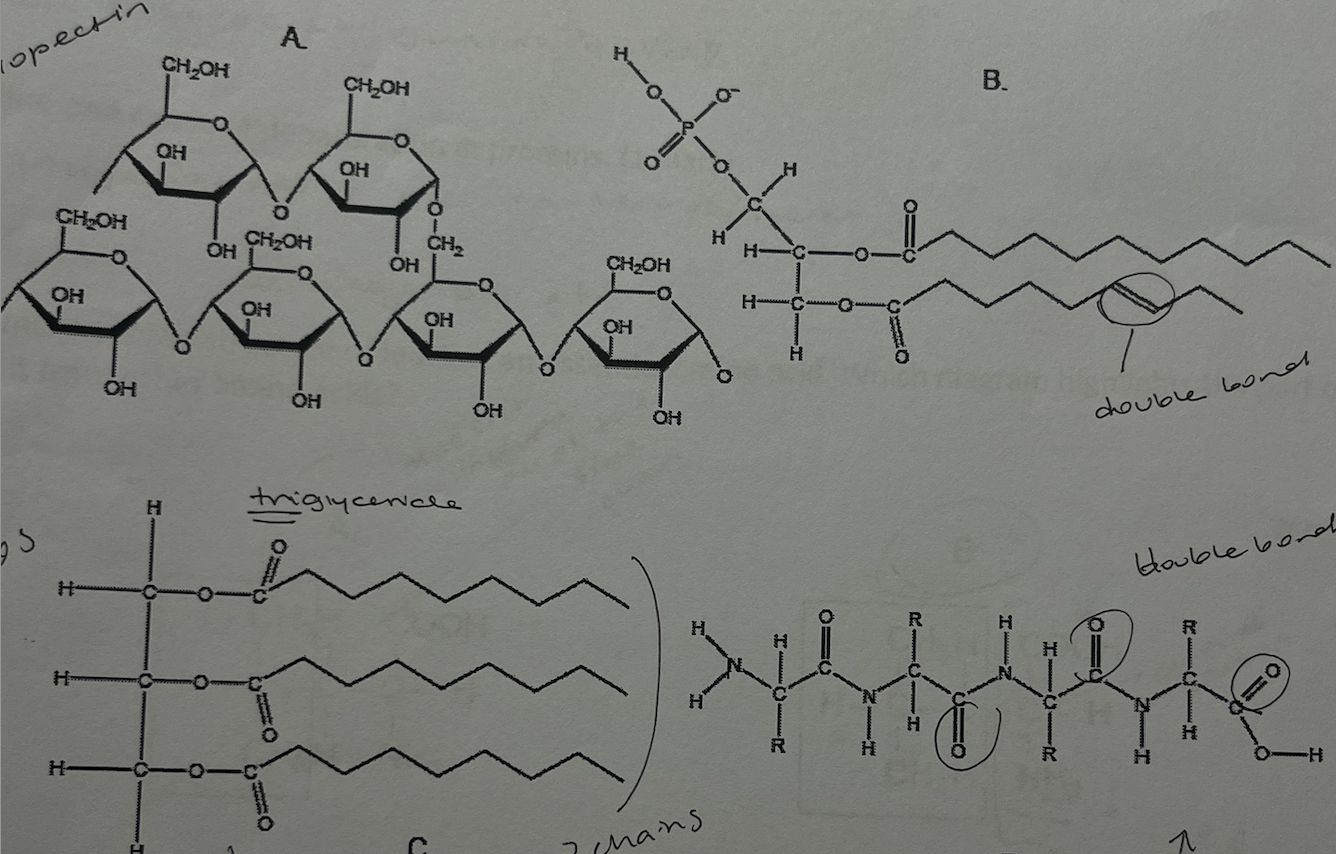
which of the molecules shown would be most suitable for long-term energy storage in humans?
c. (triglyceride)
state how many different types of amino acids there are, which can become a part of a polypeptide when mRNA is translated [1]
20 different amino acids
outline one cause of denaturation process in proteins [1]
temperature
as temperature increases, molecules speed increases and they vibrate, causing the weak hydrogen bonds to break which messes up the protein structure, leading to a loss of function
pH
the change in pH alters the charge of amino acid side chains, breakin gthe hydrogen bonds which maintain the proteins shape, causing it to unfold and lose function.
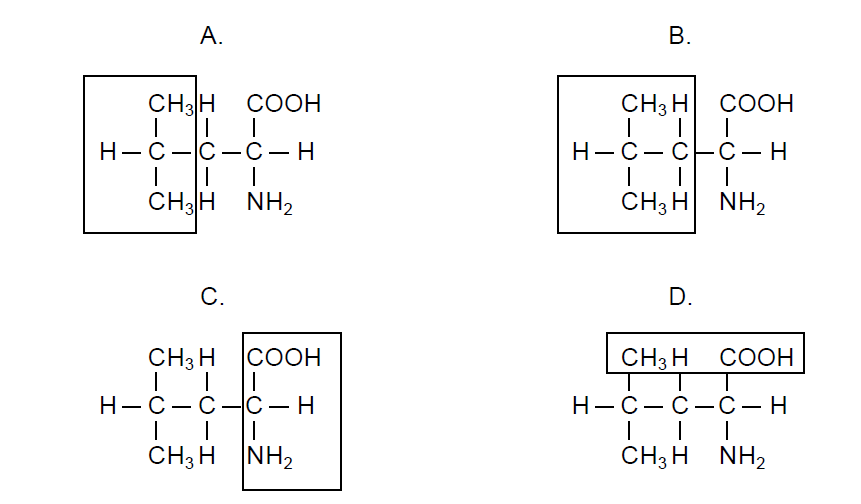
the diagrams show the structure of leucine, an essential amino acid. which diagram highlights the part of leucine that distinguishes it from other amino acids?
b. all amino acids have a carboxyl group (COOH), amino group (NH2), and H, and an alpha C
which statement applies to enzymes?
a. enzyme function depends on collisions between substrate and active sites
b. one active site typically binds to a broad range of substrates
c. the active site on the substrate is specific to one enzyme
d. when enzymes are immobilized they stop working.
a. enzyme function depends on collisions between substrate and active sites
state one function of lactase [1]
break down lactose sugar into galactose and glucose through hydrolysis
state a role of the active site of an enzyme [1]
site to which a substrate binds, bonds of substrate are broken to make a producto
outline one factor that could affect the activity of lactase [1]
temperature
as temperature increases, rate of reaction increases until it reaches a maximum rate and then decreases rapidly due to denaturation of the enzyme
pH
as pH increases, rate of reaction increases until it reaches a maximum rate and then decreases rapidly due to denaturation of the enzyme
living organisms control pH within their own tissues, what is a reason for regulating pH?
a. all parts of a body must be kept at the same pH to survive
b. many reactions can only happen at specific pH levels
c. pH affects osmosis
d. control of active transport is achieved by pH
b. many reactions can only happen at specific pH levels
what is a common feature of enzymes?
a. they all react w substrates
b. they all decrease the rate of reaction
c. they are all secreted from cells
d. they all bind to the active site of their substrate
d. they all bind to the active site of their substrate
explain the relationship between temperature and the activity of enzymes
temperature increases
molecular motion increases
frequency of collisions increase
rate of reaction increases
reaction reaches optimum temperature
enzyme reaches point where all active sites are saturated - plateau
further increase, enzyme denatures
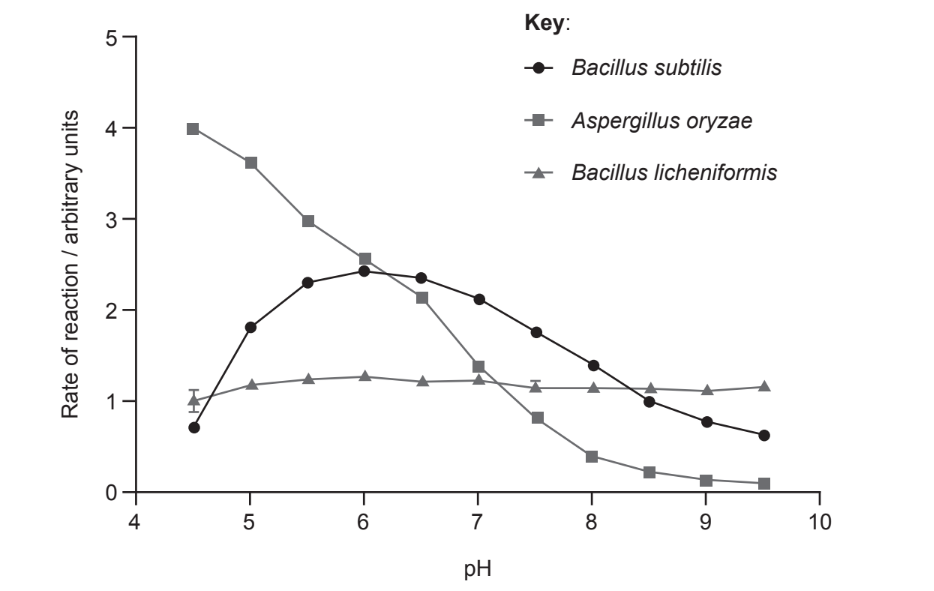
the activity of amylase from two bacterial species and a fungus was measured at different pH levels and constant temperature the results are shown in the graph. which statement about the effect of pH on amylase can be concluded?
a. A. oryzae amylase has the highest optimum pH
b. a change in pH affects amylase most in B. licheniformis
c. the optimum pH is 6 in B. subtilis
d. amylase activity at pH 8 is the lowest in B. licheniformis
c. the optimum pH is 6 in B. subtilis

the graph shows the effect of increasing the substrate concentration on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. what is occuring during the phase indicated by section Y on the graph?
a. the active site of the enzyme is saturated
b. the enzyme becomes denatured
c. the substrate concentration has risen too high
d. the optimum rate is reached
a. the active site of the enzyme is saturated
yersinia pestis is a bacterium that caused an outbreak of bubonic plauge in the 14th century. it normally produces ATP in the presence of oxygen but can still produce ATP if oxygen is absent. which term describes this characteristic?
a. facultative respiration
b. facultative anaerobe
c. obligate anaerobe
d. obligate aerobe
b. facultative anaerobe
discuss the benefits and risks of using DDT to control mosquitoes [3]
DDT kills/repels (adult) mosquitoes and larvae
DDT prevents/redices the spread of malaria
accumulation in fat tissues may harm humans / have adverse human health effects
biomagnification of DDT higher up food chain damages organism / top predator
is harmful to other insects
mosquitoes become resistant over time
outline the environmental concerns surrounding marine macroplastic pollution [2]
persistent / accumulation in oceans OR consumed / mistaken for food
laysan albatrosses feed plastic to chicks / chicks unable to regurgitate plastic
damages internal organs / intestines
animal becomes entangled in plastic
degrades / broken into microplastics that can be toxic / accumulate
the micrographs show two examples of atypical cells (aseptate fungal hyphae / striated muscle fibres). which features shared by both types of cells makes them atypical?
a. both have cell walls
b. both have several nuclei
c. both lack membrane-bound organelles
d. both are divided into compartments
b. both have several nuclei
how is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
a. eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized, whereas prokaryotic cells are not.
b. prokaryotic cells do not contain ribosomes, whereas eukaryotic cells do
c. eukaryotic cells contain DNA, whereas prokaryotic cells do not
d. prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, whereas eukaryotic cells do not
a. eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized, whereas prokaryotic cells are not.
draw a fully-labelled diagram of a bacterial cell.
plasmids
capsule
cell wall
plasma membrane
70s ribosomes
flagellums
nucleoid region (DNA) nucleoid
pilus
cytoplasm
identify organelles i to iii
i - nucleolus
ii - rough endoplasmic reticulum
iii - lysosome
using evidence from the micrograph, deduce whether the cells are prokaryotic or eukaryotic [2]
eukaryotic
cell membrane
cell wall
membrane-bound nucleus
compartmentalized cytoplasm
mitochondria
prokaryotic
small and cannot be seen
state the function of flagella and ribosomes in prokaryotic cells:
flagella: ___________
ribosomes: ________
flagella: movement / locomotion
ribosomes: protein systnehsis / amino acids / translation
state one component of a cell that is not considered an organelle [1]
cytoplasm
cell wall
cytoskeleton
state the location of the process of transcription [1]
{transcription: dna → mRNA, translation (ribosome): mRNA → protein}
eukaryotic: nucleus
prokaryotic: cytoplasm
explain the advantages of compartmentalization within the cell
more efficient division of labor
reaction molecules are stored in one area
reactions are separated, allowing for different pH in different parts of the cell
also helps to make the labor more efficient as it allows reactions to happen in its. optimal state of pH/temperature
harmful substances are isolated
digestive enzymes from lysosomes are contained
define cell fractionation
extract and separate different cellular components (organelles) while preserving their individual function for further study
{ one way to do this is through centrifugation }
in multicellular animals, embryonic stem cells have the ability to differientiate into a range of cells with different functions. what is the term used to describe cells with this property?
a. pluripotent
b. multipotent
c. totipotent
d. specialized
a. pluripotent
what best describes stem cells?
a. cells found only in the early embryo
b. multipotent embryonic cells that can differentiate into all cell types
c. totipotent stem cells that are found in specific niches in adults
d. pluripotent stem cells that may differentiate into blood cells
d. pluripotent stem cells that may differentiate into blood cells
differentiate between totipotent and multipotent stems [2]
totipotent - only present in embryonic development
is able to differentiate into all different types of cells
multipotent - present after embryonic development / during an organisms’ lifetime
is able to differentiate into multiple different cell types {i.e. blood / neuronal}
population
group of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time and are able to interbreed
community
group of populations living and interacting within an area
systematic sampling
line / grid set up and counting is carried out every specified regular interval
random sampling
randomly chosen zones of population’s geographic distribution are sampledca
carrying capacity
maximum number of individuals that a particular habitat can support
density-independent factors
factors that change the size of population NOT based on its density (forest fire, volcanic eruption, natural disaster…)
** affects individual same as group
density-dependent factors
factors that change the size of population based on its density (disease, little food, competition…)
intraspecific
individuals of the same species
interspecific relationships
individuals compete with other individuals (fight for water, food, space/shelter, mates…)
** international relations
mutualism
types of interspecific cooperation that benefits both species
plant root nodules & bacterias
mycorrhizae in orchidaceae
zooxanthellae in hard corals
allelopathy
production of secondary metabolites that influence growth and success of other organisms
inhibiting seed germination of competitors
interfering with nutrient uptake
killing nearby bacteria
niche
unique role organism plays in community
heterotrop
eat organisms for energy and nutrition
autotroph
make their own organic molecules as a source of food through photosynthesis / chemosynthesis
saprotroph
live on / in non-living organic matter, secreting digestive enzymes then absorbing the products of digestion
lianas
vines that take root on the forest floor and use trees as scaffolds allowing them to grow into the canopy to obtain more light
fundamental niche
potential niche that species could inhabit given the species’s adaptations and its tolerance limits
realized niche
actual niche species inhabits
principle of competitive exclusion
no two species in a community can occupy the same niche (population decreases, then it will be replaced)
decomposer
break down non-living food sources such as feces, dead organisms, or fallen leaves
biome
large community of plants and animals (desert, tropical forest, or grassland)
peat
waterlogged soil found in wetlands made with 30% organic matter and has high soil acidity