9-11
1/264
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
265 Terms
Who is Israel “Izzy” Kamakawiwo’ole?
Somewhere over the rainbow
He was obese - up to 757 pounds
Age 38 he died of heart failure at Medical Center Honolulu in 1997
What did Hawai’i do when Izzy died?
Flew state flag at half-staff the day of his funeral
body was laid in state at the Capitol in Honolulu - only private citizen ever so honored
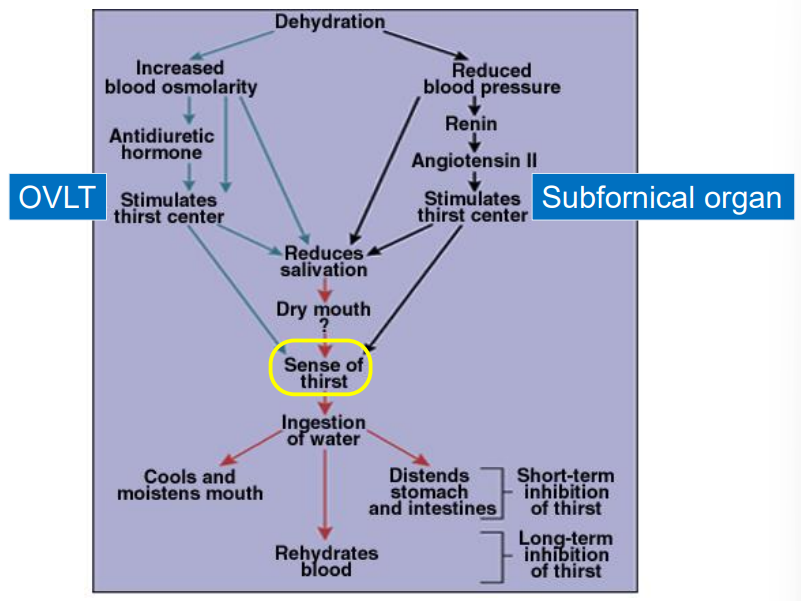
What do homeostatic systems do?
Use our behavior to keep things balanced
What is the main homeostatic mechanism?
Negative feedback system
What happens if a desired set point is deviated from?
compensatory action begins
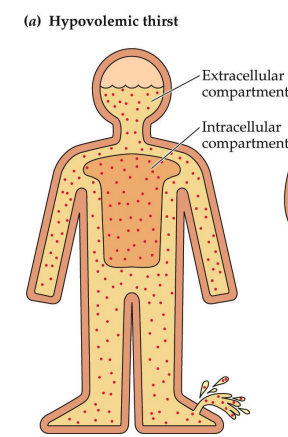
What is Hypovolemic thirst?
Stimulated by low extracellular/intravascular volume
not enough water - due to bleeding, sweating, etc.
caused by actual loss of volume
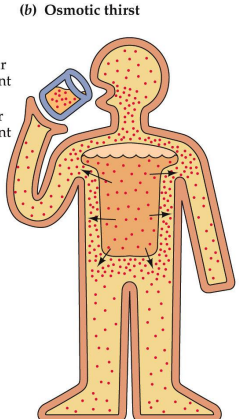
What is Osmotic thirst?
stimulated by high extracellular solute concentration
more salt than water - too much salt (getting thirsty after eating something salty)
caused by a change in concentration, not volume
What is hypovolemic thirst triggered by?
triggered by loss of water volume - concentration is not changed
low blood pressure
What is the Hypovolemic thirst pathway?
baroreceptors in blood vessels and heart - detect initial volume drop
sense blood pressure, keeps blood pressure balanced
Brain activates thirst and salt craving
Arteries constrict to raise BP
Vasopressin (ADH) is released from PP - causes vessel constriction/reduced blood flow in bladder
Why do people with diabetes insipidus have chronic thirst?
Vasopressin is not produced, so kidneys send more urine to the bladder - they are always in hypovolemic thirst
Baroreceptors use what kind of ion channel?
A. Voltage
B. Mechanical
C. Ligand-gated
D. Electrical
B. Mechanical
What gets released due to hypovolemia? What does it do?
vasopressin - constricts blood vessels and so reduces blood flow to bladder
Vasopressin deficiency
Kidneys send more urine to the bladder → chronic thirst
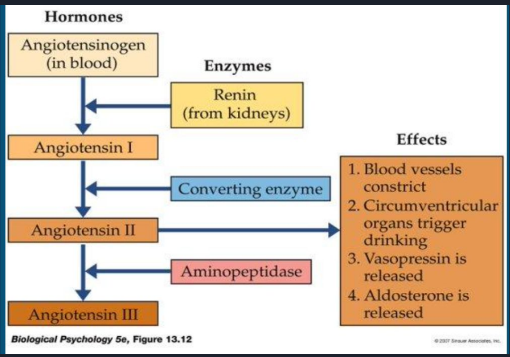
Angiotensin Cascade diagram
Know every detail
What triggers the cascade?
Blood volume decreases → kidneys release renin → formation of angiotensin II
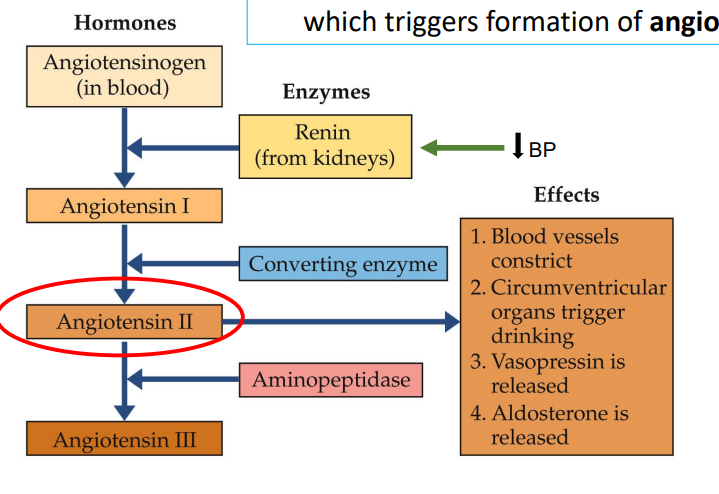
What is the main hormone pathway of the angiotensin cascade?
Angiotensinogen (in blood)
Renin (from kidneys) convert to Angiotensin I
Angiotensin I
Converting enzymes convert to Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II
Aminopeptidase converts to Angiotensin III
Angiotensin III
What are the effects of the release of angiotensin II?
Blood vessels constrict (raise BP)
Circumventricular organs trigger drinking
Vasopressin is released
Aldosterone is released (manage salt levels in blood)
What is the most powerful BP regulator in the brain?
Angiotensin II - High BP drugs block this to lower BP
Where does angiotensin II circulate?
subfornical organ (SFO)
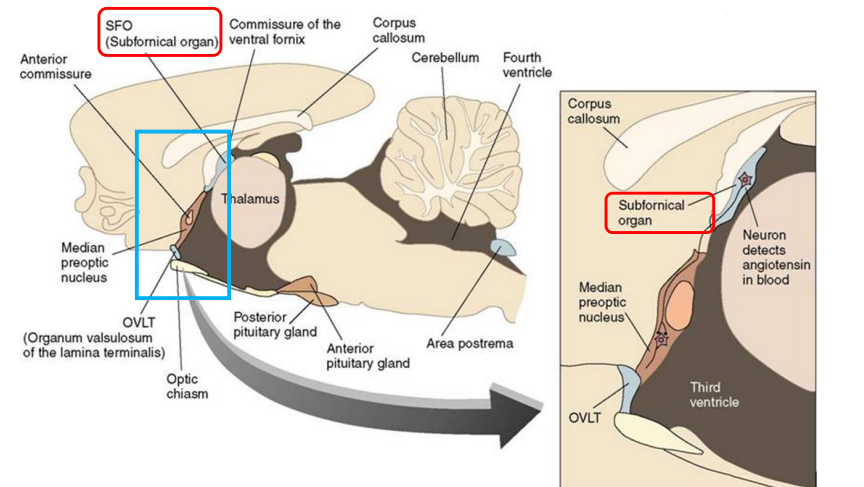
What does the angiotensin II in the subfornical organ signal to other brain sites?
initiate drinking
What is the Angiotensin II/SFO pathway? What type of thirst does this control?
Angiotensin II → SFO → other brain areas → drinking
Hypovolemic thirst
What is the process for osmotic thirst?
Water can pass through the semipermeable membrane - salt cannot
too much salt - cells shrink - drink water - water moves into cells - cells grow back
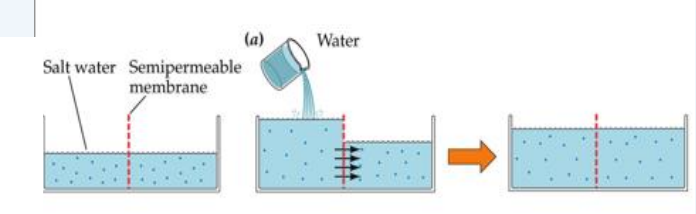
What responds to the rise in blood osmotic pressure? What triggers it, and what is the response?
Osmosensory neurons in anterior hypothalamus (OVLT)
Trigger: blood osmotic pressure rises → cell membranes shrink → mechanical-gated Na+ channels open
Response: OVLT causes pituitary to release ADH
OVLT/SFO diagram
A fall in blood angiotensin II level
A. Causes vasodilation (flushing)
B. Makes one feel thirsty
C. Raises blood pressure
D. None of the above
A. Causes vasodilation (flushing)
Why don’t diets work?
Energy expenditure adjust in response to nutrition
start of a diet - basal metabolic rate falls - prevents losing weight
only a diet that you stick to for life works

What happens at the start of a diet?
BMR falls - our body doesn’t want us to lose weight
The amount of energy spent is adjusted in response to what we eat
What does reduced food intake do for rats?
promotes up to 40% longetivity in rats
What is the basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
energy required to fuel brain/body and maintain temperature
what percentage of energy do sedentary students use
75%
Of women on a diet, [amount] who failed to lose weight had [high/low] BMRs
1/3, low
How much of your BMR does heredity account for?
40%
What can increase your BMR?
physical activity

What is glucose?
Main body fuel
What happens to children who cannot pass glucose across their blood-brain barrier?
Brain never sees glucose - it dies
What is glycogen?
a form of glucose that is stored in the liver for the short term
What is the process of converting glucose to glycogen using insulin?
Glycogenesis
What is used for long-term storage?
Lipids/fat tissue
What are the metabolic rates across the four stages of life?
Birth to Age 1: Peak cal burning
Age 1 - Age 20: Slow metabolism
Age 20 - Age 60: Plateau Metabolism
Age 60 - death: 1% a year decline
How does the brain decide when to start or stop eating?
Integrating of insulin/glucose levels with other signals
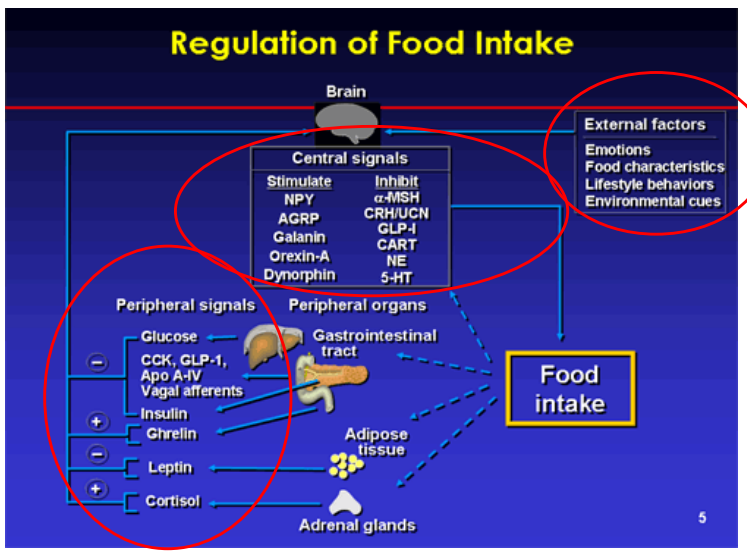
What are the external factors that regulate food intake?
Emotions
Food characteristics
Lifestyle behaviors
Environmental cues
What are the central signals that stimulate food intake?
NPY
AGRP
Galanin
Orexin-A
Dynorphin
What are the central signals that inhibit food intake?
α-MSH
CRH/UCN
CLP-I
CART (cocaine-amphetamine regulated transcript/adderall)
NE (norepniephrine)
5-HT (serotonin)
What are the peripheral signals that inhibit food intake?
Glucose
CCK, GLP-1, Apo A-IV, Vagal Afferents
Insulin
Leptin
What are the peripheral signals that stimulate food intake?
Ghrelin
Cortisol
What is leptin
hormone secreted by fat cells, leads to a reduction in weight due to appetite inhibition
What produces leptin?
Fat cells
What causes a false low report of body fat? What can this cause?
Defects in leptin production/sensitivity - causes overeating
Why are people obese?
Leptin resistance
What does overnutrition cause?
inflammation of the hypothalamus
obesity, diabetes, heart disease
What is Ghrelin?
Appetite stimulant
Where is Ghrelin released from?
stomach/gut endocrine cells
When do Ghrelin levels rise and fall?
Rise during fasting, drops after eating
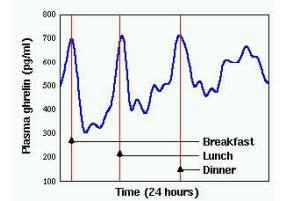
What do elevated levels of Ghrelin cause?
Prader-Willi Syndrome - fenetic disease that causes a sense of never being full or satisfied
Blood signals that stimulate appetite include
A. Rising ghrelin
B. Rising cortisol
C. Falling GLP-1
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
What is the hypothalamus nicknamed?
“The hunger control center”
What are the two hunger control centers in the hypothalamus?
Lateral hypothalamus (LH)
Ventromedial hypothalamus (VH)
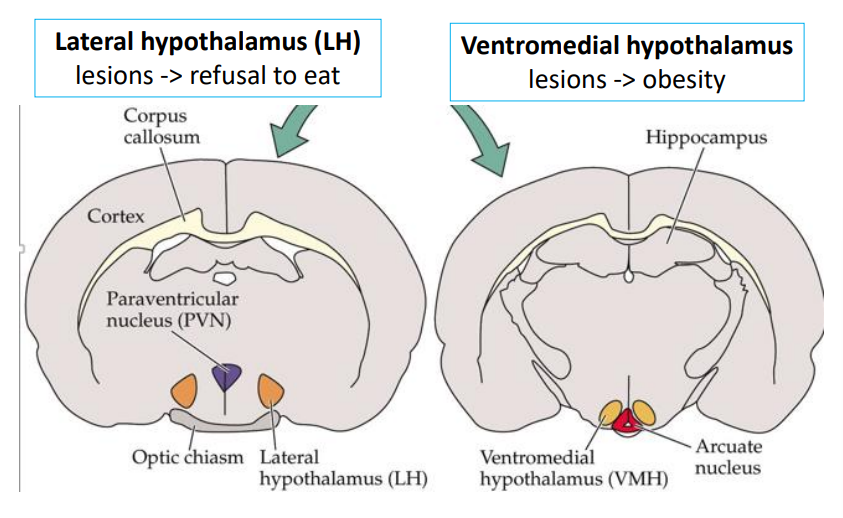
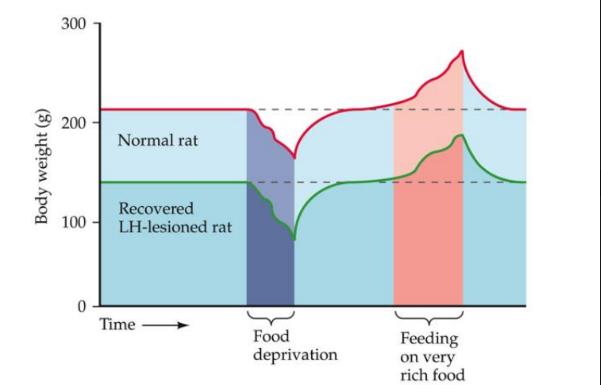
What do leisions to the Lateral hypothalamus (LH) do?
animals stop eating
resume and stabilize their weight at a new, lower level
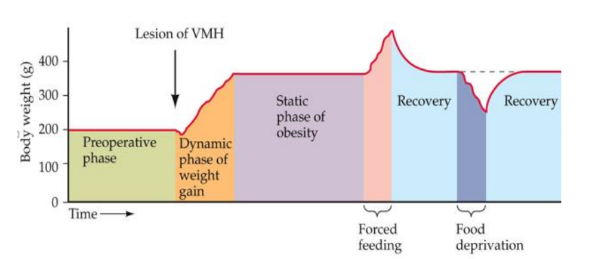
What do lesions to the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) cause?
animals overeat until they become obese
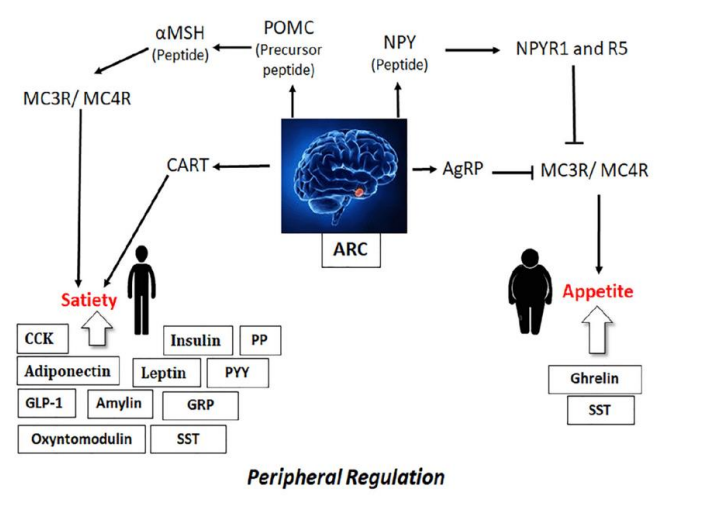
NPY/AgRP and POMC/CART have [similar/opposing] effects
opposing
What do NPY/AgRP neurons do? What effect does leptin have on them?
produce neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP)
stimulate appetite and lower metabolism - weight gain
Leptin inhibits AgRP neurons
What do POMC/CART neurons do? What effect does leptin have on them?
produce Pro-OpioMelanoCortin and CART
inhibit appetite and raise metabolism - weight loss
Leptin stimulates POMC neurons
What do VMH lesions destroy?
hunger-ending PVN
what do Lateral Hypothalamus (LH) lesions destroy?
hunger-causing LHA
What does Ghrelin stimulate?
AgRP neurons
POMC vs. ARC - the body talks to the brain, peripheral regulation (diagram)
Can overeating cause brain damage?
yes - high-calorie diets cause hypothalamic scarring, microglial activation, and fewer POMC neurons
What is the pathway of overeating-related brain damage?
Overeating → hypothalamic inflammation → inhibits neurogenesis, resets your set point
Pathway of overeating-related brain damage explained
Overeating → hypothalamic scarring → reduced POMC neurons → increased appetite + lowered metabolism
can be fixed by stopping overeating
Can the brain recover from overeating-related damage?
yes, if overeating stops - newborn hypothalamic cells can become POMC neurons
What is the lifetime prevalance of eating disorders in women vs men?
1/200 - women
1/2000 - men
What is Anorexia Nervosa?
Restricting or Binge-eating/purging type
Refusal to maintain body weight
Fear of weight gain
Body image disturbance
How do eating disorders affect the thyroid?
thyroid affects metabolic rate
What are some of the other symptoms of anorexia?
Thinning of bones
Brittle hair and nails
Dry, yellowish skin
Mild anemia, muscle weakness, lethargy
Severe constipation
Low blood pressure, slow breathing, pulse
drop in body temperature
amenorrhea
What has the highest mortality rate of any psychiatric disorder?
Anorexia Nervosa
What is Bulimia?
Recurrent binge eating
Recurrent inappropriant compensatory behavior
At least 2x/wk for 3 months
In France, what is Bulimia considered as?
High-status trend - companies use it to sell gloves
IT SHOULD NOT BE CONSIDERED A TREND
What percentage of women with Anorexia or Bulimia have anxiety and depression?
anxiety - 40%
depression - 90%
Of 246 Women with an eating disorder:
30% attempted suicide
5% died.
What parts of the brain are larger in teen girls with anorexia?
insula - disgust
orbitofrontal cortex - “you shouldn’t do that”
How are eating disorders in children measured?
Kids’ Eating Disorders Survey (KEDS)
What are the trends of eating disorders in children?
3175 students in grades 5-8
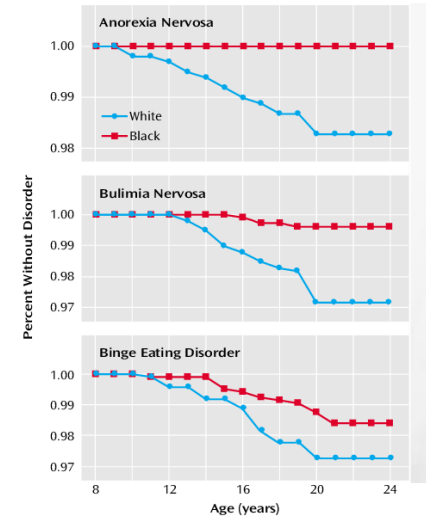
There are always more black children with eating disorders than white children.
30% dieting, 10% fasting, 5% vomiting, 2% using diet pills
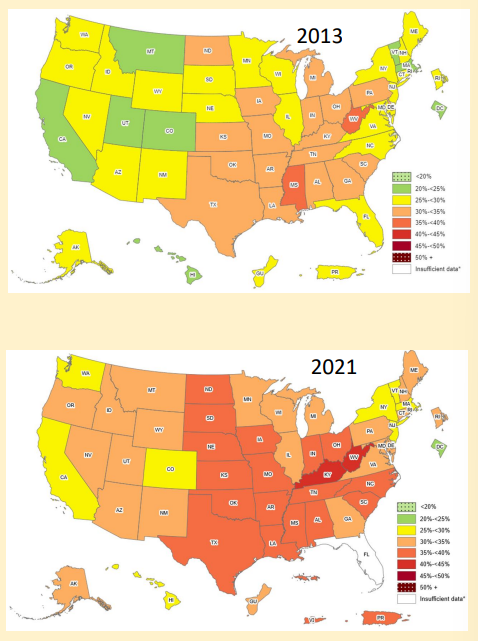
What are the obesity trends in the US from 2013-2021?
more of the US is obese
What are the sure treatments of obesity?
Eat less
daily deficit of 200 calories
hardest to do
Exercise
Strenuous aerobic activity for over 200 minutes per week
With calorie restriction
Invasive, long-lasting method: gastric bypass
shrink size of stomach via gastric pouch
reduce ghrelin and increases PYY/GLP-1
Weight loss avg. 25%
Will intake of proteins, fats, and carbs increase or decrease body weight?
increase
Will energy expenditure, physical activity, or diet-induced thermogenesis increase or decrease body weight?
decrease
What do Mounjaro and Ozempic do?
weight-loss drugs - GLP-1 acts on brain to suppress eating
decreased appetite
25-pound weight loss over 6 months
Practice Question - What are does angiotensin II act on?
The subfornical organ (SFO)
remember: Angiotensin II → SFO → other brain areas → drinking
Practice Question - What hormone is released in response to hypovolemia?
A. Vasopressin
B. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
C. Renin
D. All of the above
E. A & B only
E. A & B only
Renin is an enzyme, not a hormone!
Practice Question - Tom fell while he was running and got a fairly large cut. He would likely experience which of the
following?
A. Hypovolemic thirst and increased blood pressure
B. Hypovolemic thirst and decreased blood pressure
C. Osmotic thirst and increased blood pressure
D. Osmotic thirst and decreased blood pressure
A. Hypovolemic thirst and increased blood pressure
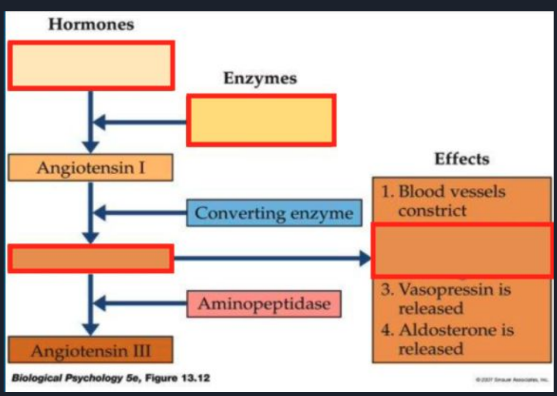
Practice Question - Fill the empty boxes
Practice Question -
___________ is triggered by low extracellular/intravascular volume.
___________ is triggered by high extracellular solute concentration.
hypovolemic thirst, osmotic thirst
Practice Question - What neuron does leptin inhibit from secreting neuropeptides?
A. AgRP neurons
B. POMC neurons
C. Anorexigenic neurons
D. Orexigenic neurons
A. AgRP neurons
Practice Question - POMC/ CART neurons produce what to inhibit appetite and stimulate metabolism?
A. Pro-opiomelanocortin
B. CART
C. Both A and B
D. AgRP
C. Both A and B
Practice Question - What is the part of the brain that activates when experiencing disgust?
A. Orbitofrontal cortex
B. Hypothalamus
C. Premotor cortex
D. Insula
D. Insula
Practice Question - What is the part of the brain that activates when thinking “I shouldn’t do that”?
A. Orbitofrontal cortex
B. Hypothalamus
C. Premotor cortex
D. Insula
A. Orbitofrontal cortex
Practice Question - At what age is metabolism at its peak?
A. Birth
B. Age 20
C. Age 60
D. Age 98
A. Birth
Practice Question - The OVLT cell membrane opens what ion channel in response to osmotic thirst?
A. K
B. Cl
C. Na
D. Ca
C. Na
Practice Question - What organ is insulin made by?
A. Liver
B. Pancreas
C. Blood
D. Fatty Tissue
B. Pancreas
Practice Question - What is the cellular mechanism of osmotic thirst?
A. Solute pass through the membrane, high solute concentration inside
B. Solute pass through the membrane, high solute concentration outside
C. Water pass through the membrane, high solute concentration inside
D. Water pass through the membrane, high solute concentration outside
D. Water pass through the membrane, high solute concentration outside
Practice Question - What detects changes in blood volume?
A. Chemoreceptors
B. Nociceptors
C. Baroreceptors
D. Volumereceptors
C. Baroreceptors