422 Exam2 3 and 4 membered heterocycles
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
3 membered ring
unsaturated suffix
irene
3 membered ring
saturated suffix
irane
4 membered ring
unsaturated suffix
ete
4 membered ring
saturated suffix
etane
5 membered ring
unsaturated suffix
ole
5 membered ring
saturated suffix
olane
6 membered ring
unsaturated suffix
ine
6 membered ring
saturated suffix
inane
7 membered ring
unsaturated suffix
epine
7 membered ring
saturated suffix
epane
8 membered ring
unsaturated suffix
ocine
8 membered ring
saturated suffix
ocane
3 member N heterocycle
saturated suffix
iridine
4 member N heterocycle
saturated suffix
etidine
5 member N heterocycle
saturated suffix
olidine
-penem definition/purpose
antibacterial antibiotics (carbapenem derivatives)
-cillin definition/purpose
penicillins
-bactam definition/purpose
beta-lactamase inhibitors (mostly monomactams)
reactivity order of beta lactams (highest to lowest)
CLavams (h=0.5)
CArbapenems
PEnams
CEphems
MOnobactams (h=0.05)
Cl-Ca-Pe-Ce-Mo
h
height of triangular pyramid with N at apex
3 points forming plane base are the 3 C attached to N
higher h: less planar, more distortion/strain, more reactive
what is the result of distortion of the amide bond planar geometry?
* makes the amide bond weaker and primes it for reaction with nucleophiles
* weaker C-N bond makes it easier to open b-lactam ring
* amide bond is supposed to have double bond character, needs to be planar for sp2 orbital overlap
other reasons for beta lactam reactivity
* if product has tetrahedral geometry, a distorted b-lactam will better resemble target, more easily forming an early transition state, react faster
* lower conjugation of C=O with N increases partial charge on C, making it a better target for nucleophiles
beta lactam reactivity and antibiotic drug properties
reactivity directly correlates with rate of antibiotic effect & metabolic degradation
what enzyme are low reactivity beta lactams more likely to inhibit?
beta lactamase
beta lactamase definition/purpose
* cleaves beta lactam ring of beta lactam antibiotics
*an enzyme responsible for antibiotic resistance in bacteria
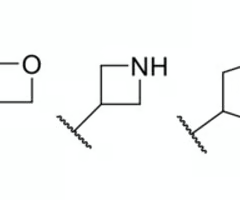
4 membered heterocycles such as azetidine and oxetane are (more/less) reactive than beta lactam rings?
less reactive, more stable
have 4 membered N-containing rings without carbonyl in ring
what is the most common purpose of three membered heterocycle drugs?
DNA alkylating agents due to the reactivity of the aziridine ring
examples: chemotherapeutic agents
why are 3 membered heterocycles highly reactive?
higher ring strain makes them more susceptible to nucleophilic attack
what might make 3 membered heterocycles unusually stable?
steric hindrance
are 3 membered heterocycles more stable or reactive?
reactive
are 4 membered heterocycles more stable or reactive?
stable
are lactones more stable or reactive?
reactive
are thiolactones more stable or reactive?
reactive
are lactams more stable or reactive?
more stable than O & S-containing heterocycles
except for b lactams in antibiotics
are saturated carbocycles (no heteroatoms) more stable or reactive?
stable
which has conformers: 3-membered or 4-membered heterocycles?
4 membered heterocycles
(have 2 envelope conformers)
TRUE OR FALSE: all four membered O-containing heterocycles are highly reactive
FALSE
steric hindrance may make unreactive
lactones (similar to lactams) are generally reactive though
what is the main reason for 3 and 4 membered heterocycles' immunogenic properties?
their relative instability from their ring strain
TRUE OR FALSE: all 3 membered heterocycles in drugs are reactive
TRUE
unless indicated otherwise
what might be the pharmaceutical result(s) of a 3 or 4 membered heterocycle functional group in a drug?
high reactivity may complicate:
* storage
* formulation
* route of administration
* off-target effects in body
beta lactam immunogenic response
* reactive beta lactam and hapten antibiotics form covalent adducts with human proteins
* xenobiotic adduct may trigger production of antibodies
why are penam antibiotics recommended to take on an empty stomach?
1. can covalently react with chemicals in food decreasing effective dose
2. can non-covalently bond to food, delaying absorbtion
If Fsp3 is less than ______ it is poorly soluble
3
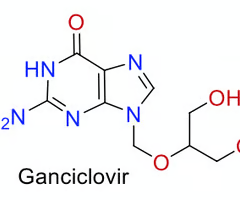
how many HB donors are there in this molecule?
4

which aromatic ring is more susceptible to oxidative metabolism?
5-membered heterocycle
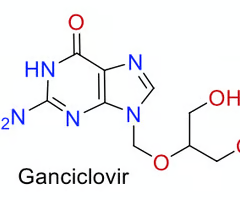
how many HB acceptors are there in this molecule?
6
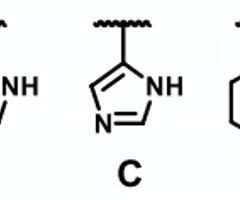
which molecule cannot serve as a HB acceptor
A
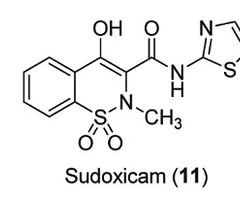
what is a potential way to prevent rapid metabolism of the thiazole group?
Add protecting group
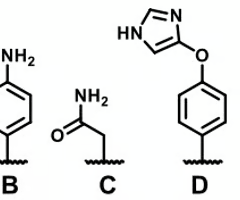
which molecules can't serve as HB acceptors
A and B
what types of drugs are the exception to the lipinski rules?
antibiotics, antifungals, vitamins, and cardiac glycosides
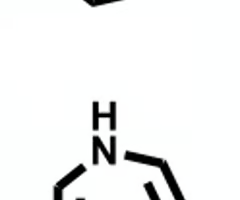
which molecule will have higher plasma binding?
azepane
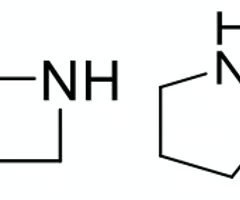
which heterocycle will have lower anticipated plasma binding?
azetidine
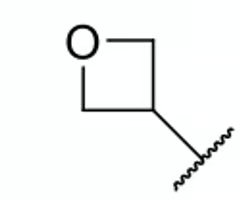
which molecule is more soluble in water?
azetidine
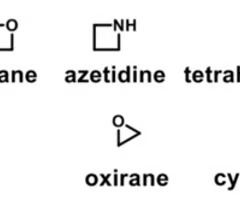
which heterocycles will readily react with cysteine side chain (nucleophile)
aziridine, furan, oxirane
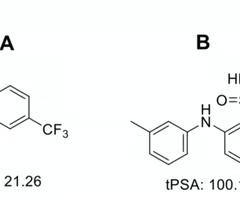
which drug is less likely to cross the blood-brain barrier
B
aromatic N containing heterocycles are weakly _________
1. acidic
2. basic
3. neutral
basic

why does pyrrole have more electron rich character than benzene
benzene has 6e per 6 atoms
pyrrole has 6e per 5 atoms
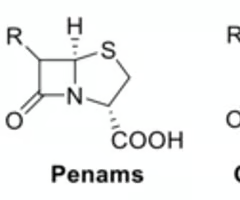
in which of these β-lactam scaffolds is the height of the pyramid the largest?
carbapenems and clavams (0.5-0.6 angstrom)
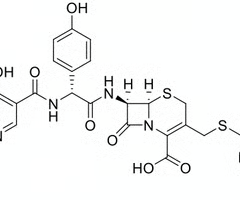
assign the following molecule to a class of β-lactams
monobactams
cephems
penams
clavams
carbapenems
cephem
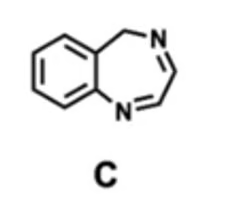
which molecule is most likely to improve dissolution? why?
C, it is non-planar
rank the reactivity of β-lactams in order of most reactive to least reactive
cephems
penams
carbapenems
monobactams
clavams
clavam=carbapenem > penams > cephems > monobactams
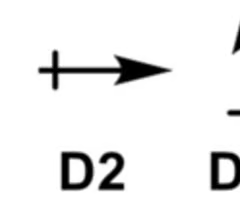
what is the correct dipole moment?
D3
beta-lactam antibiotics inhibit what enzyme?
DD-transpeptidase
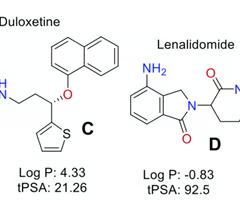
which drug is a better candidate for CNS application?
deloxetine
pKa < pH
Protonated or Deprotonated
deprotonated (ionized if COOH)
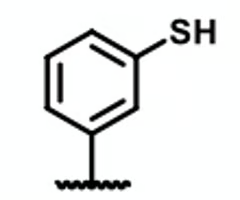
T or F? this molecule is a hydrogen bond donor
false
T or F? 3 & 4 membered saturated heterocycles are planar
false they are non-planar
T or F? aromatic N,O,S containing 5-membered heterocycles are never used to build drug molecules.
False, we just have to minimize their reactivity/metabolism
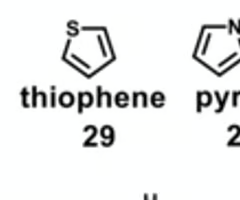
which aromatic compound is most likely to undergo rapid metabolism?
furan
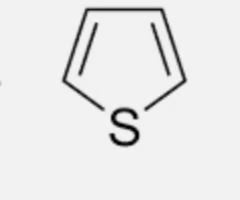
predict the dipole moments of these heterocycles
furan: points down
thiophene: points down
pyrrole: points up
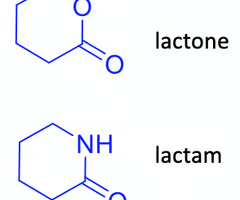
does hydrolysis in vivo occur more rapidly in lactams or lactones? why?
lactones, C-O is a weaker bond than C-N
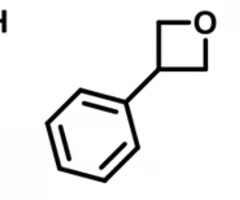
which of these heterocycles will have a higher anticipated plasma binding?
molecule with thiotane
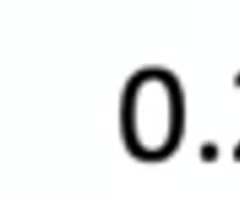
match the these heights with the following β-lactams
1. cephems
2. monobactams
3. penams
monobactams 0.05-0.1
cephems 0.2-0.25
penams 0.4-0.5
what are the lipinski rules?
MW > 500
Log P > 5
More than 5 HB donors
More than 10 HB acceptors
which aromatic compound is least likely to undergo rapid metabolism?
napthalene
Is this molecule aromatic?
no
Are these 4-membered heterocycles generally reactive or non-reactive?
non-reactive
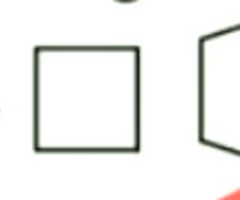
are these carbocycles generally reactive or non-reactive?
non-reactive
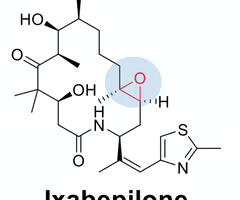
predict if the indicated epoxide will be reactive or non-reactive. why?
non-reactive, steric hinderance
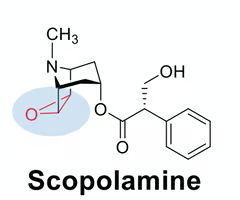
predict if the indicated epoxide will be reactive or non-reactive. why?
non-reactive, steric hinderance
which of the following heterocycles are prone to causing allergic rxns
oxirane
what type of heterocycles do NOT have acidic or basic properties?
oxygen and sulfur containing heterocycles
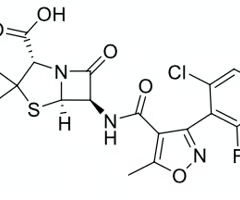
assign the following molecule to a class of β-lactams
monobactams
cephems
penams
clavams
carbapenems
penam

which of these heterocycles will have a higher anticipated plasma binding?
piperidine
pKa > pH
Protonated or Deprotonated
protonated (ionized if amine)
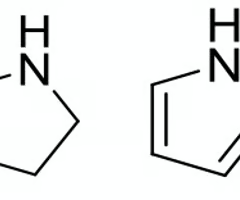
which heterocycle is more lipophilic?
pyrrole
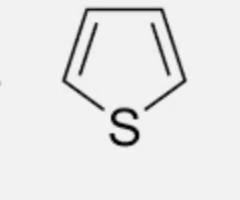
rank these heterocycles from least lipophilic to most lipophilic
pyrrole < furan < thiophene
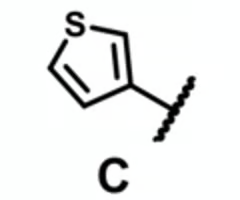
which molecule is likely to have the least plasma binding?
pyrrolidine
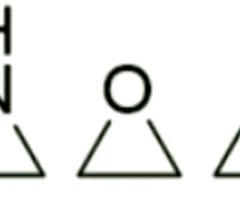
Are these 3-membered heterocycles generally reactive or non-reactive?
reactive
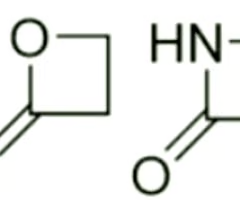
predict if the indicated epoxide will be reactive or non-reactive. why?
reactive, open to nucleophilic attack
are these lactones and lactams generally reactive or non-reactive? why?
reactive, readily hydrolyzable
how do you calculate Fsp3?
sp3 carbons/total carbons
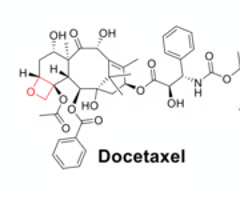
Name the heterocycle indicated in red and predict if it will be reactive or non-reactive. why?
taxol: oxetane, non-reactive, steric hinderance
docetaxel: oxetane, non-reactive, steric hinerance
orlistat: lactone, reactive, readily hydrolyzable
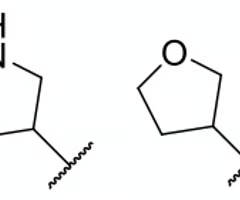
which molecule is less soluble in water?
tetrahydrofuran
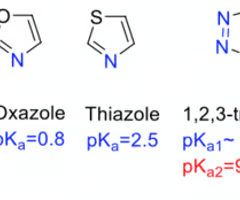
Which heterocycle should be used instead of the carboxylic acid to mimic its electronic and acidic properties?
tetrazole
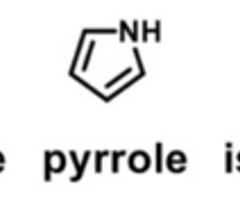
which heterocycles can serve as both a HB donor and HB acceptor
tetrazole and imidazole
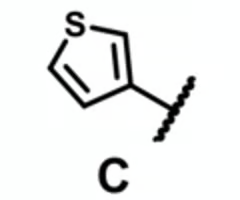
which molecule is likely to have the highest plasma binding?
thiophene
what TPSA corresponds to drugs that tend to be poorly blood-brain barrier permeable?
TPSA > 90
what TPSA corresponds to drugs that tend to be poorly cell membrane permeable?
TPSA > 140
T or F? 5-membered heterocycles are universal building blocks in drug molecules
true