w12 vertebral column + C-spine
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
how many true vertebrae are there
24
which sections of the spine are known as true vertebrae
cervical, thoracic, lumbar
how many cervical vertebrae are there
7
how many thoracic vertebrae are there
5
how many fused vertebral segments are there (opposite of true vertebrae)
9
what sections of the spine are known as fused segments
sacral, coccygeal
how many sacral vertebrae are there
5
how many coccygeal vertebrae are there
3-4
describe the curves of the spine in the fetal stage
concave anteriorly; primary curve
describe the curves of the spine into infancy and adulthood
secondary curvatures develop that are convex anteriorly
which sections of the spine are primary curves
thoracic, sacral/coccygeal
which sections of the spine are secondary curves
cervical, lumbar
describe the curvatures of the spine in the elderly stage
secondary curves start to disappear, primary curve of the upper back becomes pronounced to make a hunchback
describe kyphosis
exaggerated concave curvature of the thoracic spine; hunchback
causes of kyphosis (3)
old age, osteoporosis, trauma
describe lordosis
abnormal curvature of the lumbar spine; causes swayback deformity
causes of lordosis (3)
old age, osteoporosis, trauma
describe scoliosis
lateral S shape curve of the spine (primarily in the thoracic spine)
shape of the vertebral body
short cylinder
structure of the body
spongy bone surrounded by cortical bone
describe the body superior and inferior surfaces
roughened for intervertebral disc attachment
what are the pedicles (structurally)
short rounded bony processes
where are the pedicles located
project backwards from the vertebral body
on an AP radiograph, what do the pedicles look like
oval
what are laminae
flat plates of bone
where are laminae found
extend from pedicles to join at midline
which directions do laminae project
posteriorly and medially
what structure do laminae form at midline
spinous process
what are the transverse processes
bony projections from the junction of the pedicle and lamina
role of transverse processes
attachment site of longitudinal ligaments and muscles
what are spinous processes
projections from midline
what are spinous processes formed by
fusion of the laminae
what is another term for the vertebral arch
neural arch
where is the vertebral/neural arch found
posterior to the vertebral body
what structures form the vertebral arch
pedicles, laminae
within the body, what structure does the vertebral arch form
vertebral foramen
what structure passes through the vertebral foramen
spinal cord
list the two articular processes found on each vertebra
superior, inferior
where are the superior and inferior articular processes found
project superiorly and inferiorly from the junction of the pedicle and lamina
what structures are found on the superior and inferior processes
facets
what direction does the superior facet face
posteriorly
what direction does the inferior facet face
anteriorly
what does the superior articulating facet articulate with
the inferior articulating facet of the vertebra above it
name the joint of the superior and inferior articular facets (2 names)
zygapophyseal, apophyseal
what type of joint are zygapophyseal joints
synovial plane joints
what are articular pillars
vertebral column of bone between the superior and inferior articular processes on both sides of the spine
where are the articular pillar and zygapophyseal joints located
lateral and posterior to the vertebral bodies
role of articular pillars
support the spine
what is the intervertebral foramina
small hole formed by the superior and inferior vertebral notches of adjacent vertebrae
what structure anteriorly borders the intervertebral foramina
vertebral body and disc
what structure posteriorly borders the intervertebral foramina
zygapophyseal joint
role of intervertebral foramina
passageway for spinal nerves and blood vessels exiting from the spinal cord
structure of intervertebral discs
circular pad of fibrocartilage; outer fibrous ring surrounding an inner gelatinous layer
what type of joint is the intervertebral disc
symphysis
in the cervical spine from c3-c7, there is another type of joint. name this
uncovertebral joint
describe uncovertebral joints
on the top left and right edges of the body are raised ridges of bone which articulate with the inferolateral edge of the body above it
to form uncovertebral joints, on the top left and right edges of the cervical vertebral body are raised ridges of bone. what are these called
uncinate processes
role of uncovertebral joints
provide stability and mobility during movement, limit lateral movement of cervical vertebrae
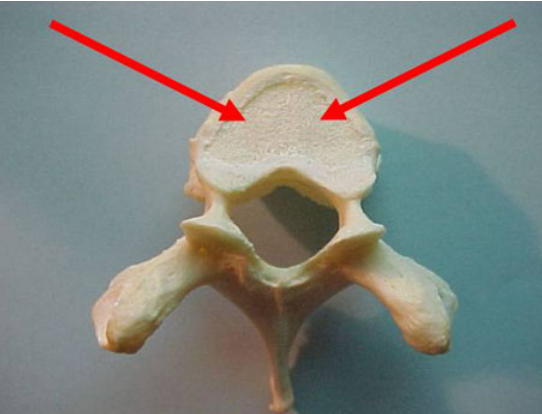
what is this
body
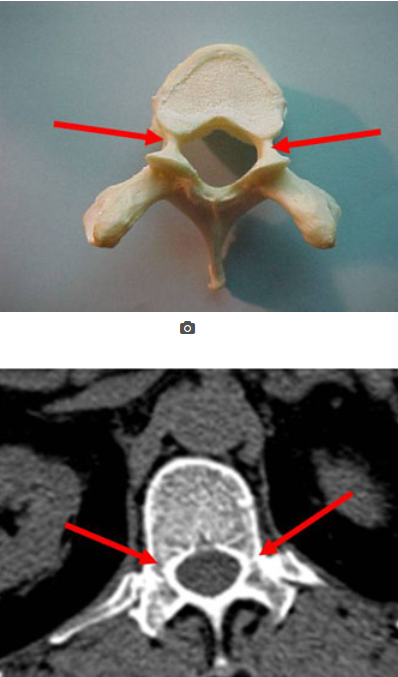
what is this
pedicles
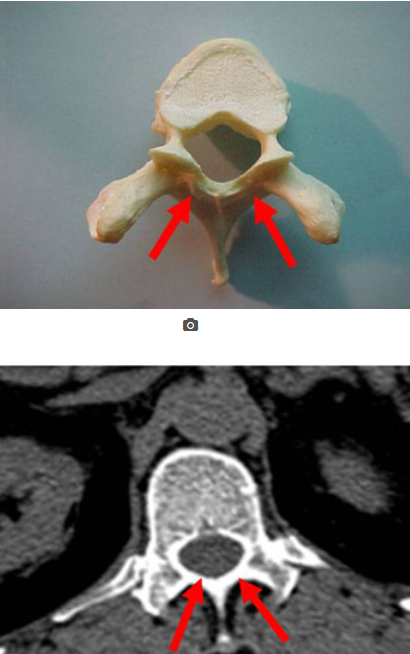
what is this
laminae
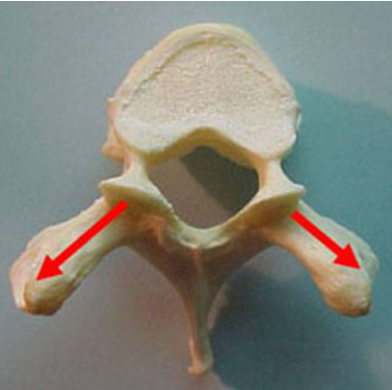
what is this
transverse process
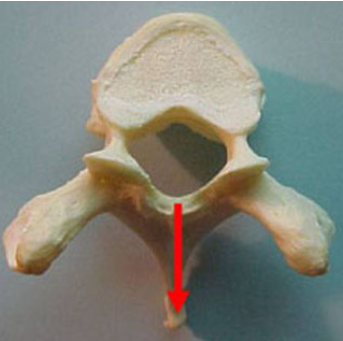
what is this
spinous process
what is the red circle
vertebral foramen
what is this
articular pillar
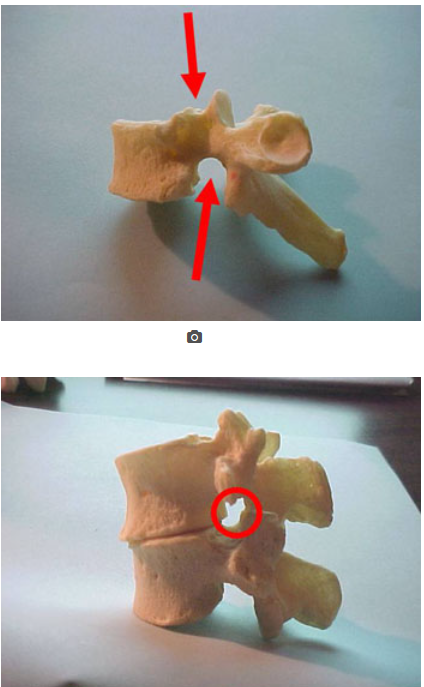
what is this
intervertebral foramina
which C vertebrae are the typical ones
3-6
describe the body of a typical c vertebrae
more wide than deep
body size for c vertebrae
small
neural arch size for c vertebrae
large
neural foramen shape for c vertebrae
triangular
describe the spinous process of c spine (2)
short, bifid
size of transverse processes of c spine
short
c spines have small foramen. what are these called
foramen transversarium
role of foramen transversarium
vertebral arteries go through these
what direction is the intervertebral foramina (2)
face 45 degrees from the midsagittal plane, 15 degrees inferiorly from the horizontal plane
what direction do the zygapophyseal joints point
inferiorly from anterior to posterior
what is c1 called
atlas
shape of the atlas
ring shaped
describe the sizes of the anterior and posterior arches of the atlas
anterior is smaller, posterior is larger
what feature does each arch of the atlas contain
small tubercle
what does the posterior tubercle of the atlas represent
underdeveloped spinous process
what surface feature does the anterior arch of the atlas have
small articular facet
the anterior arch of the atlas has a small articular facet. what is this for
the odontoid/dens of c2
describe the transverse processes of the atlas
longer than other c vertebrae
role of transverse processes of the atlas
act as levers for muscles that turn the head
what surface feature is found on either side of the arches on the atlas
lateral masses
superiorly, what do the lateral masses of the atlas articulate with
the base of the skull (occipital bone)
the lateral masses of the atlas articulate superiorly with the occipital bone of the skull. what joint is this
atlanto-occipital
inferiorly, what do the lateral masses of the atlas articulate with
superior facets of c2
the lateral masses of the atlas articulate inferiorly with the superior facets of c2. what joint does this form
atlanto-axial
what structure is located within the vertebral foramen of the atlas
transverse ligament
where is the transverse ligament of the atlas located
divides the vertebral foramen into anterior and posterior halves
the transverse ligament divides the vertebral foramen into anterior and posterior halves. what does the anterior part hold
the dens of c2
the transverse ligament divides the vertebral foramen into anterior and posterior halves. what does the posterior part hold
the spinal cord
what is c2 called
the axis
T or F: there is no intervertebral disc between c1 and c2
true
what special feature does c2 have
has the odontoid
what is another term for the odontoid of c2 (2)
peg, dens
structurally, what is the odontoid of c2
large finger-like process