Week 9: Caring for People with Liver Failure, Cirrhosis, and Upper GI Bleeding
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Cirrhosis
-end stage of chronic liver failure
-scar tissue blocks the flow of blood and bile thru the liver
-portal hypertension occurs (blood cannot freely pass thru now)
S/s of compensated Cirrhosis:
-minimal symptoms
-fatigue
-enlarged liver
-RUQ abdominal discomfort
S/s of decompensated Cirrhosis:
-jaundice
-hematological problems
-endocrine problems
-portal hypertension and esophageal and gastric varices (life threatening if pop)
-abdominal ascities and peripheral edema
S/s of upper GI bleed:
-melena (shiny, tar-like, fetid smelling stools), hematemesis
Hematochezia
passing of bright red blood per rectum indicating lower GI bleed source
Lab tests for Cirrhosis:
-liver enzymes: ELEVATED
-bilirubin: ELEVATED
-Albumin: DECREASED
-PT: EXTENDED
Nursing considerations for blood problems from Cirrhosis:
-cirrhosis causes blood problems: liver cannot produce vit K and clotting factors
-monitor for s/s of bleeding
-avoid aspirin and NSAID
-avoid IM injections, NG tube, unnecessary trauma
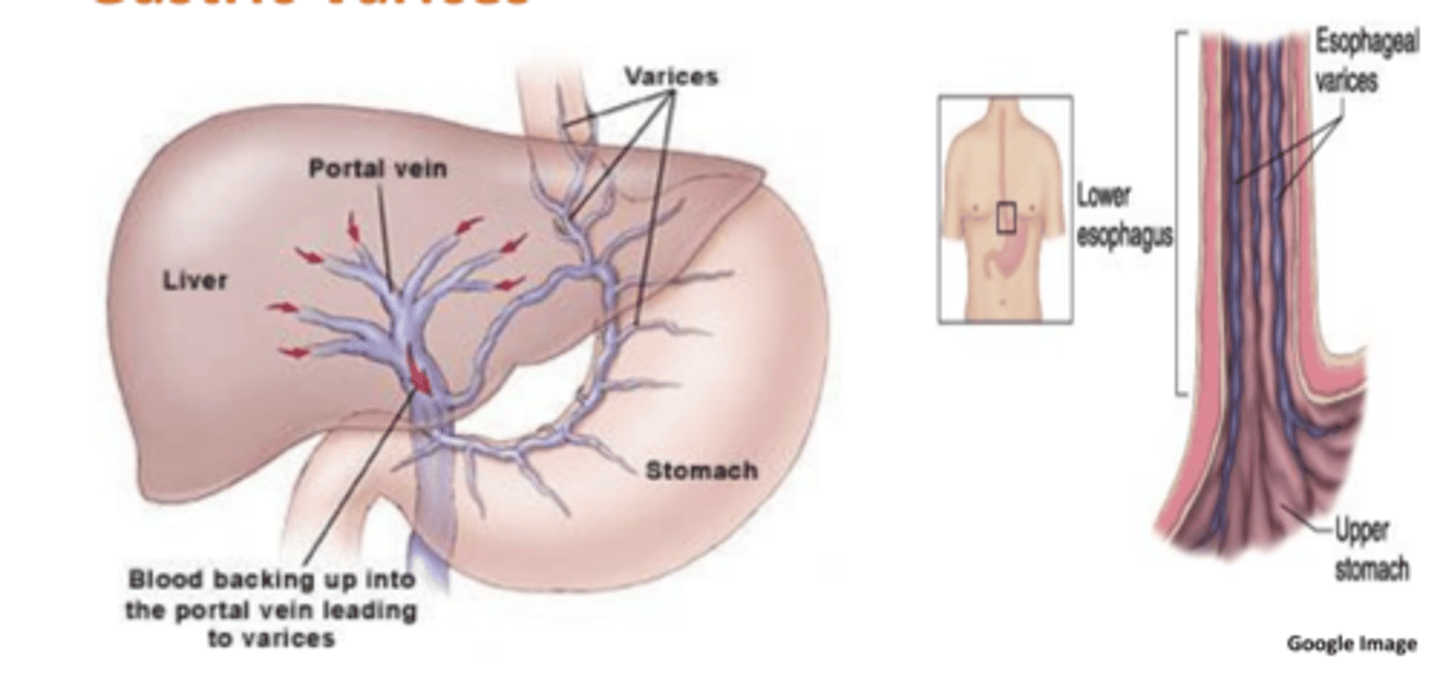
Major complications from Cirrohsis:
-portal hypertension
-esophageal and gastric varices
nursing considerations for active bleeding varices
PROTECT airway
RRT
2 large bore IV
crystalloids and blood products
VS monitoring
somatostatin and octreotide- vasoconstrict
vasopressin- decreases blood flow to abdomen → lower portal pressure
beta blockers
endoscopic sclerotherapy
banding
minnesota tube
How to prevent varices from bleeding:
-administer beta adrenergic blockers (decreases force of heart contraction--> decreases BP--> decreased pressure)
-advise avoiding NSAID, aspirin, and alcohol
-shunts can be placed
causes of upper GI bleed
50% is peptic ulcer disease → distended abdomen w/ hyperactive bowel sounds
mallory-weiss tear → vomiting blood, coughing
varices
gastritis
Nursing considerations for upper GI bleed:
-protect patient airway
-maintain hemodynamic stability (2 large bore IV and give blood products)
-monitor for ST changes or MI
-administer sedation and monitor patient during endoscopic procedures
-have suction ready and nearby
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
a stent is placed between the portal vein and the hepatic vein
-opens channels and decreases pressure
-used to control esophageal varices and ascities
Ascites
accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity
-caused by portal hypertension and excess fluid absorption
Nursing considerations for ascities:
-maintain HOB at 30-45*
-monitor VS
-auscultate lung sounds
-administer diuretics furosemide(K wasting) and Spironolactone (K sparing) (monitor Na and K before and after admin)
-administer 25% albumin IV solution to increase pressure (pulls fluid into blood vessels)
-place patient on sodium and fluid restriction
Nursing considerations for Abdominal paracentesis:
removal of many liters of ascites fluid to temporally reduce intra abdominal pressure
-have patient empty bladder prior to procedure
-cover puncture site with dry sterile gauze
-monitor for hypovolemia (lots of fluid lost)
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE):
potentially reversible decline in brain function that occurs in persons with end stage liver disease
-toxins that are normally removed accumulate in the blood and brain
S/s of hepatic encephalopathy:
-changes in personality, memory, concentration
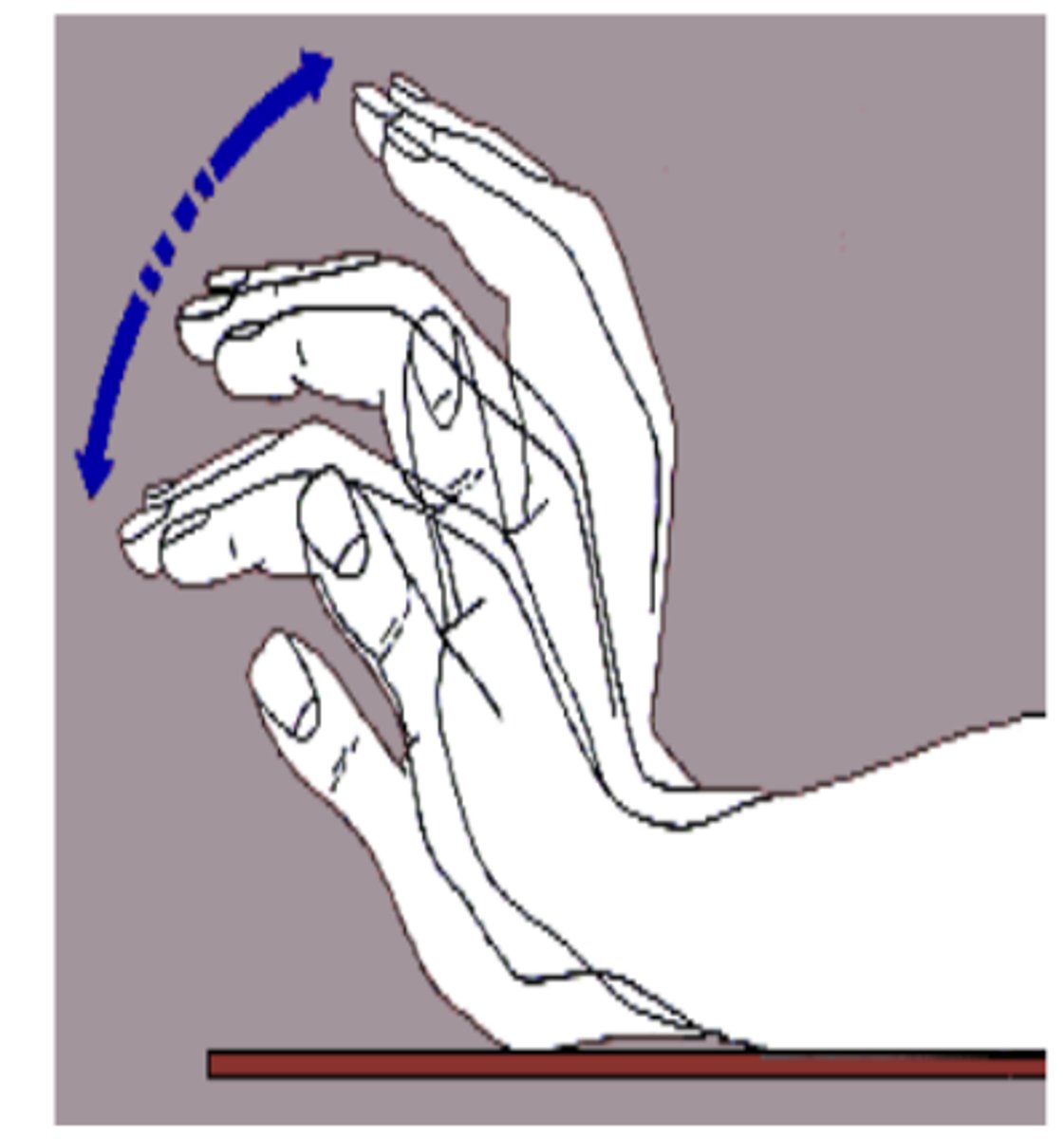
-asterixis (liver flap)
-slurred speech
-hyperreflexia
-lethargy that can go to coma
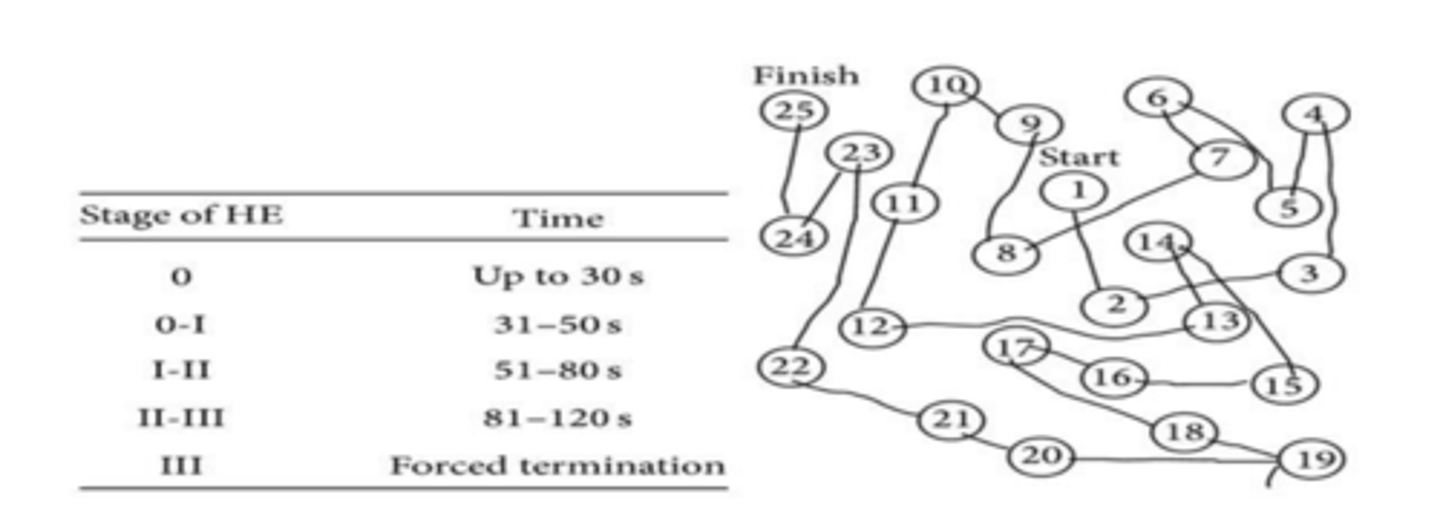
Diagnostic test for Hepatic encephalopathy:
connect the numbers test
-diagnosis cognitive impairment
serum ammonia levels (increased)
Nursing considerations for hepatic encephalopathy:
-ensure patient safety
-identify and remove cause (GI bleed, infection, constipation, high protein)
-HC can worsen after shunt placement
-administer lactulose or rifaximin
How does Lactulose work?
laxative that prevents absorption of ammonia in the colon
-goal is 2 to 3 stools per day
Hepatorenal syndrome
development of renal failure in a person with end stage liver disease
-rare but serious
Nursing considerations with nutrition and cirrhosis:
-should be on high calorie, low sodium diet
-Hepatic Aid 2 is a dietary supplement
-encourage frequent small snacks
-vitamin supplements
-may need supplemental enteral feedings
indications and purpose of minnesota tube
last resort-emergency measure when other treatments are unavailable for gastric/esophageal bleeding
compresses bleeding
why does HE become worse after TIPS procedure?
blood flow is diverted away from liver→ inability to breakdown ammonia= increased levels
how can encephalopathy develop?
GI bleed
Infection
constipation
high protein intake
use of psych meds
do patients experience abdominal pain with popped varices?
NO!! no pain is a classic sign that its a varice and not bleeding ulcer
west haven criteria for 4 stages of HE
measures consciousness, intellect and behavior, neuro findings
0=normal
1= mild, impaired
2= lethargic, disoriented, asterixis
3= arousable, bizarre behavior, hyperreflexia
4=coma
purpose of rifaximin in treating HE
reduces normal bowel flora, which diminishes protein breakdown