Module 6 - Organic Chemistry & Analysis
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OCR Chemistry A - Work in progress :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
C6H6 / cyclic / Kekulé model / delocalised model
Benzene
Formula: ___________
Structure: __________
Ways of representing it: _______________ & _______________
carbon planar ring w alternating single & double bonds
What did Kekulé propose that benzene was made up of?
electrophilic addition / bromine water / bond lengths / hydrogenation / exothermic
Evidence for Benzene’s Structure
Lack of reactivity - doesn’t undergo ______________________ or decolourise _____________.
____________________ between that of C=C and C-C.
Enthalpy change of __________________ less _________________ than expected pf cyclohex-1,3,5-triene.
electron orbitals overlap w delocalised ring & increase electron density / 2, 4 & 6 / increase / 2, 4 & 6 / OH & NH2
Electron Donating (Activating) Groups
Why is it called an electron-donating group?
Which carbons do they direct electophilic subsititution to?
Which carbons do they ____________ electron density?
What are some examples?
no orbitals overlap w delocalised ring & electronegative / 3 & 5 / withdraw / 2, 4 & 6 / NO2
Electron Withdrawing (Deactivating) Groups
Why is it called an electron-withdrawing group?
Which carbons do they direct electophilic subsititution to?
Which carbons do they ____________ electron density?
What are some examples?
conc sulfuric acid
What is the catalyst used in the nitration of benzene?
benzene + haloalkane / halogen carrier / alkylbenzene + hydrogen halide
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions
What are the reactants?
What is the catalyst used?
What are the products?
benzene + acyl chloride / halogen carrier / phenylketone + hydrogen halide
Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reactions
What are the reactants?
What is the catalyst used?
What are the products?
anion / stabilised / lone pair / delocalised pi system
Phenol - Weak Acid
More acidic than other alcohols.
Acidic because the resulting ________ is _____________ by donation of the ____________ into the ___________________ of the benzene ring.
This spreads the charge over the entire molecule and, in doing so, stabilises the negative charge.
lone pairs / p orbital / overlaps / partially delocalised / pi / electron density
Phenol’s Reactivity Compared to Benzene
The -OH group means that phenol is more likely to undergo electrophilic substitution than benzene.
One of the _______________ of electrons in a ___________ of the oxygen atom ________ with the delocalised ring of electrons in the benzene ring therefore it is __________________ into the ______ system.
This increases the __________________ of the ring, making it more likely to be attacked by electrophiles.
carboxylic acids / primary alcohols / n/a / secondary alcohols
Carbonyls
What are aldehydes oxidised to? What are they reduced to?
What are ketones oxidised to? What are they reduced to?
orange / green
Aldehyde Oxidation Using H2SO4 + K2CrO7
What is the initial colour of the dichromate solution?
What colour does this turn?
orange precipitate forms / compare crystals’ mp with database / blue / brick red / blue / blue / silver mirror forms / remains clear
Identifying Aldehydes & Ketones
2,4-DNP
Carbonyl: ______________
_____________________________
Benedict’s and Fehling’s solution
Aldehydes: ______ → _________
Ketones: _____ → _____
Tollen’s reagent
Aldehydes: ______________
Ketones: ______________
NaBH4 / hydride ion / dative covalent bond / pi bond / heterolytic fission / protonated
Nucleophilic Addition of Carbonyls → Alcohols Using _________
Lone pair of electrons from ______________ attracted & donated to delta positive carbon atom in the aldehyde or ketone C=O double bond.
______________________ forms between the ion & carbon atom of the C=O double bond.
____________ in C=O double bond breaks by __________________ forming a negatively charged intermediate.
Oxygen atom of the intermediate donates a lone pair of electrons to a hydrogen atom in a water molecule. Intermediate has then been _____________ to form an alcohol.
hydroxynitriles / NaCN/H+ / cyanide ion / dative covalent bond / pi bond / heterolytic fission / protonated
Nucleophilic Addition of Carbonyls → _______________________ Using _________
Lone pair of electrons from ________________ attracted & donated to delta positive carbon atom in the aldehyde or ketone C=O double bond.
______________________ forms between the ion & carbon atom of the C=O double bond.
____________ in C=O double bond breaks by __________________ forming a negatively charged intermediate.
Intermediate _________________ by donating a lone pair of electrons to a hydrogen ion, to form the product.
water removal from 2 carboxylic acid molecules
How are acid anhydrides formed?
heat dilute acid under reflux / carboxylic acid + alcohol / yes
Acid Hydrolysis of Esters
What conditions are required?
What are the products?
Is the reaction reversible?
heat dilute alkali under reflux / carboxylate salt + alcohol / no
Alkaline Hydrolysis of Esters
What conditions are required?
What are the products?
Is the reaction reversible?
carboxylic acid + sulphur dichloride oxide / hydrogen chloride + sulphur dioxide gases / fractional distillation
Preparation of Acyl Chlorides
What are the reactants in their production?
What else is produced?
How are excess reagents removed?
esters / esters / carboxylic acids / amides
Reactions of Acyl Chlorides
What do reactions with alcohols form?
What do reactions with phenols form?
What do reactions with water form?
What do reactions with ammonia / amines form?
water / alcohol / ammonia / C d+ / nucleophile & carbonyl carbon / Cl- / proton
Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination of Acyl Chlorides (/ Acid Anhydrides) → Amides / Carboxylic Acids / Esters
Lone pair of electrons from the nucleophile (____________/_____________/___________) attracted to & donated to ___ in the C=O group of the acyl chloride.
Dative covalent bond formed between ______________________ atom. Pi bond of the C=O group breaks, forming a negatively charged intermediate.
A one pair of electrons on oxygen reforms the C=O double bod, causing a ________ to be removed. A __________ is also then lost to complete the elimination.
1+ H in NH3 replaced with organic group
When do you get an amine?
1 & 2 / 2 & 1 / 3 & 0
Classifying Amines
How many R groups & H groups do primary amines contain?
How many R groups & H groups do secondary amines contain?
How many R groups & H groups do tertiary amines contain?
quaternary ammonium cation
What is formed if the nitrogen atom is bonded to 4 alkyl groups?
nitrogen’s lone pair of electrons accepts protons by dative covalent bonding
Why are amines bases?
haloalkane dissolved in ethanolic ammonia to form ammonium salt / aqueous alkali added
What are the 2 steps in aliphatic amines preparation?
nucleophilic substitution
What type of reaction is the synthesis of amines by heating a haloalkane with an excess of ethanolic ammonia?
nitrobenzene / tin / conc HCl / phenylammonium chloride / NaOH / phenylamine
Reduction of Nitro Compounds to Make Aromatic Amines
Heat under reflux: ________________ + ___________ + _________ → ______________________
Add an excess of _________ to produce _____________________.
CONH2 / carboxylic acids / C=O pulls electrons away from rest of CONH2 group
Amides
What is their functional group?
What are they derivatives of?
Why do they behave differently from amines?
acidic + basic groups in same molecule
Why are amino acids described as amphoteric?
carbon atom bonded to 4 different groups
In organic chemistry, what is a chiral centre?
non super imposable mirror images
What are optical isomers?
amine + carboxyl groups attached to same carbon
What characterises an alpha amino acid?
RCH(NH2)COOH
What is the general formula of an amino acid?
carboxyl / alcohol / strong acid catalyst / ester
The _____________ group in an amino acid can react with an ______________ in the presence of a ____________________ to form an ________.
dicarboxylic acid + diol / alkali / acyl chloride or dicarboxylic acid + diamine / acid
Condensation Polymers
Polyesters
What 2 monomers each with 2 functional groups can they be made from the reaction of?
What can you use to hydrolyse them easily?
Polyamides
What 2 monomers each with 2 functional groups can they be made from the reaction of?
What can you use to hydrolyse them easily?
amines by reacting with H2 in nickel catalyst presence
What and how are nitriles reduced to?
carboxylic acids by heating with dilute aqueous acid
What and how are nitriles hydrolysed to?
ethanolic NaCN or KCN / increases / nucleophilic substitution / HCN / nucleophilic addition
Nitriles
What are haloalkanes reacted with to form them?
What happens to the length of the carbon chain?
What is the mechanism of this reaction?
What are aldehydes / ketones reacted with to form them?
What is the mechanism of this reaction?
filtration under reduced pressure / recrystallisation / mp determination
What are the 3 methods which can be used to purify organic solids?
Buchner flask & funnel / pressure tubing / filter paper / access to filter or vaccum pump
What apparatus is needed for filtration under reduced pressure?
pressure tubing / Buchner flask / Buchner funnel / filter paper / solid crystals
Filtration Under Reduced Pressure
Connect one end of the ____________________ to the vacuum outlet or to the filter pump whilst attaching the other end of the rubber tubing to the __________________.
Fit the __________________ to the Buchner flask ensuring that there is a good tight fit. This is usually obtained using a Buchner ring or a rubber bung.
Switch on the vacuum pump, or the tap, to which your filter pump is attached & check for good suction by placing your hand across the top of the funnel.
Place a piece of _________________ inside the Buchner funnel and wet this with the same solvent used in preparing your solid. You should see the paper being sucked down against the holes in the funnel. To filter your sample, slowly pour the reaction mixture from a beaker into the centre of the filter paper.
Rinse out the beaker with the solvent so that all of the _____________________ collect in the Buchner funnel.
Rinse the crystals in the Buchner funnel with more solvent and leave them under suction for a few minutes so that the crystals start to dry.
dissolve in minimum amount heated solvent / cool, filter, dry
How do you recrystalise impure crystals to form a pure solid sample?
under reduced pressure / min solvent vol / cool solution & filter solid / cold solvent
Purification of Inpure Solution
Cool reaction mixture
Filter product _________________.
Dissolve impure solid in ___________________,
________________________.
Wash with ____________ and dry.
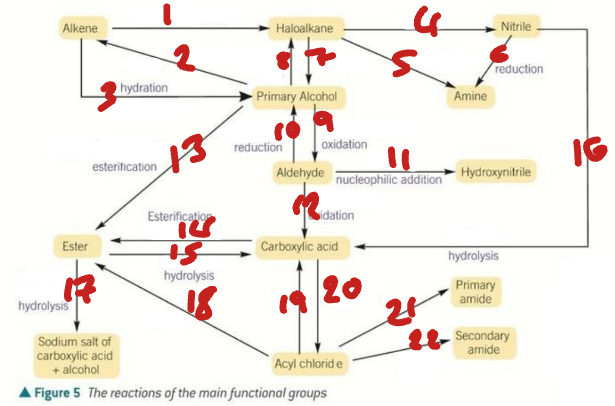
alkene / haloalkane / nitrile / primary alcohol / amine / aldehyde / hydroxynitrile
Label the Products of the Synthetic Routes (1→7)
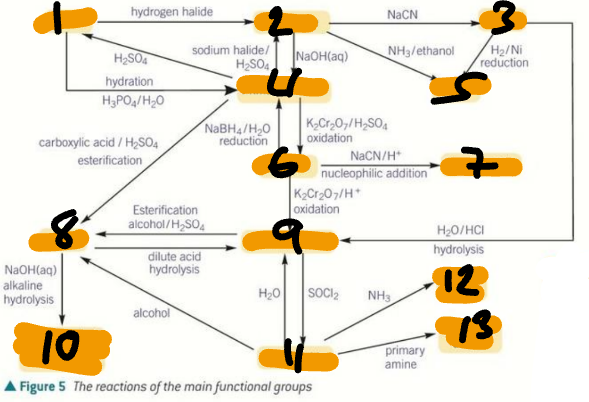
ester / carboxylic acid / carboxylate salt + alcohol / acyl chloride / primary amide / secondary amide
Label the Products of the Synthetic Routes (8→13)
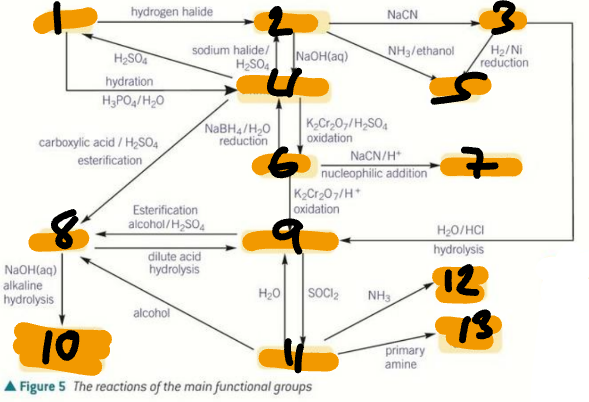
HX / H2SO4 / H2O + H+ / NaCN / NH3 + C2H5OH
Label the Conditions of the Synthetic Routes (1→5)
H2 + Ni / OH- / NaX + H+ / Cr2O72- + H+ / NaBH4 + H2O
Label the Conditions of the Synthetic Routes (6→10)
NaCN + H+ / Cr2O72- + H+ / RCOOH + H+ / ROH + H+ / H+ / H2O + H+
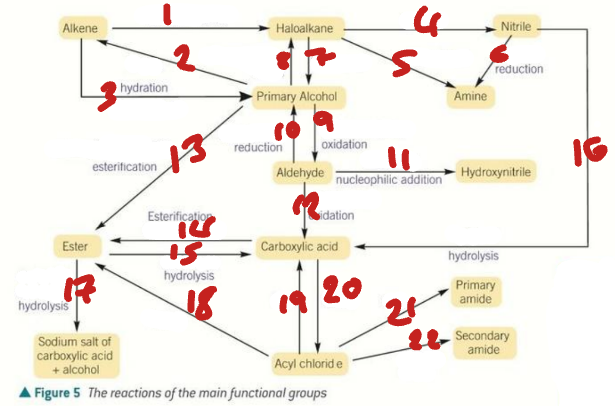
Label the Conditions of the Synthetic Routes (11→16)
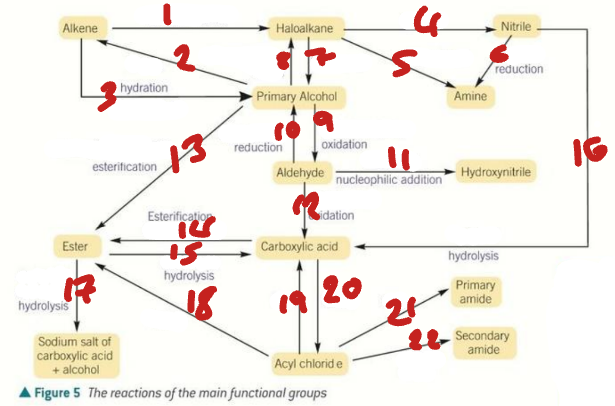
NaOH / ROH / H2O / SOCl2 / NH3 / RNH2
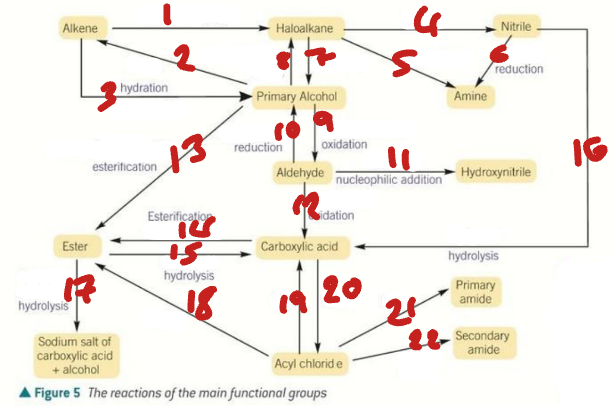
Label the Conditions of the Synthetic Routes (17→22)
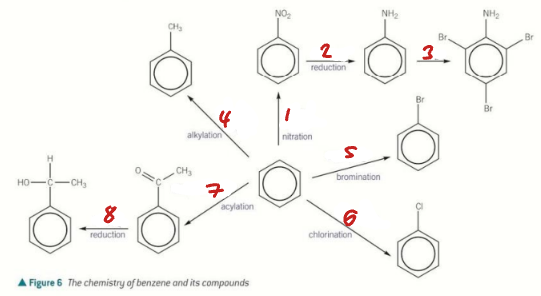
HNO3 + H+ / Sn + H+ / Br2 / CH3Cl + AlCl3
Label the Conditions of the Synthetic Routes (1→4)
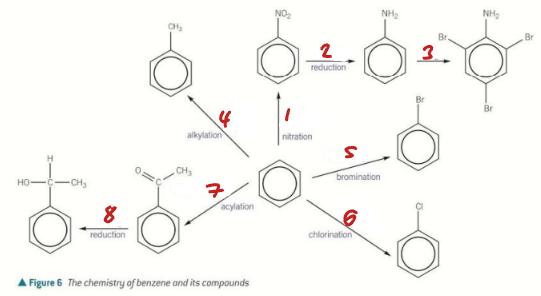
Br2 + FeBr3 / Cl2 + AlCl3 / CH3COCl + AlCl3 / NaBH4
Label the Conditions of the Synthetic Routes (5→8)
magnetic field / odd nucleon number / radio waves / resonance
NMR Spectroscopy
What do spinning nucleons have around them?
What is required for this?
What is needed for them to oppose the magnetic field?
What is the movement between energy levels (alignment vs opposition to magnetic field) called?
don’t produce signals in NMR frequency ranges / nucleon even number / CDCl3
NMR Spectroscopy - Deuterated Solvents
Why are they used?
Why do they have this ability?
What’s an example?
TMS / (CH3)4Si / nucleus / nuclear magnetic resonance / chemical environment / electronegative atom proximity / pi bonds / shielding
NMR Spectroscopy - Chemical Shift Value
Shift in frequency, compared to _____ (chemical formula: _________) required for a _________ to undergo ___________________.
The shift depends on the ____________________, especially caused by _______________________ or _____________.
The greater the _______________, the greater the chemical shift value.
signal on spectrum at specific x axis point / environment / delta / ppm
NMR Spectroscopy - Chemical Shift Value
How do chemists see the chemical shift value?
What must be the same for the nuclei to produce a signal at the same chemical shift value?
What is its sign? It’s units?
different C environments number - peaks number / carbon environment types - chemical shift
13C NMR Spectroscopy
What are the 2 important pieces of information that gives about the molecule?
How is this information found?
signal ratios / proton frequency ratio in same environment / fine splitting patterns / n-1
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
What’s the extra piece of information that 1H NMR gives us over 13C NMR?
What does this reflect?
What do the main signals that represent different chemical environments have?
How do you work out the number of 1H's on adjacent carbon from this?
integration traces or ratio numbers / relative peak areas / non-equivalent / spin-spin splittig pattern
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
Similar information to a carbon-13 NMR spectrum but for protons:
Number of different proton environments - from the number of peaks
Types of proton environments present - from the chemical shift.
2 extra pieces of info:
Relative numbers of each type of proton - from ______________________________ of the ____________________,
Number of _________________ protons adjacent to a given proton - from the _____________________.
OH & NH / D2O / CH3OD / chemical shift range
Proton NMR Spectroscopy - Proton Exchange
Used to identify ___(1)___ protons.
A proton NMR spectrum is run as normal.
A small volume of ___(2)___ is added, the mixture is shaken and a second spectrum is run.
Deuterium exchanges and replaces the OH and NH protons in the sample with deuterium atoms.
EG CH3OH + ___(2)___ ⇌ ___(3)___ + HOD
Second spectrum is essentially being run on ___(3)___. As deuterium does not absorb in this ___(4)___, the peak for the ___(1)___ group disappears.
not usually involved in spin-spin coupling so peaks broadened
In proton NMR spectroscopy, why is assigning OH & NH protons difficult?
each proton splits other’s signal
In proton NMR spectroscopy, why do splitting patterns occur in pairs?
add Na then squeeky pop test
How do we test for alcohols? (not using carboxylic acids or acidified potassium dichromate)