Laboratory 14 - The Digestive System (Pt 1)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:25 PM on 2/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
1
New cards
The digestive system can be divided into two components. What are they?
- The digestive tract.
- Accessory organs.
- Accessory organs.
2
New cards
What is the digestive tract?
A hallow tube extending from mouth to anus.
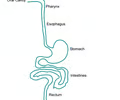
3
New cards
What are accessory organs?
They aid in digestion but food doesn't pass through them.
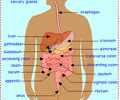
4
New cards
What do the accessory organs include? (6)
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Salivary glands
- Liver
- Gall bladder
- Pancreas
- Tongue
- Salivary glands
- Liver
- Gall bladder
- Pancreas
5
New cards
The mouth has been specialized for what?
Ingestion and the mechanical processing of food.
6
New cards
The teeth are located in the mouth and are surrounded by a delicate mucosa called what?
Gingiva (or gums).
7
New cards
The roof of the mouth is formed by what?
The hard palate (anteriorly) and the soft palate (posteriorly).
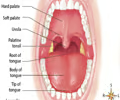
8
New cards
The mouth cavity is filled by what accessory organ?
The tongue.
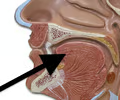
9
New cards
The tongue functions in what three things?
Food manipulation, taste, and speech.
10
New cards
What nerves innervate the tongue?
- Facial nerve (VII)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- Vagus nerve (X)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- Vagus nerve (X)
11
New cards
What is mastication? This is done by what?
Chewing. Performed by teeth.
12
New cards
What are the different types of teeth?
Incisors, canines, premolars, molars.
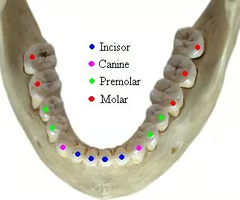
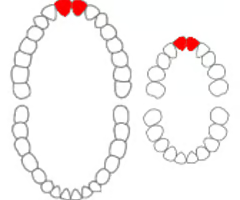
13
New cards
What shape are incisors and what do they do?
Chisel-shaped. They are used for cutting and shearing food.
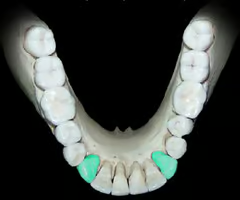
14
New cards
What shape are canines and what do they do?
Pointy (aka as cuspids), with a single cusp. They are used for shredding food.
15
New cards
What shape are premolars and what do they do?
Bicuspid (2 cusps). Adapted for crushing and cracking food.
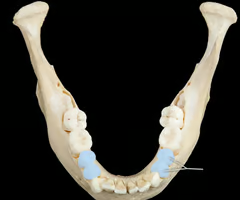
16
New cards
What shape are molars and what do they do?
Tricuspid (3+ cusps). Adapted for grinding food into fine pieces for chemical digestion.
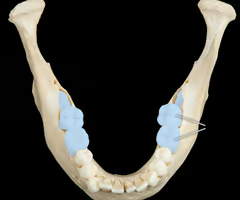
17
New cards
Humans and all other mammals have two sets of teeth in their lifetime. What are the two stages called?
- Deciduous (primary/baby teeth)
- Permanent (secondary/adult teeth)
- Permanent (secondary/adult teeth)
18
New cards
When do teeth start appearing in babies?
Around six months.
19
New cards
When is the deciduous teeth completed?
Around age six.
20
New cards
Deciduous teeth are a total of \__ teeth.
20
21
New cards
What is a dental formula?
The way teeth are described by name and number. It represents ONE top half (top number) and ONE bottom half (bottom number) of the jaw.
22
New cards
What is an infant's dental formula?
I 2/2, C 1/1, P 0/0, M 2/2
23
New cards
When does permanent teeth begin pushing out on deciduous teeth?
Around age six until 11 or 12.
24
New cards
In the adult, how many teeth are in each jaw?
16.
25
New cards
In the adult, how many teeth are there in total?
32.
26
New cards
What is an adult's dental formula?
I 2/2, C 1/1, P 2/2, M 3/3
27
New cards
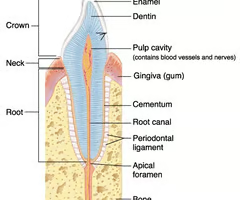
All teeth are constructed on a basic plan of two principal parts. What are they?
- The crown (visible)
- The root (in alveolus - the bony socket of the maxilla or mandible)
- The root (in alveolus - the bony socket of the maxilla or mandible)
28
New cards
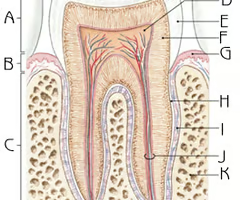
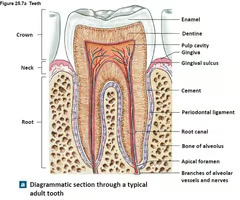
Where is the enamel of a tooth?
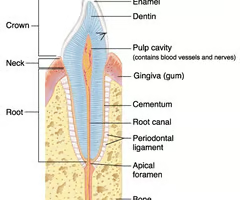
29
New cards
Where is the crown of a tooth?
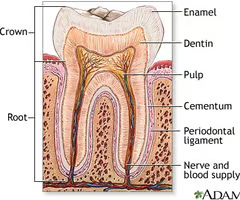
30
New cards
Where is the dentin of a tooth?
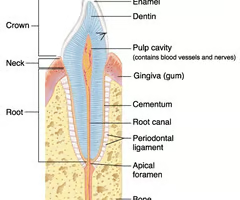
31
New cards
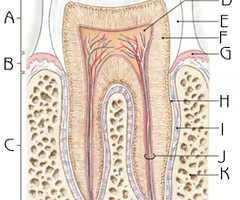
Where is the alveolar bone (bony socket) of a tooth?
(K)
32
New cards
Where is the root canal of a tooth?
33
New cards
Where is the cementum if a tooth?
34
New cards
Where is the gingiva of a tooth?
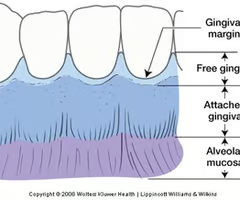
35
New cards
Where is the root of a tooth?
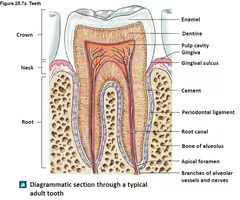
36
New cards
Where is the periodontal membrane of a tooth?
(I)
37
New cards
Where is the pulp cavity of a tooth?
38
New cards
The salivary glands are considered accessory organs in the mouth. How many are there?
Three.
39
New cards
What are the three salivary glands?
- Parotid glands
- Sublingual glands
- Submandibular glands
- Sublingual glands
- Submandibular glands
40
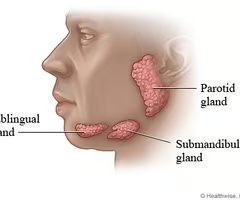
New cards
Describe the partoid gland.
- Largest of the three glands
- Irregular shape
- Overlaps the masseter muscle
- Irregular shape
- Overlaps the masseter muscle
41
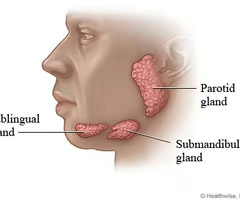
New cards
Describe the sublingual gland.
- Smallest of the three glands
- Are deep and anterior to the submandibular glands
- Are deep and anterior to the submandibular glands
42
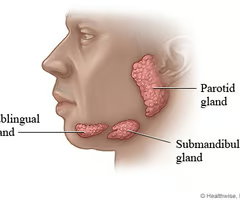
New cards
Describe the submandibular gland.
- Inferior to the parotid gland
- Situated along the inner surfaces of the mandible
- Situated along the inner surfaces of the mandible
43
New cards
All the salivary glands does what?
They secrete saliva.
44
New cards
What are the functions of saliva? (3)
- Lubrication of the mouth
- Moistening food
- Dissolving chemicals so they can be tasted.
- Moistening food
- Dissolving chemicals so they can be tasted.
45
New cards
Saliva contains what enzyme that is important in the breakdown of carbohydrates into simple sugars?
Salivary amylase.
46
New cards
After the mouth, food goes where to get into the esophagus?
Into the oropharnyx and then the laryngopharynx.
47
New cards
Is the nasopharynx part of the digestive tract?
No.
48
New cards
Food chewed in the mouth is called what?
Bolus.
49
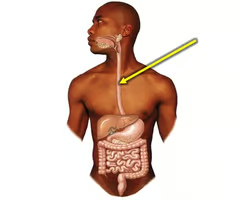
New cards
What is the esophagus?
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
50
New cards
How is food prevented from going into the trachea?
While swallowing, the epiglottis folds over and seals the trachea and directs food into the esophagus.
51
New cards
What is choking caused by?
Food accidentally making its way into the trachea.
52
New cards
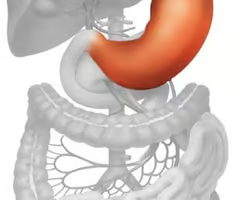
What is the stomach?
A large, crescent-shaped organ that is the site of the beginning of protein digestion.
53
New cards
The stomach has an extra layer of smooth muscle. Why?
It helps to protect the stomach by the chemical digestion that occurs within and it also helps in the moving the the stomach to churn food.
54
New cards
The stomach has also act as what?
A temporary storage site for food.
55
New cards
Food in the stomach mixed with stomach acid is called what?
Chyme.
56
New cards
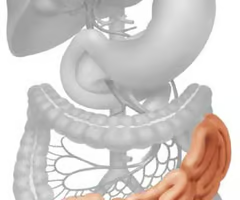
The small intestines is the \_______ digestive organ of the body.
primary
57
New cards
Where is the chemical digestion of food completed?
In the small intestines.
58
New cards
Where does the absorption of nutrients occur?
In the small intestine.
59
New cards
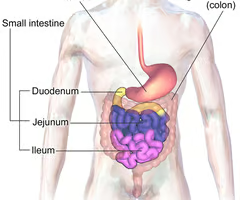
What are the three parts of the small intestine from beginning to end?
- Duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
60
New cards
The duodenum recieves partially digested food and secretions from what?
The pancreas, the liver, and the gallbladder.
61
New cards
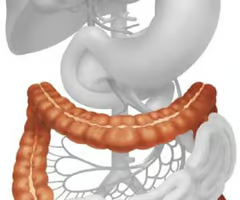
Where is the large intestine?
Between the Ileum and the anus.
62
New cards
What is the major function of the large intestine?
Water absorption.
63
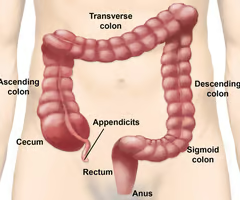
New cards
What is the first part of the large intestine?
The cecum.
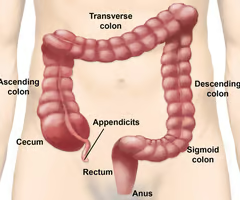
64
New cards
What is attached to the cecum?
The vermiform appendix.
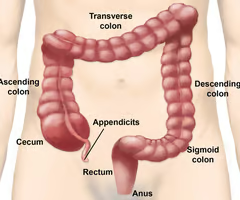
65
New cards
From the cecum, what follows?
The ascending colon.
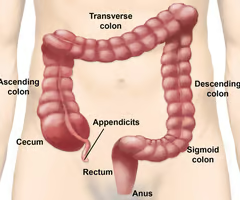
66
New cards
The ascending colon turns into what?
The transverse colon.
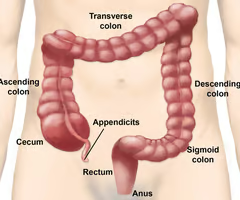
67
New cards
The transverse colon turns into what?
The descending colon.
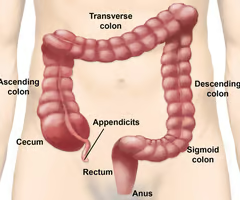
68
New cards
The descending colon forms and s-shape at the end, called what?
The sigmoid colon.
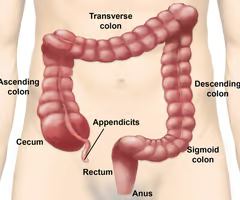
69
New cards
The sigmoid colon continues to what?
The rectum.
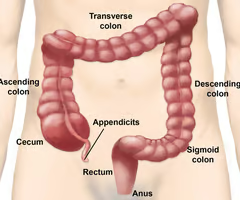
70
New cards
The rectum leads to what?
The anus.
71
New cards
There are three accessory organs found in the abdominal cavity. What are they?
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
72
New cards
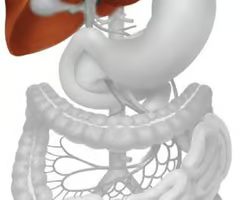
Where is the liver located?
In the upper right quadrant, immediately beneath the diaphragm.
73
New cards
What is the digestive function of the liver?
The production and secretion of bile.
74
New cards
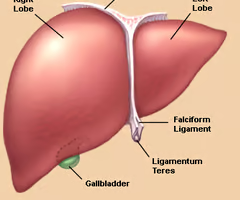
The liver is divided into how many lobes?
Two.
75
New cards
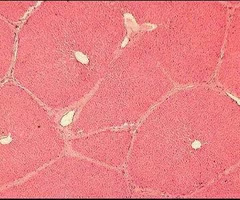
Lobes of the liver is made out of what?
Lobules.
76
New cards
Describe the shape of lobules.
Roughly hexagonal shape, consisting of plates of liver cells or hepatocytes. These radiate from a central vein.
77
New cards
Hepatocytes manufacture bile, which does what?
It is a fat emulsifier which is secreted into tiny channels, bile canaliculi.
78
New cards
At the corners of each liver lobule is what?
A portal triad.
79
New cards
What is the portal triad?
The hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct.
80
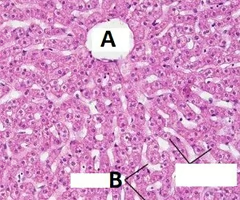
New cards
Blood from both hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery flow from the triad region into what?
The liver sinosoids. (B)
81
New cards
What are liver sinosoids?
Capillary channels located between the hepatocytes.
82
New cards
From the liver, blood goes where?
Empties into the central vein, eventually entering the hepatic veins which carry blood to the inferior vena cava.
83
New cards
What is the gallbladder?
A green coloured muscular sac attached to the ventral surface of the liver.
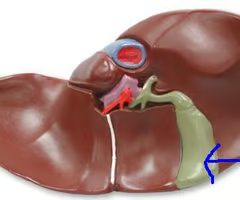
84
New cards
Bile produced in the liver is is stored and concentrated where?
The gallbladder.
85
New cards
What is the pancreas?
A large organ lying in between the stomach and duodenum.
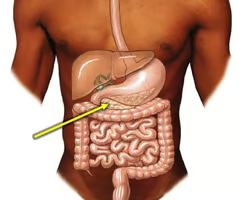
86
New cards
The pancreas is 98% what?
Endocrine glands.
87
New cards
Endocrines are ductless glands consisting of groups of cells called what?
Islets of Langerhans, which releases hormones into the blood.
88
New cards
Where is the spleen?
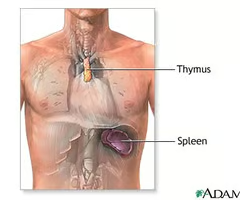
89
New cards
Is the spleen part of the digestive system?
No.
90
New cards
The serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and covers most of the abdominal organs called what?
The peritoneum.
91
New cards
The peritoneum can be divided into what two parts?
The visceral peritoneum which covers the external surface of most of the digestive organs and the parietal peritoneum, lining the walls of the abdominopelvic cavity.
92
New cards
What is the function of the fluid produced by the peritoneum?
It helps to prevent friction between organs.
93
New cards
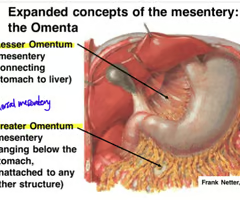
What are mesenteries?
Folds of peritoneum that hold digestive organs in place. They contain blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
94
New cards
What is the omentum?
A mesentery that hangs free in the abdominal cavity or connects organs to each other.
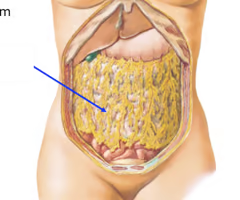
95
New cards
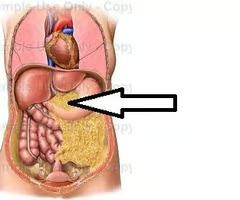
Where is the greater omentum?
It is a double-walled peritoneal sac that extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, over the small and large intestines.
96
New cards
Attached to the left side of the greater omentum is what?
The spleen.
97
New cards
Where is the lesser omentum?
Between liver and stomach.
98
New cards
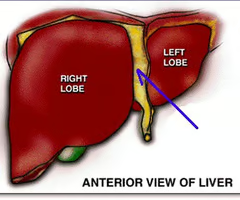
What is the falciform ligament?
It connects liver to anterior abdominal wall.
99
New cards
What is the mesentery that connects the different parts of the small intestine to each other?
Mesentery proper.
100
New cards
How many layers compose the wall of the digestive tract from the esophagus and extending to the anal canal?
Four.