Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:07 AM on 3/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
1
New cards
genetic background
the term “ancestry” in forensic anthropology refers to a person’s ___
2
New cards
false
True or false: Races represent different evolutionary lineages.
3
New cards
Carolus Linnaeus
anthropologist who likened racial groups to the animals originating from the same regions
4
New cards
true
True or false: There is more variation within than between racial groups.
5
New cards
false
True or false: Living phenotype can be determined from skeletal remains if some soft tissue is present.
6
New cards
isotope
Stable ___ profiles found in body tissues can predict geographic origin, region of birth, long-term residence, travel history, etc.
7
New cards
white
Which ancestry group(s) has/have projecting noses?
8
New cards
black, asian
Which ancestry group(s) has/have nonprojecting noses?
9
New cards
white
The root of the nose (nasion) belonging to which ancestral type is high and narrow?
10
New cards
black
The root of the nose (nasion) belonging to which ancestral type is low and rounded?
11
New cards
asian
The root of the nose (nasion) belonging to which ancestral type is low and ridged?
12
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has a high nasal bridge?
13
New cards
black, asian
Which ancestral groups have a low nasal bridge?
14
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has a pronounced nasal spine?
15
New cards
white
In which ancestral group is the lower border raised into a sill, forming a sharp wall?
16
New cards
black
In which ancestral group is the lower border guttered, meaning the floor of the nose merges with the anterior maxillae?
17
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has the narrowest nasal opening, resembling an isosceles triangle?
18
New cards
black
Which ancestral group has the widest nasal opening, resembling an equilateral triangle?
19
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has a straight/vertical, nonprojecting facial profile?
20
New cards
black
Which ancestral group has a projecting facial profile?
21
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group’s lower eye border (cheekbone-like) is projected?
22
New cards
white, black
Which ancestral groups have a narrow face shape?
23
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group has a wide face shape?
24
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has angled (sadboi) eye orbits?
25
New cards
black
Which ancestral group has rectangular eye orbits?
26
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group has round eye orbits?
27
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has the most pronounced browridges and muscle striations on the skull?
28
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group exhibits the most complex cranial sutures?
29
New cards
Wormian bones
accessory bones in the lambdoid suture
30
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group is most likely to exhibit Wormian bones?
31
New cards
black
Which ancestral group exhibits a slight concavity in the postcoronal area (behind the bregma) which flattens the sagittal contour?
32
New cards
white
Dental crowding is most likely in which ancestral group?
33
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has the smallest jaw?
34
New cards
black
Which ancestral group has the largest jaw?
35
New cards
white
Which ancestral group has a parabolic (almost V-shaped) dental arch of the upper jaw?
36
New cards
black
Which ancestral group has a hyperbolic (rectangular or U-shaped) dental arch of the upper jaw?
37
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group has a rounded dental arch of the upper jaw?
38
New cards
asian
Which ancestral group has shovel-shaped incisors (almost hollowed out in the middle)?
39
New cards
black
Which ancestral group is most likely to exhibit Cusp 7 and the Bushman Canine?
40
New cards
black
Which ancestral group has a straight femoral shaft?
(as opposed to exhibiting anterior curvature)
(as opposed to exhibiting anterior curvature)
41
New cards
white
Heavy/thick/massive postcranial bones with heavy muscle markings indicate ___ ancestry
42
New cards
black
Light/thin postcranial bones with slight muscle marking indicate ___ ancestry
43
New cards
white
Large joint surfaces on long bones indicate ___ ancestry
44
New cards
black
Slender joint surfaces on long bones with small articular heads & joint surfaces indicate ___ ancestry
45
New cards
white
a wide and rugged pelvis indicates ___ ancestry
46
New cards
black
a high and narrow pelvis indicates ___ ancestry
47
New cards
shallow; deep
The lumbar curve of the vertebral column is ___ in whites and ___ in blacks
48
New cards
black
Of what ancestry is this skull?
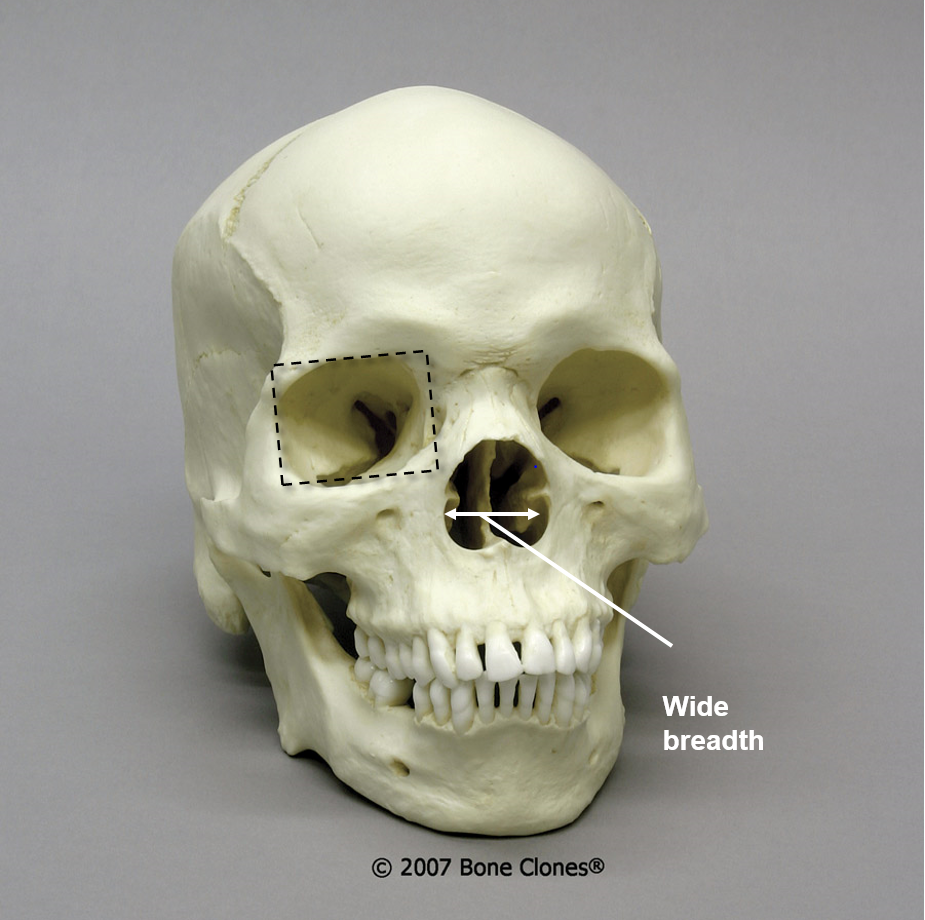
49
New cards
asian
Of what ancestry is this skull?
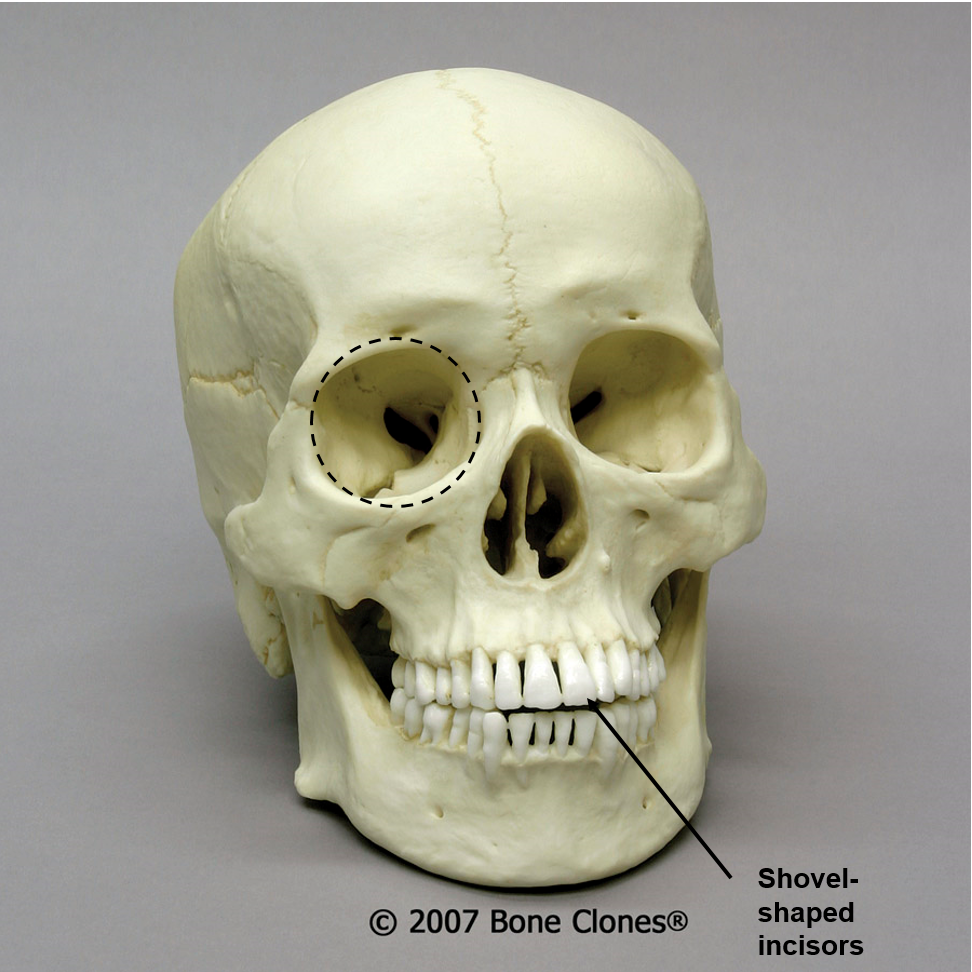
50
New cards
white
Of what ancestry is this skull?
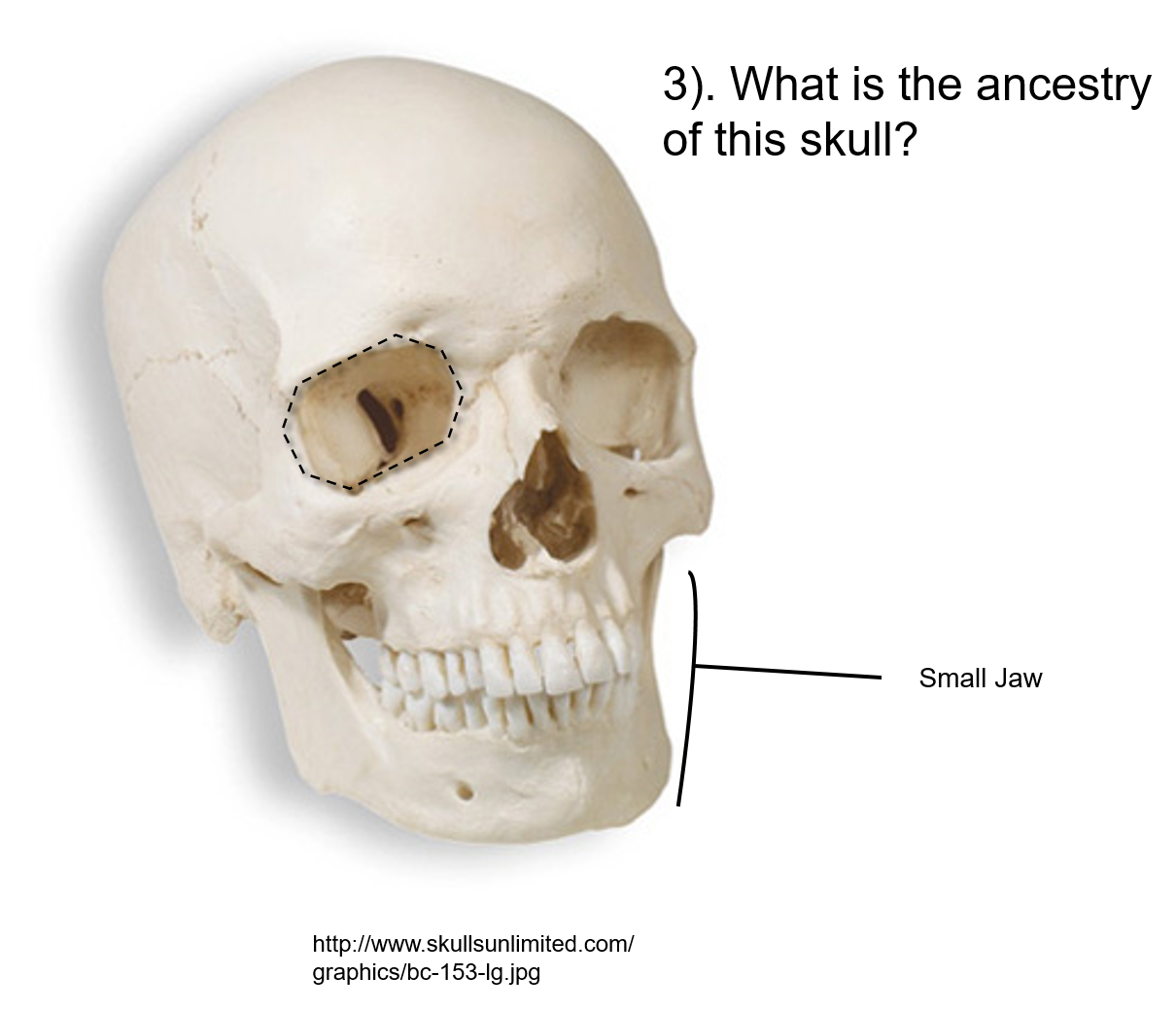
51
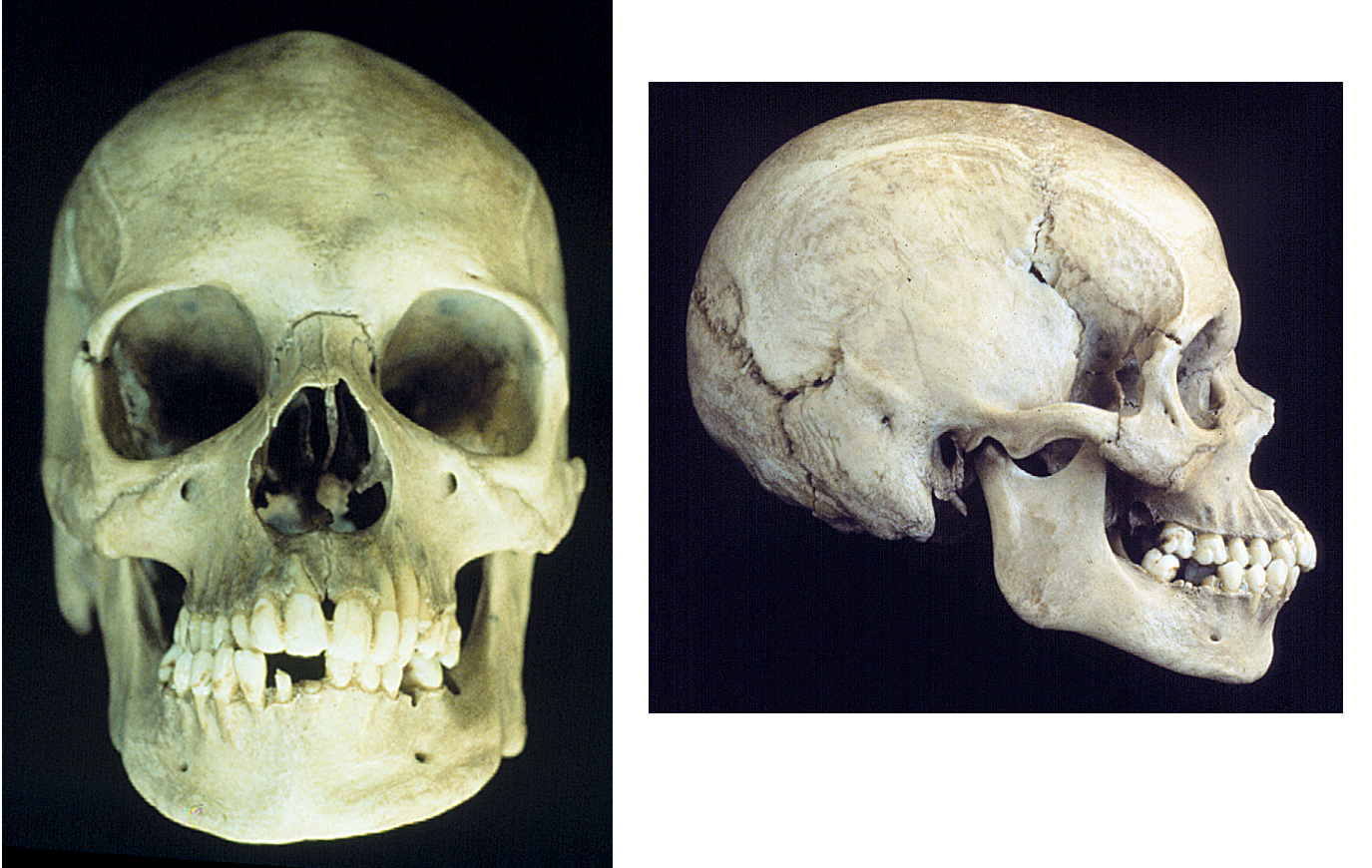
New cards
asian
Of what ancestry is this skull?
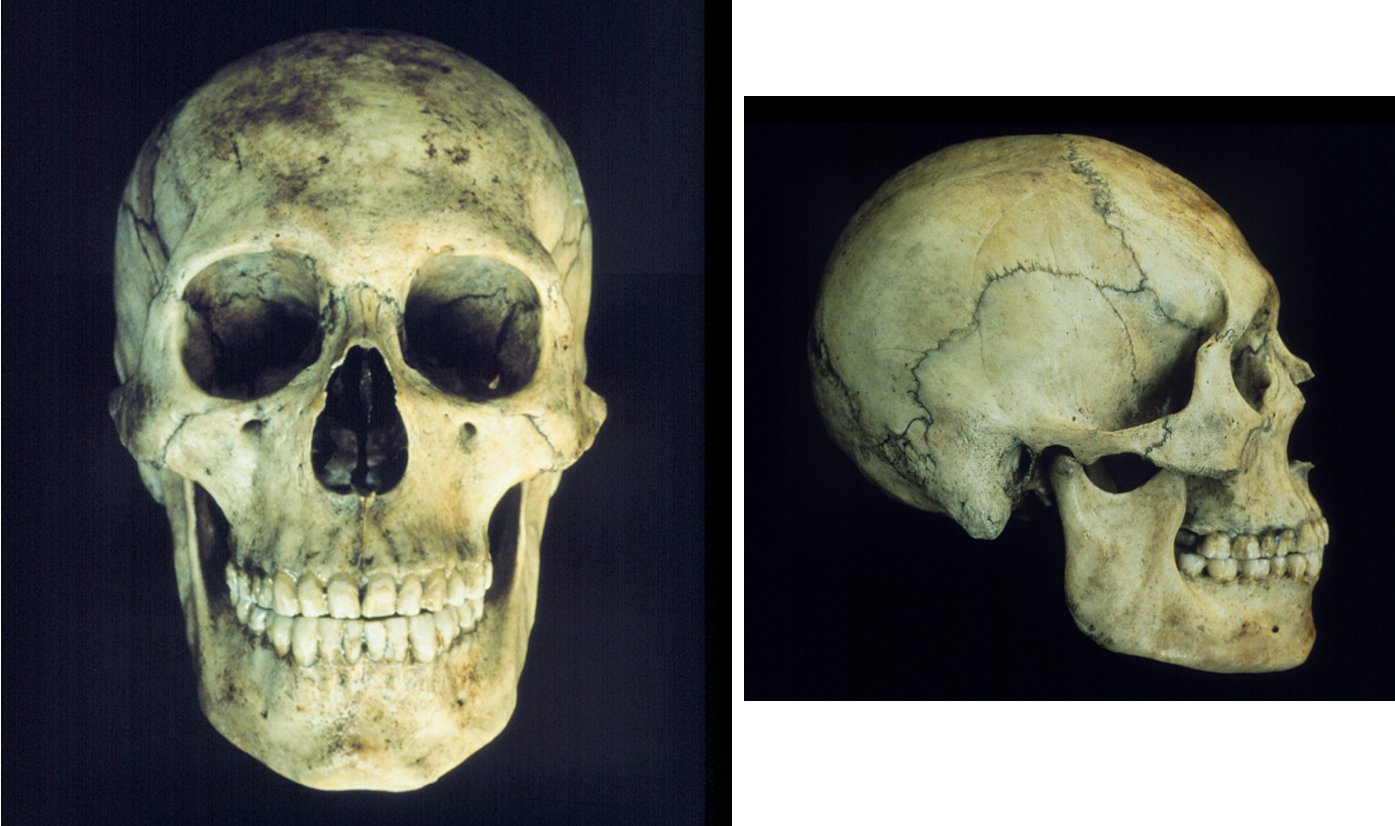
52
New cards
white
Of what ancestry is this skull?
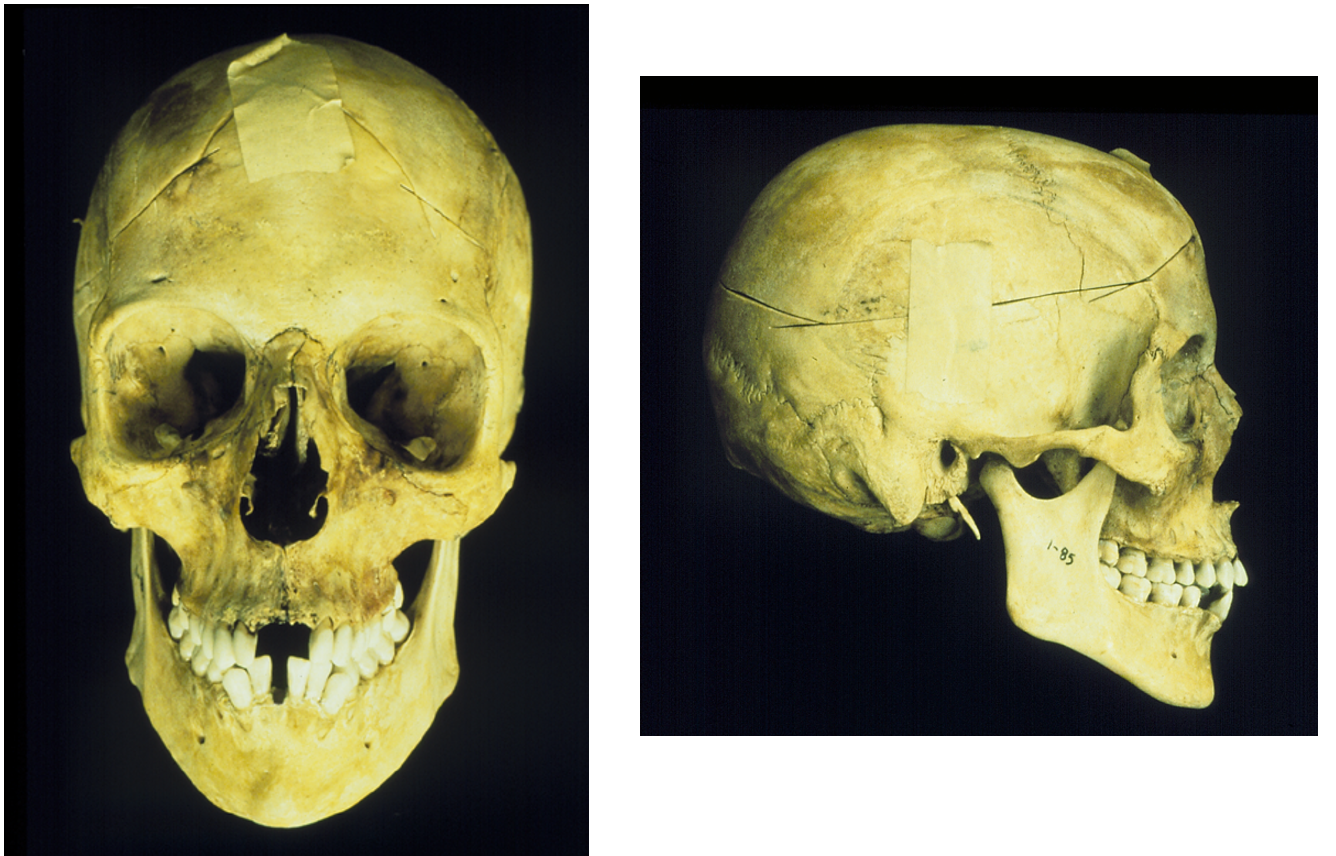
53
New cards
black
Of what ancestry is this skull?
54
New cards
female
The (male/female) pelvis is wider.
55
New cards
male
The (male/female) subpubic angle is angular and v-shaped
56
New cards
female
The (male/female) subpubic angle is rounded.
57
New cards
obturator foramen
opening in the pelvis encircled by the ilium, ischium, and pubis
58
New cards
male
The (male/female) obturator foramen resembles a flattened isosceles triangle.
59
New cards
female
The (male/female) obturator foramen resembles an equilateral triangle.
60
New cards
pelvic inlet
space enclosed by os coxae and sacrum when viewed superiorly
61
New cards
male
The (male/female) pelvic inlet is heart-shaped.
62
New cards
female
The (male/female) pelvic inlet is oblong.
63
New cards
males
The greater sciatic notch is narrower in (males/females).
64
New cards
females
The sacrum is short and broad in (males/females)
65
New cards
males
The sacrum is long and narrow in (males/females).
66
New cards
females
Only (males/females) have the ventral arc.
67
New cards
females
Only (males/females) have a subpubic concavity.
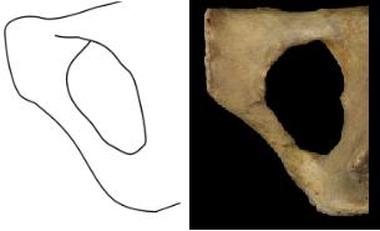
68
New cards
females
The preauricular sulcus is more pronounced in (males/females).
69
New cards
preauricular sulcus
groove of bone in the ilium helpful for distinguishing sex
70
New cards
childbirth
The preauricular sulcus is deepened in women following ___
71
New cards
heavy lifting
The preauricular sulcus may appear in men who perform ___ over long periods of time.
72
New cards
males
The acetabulum is larger in (males/females).
73
New cards
male
The (male/female) skull is more robust.
74
New cards
males
(Males/females) have more sloping foreheads.
75
New cards
male
The occipital protuberance and nuchal crest are more pronounced on the (male/female) skull.
76
New cards
males
The upper interior of the eye socket, also called the supraorbital margin, is rounded in (males/females).
77
New cards
males
(Males/females) have a 90 degree angle to the mandible and ascending ramus.
78
New cards
males
(Males/females) have larger, broader maxillae.
79
New cards
females
(Males/females) have a slanted angle to the mandible and ascending ramus.
80
New cards
females
(Males/females) have a narrower, longer nasal cavity.
81
New cards
females
(Males/females) have high foreheads.
82
New cards
females
(Males/females) have a pointed mental eminence.
83
New cards
just born
How old was this individual at death?
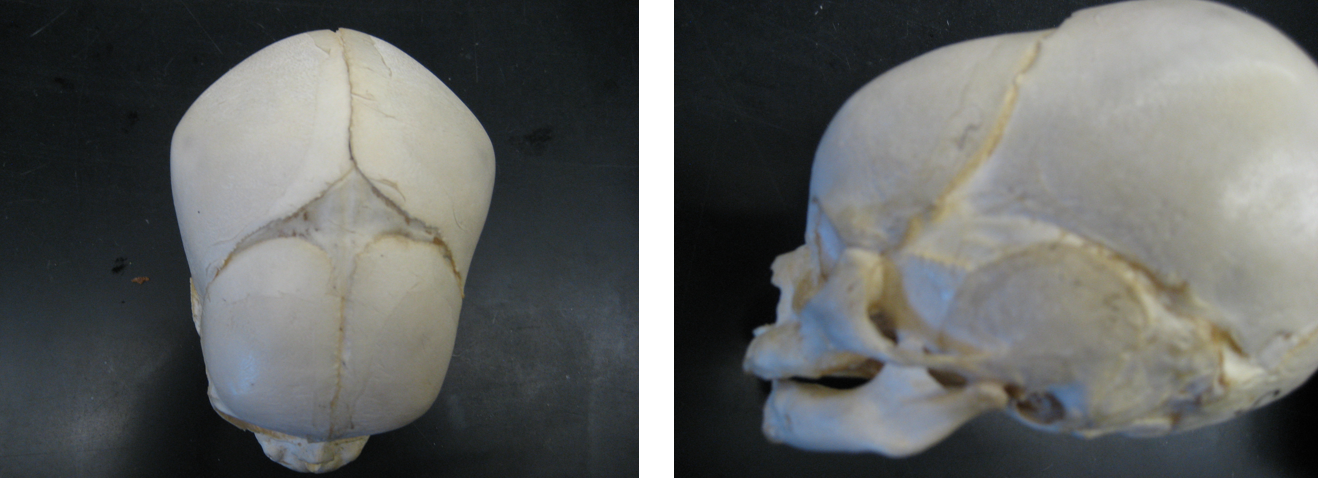
84
New cards
second year
All fontanelles (gaps in skull sutures) close by the end of the ___
85
New cards
25
After approximately what age have the majority of epiphyses fused in the skeleton?
86
New cards
2-12 months
Mastoid fontanelle fusing time
87
New cards
2 months
Posterior fontanelle fusing time
88
New cards
2 years
Anterior fontanelle fusing time
89
New cards
3 months
Sphenoidal fontanelle fusing time
90
New cards
metopic suture
suture which initially separates the right and left halves of the frontal bone
91
New cards
second year
The right and left halves of the mandible fuse by the end of the ___
92
New cards
10
Cranial fusions occur prior to age ___
93
New cards
tooth formation/eruption
Most reliable method for aging subadults
94
New cards
10
When do epiphyses BEGIN to fuse in the skeleton?
95
New cards
young
The pubic symphysis of a (young/middle/older) adult exhibits ridges separated by furrows running transversely across its surface.
96
New cards
middle
The pubic symphysis of a (young/middle/older) adult is flat and smooth with fine texture.
97
New cards
older
The pubic symphysis of a (young/middle/older) adult is granular, pitted, and eroded.
98
New cards
b
Which individual is older?
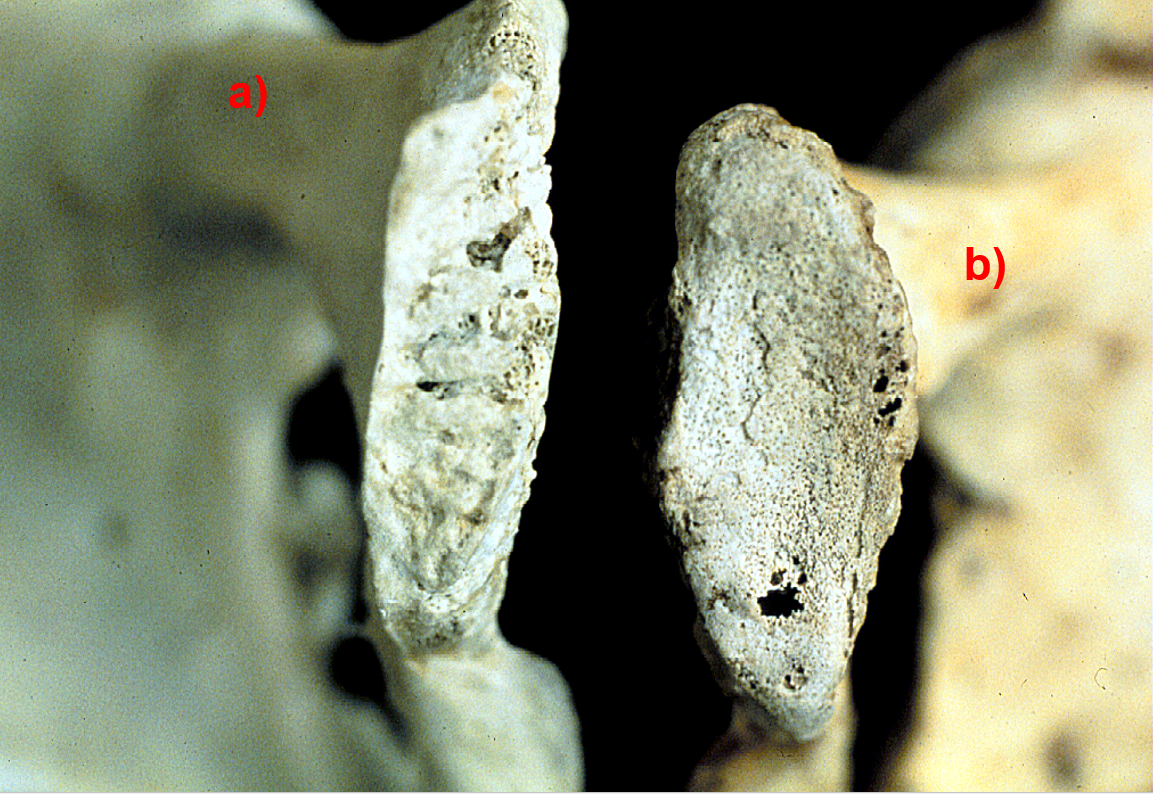
99
New cards
young
The auricular surface of a (young/middle/older) adult is coarse-grained and granular.
100
New cards
middle
The auricular surface of a (young/middle/older) adult is fine-grained and dense.