Behavioural approach to explaining phobias
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what is the two process model and who put it forward
Mowrer (1960)
Phobias are learnt by classical conditioning and maintained by operant conditioning
Classical Conditioning
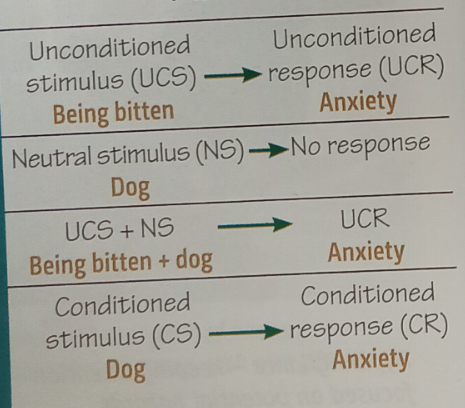
who studied Little Albert
Watson and Rayner (1920)
How was little Albert conditioned
Whenever Albert played with a white rat, a loud noise was made
The noise caused a fear response
Rat did not create fear until bang and rat where paired together
Albert showed fear response every time he saw rat
Generalisation of fear to other stimuli
Litte Albert also showed a fear response to other white furry objects
e.g fur coat and Santa claus beard
How are phobias maintained
Operant conditioning (negative reinforcement)
Negative reinforcement in conditioning
When a person behaves in a way to avoid something upleasant
When a person with a phobia avoids a phobic stimulus they escape the anxiety they would have experienced
This reduction in fear negatively reinforces the avoidance behaviour and the phobia is maintained
Example of negative reinforcement (coulrophobia)
If someone has a fear of clowns they will avoid circuses and other situations where they may encounter clowns
The relief felt from avoiding clowns negatively reinforces the phobia and maintains it
One strength is real world application
The ideaof phobias eing maintained by avoidance helps explain why exposure therapy is beneficial
Itdentiifes a means of treating phobias
One limitation is the inability to explain cognitive aspects of phobias
two process model explains behaviour
However phobias also have a significant cognitive component e.g irrational beliefs about the phobic stimulus
This means the two process model doesn't fully explain the symptoms of phobia
Another strength is evidence linking phobias to bad experiences
De Jongh et al. found 73%of dentist phobics experienced a trauma
Further support came from the control group with low dental anxiety where only 21% had experienced a traumatic event
This confirms the association between stimulus (dentistry) and an unconditioned response (pain) leads to phobia
Counterpoint
Not all phobias appear after a bad experience
e.g. snake phobias occur in populations where very few people had any experience of snakes
Not all frightening experiences lead to phobias