Critical Care Nursing: Hemodynamics, Pain, and Monitoring
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What is the definition of critical illness or injury according to CMS?
A condition that acutely impairs one or more vital organ systems with a high probability of imminent or life-threatening deterioration.
What are examples of conditions that may require critical care?
Respiratory failure, shock, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, gunshot victims, motor vehicle crashes.
What is the nurse-to-patient ratio in an ICU?
1 nurse to 1 patient.
What is the difference between ICU and CCU?
ICU focuses on medical and surgical care, while CCU is specifically for coronary care.
What is intermediate care?
A level of care for patients too sick for the floor but not sick enough for critical care, typically with a 3-4:1 nurse-to-patient ratio.
What is the primary focus of the Emergency Department (ED)?
Acute stabilization of patients.
What is the role of the critical care nurse as an advocate?
Protecting patient rights, assisting in decision-making, and keeping the patient and family informed.
What is the importance of clinical judgment in critical care nursing?
It involves critical thinking skills to identify patient needs and make informed decisions.
What is the significance of assessments in critical care?
They form the basis of the plan of care and help in early identification of changes in patient condition.
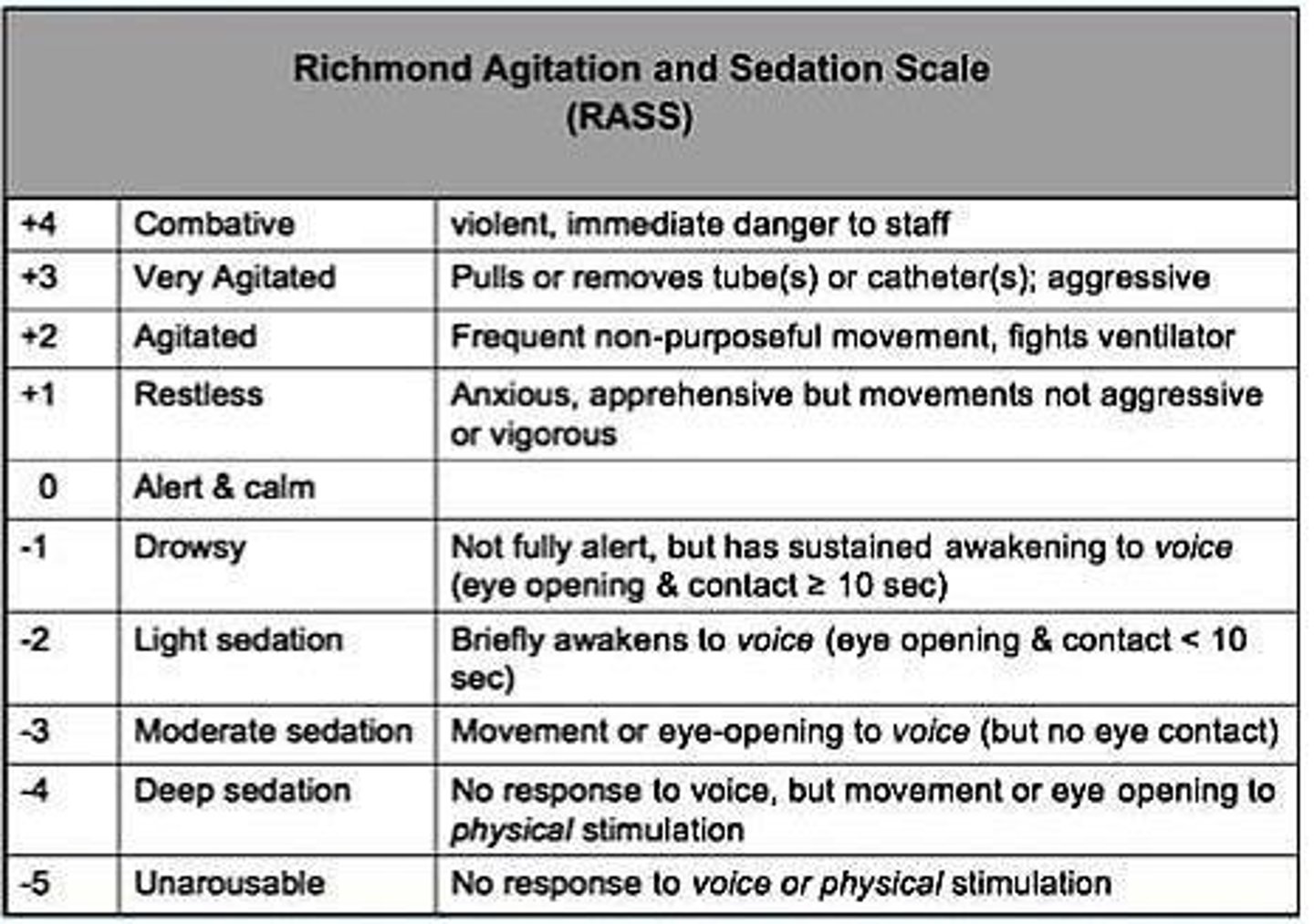
What does the Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale (RASS) measure?
It assesses the level of sedation or agitation in patients.
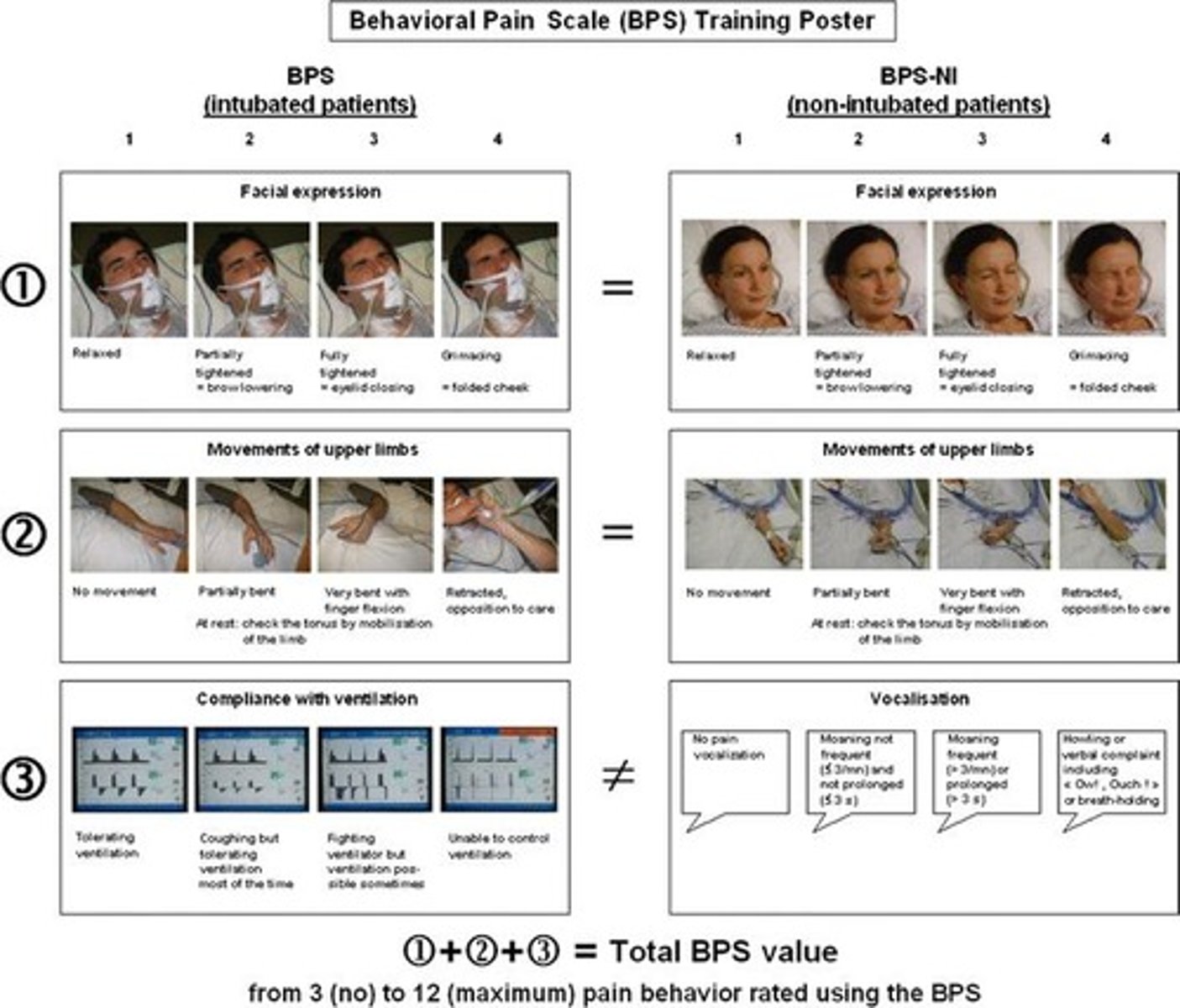
What is the Behavioral Pain Scale (BPS)?
A tool that scores pain based on observable behaviors in nonverbal patients, with a score of >5 indicating pain that needs to be addressed.
What is the Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT)?
A tool that assesses pain in nonverbal patients, scoring from 0-8, with >3 indicating pain that needs to be addressed.

What is the definition of nociceptive pain?
Acute and traumatic pain resulting from damage to organs or tissue.
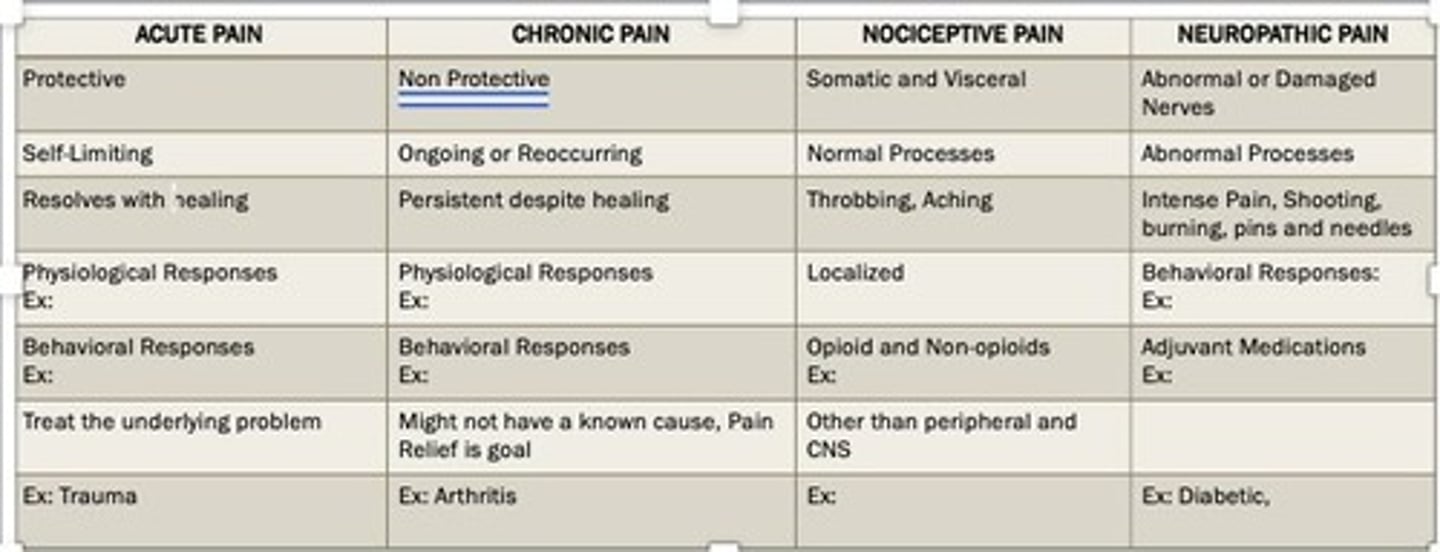
What is neuropathic pain?
Pain resulting from nerve damage, often requiring treatments like Gabapentin.
What is the significance of self-report in pain assessment?
Self-report is the most reliable diagnostic measure of pain.
What is Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA)?
A method of pain control allowing patients to self-administer medication at safe doses.
What should be done if a patient has elevated potassium levels?
Check BUN and creatinine levels to rule out hemolysis from blood sample collection.
What is the recommended frequency for pain assessment in critical care?
Every 2 hours and with vital signs.
What is the significance of telemetry in critical care?
It allows continuous monitoring of the patient's heart rhythm.
What is the role of collaboration in critical care nursing?
Coordinating and organizing care with the healthcare team, including case management.
What are the signs and symptoms (S/S) that critical care nurses should monitor?
Changes in vital signs, altered level of consciousness, and pain levels.
What is the purpose of a rapid response team?
To provide immediate assistance to prevent patient deterioration.
What is a Code Blue?
A medical emergency indicating a patient requiring immediate resuscitation.
What is the importance of cultural diversity in critical care?
It involves incorporating patients' cultural values and beliefs into their care.
What should a nurse do if they are unsure about a patient's treatment plan?
Consult with the healthcare team or ethics committee for guidance.
What is the nursing process in critical care?
A systematic approach involving assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
What is the significance of thorough documentation in critical care?
It ensures accurate communication of patient status and care provided.
What is a Loading Dose in critical care?
A bolus dose administered to quickly achieve therapeutic drug levels.
What does PCA stand for in medication administration?
Patient-Controlled Analgesia.
What is the purpose of assessing patients every 2 hours (Q2H) and as needed (PRN)?
To monitor pain levels and adjust treatment accordingly.
What medications are typically used for pain management in critical care?
Morphine or Dilaudid.
What characterizes agitation in critical care patients?
Hyperactive movements, self-harm, and physical aggression.
What can cause agitation in critical care patients?
Pain, anxiety, hypoxia, ventilator dyssynchrony, and positioning.
What is the Sedation Agitation Scale used for?
To assess the level of sedation and agitation in patients.
What does a score of 3 or 4 on the Sedation Agitation Scale indicate?
The patient is calm or sedated.
What is the Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS) used for?
To measure sedation levels in patients.
What does a RASS score of 0 to -3 indicate?
The patient is calm to moderately sedated.
What is delirium in critical care patients characterized by?
Disorientation, impaired memory, altered sensory perceptions, and inappropriate behavior.
What is 'ICU psychosis'?
A term used to describe delirium in critically ill patients.
What is the CAM-ICU scale used for?
To diagnose delirium in ICU patients.
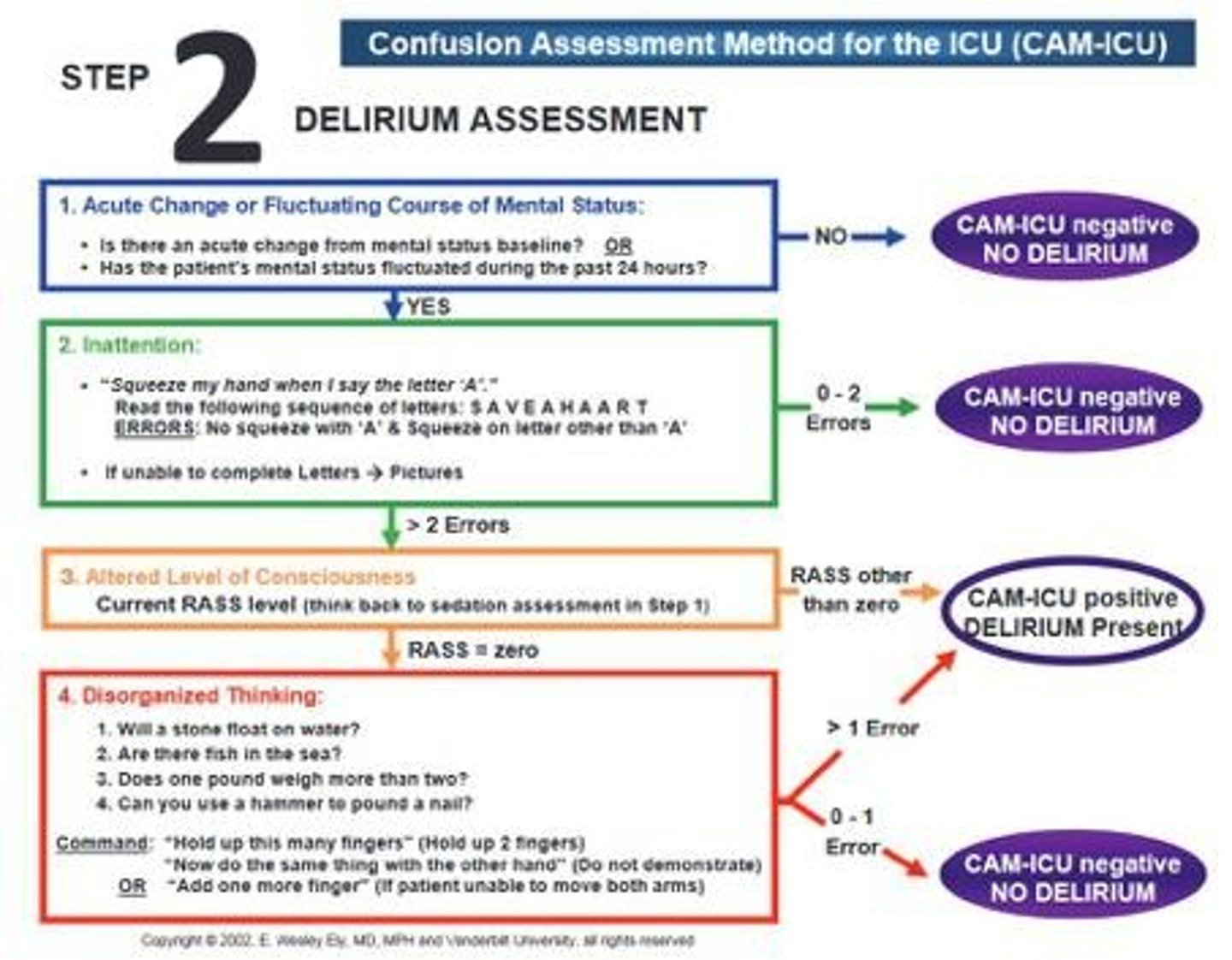
What can cause delirium in critically ill patients?
Sepsis, critical illness, or other organ dysfunction.
What are common treatment options for delirium?
Antipsychotics like Haldol and supportive care.
What is the mechanism of action of Haldol (Haloperidol)?
It blocks dopamine-mediated neurotransmissions in the brain.
What are nursing implications when administering Haldol?
Monitor for prolonged QT interval, hypotension, and tachycardia.
What is the ideal blood glucose level for critically ill patients?
140-180 mg/dL.
What is the significance of hyperglycemia in critical care?
It can indicate insulin deficiency and increased metabolic demand.
What is the role of stress in critical care patients?
It can lead to hypoxia, nutritional imbalances, and changes in vital signs.
What is the impact of stress on the endocrine system?
It triggers the release of cortisol and catecholamines, affecting metabolism.
What is the importance of organization and prioritization in critical care?
To effectively manage patient care and respond to acute needs.
What is post-intensive care syndrome (PICS)?
A condition affecting patients after ICU stay, leading to muscle weakness and cognitive problems.
What should be assessed before conducting a CAM for delirium?
The RASS score.
What is a common antidote for benzodiazepines?
Flumazenil.
What can rapid withdrawal from benzodiazepines cause?
Seizures, irritability, and visual disturbances.
What are the different types of delirium?
Hypoactive, hyperactive, and mixed delirium.
What are key signs of pain in critical care patients?
Guarding, pulling away, and grimacing.
What is the normal range for cardiac output?
4-8 L/min
What does CI stand for in hemodynamics?
Cardiac Index
What is the normal range for cardiac index?
2.5-4 L/min/m²
What is the normal stroke volume range?
60-100 ml/beat
What is the normal ejection fraction (EF)?
Greater than or equal to 60%
What does PCWP stand for and what is its normal range?
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure; 4-12 mmHg
What is the formula for Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
(Systolic + 2 * Diastolic) / 3
What is the significance of a MAP greater than 60 mmHg?
Necessary to perfuse the coronary arteries
What is preload in the context of cardiac function?
The volume required to stretch the cardiac muscle fibers in the atria and ventricles
What does afterload refer to?
The resistance or pressure the heart must overcome to eject blood
What is contractility?
The strength of the cardiac muscle to push blood from the ventricles
What is pulse deficit?
When the apical and peripheral pulse are not equal
What is pulse paradoxus?
A decrease of >10 mmHg in arterial pressure during inhalation
What is the primary goal of hemodynamic monitoring?
To maintain adequate tissue perfusion and assess the body's response to oxygen demands
What does the Frank-Starling Law describe?
The relationship between stroke volume and end-diastolic volume
What is the effect of high heart rate on cardiac output long-term?
It can decrease cardiac output due to insufficient filling time
What are positive inotropes?
Medications that increase the strength of heart contractions
What are negative inotropes?
Medications that decrease the strength of heart contractions
What is the significance of a high preload?
It indicates more stretching of the heart muscle, which can affect stroke volume
What are the common methods of non-invasive blood pressure monitoring?
Oscillometric and auscultatory methods
What is the purpose of a pulmonary artery catheter?
To measure pressures in the pulmonary artery and assess cardiac function
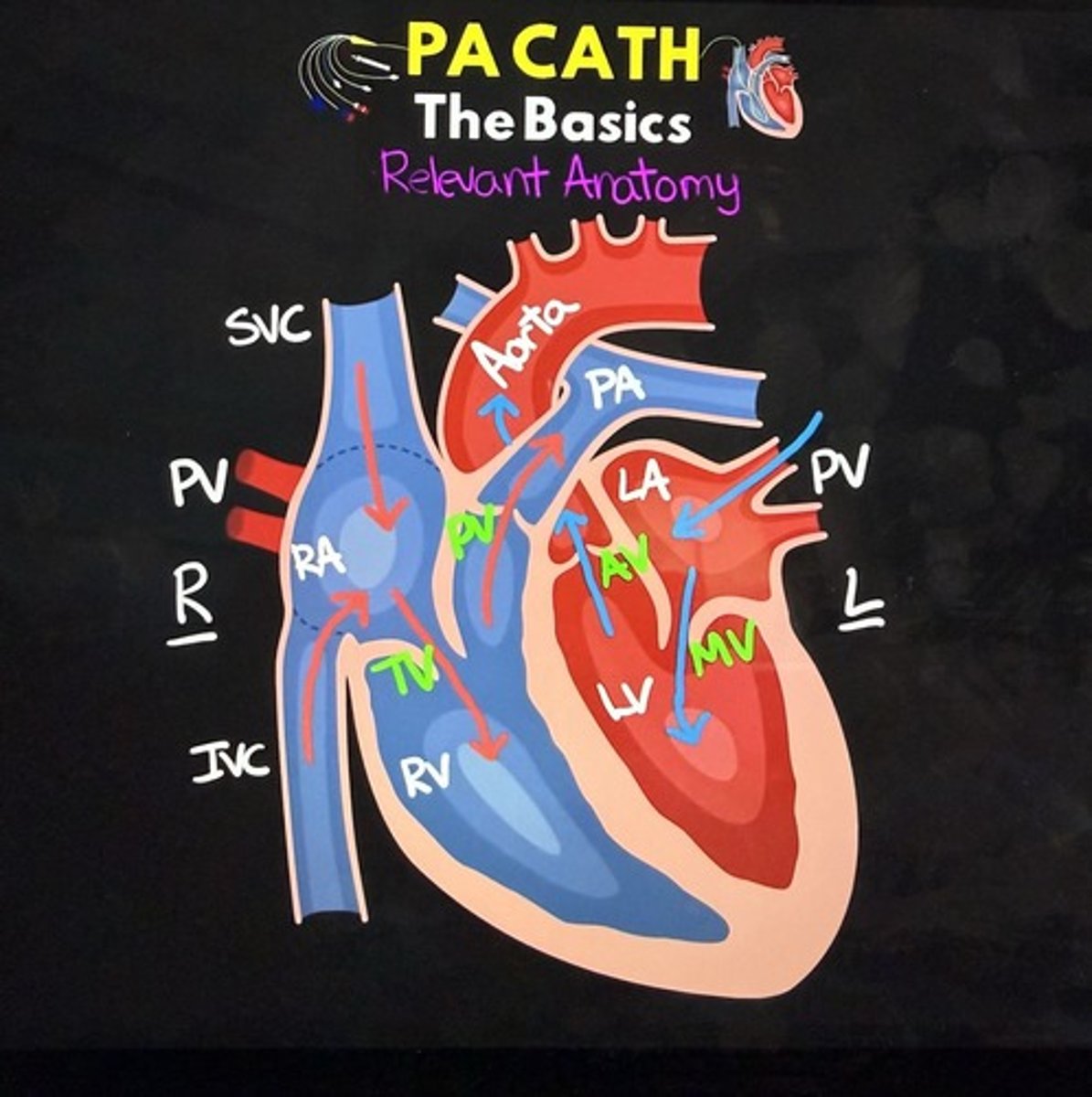
What is the normal range for pulmonary artery pressure?
15-25/8-15 mmHg
What does a high systemic vascular resistance (SVR) indicate?
Increased afterload on the left ventricle
What is the role of vasopressors in hemodynamics?
To increase blood pressure in shock states
What is the effect of pulmonary hypertension on the heart?
It can cause the heart to enlarge and affect preload
What does inadequate ventricular filling indicate?
A decrease in preload
What does inadequate ventricular ejection indicate?
An increased afterload
What is the purpose of the Balloon Inflation Port in a pulmonary artery catheter?
To obtain Pulmonary Artery Occlusion Pressure (PAOP) by inflating with <1.5mL of air.
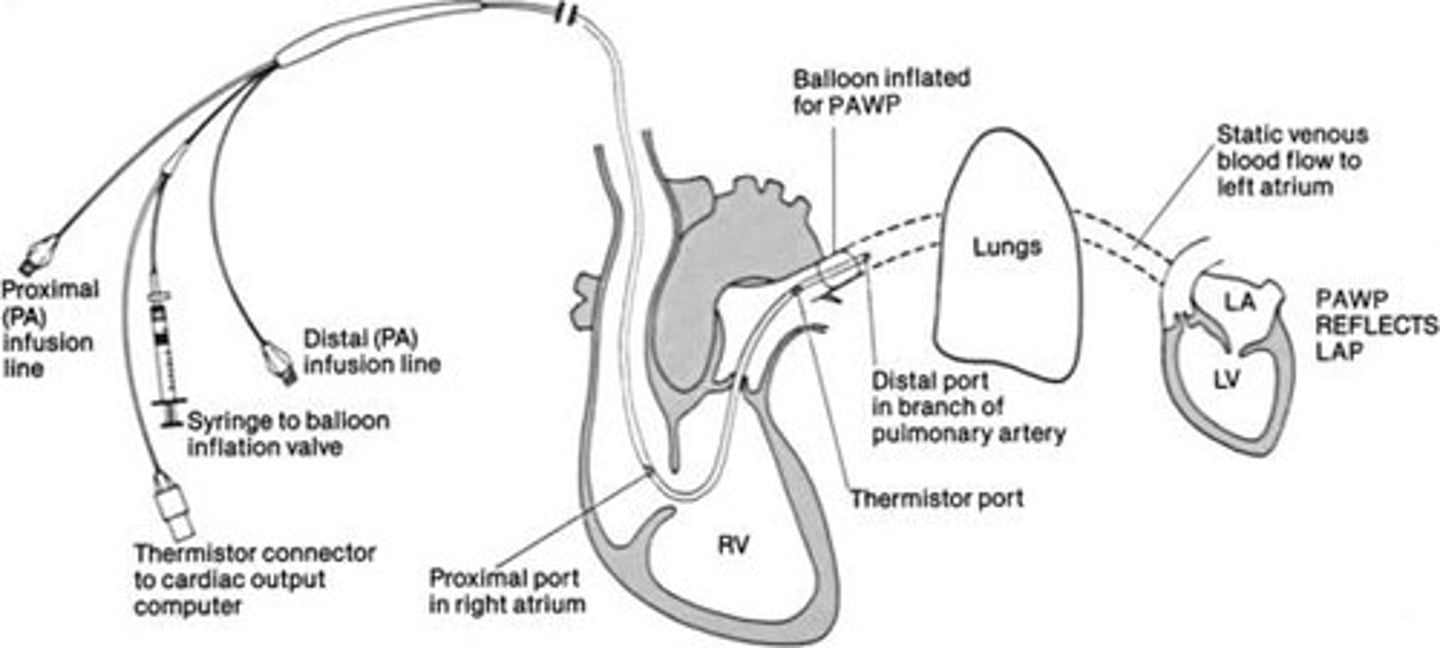
What does the Ventricular Infusion Port in a pulmonary artery catheter allow?
Administration of IV fluids and drugs.
What does the Cardiac Output Port measure?
It measures blood temperature to assess core body temperature continuously.
What is the normal range for Central Venous Pressure (CVP)?
2-6 mmHg.
What are common complications of arterial lines?
Hemorrhage, hematoma, thrombosis, proximal or distal embolization, pseudoaneurysm, and infection.
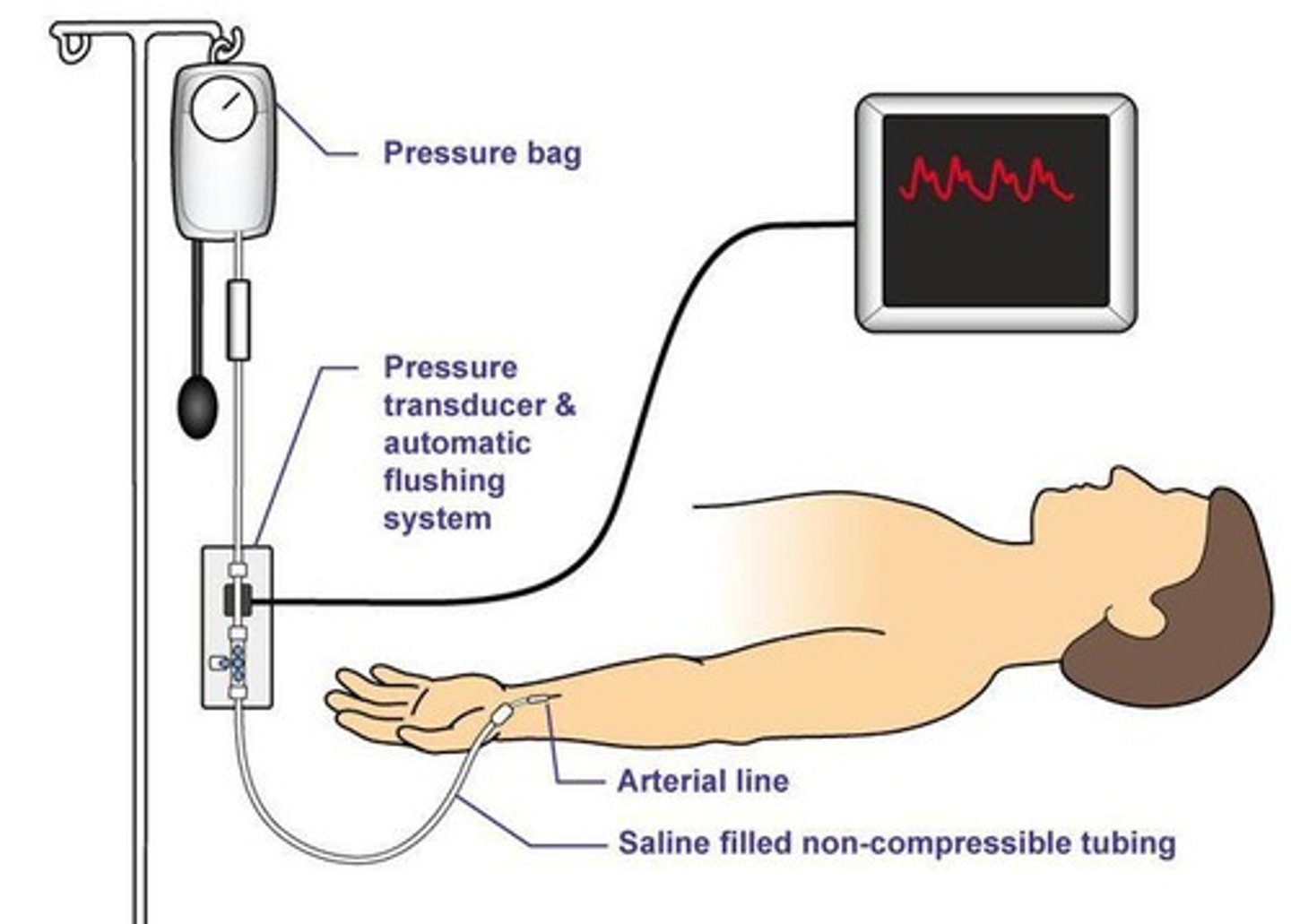
What is the primary use of an arterial catheter?
To measure blood pressure and allow for continuous blood sampling.
What should be done to prevent thrombus formation in arterial lines?
Provide continuous infusion of heparin solution.
What is the significance of the phlebostatic axis in hemodynamic monitoring?
It is the anatomical reference point for leveling the transducer to ensure accurate pressure readings.
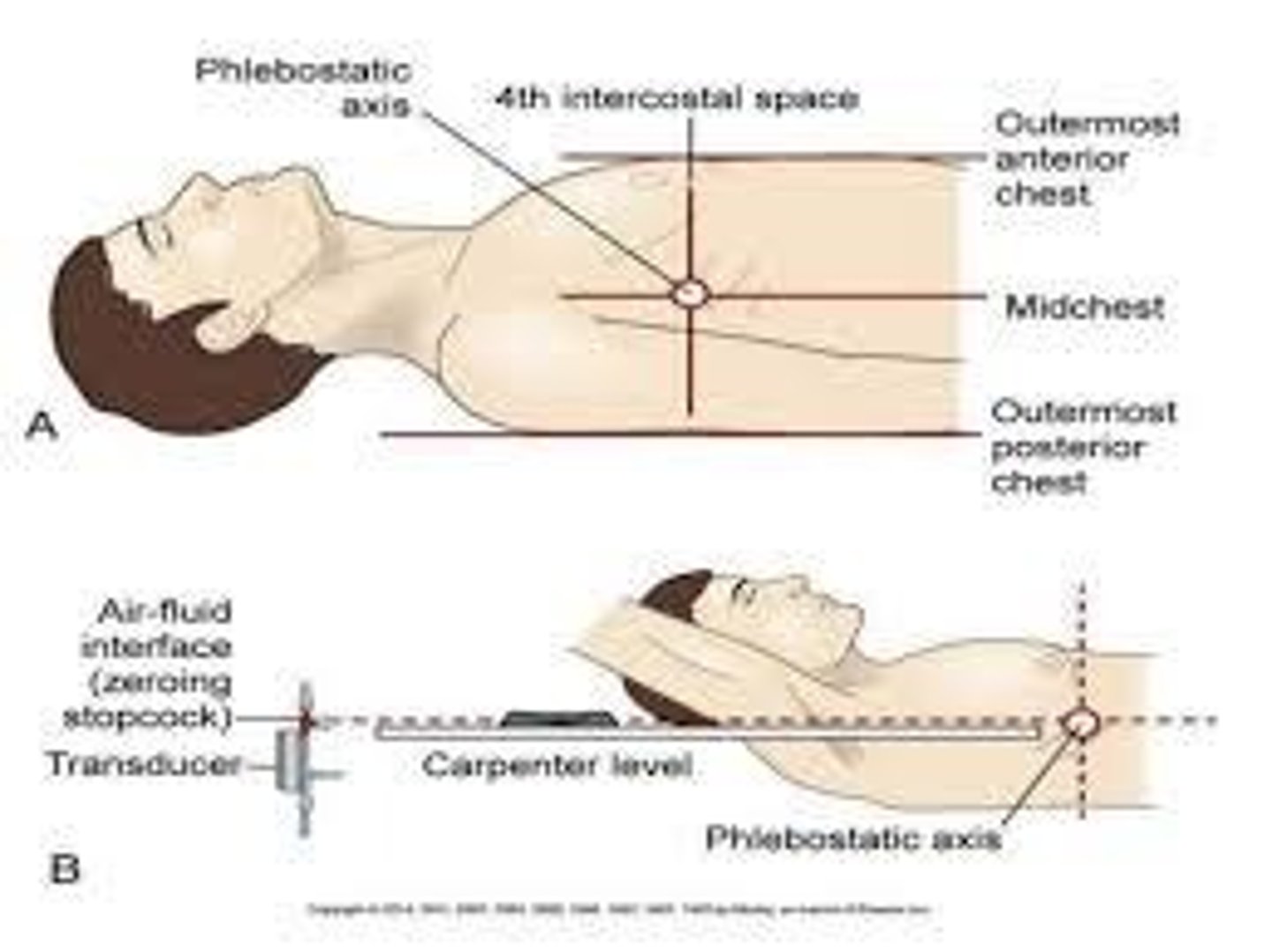
What is the purpose of zeroing in hemodynamic monitoring?
To use atmospheric pressure as a reference standard to ensure accurate pressure measurements.
What is the recommended patient positioning for stable patients with a pulmonary artery catheter?
30-60 degrees head of bed elevation.
What should be done to prevent air embolism in arterial lines?
Purge air bubbles, ensure the drip chamber is full, and use a continuous flush device.
What is the role of a Swan-Ganz catheter?
To monitor hemodynamics, including cardiac output and pulmonary artery pressures.
What is the recommended frequency for sterile dressing changes on central venous catheters?
Every 72 hours or when the dressing is solid or loose.
What does an over-dampened arterial line waveform indicate?
It may indicate low blood pressure due to inadequate pressure in the flush bag or blood clots.
What is the significance of a square wave test in hemodynamic monitoring?
To assess the damping of the arterial line system and ensure proper function.
What are the nursing management steps for a pulmonary artery catheter?
Monitor for bleeding, infection, secure lines, and ensure caps are on.
What is the purpose of the continuous infusion of heparin in central venous catheters?
To prevent thrombus formation.
What should be monitored after the removal of a central venous catheter?
Apply pressure for 10+ minutes to prevent hemorrhage.