TLIB3123 Apply awareness of motive power unit fundamentals
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Each “A” series Electric Multiple Unit (EMU) is equipped with how many traction motors
6
What is the A series max speed?
110 km/h
How many cars does each A series compose of, how long are they each, and what are they named?
Each A series EMU consists of two cars which are 48.42 metres in length. These are Driver Module A (DMA) and Driver Module B (DMB) car.
What are the cars of the A series named?
How are the ends of each end numbered?
Driver Module A (DMA) car, Driver Module B (DMB) car
No1 end = driving compartment end
No2 end = ends that are joined together (semi-permanently coupled)
The No1 end of the A and B series DMA car will face towards _____ or ______
Fremantle or Yanchep (previous endpoint Butler)
the No1 end of the DMB railcar of A and B series will face towards…
Armadale/Midland or Mandurah
If you’re approaching a caution, what’s a good rule of thumb speed to reduce to
Half the track speed.
In an assessment, don’t pass a caution leaving it in power - usually at least minimum brake
How many traction motors does a B series EMU have?
8
What is the max speed of the B series
130km/hr
Are B series vehicles permanently or semi-permanently coupled?
Permanently (with semi=permanent couplers)
How many car-sets can the B series have?
Vehicles are permanently coupled into 3 car sets
3 car sets may be coupled into 6 car sets
In the A series, how can you tell which end is the A car?
The car number will start with an even number (maybe always 2??)
How is each car named in a B series set?
DMA-car → T-car → DMB car
On the A series, what does the pantograph use to rise to the OLE?
Compressed air (aux compressor feeds into aux reservoir)
There are 10 components of the A series air system - name as many as you can
Pantograph
main compressor
auxiliary compressor
main reservoir tanks
main reservoir pipes/hoses
horn
wiper/washer
passenger doors
spring park brakes
air suspension
Which 7 pneumatic equipment types does the A series main reservoir air tanks supply air to?
Spring Park Brake
Air Suspension
Window Washer, Wiper
Pantograph
EBC5 units/EP bakes
Passenger doors
Horn
What does the Main Compressor Governor do?
Is an electrical switch that opens and closes by Main Reservoir Air Pressure.
It starts and stops the compressor when the minimum or maximum pressure is reached in the main reservoir tanks.
What does MCB stand for
Main Circuit Breaker
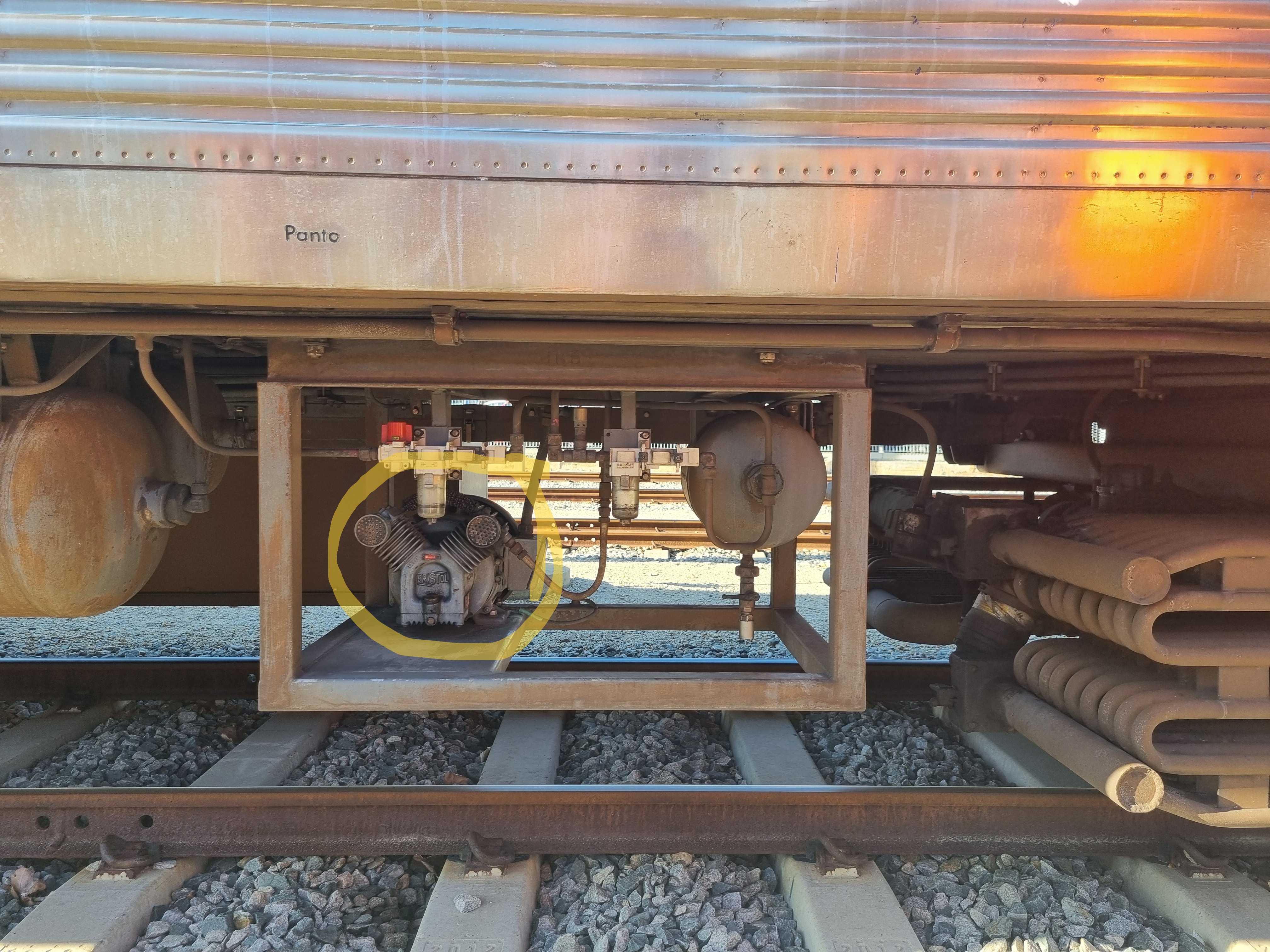

What is this (yellow highlighted)?
Auxiliary compressor
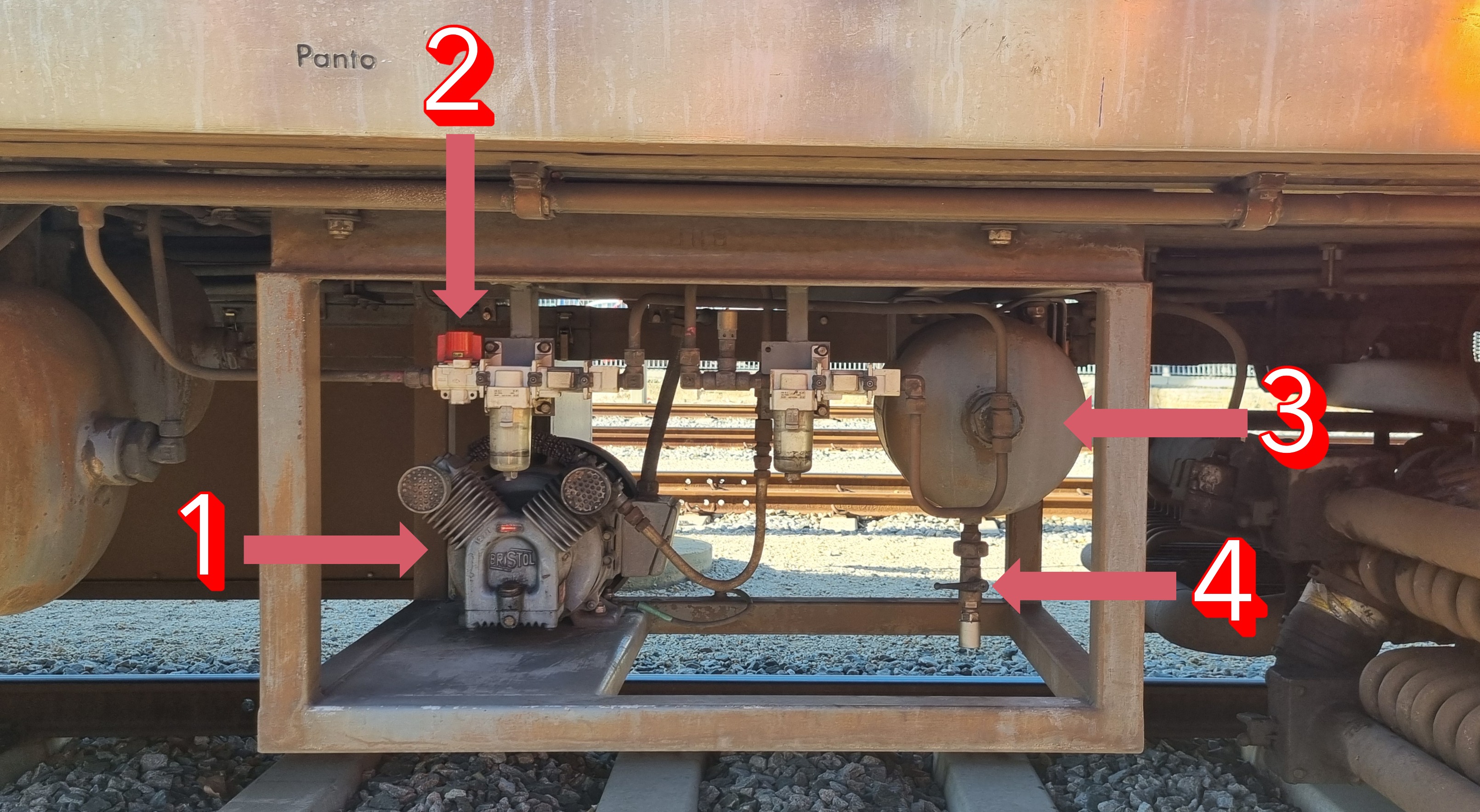
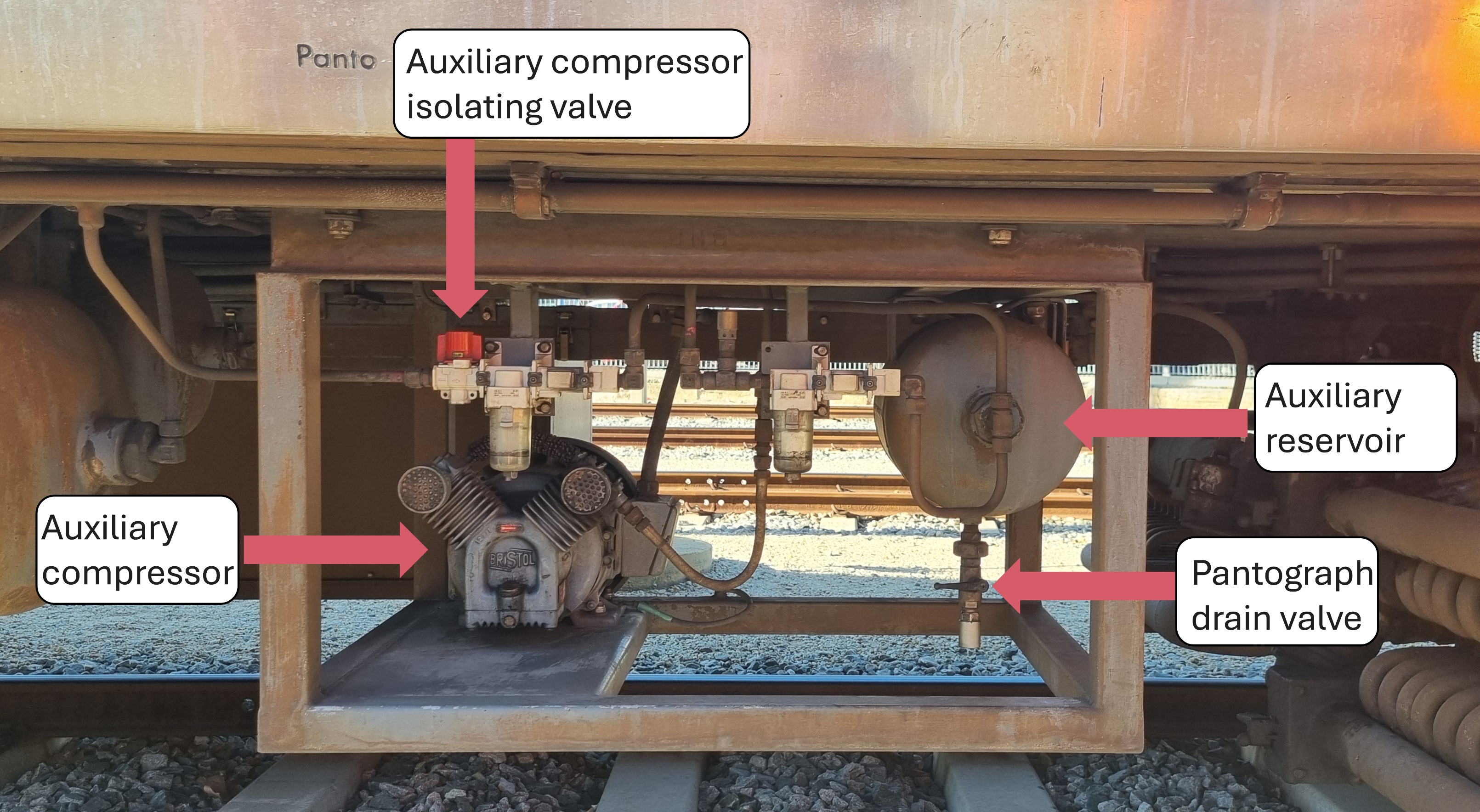
What are each of the numbered components?
Auxiliary compressor
Auxiliary compressor isolating valve (usually red, can be black)
Auxiliary reservoir
Pantograph drain valve (black)
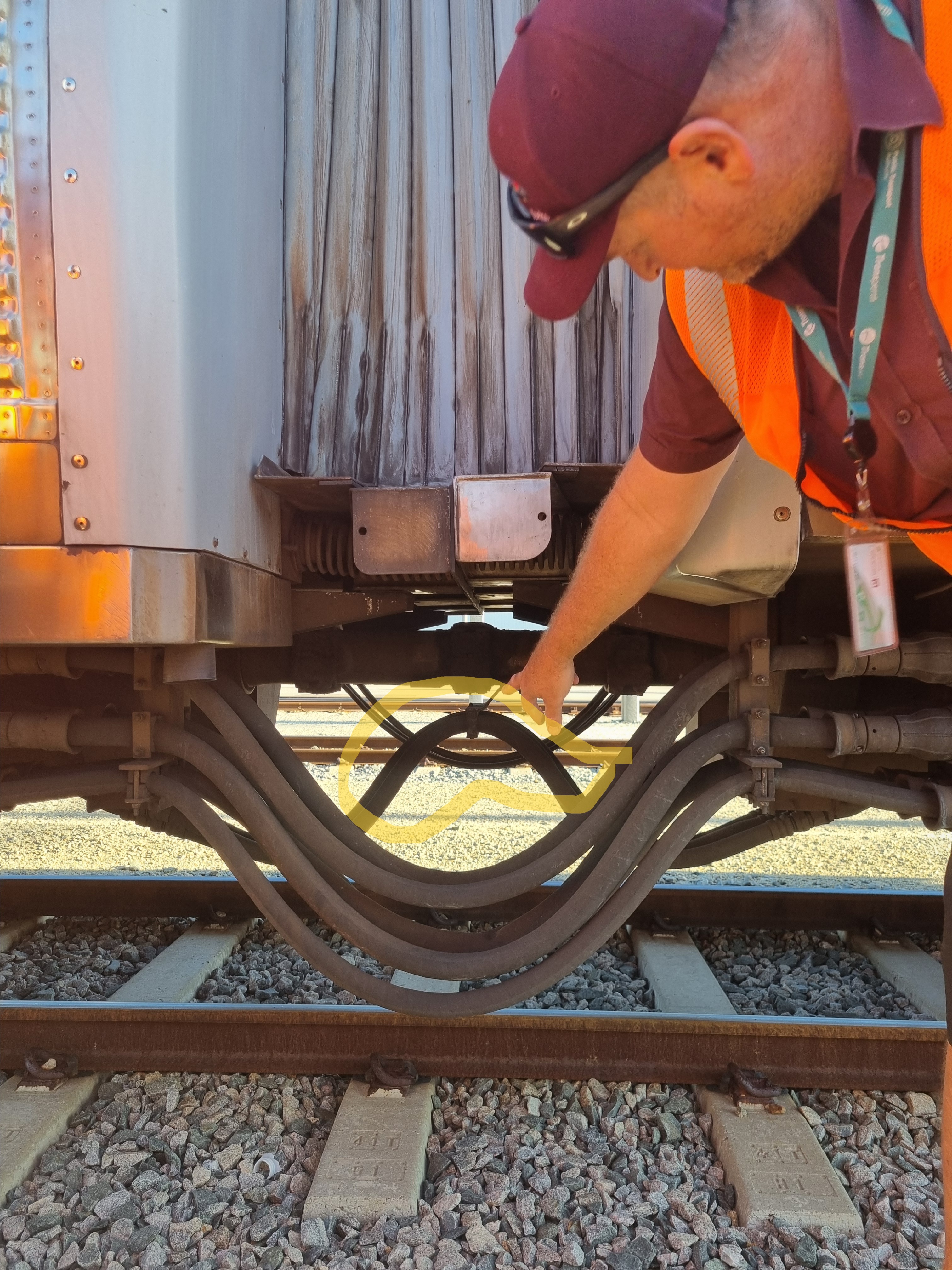

What is Mark pointing to on the A series (highlighted in yellow), and where is it located?
Flexible pneumatic hose.
Located between EMU A Series between DMA No.2 end and DMB No.2 end
Name the 7 components of the High Voltage Equipment
Pantograph - held down by spring pressure, pushed up by air pressure in panto lifting cylinder with air from aux compressor.
High Voltage Potential Transformer - next to panto.
Main Circuit Breaker (MCB) - DMA car - white - two contact heads forced together by compressed air piston - MCB will not close unless panto raised and line to voltage present, then current passes to Main Transformer (underframe). Will open if air pressure falls below 340kpa.
High Voltage Cable
Current transformer
Ground switch - drivers cannot access - via interior cab. When closed, connects MCB to Traction Return rail via metal body of car
Lightening arrestor
What does the Main Converter do?
Convert AC to DC
What is the APC and what does it do?
Automatic Power Control
Opens the MCB (disconnect power to railcar) when approaching neutral section, close MCB when panto entered live section
What does the Main Transformer on the A series do?
Converts line voltage (25KV) to:
1003 AC voltage to Main Converter, and
849 AC to Aux Converter
What does the Main Converter do?
Converts AC voltage from Main Transformer to DC voltage for traction motors
What does the Auxiliary Converter do?
Converts volts and phases to supply power to:
Main Compressor
Auxiliary Transformer
Dynamic Brake Resistor grid blowers
Air Con Units
Main Transformer Oil Cooling Pump
Saloon lights
What does the Auxiliary Transformer do?
Transforms AC volts and phase, then supplies power to combined Battery charger and Supply unit, which supplies power to:
wipers
cleaning outlets
video recorder
foot heater in cab
What do Unit Wires do and where are they located on the A series?
What does the Battery do and where is it located on the A series
Provide initial source of low-voltage DC current (110v) to start auxiliary equipment during prep of train i.e. aux compressor
What do the Driver’s Circuit Breakers do and where are they located on the A series?
Interrupt current flow to protect the equipment and to prevent fire
What does the EBC5 unit do?
Blend both dynamic and friction braking systems
How are park brakes applied and released (mechanism)?
Applied by springs, released by air
What is door traction interlock?
If doors open, cannot go into power
Where in the main converter on the A series railcar? What does it do?
DMA 1 RHS
Convert AC to DC
Auxiliary transformer on A series - what does it do? where is it? can we go into it?
Powers the
Battery charger
Cab lights
cleaning outlets + wipers
Foot Heater
Video cameras
DMB middle RHS
Yes
What does the battery do
Provide secondary power supply to aux compressor and other minor electrical components
What does PEI stand for and where are they on A series?
Passenger Emergency Intercom
How do you apply emergency brake in A series?
Red lever in driver’s cabin
Where in the A series cabin are the circuit breakers?
Rear Switch Panel
Who can give permission to touch sealed circuit breakers in the cabin (e.g. ATP)?
DC
Which electrical boxes are train drivers allowed to access on an A series, where are they, what do they contain?
UK 39 Box - circuit breakers
UK 40 Box - circuit breakers
Aux transformer / 20 Box - DMB no.1 RHS - circuit breakers, feeds batteries and charges Aux Transformer
Battery Fuse Box
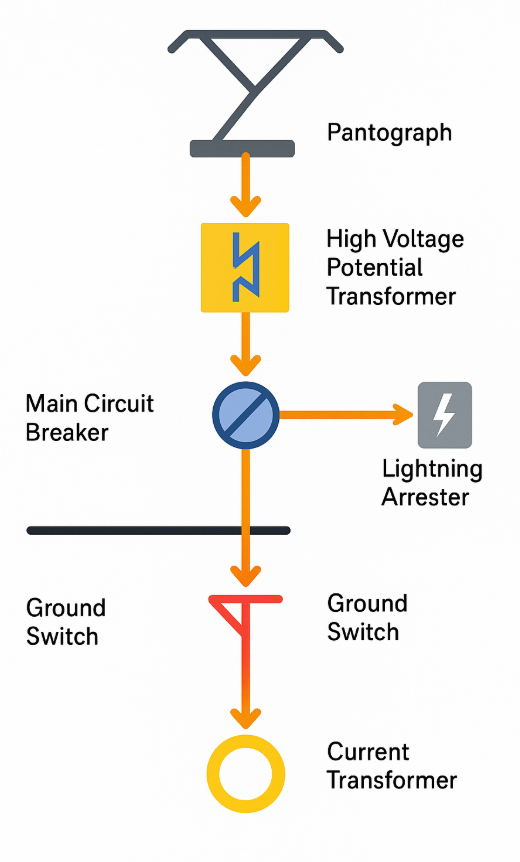
Describe the current path of high voltage equipment on the train roof, and other components that are present + what they do
Pantograph (brings 25KV down from overhead line) →
high voltage potential transformer (Measures the voltage coming in from the overhead line)→
Main Circuit Breaker + lightening arrestor →
(under roof)
Ground Switch →
current transformer
What does the battery provide power to?
What two types of bogies are there, and how many on each of A and B series?
Motor Car (traction motor-driven), Trailer Car (lazy bogie)
A series: 2 motor bogies DMA, 1 DMB, 1 lazy DMB no.1
B series: 2 motor bogies on DMA and DMB, 2 trailer on T car
How do the Park Brakes operate and where are they located?
Spring applied, air released
On RHS of each motor bogie
How is a service brake applied?
Air operated disc callipers
What 2 types of couplers are used on A and B series?
Automatic Scharfenberg Coupler (drive cabs both series) - auto connects air lines and electric cables
Semi-permanent Bar Couple (car joiners)
Name the controllers used for driving in the A and B series
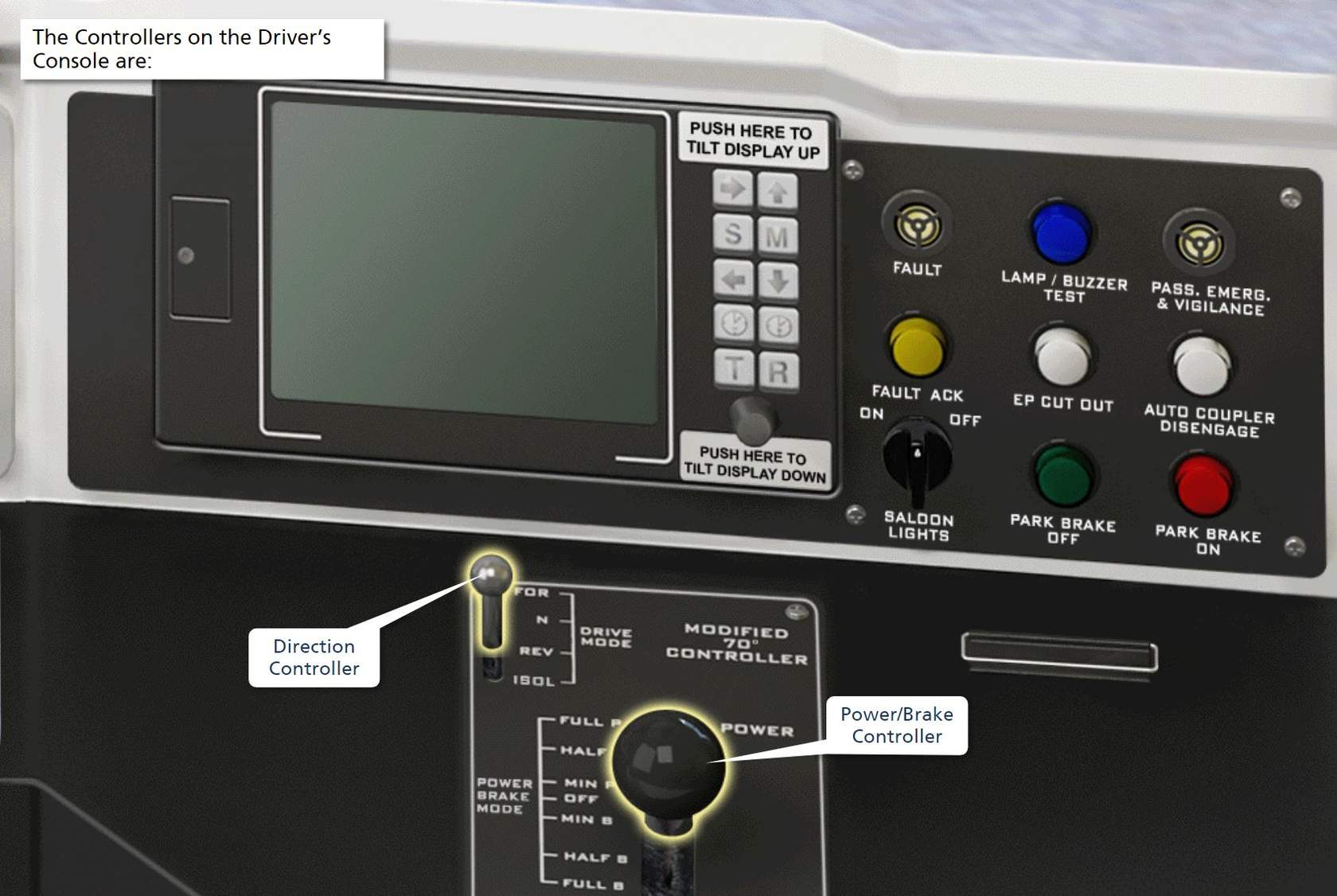
Direction Controller
Power/Brake Controller
Where do Train Wires run, how are they joined between cars, where located, what voltage carried?
Run length of whole train
Joined by electrical connectors of Scharfenberg Couplers
LHS of train on no2 ends A series
Carry 100v for control circuits
What are brake pads held in place by?
Brake callipers
What happens in Dynamic braking?
When dynamic brake is in operation, the traction motors are converted to generators - momentum of train source of energy for generator
What does the EBC 5 unit do, is it electrically or pneumatically controlled, how does it operate, where located?
Blends dynamic and friction braking systems
Electrically
Air pressure received at the brake cylinders is controlled by two different components - driver’s Brake Controller (electric signals to EBC 5 to set braking demand). Uses dynamic and pneumatic braking . ATP connected to EBC 5 to allow intervention prn
DMA - 1 unit on 2 end RHS, DMB - 2 units on RHS (one for power, one for trailing)
How do you activate the driver’s cab?
Placing the Direction Controller in Neutral position
What does the Control Circuit Governor (CCG) do?
Ensures that there is enough Brake pipe (BP) pressure to operate the Auxiliary brake
How does the electro-pneumatic brake work?
Uses electrical signals received by the Drivers Controller to control the air pressure received by the brake cylinders
What type of braking does the B Series primarily use?
Dynamic braking (electric regenerative), then pneumatically operated friction braking if needed
How is friction braking achieved?
Air Operated Disc Callipers on the DMA, DMB and T car
What does the Brake Computer Unit (BCU) do?
determines the required friction braking needs to meet the total braking demand (Regenerative + Friction) and then allows MR air into the brake cylinders, with the use of dynamic brake to slow and stop the railcar
Where is the main transformer on the B series?
T car
What colour can marker lights be, where are they, when are they each colour?
Red when trailing, white when leading. On driver ends lower half
What does the RAPID Drivers Display Unit show?
touch screen panel which is a fully automated announcement system that works by GPS and is only installed on the A series railcars.
What is an Intelligent Display Unit (IDU) and what series is it on?
B series - RHS dash
Display events, and also the train status and is used as a Man Machine Interface (MMI) to the systems on the train.
What series has the Train Management System, what does it do?
B series
comprehensive fault indication system, the train management system (TMS), provides up to the second fault information to the driver via a touch screen in the cab. The function of the TMS is to monitor:
Traction
Friction Brake Control
Door Control System
Air Conditioning Control
High Voltage Control
Motor Converter Control
Auxiliary Power Control
Train Diagnostic System
What shows faults in the A series cab?
Fault Indication Panel - RHS dash
What does PEI stand for and where located on A series and B series?
Passenger Emergency Intercom
A series: RH1/LH2/RH3/LH4
B series:
What does LCM stand for, what series is it on, where is it located, what does it do?
Line Converter Module
B series
LHS DMB, RHS DMA
Convert AC from main transformer to stable DC voltage and feed back to catenary wire.
What does MCM stand for, what series is it on, what does it do?
Motor Converter Module - Feeds traction motors with variable AC voltage
B series
(The Motor Converter Module (MCM) takes DC power from the LCM and converts it into three-phase AC power to drive the traction motors.)????
What are the cameras called that face out from driver’s cabin to track?
Forward-facing cameras
What does PDS stand for and what does it do?
Platform Detection System
Prevents the unsafe release of railcar saloon doors if a platform has not been detected on the correct side adjacent to the railcar at the time the door release is attempted.
Where is the Main Compressor located on the B series
Centre of T car
On the B Series, what must you always do on your morning check w respect to couplers
Check that both set to electrical
In A series, what 2 systems control friction braking
EBC 5 and shadow brake
Brake computer unit on B series - what does it do
determines necessary pressure required for friction breaks (doesnt blend with dynamic which is always on, only determines when to add friction brake)
What causes spring park brakes to apply the brake pads to the brake disc on the EMU?
Release / exhaust of air from spring park brake unit
How check oil gauges on A and B series
A series: Qualitrol
B-series: Shot glass / sighter glass
What does door traction interlock system do?
Can’t move train when doors are open
Where the circuit breakers are in the cab - name of locker?
MEL locker (M Electric Locker)
In the B series, how do you isolate doors 49 to 79, and 80 onwards?
Above each door
3-way valve, used in breakdown scenario
What colour are the bogie isolation switches on B Series
Blue switch
Two brake types on B series
EP (electropneumatic) and shadow break
What boxes can you go into on an A series exterior?
39 Box
40 Box
Battery fuse box
Aux transformer
How many doors does the A series 2 car set have and how are they numbered?
8 doors
L1, R1, L2, R2, L3, R3 etc
Which car is the pantograph located on for each of the A and B Series?
A Series - DMA car
B Series - T car
Which is the T car no.1 and no.2 ends?
No.1 by DMA, No.2 by DMB
Where is the main compressor, main res, and EBC5, aux compressor units of the A series?
DMB LHS: main compressor, main res
DMB RHS & DMA RHS: EBC 5
DMA RHS: aux compressor
What colour are saloon door isolating valves on A series on the exterior?
Yellow
What colour are the Local Supply isolating valves on the A series and how many are there?
Blue
2 on the RHS no.2 ends, 1 in each cab cabinet RHS of dash = 4
Where is the Emergency Brake in the A series?
Red level on vertical surface RHS of dash
What do they flexible pneumatic hoses do?
Supplies MR, BP and Local Supply air between the DMA and DMB cars
Where are the main and aux compressors and air res’s on the B Series?
Main compressor RHS T car, 200L air res next to it
Aux compressor LHS T Car, 125L res next to it
What does the Air Raft on the B Series contain?
Isolation valves for:
MR supply to Brake Unit
Park Brake Supply
Air Suspension
What does the Main Converter on the A series do and where is it?
Changed 1003 AC voltage from Main Transformer to 750 DC volts for traction motors
on DMA car
On the B series, where are the Main Compressor and aux compressor located, and what do each do
On the T car (aux LHS, Main RHS)
Main Compressor - supplies compressed air to the system
Aux Compressor - battery operated to supply compressed air to pantograph (and close MCB)
What is the main function of isolating valves?
can be closed to protect faulty equipment or stop an air leak by isolating the piece of pneumatic equipment from its air supply.
On the B series, name the components of the air raft, where they are, what they do, and where air rafts are located
MR supply to Brake Unit - top left - isolates MR supply to brake computer to release service brakes (failed car only)
Air suspension isolation - top right
3-way valve - Park Brake supply from MR/BP - transfers air from main res to brake pipe to park brakes