Space Exploration P2
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Grade 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
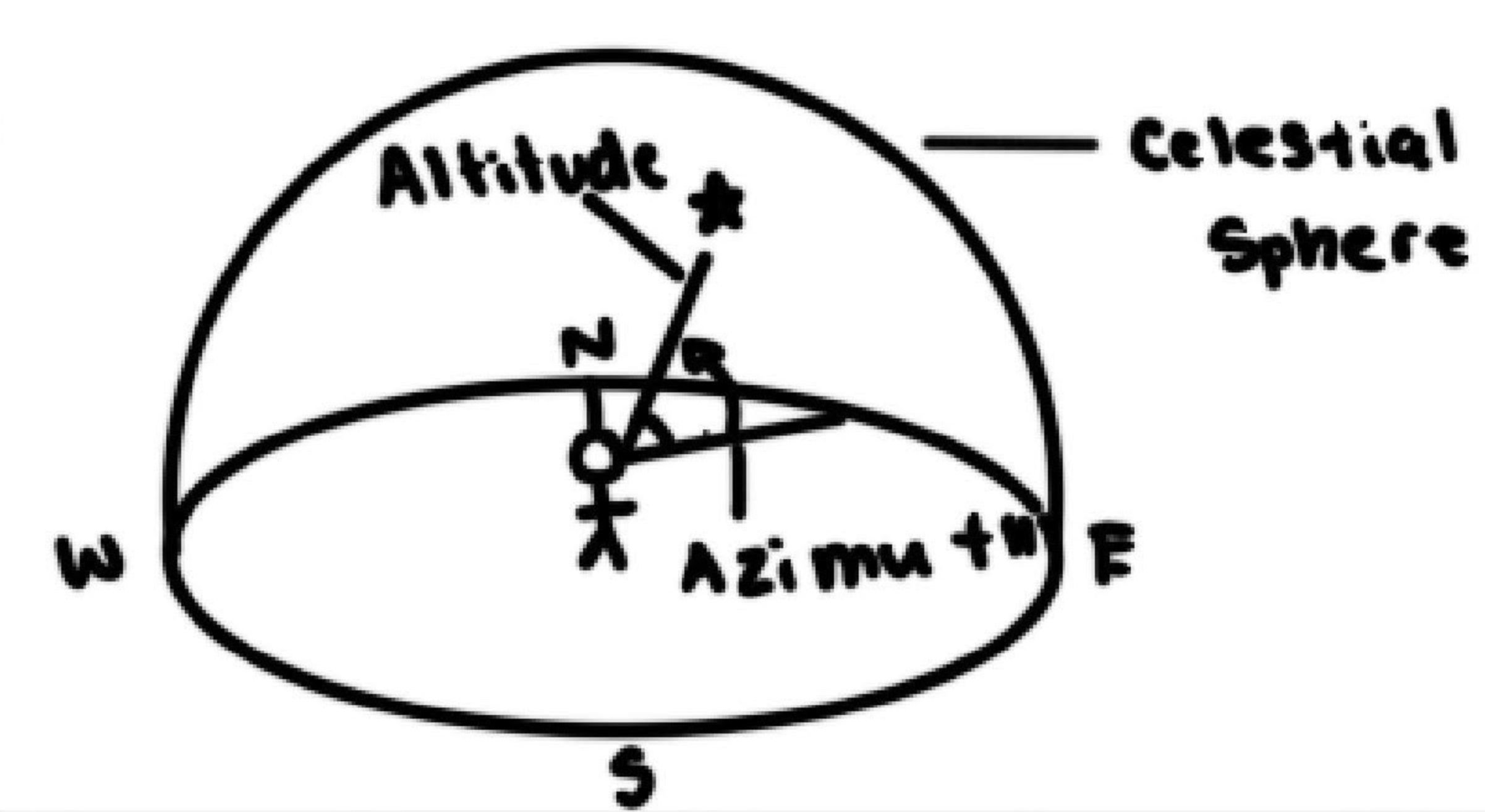
What coordinates did people give to accurately measure the position of stars in the sky?
Azimuth and Altitude
Azimuth
The angle measured clockwise from north
Altitude
The angle measured above the horizon in degrees
Zenith
The point directly above the observer (has the altitude of 90°)
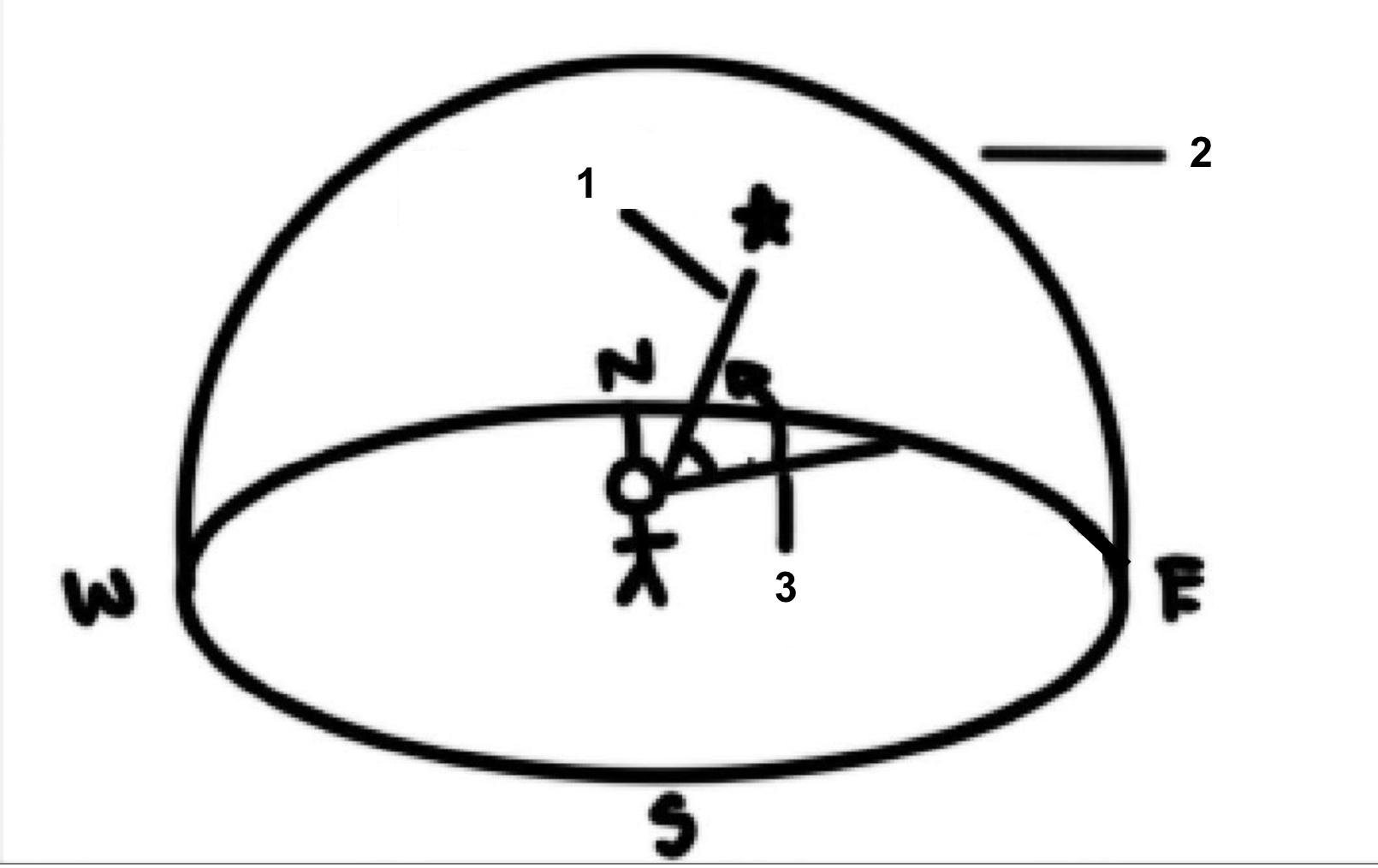
Label the diagram
Astrolabe
An instrument used to measure the altitude and azimuth of a distant object
How do you measure azimuth and altitude?
Azimuth ~
Use a compass to identify North
Hold the astrolabe and align it with North
Use alidade to identify and record the angle between North and the star
Altitude ~
Hold the astrolabe vertically at eye level and align the 0° with the horizon
Use the alidade to identify and record the angle upwards from the horizon
Alidade
The part of an astrolabe that rotates
Percentage of Error
When you take or use measurements to do triangulation there may be human error
What is the formula to calculate the percentage fo error?
% Error = Model distance- Actual distance/ Actual distance x 100
Explain how you would complete this problem: Lily measured the angle to a distant star, and record 45°. The real theoretical angle is 44.76°. What is Lily’s percentage of error?
Start with the formula of %E=MD-AD/AD x100
Enter in the numbers given by the question
Calculate the formula and get the answer
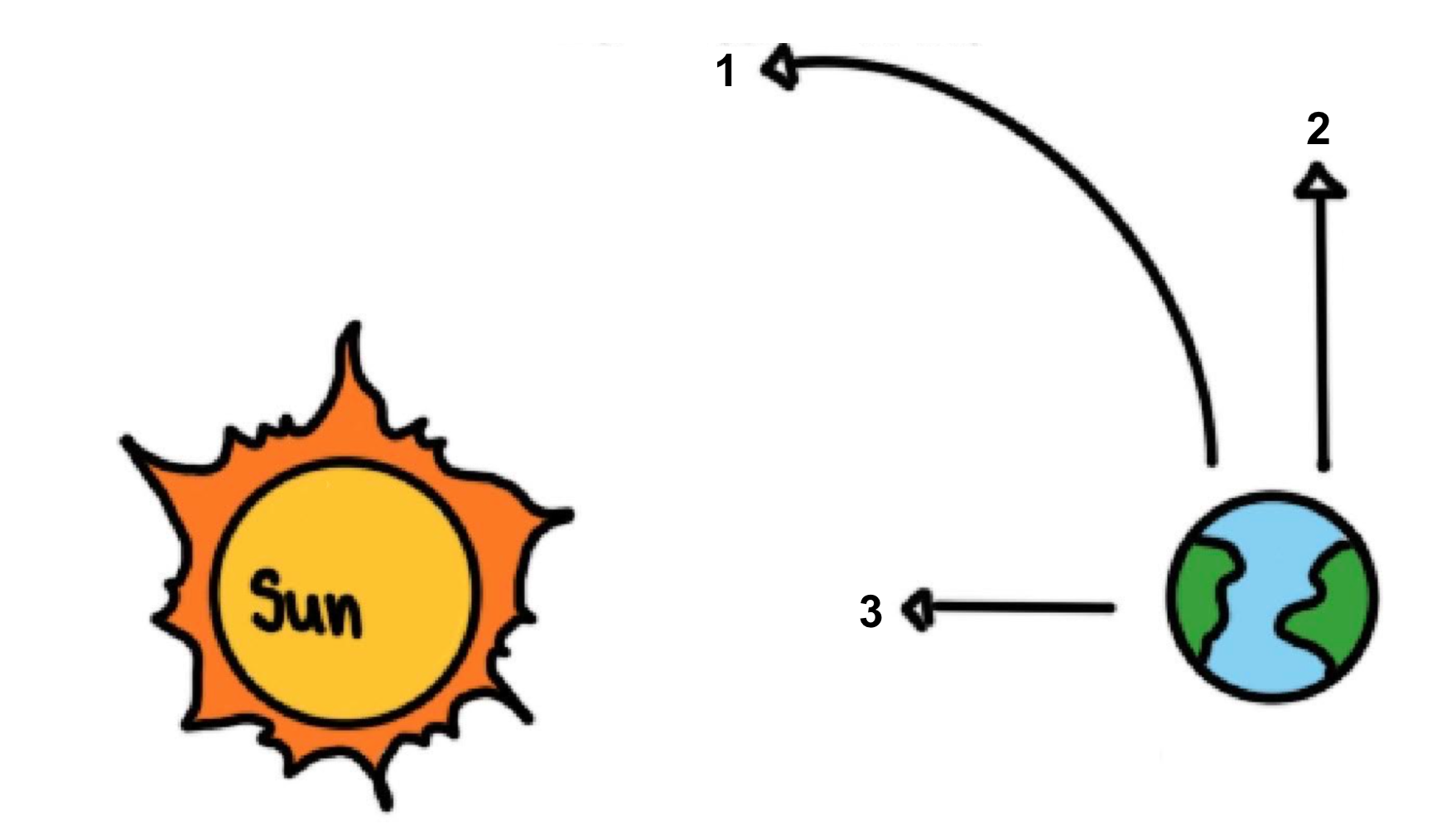
Ellipse
Shaped like a squished circle
In what shapes do our planets orbit?
The planets orbit in ellipses around the sun
Who calculated the orbits of the planets?
Kepler
What did Galileo observe?
Observed that Jupiter has many moons, so Earth could not be the only centre orbited by foreign objects
That the moon has craters
That the sun has sunspots, suggesting that it rotates
That stars are much farther than we originally thought
Who figured out why the planets orbit in ellipses?
80 years after Kepler proposed the idea, Newton explained why they orbit in ellipses- came up with the Universal Law of Gravitation
What does gravity do?
Gravity between objects pull them together, when no force acts on them an object will move in a straight line at a constant speed
Universal Law of Gravitation
All objects attract other objects based on their mass (explains the planets elliptical orbits)
Label the diagram
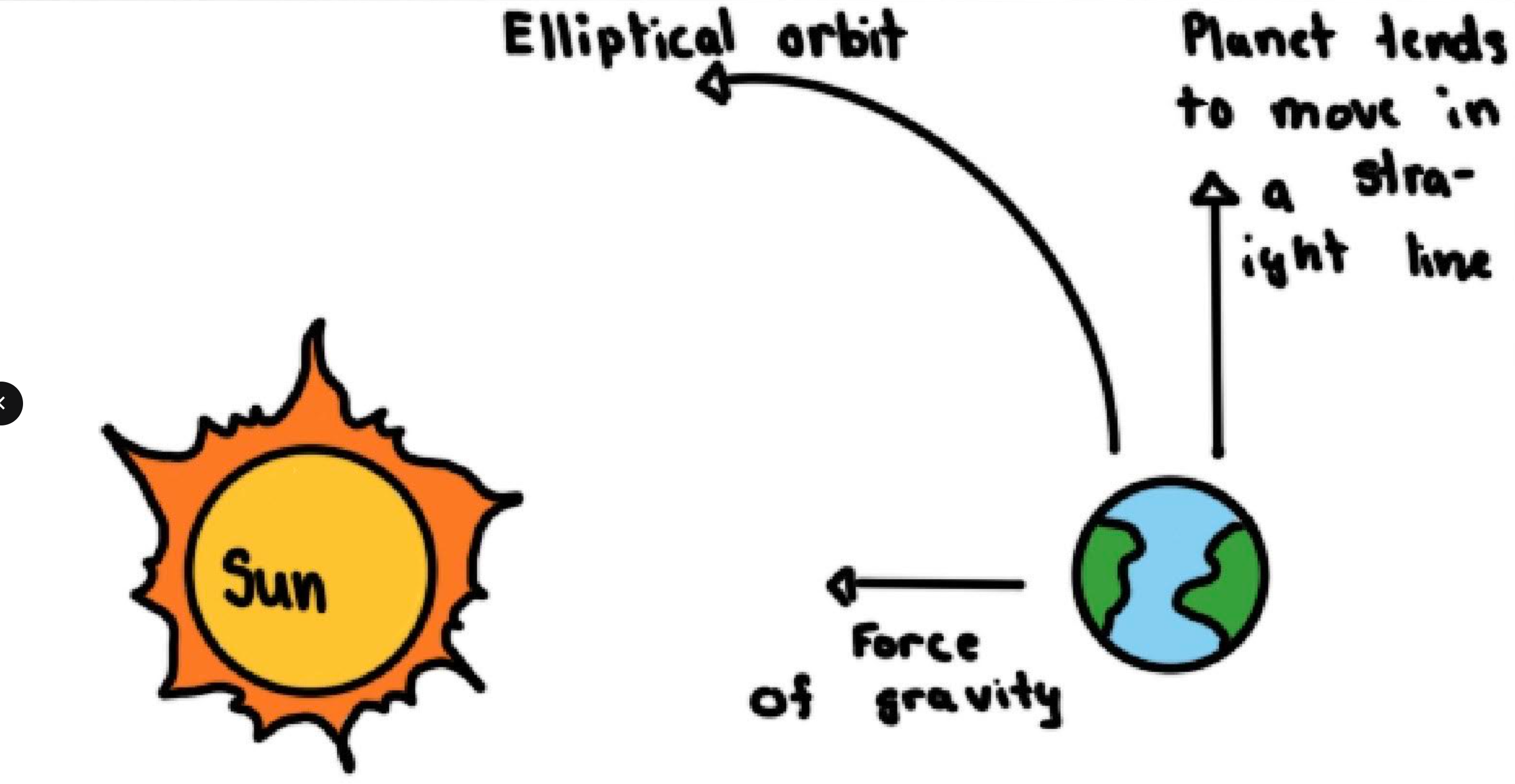

Who studied sunspots?
British astronomer Richard Carrington
What did Carrington observe?
In 1859, Carrington descried that the sun can release intense bursts of radiation (solar flares). These can disrupt signals and influence the northern lights.
Who is Richard Tousey?
Another scientist who studied the sun and observed that the sunspots will occasionally eject large masses of energetic, magnatized plasma during solar flares.
Solar winds
High energy particles that stream off the sun
What protects us from solar winds?
The atmosphere
What is the Hertzsprung Russell?
A graph that plots stars based on their luminosity and temperature
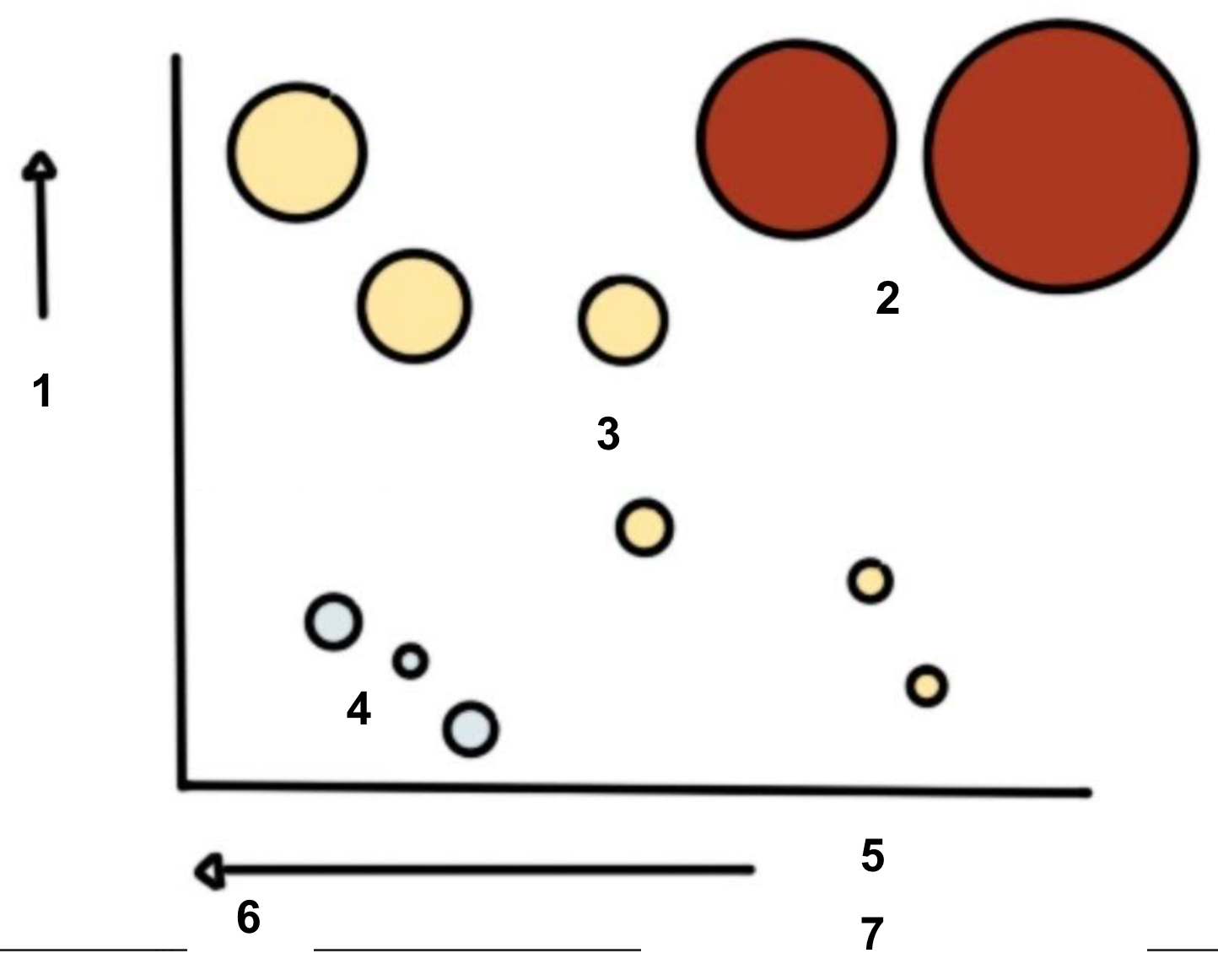
Label the diagram
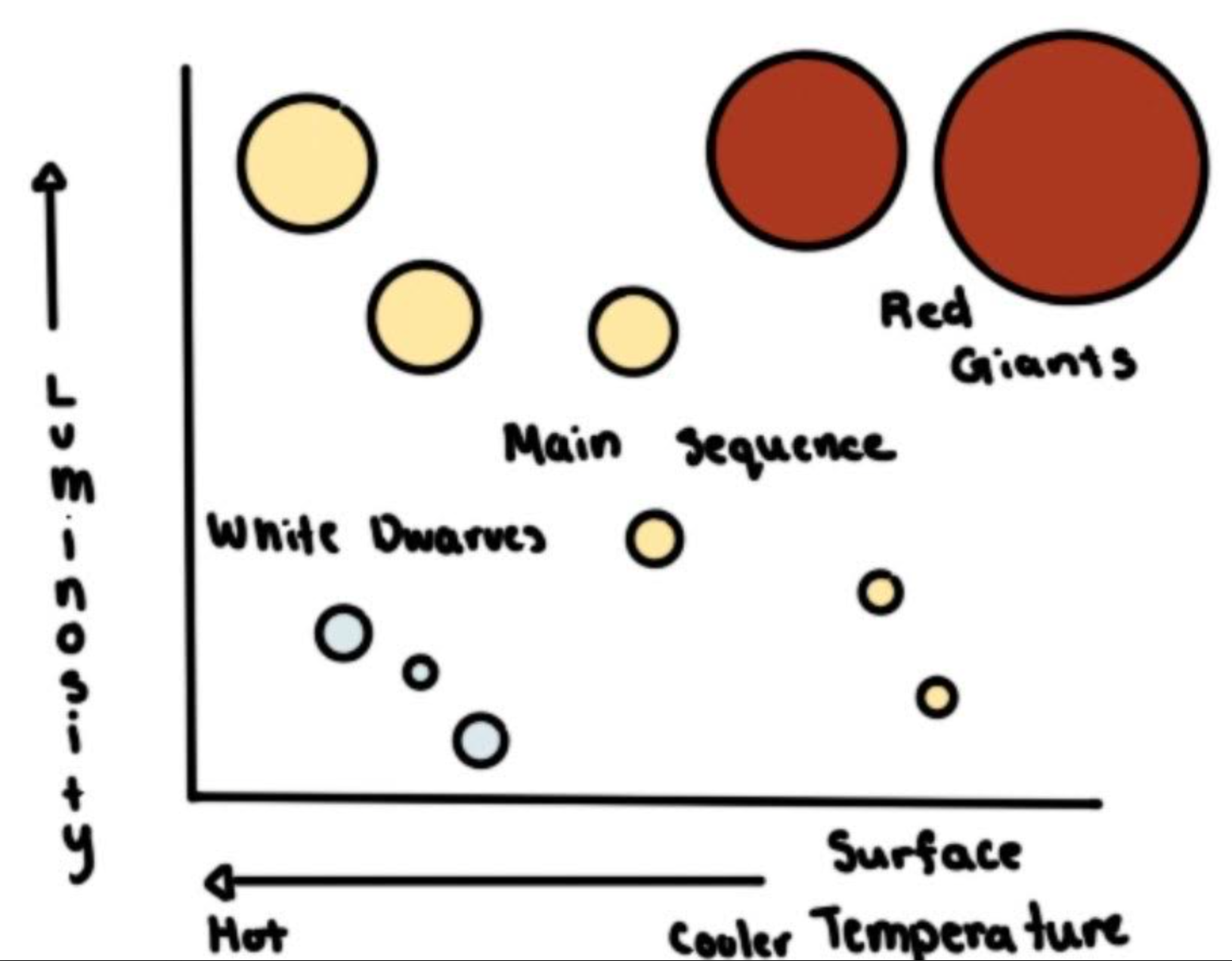
What kind of star is our sun?
Our sun is a red giant
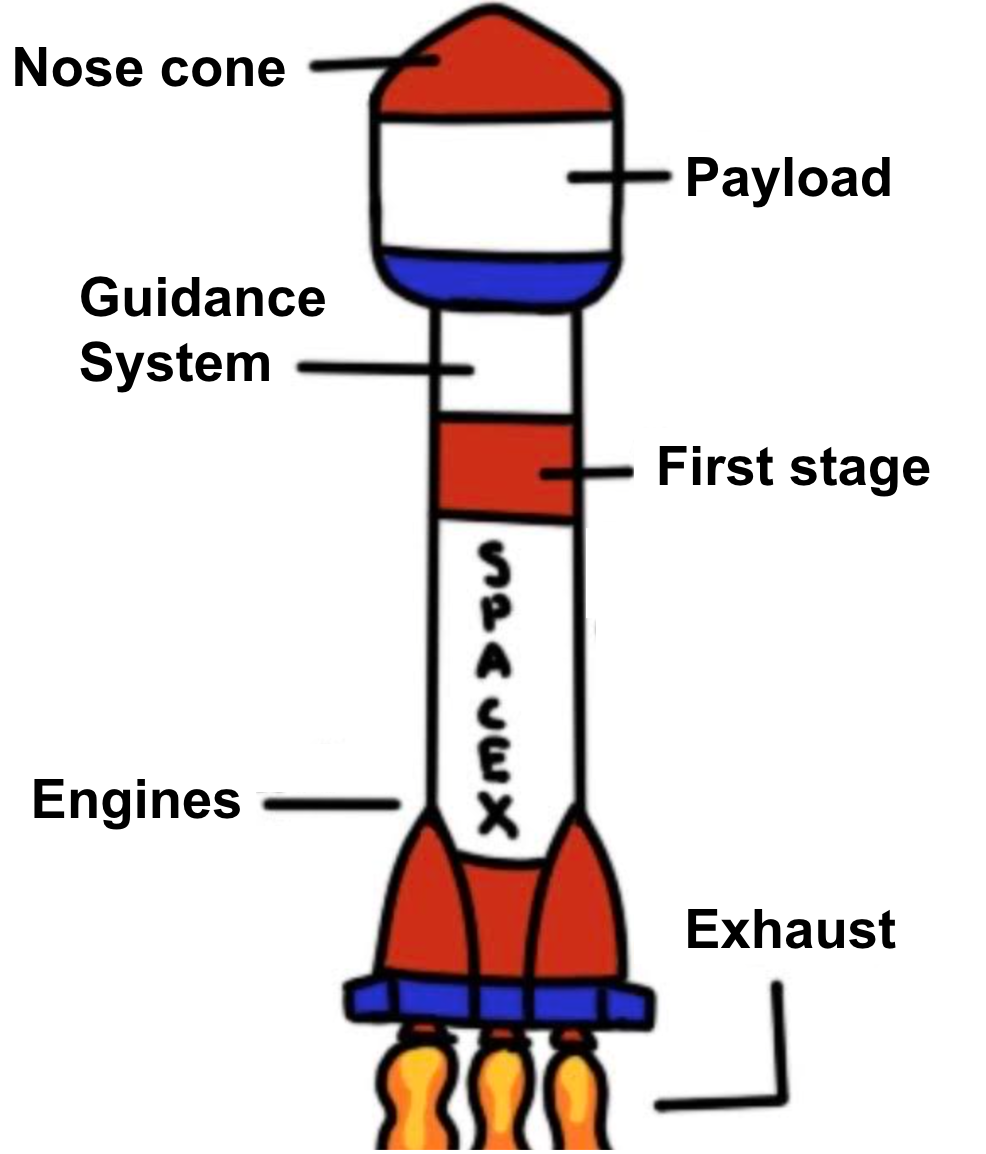
Rocket
A tube that contains a combustible material in one end and a payload on the other
Payload
A device or material that the rocket carries (e.g. explosive, device, person, etc.)
Nose cone
Helps the rocket moves slowly
Guidance system
Steers rocket
Engines
Provide thrust for lift off
First stage
The main body, contains fuel
Exhaust
Gases pushed out by engine
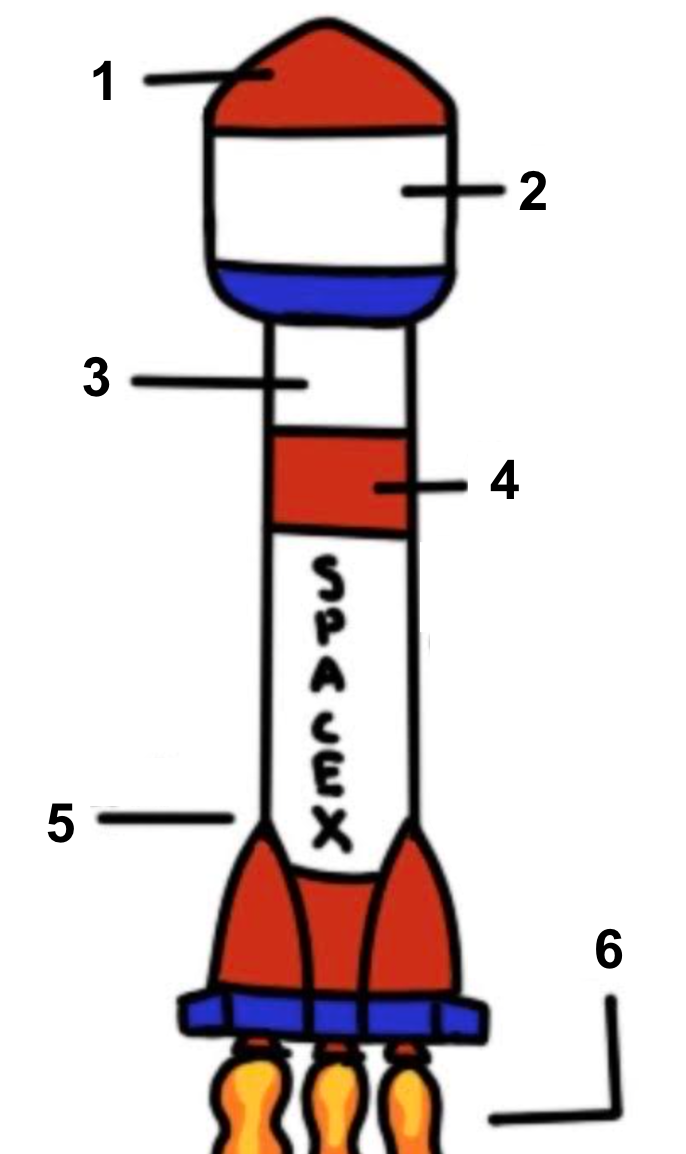
Label Diagram
Staged rocket
A stage is a section that drops off once the fuel is used up, remaining part is lighter, flys faster and higher
Gravitational assist
A method of acceleration which enables a spacecraft to gain extra speed by using the gravity of a planet
Why was gravitational assist developed?
We are unable to send heavy spacecrafts on long journeys (fuel runs out)
What are Voyager 1 and 2?
Space probes built by NASA in the 1970s that used gravitational assist
Describe Voyager 1s journey
Faster, reached Jupiter in 1979 and went to Saturn
Describe Voyager 2s journey
Slower, fixed path, reached Jupiter 4 months after Voyager 1, later going to Uranus and Neptune and now visited farther out planets
Artificial satellite
A device made by humans (e.g. spacecraft or telescope) that will stay in orbit
Naturally occurring satellite
Not man made (e.g. moon or Earth around the Sun)
Geosynchronous orbit
These satellites move in the same direction as Earth’s rotation, are synced with Earth’s orbit (takes 24hrs to orbit Earth). They appear to be motionless from Earth’s surface
Low Earth Orbit
Placed 200-800km above the ground, completes one orbit around Earth in about 1.5hrs (circles Earth faster than it rotates)
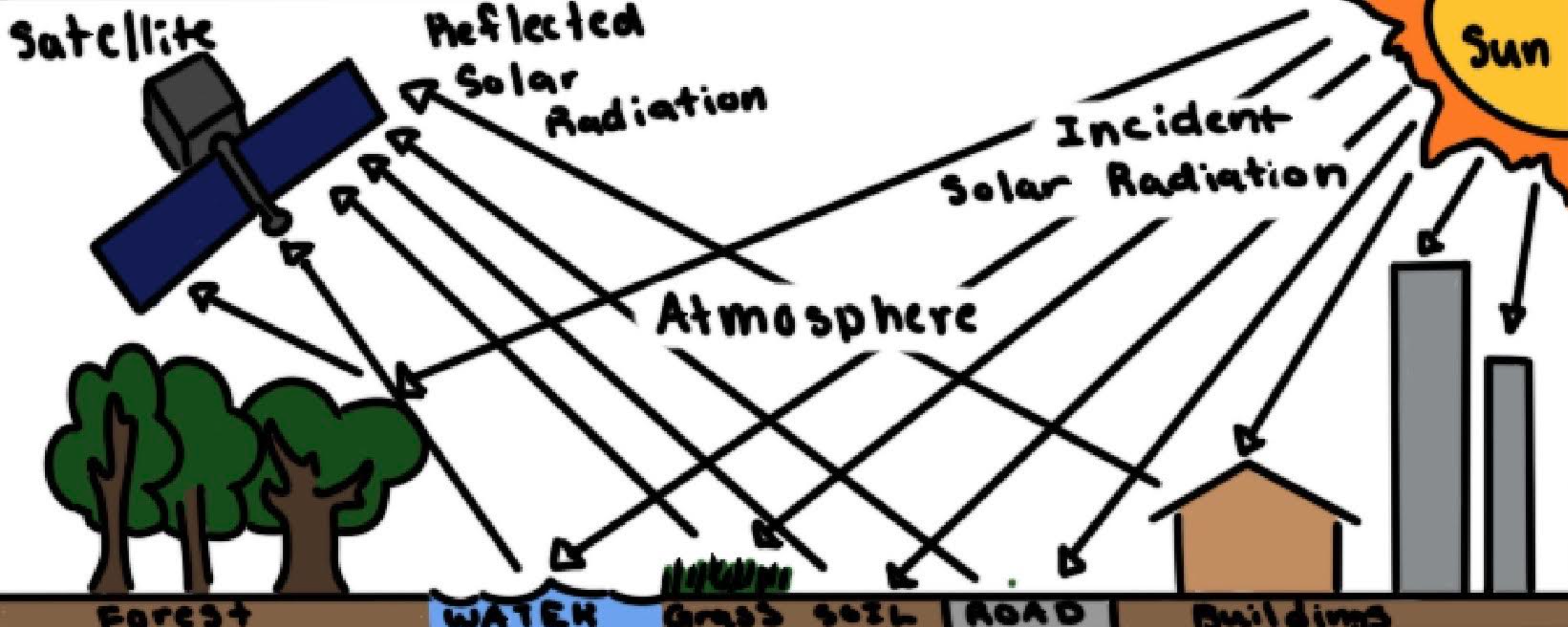
Remote sensing
The science of taking measurements from space (or any planet)
GPS stands for
Global Positioning System
GPS
A fleet of GPS satellites above Earth and small handheld GPS on Earth can help you calculate your position in 30 min
How many GPS satellites are above you at all times?
3
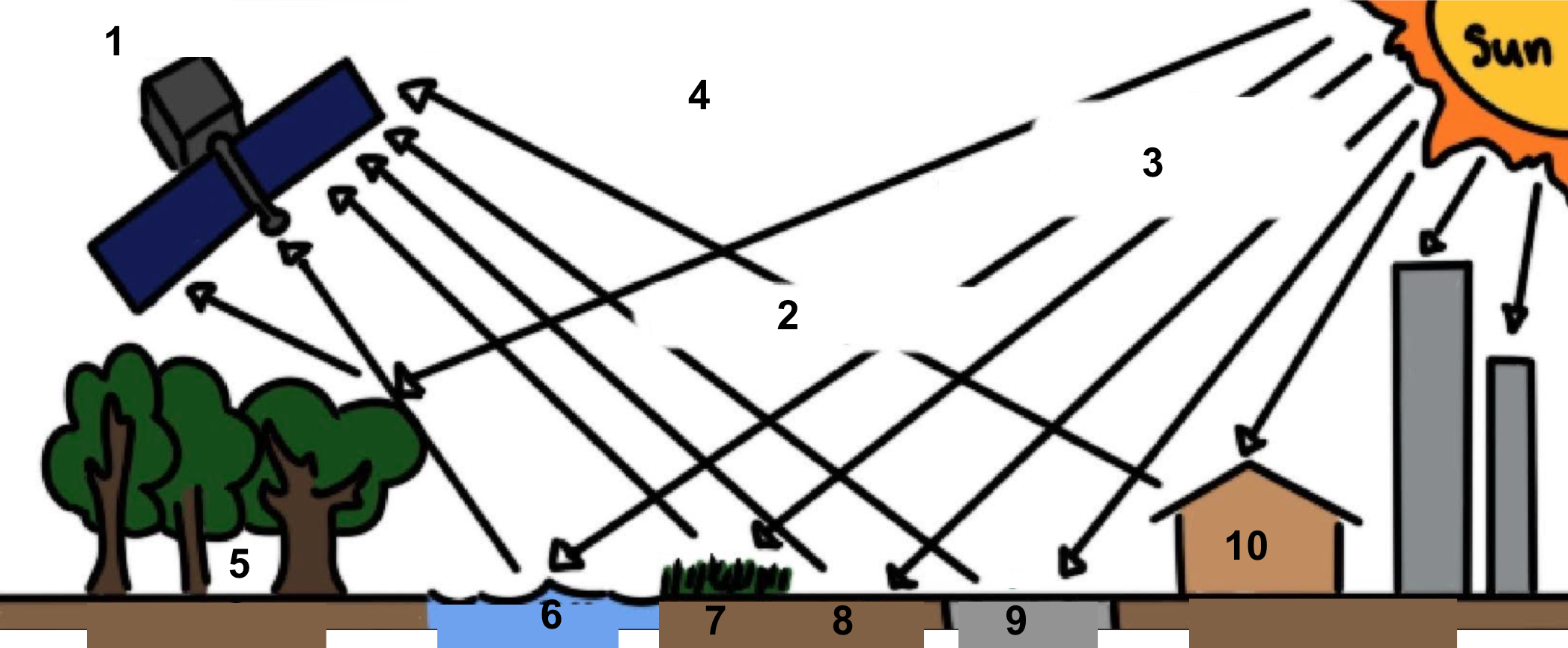
Label Diagram
What are the effects of microgravity on the human body?
Humans experience weightlessness due to weak gravity. This can cause a decrease in bone density, muscle atrophy, coordination concerns, cardiovascular concerns (weakened heart, produces less plasma in space)
What are the effects of temperature in space on the human body?
Without a protective atmosphere temperatures can be very hot or very cold. This isn’t always survivable and protective equiptment is required
What are the effects of oxygen in space?
There is barely any, we need to bring O2 supplies. Reduced oxygen can cause dizziness, impaired judgment and death
What are the effects of air pressure on the human body in space?
Space has no air pressure, unprotected human cells will expand/burst. Fluids in the human body will heat more easily and gases dissolved in bodily fluids are released
What happens to food and water in space?
There are no natural food and water source, food must be made, brought or grown in space. Water must be conserved and recycled (This is very hard todo and is expensive)
What is the effect of radiation on the human body in space?
We have very little protection from forms of radiation in space. Radiation can effect all cells in the human body and can cause cancer, cataracts, and cardio vascular concerns
Space junk
Satellites that are no longer used and other debris left in space as waste
What dangers can space junk cause?
Can collide with spacecrafts and active satellites (dangerous and can cause damage)
What can distance, isolation and confinement cause?
Astronauts can cause physcological and mechanical difficulties/problems. They can experience low morale or depression, decline in cognition, and difficulty with sleep and supplies
Primary Life Support System
PLSS, Provides O2 and pressure to the suit
Secondary oxygen
Supplies O2 if primary oxygen fails or runs out
Cuff checklist
Instructions for during a EVA
EVA stands for
Extravehicular activity, going outside a space craft
Helmet and Visor
Regulates temperature and O2 and pressure in the head area protects from sunlight/ UV
Display and control module
Controls the PLSS
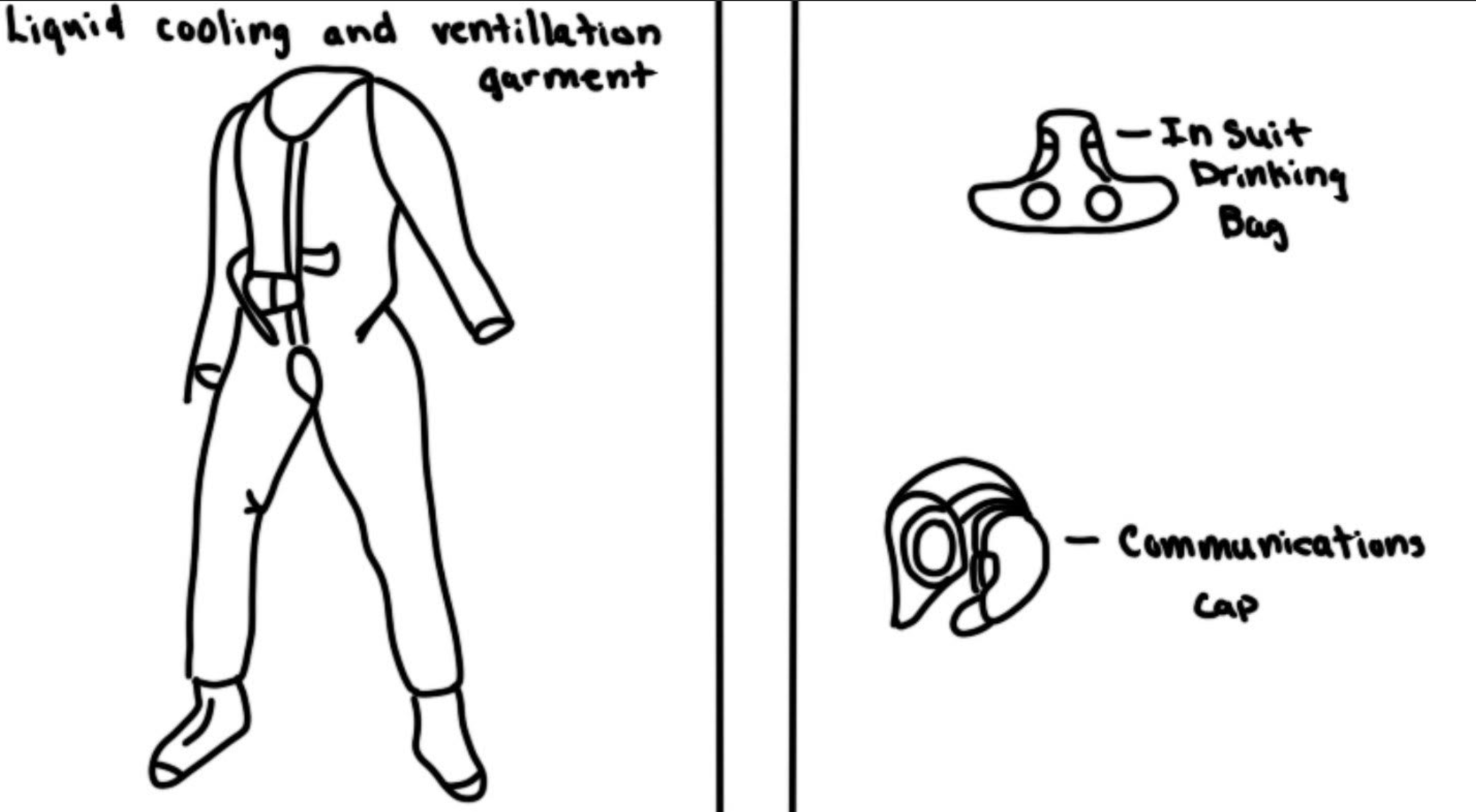
In suit drinking bag
Water supply during a EVA
SAFER
Similar to a jet pack if the astronaut becomes detached during an EVA
Tethers
Keeps astronauts attached during an EVA
Communications cap
Allows for easy communication (radio or internet) during a EVA
Liquid cooling and ventilation suit
Absorbs heat when need or provides heat when astronaut is cold, wicks sweat away from skin
How can most hazards in space be mitigated?
By a space suit
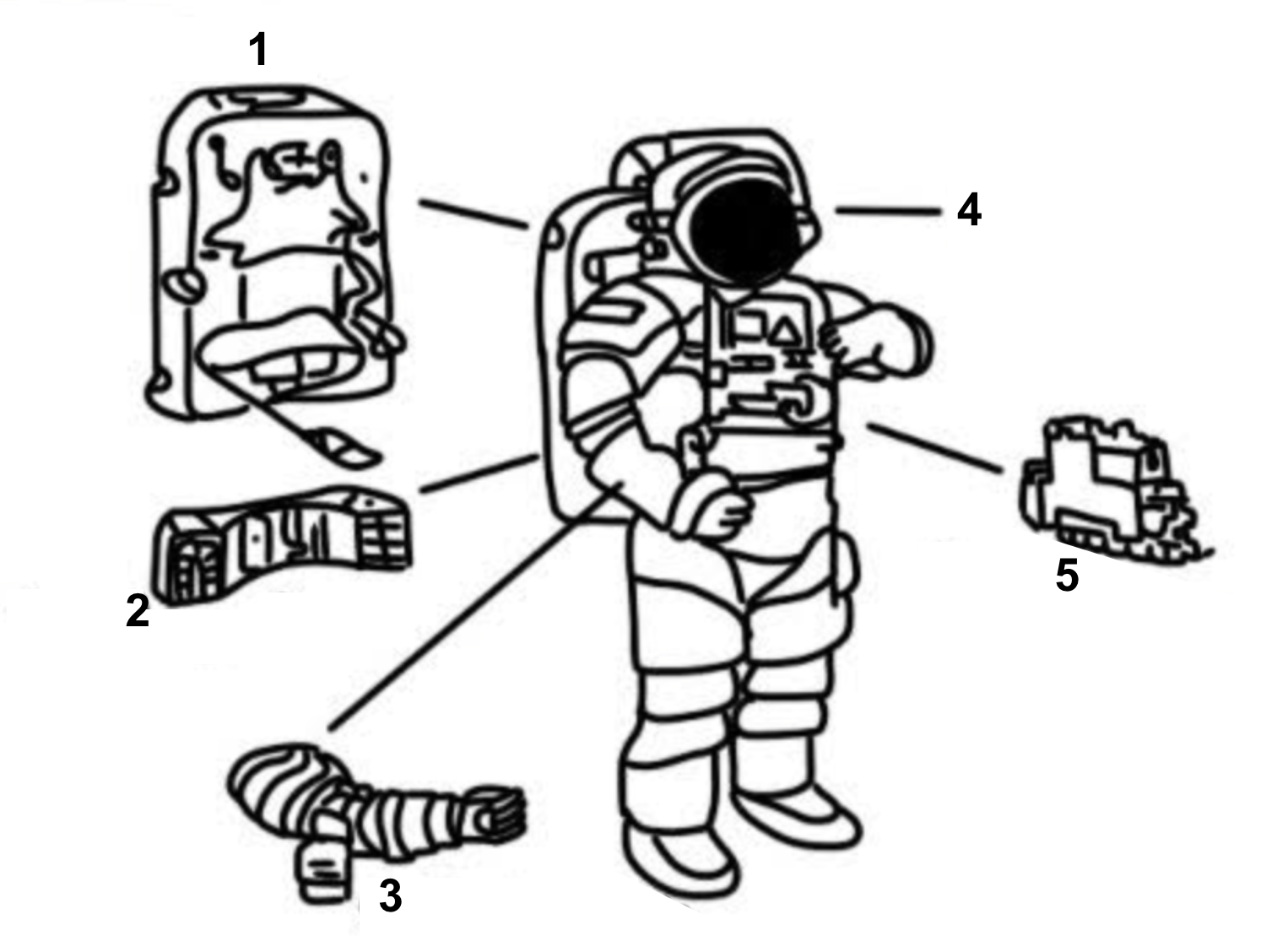
Label diagram
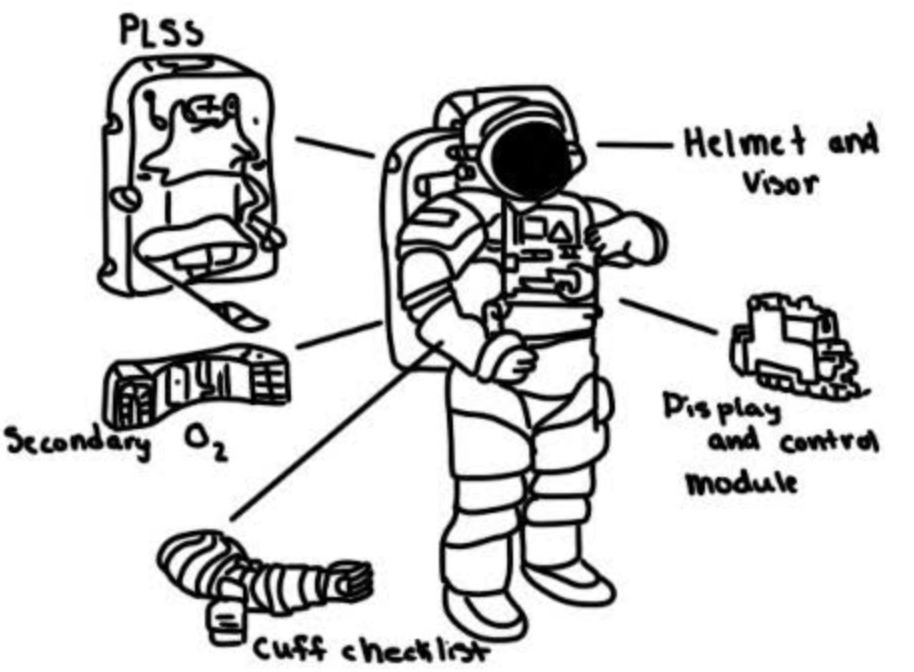
Label diagram