IB Economics Review (Macroeconomics)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
National Income Accounting
Methods for measuring the size of an economy
1) Expenditure
2) Income
3) Output
Gross Domestic Product
Total values of all final goods and services produced in a country
Gross National Income
The total value of all final goods and services produced by people of a country
Real GDP/GNI
Total value of all final goods and services produced (adjusted for inflation)
Real GDP/GNI per capita
Average income, adjusted for inflation
Real GDP/GNI per capita PPP
Average income, adjusted for inflation and cost of living comparison
Business cycle
Increase and decrease of GDP over time
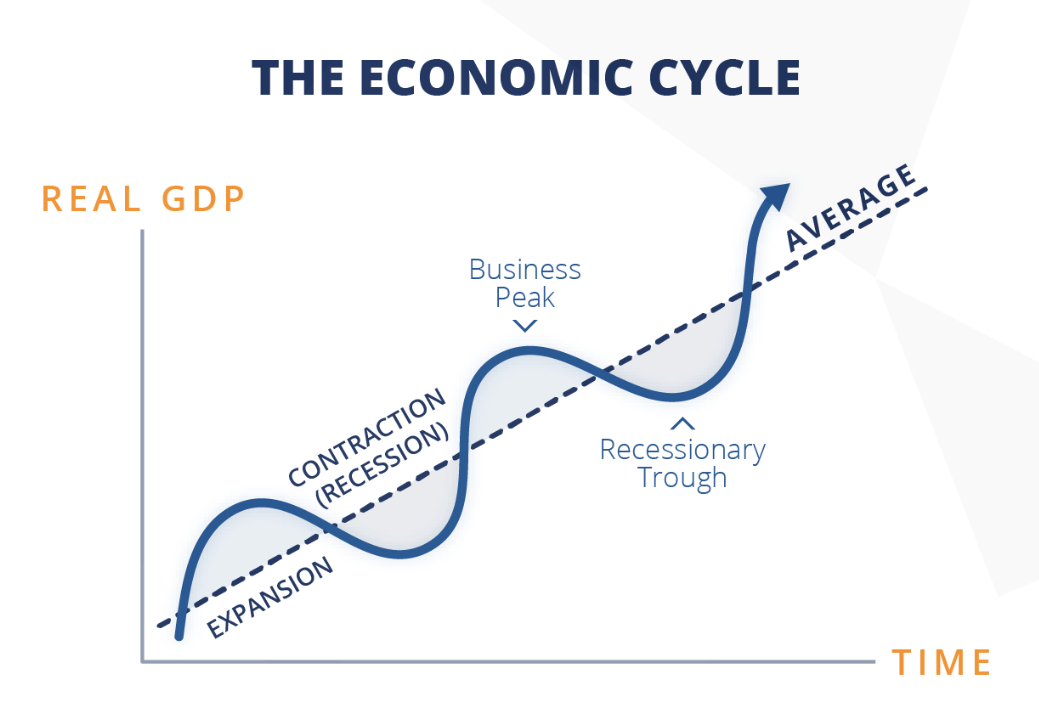
Contraction
Decrease of GDP
Economic Growth / Expansion
Increase of GDP
Recession
Contraction lasting 2+ quarters
OECD Better Life Index
Composite quality of life measure
Happiness Index
Compares reported life satisfaction
Happy Planet Index
Includes life satisfaction and carbon footprint
Aggregate Demand (AD)
Demand for all goods and services / Total spending in an economy
C + I + G + (X-M) = AD
Determinants of AD
Income, wealth, interest rates, business and consumer confidence
Aggregate Supply (AS) / Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
Supply of all goods and services / Total production in an economy
Determinants of AS
Factors of Production, technology, government regulations
Full employment
Maximum number of people working
Natural unemployment
~ 3%
Consistent level of unemployment
Includes structural, seasonal and frictional
Unemployment rate
people looking for work / total labor force
Cyclical unemployment
increase in unemployment as a result of contraction/recession in a business cycle
Structural unemployment
Results from skills gaps / Mismatch between workers and the available jobs
Frictional unemployment
Between jobs, holding up for something better
Seasonal unemployment
Periods that have more unemployment
Summer/winter layoffs
Consumer Price Index
Measures inflation, market “basket” of goods
2% inflation is good!
Demand-pull Inflation
Increasing spending drives up prices
Cost-push inflation
Supply-side inflation
Increase costs of factors of production
Deflation
Falling prices on average, not good!!
Disinflation
Decreasing rate of inflation, 6% → 2%
Good!!
Distribution of income
Difference between income of different groups
REdistribution of income
Government changes the distribution, takes money from rich and gives it to the poor
Gini Coefficient
Measures income inequality in a country
Absolute Poverty
Internation poverty line ($2.15 / day)
Relative Poverty
Compared to national cost-of-living or median income
Multidimensional Poverty Index
Directly measures material deprivation
Access to clean water, schools, etc.
Progressive tax
More tax on the rich than poor
Proportional tax
Everyone pays the same rate
Larger impact on the poor
e.g. sales tax
Regressive tax
More tax on poor than rich
e.g. fees for licenses, parking, admission to museums and parks, and tolls for roads, bridges, and tunnels.
Human Capital
Labor force skills and abilities
Gets better with each generation
Transfer payment
Government redistributing money
e.g. social security
Universal basic income
Government provides transfer payments to all residents
Interest Rates
Amount paid to the bank on a loan
Price of borrowing
Expansionary monetary policy
Lowering interest rates to boost AD and increasing employment
Contractionary monetary policy
Raising interest rates to limit AD and decrease inflation
Real Interest Rate
Interest rate - rate of inflation
Expansionary fiscal policy
Using government spending to boost AD
Contractionary fiscal policy
Reducing government policy to limit AD
(This never really happens)
Inflationary gap
Inflation above the target rate
Recessionary gap
Economic growth below zero
Market based supply-side policy
Reaganomics → low gov involvement, low taxes
Privatization
Reducing government programs over to private companies or corporations
Deregulation
Reducing government regulations on industry
Interventionist supply-side policies
Using government programs to support firms. Investings in education, infrastructure and training