HTN/HLD
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
LDL
“bad cholesterol”
increased by cholesterol, saturated + trans fats
primary target of these drugs
VLDL
“very low density lipoproteins”
secreted by liver
some convert to LDL
increased by sucrose, fructose, excess calories
also is the carrier of TGs to peripheral tissue
bad in 3 freakin ways
triglycerides
really high —> risk for pancreatitis
increases after eating; so take labs BEFORE eating
can be drug-induced (TPN, propofol, alcohol)
increased by
total fat
alcohol
excess calories
HDL
“good cholesterol
anti-atherosclerotic effect
bc takes cholesterol away from artery walls
HDL helps get rid of cholesterol!! so good for CV pts to have a lil high HDL
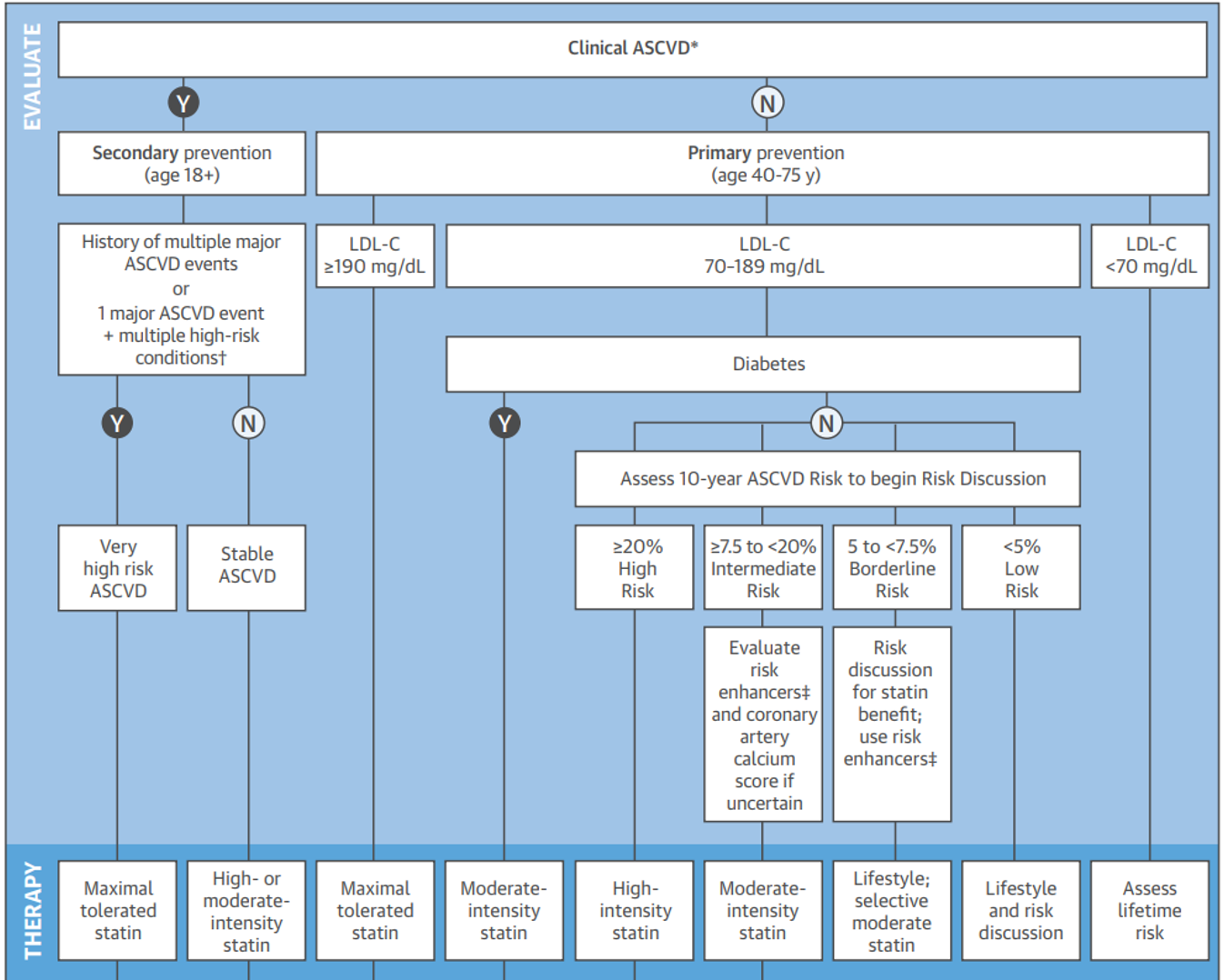
primary treatment algorithm (she will give this)
if they already have CV disease, need to go to secondary to prevent further events
first look at LDL
check if they have DM
if no DM, look at framingham risk score to see if high mod or borderline risk
anybody with intermediate risk or higher, DM, or CV event —> statin!!!
do they have an event or not? what’s their LDL? do they have DM? what’s their framingham risk?
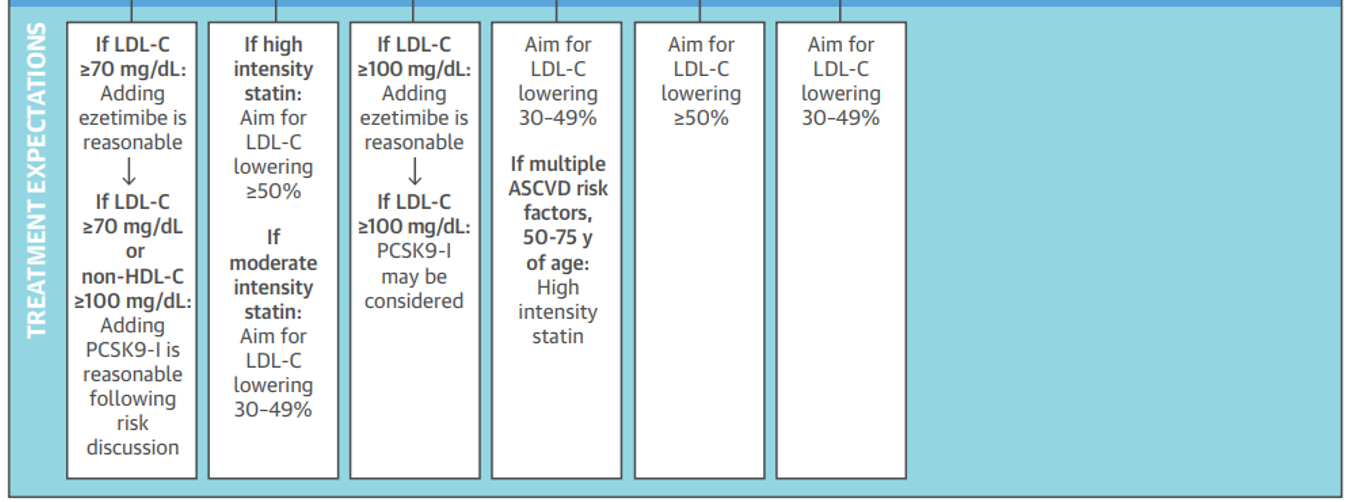
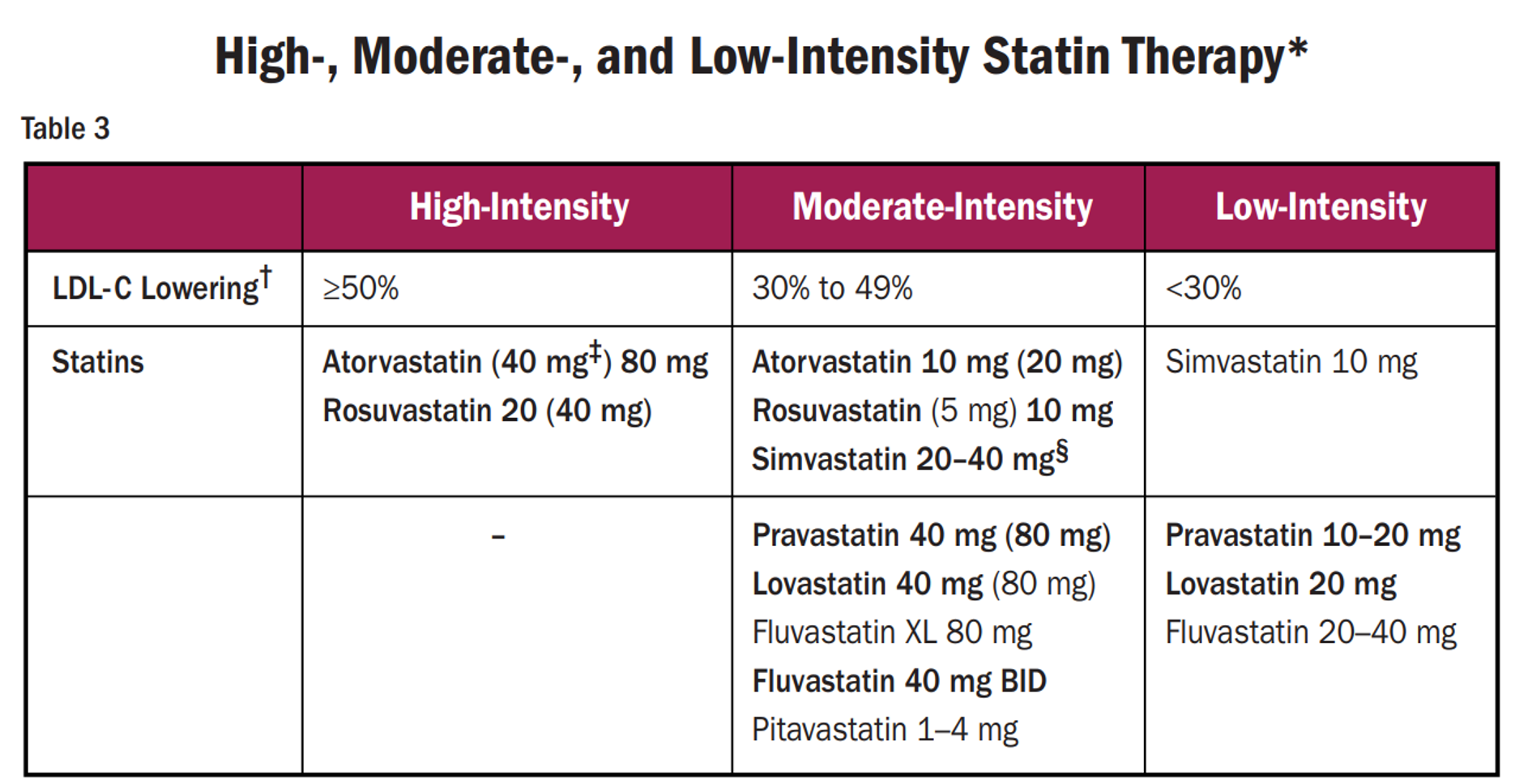
KNOW THE EXTREMES**
high intensity
atorvastatin 40 or 80mg
rosuvastatin 20 or 40mg
this is the only way to to lower LDL by 50% or more
which patients have risks outweighing benefits for statins?
maintenance HD
LDL <70
Class 2-4 HF
risk for adverse effects too high
initial evaluation labs
fasting lipid panel:
LDL, TG, ALT, CK (if indicated), A1C (statins increase risk for developing DM); Hx of prior/current muscle Sx
fasting lipid panel
to assess adherence and predicted response; repeat at 4-12 weeks then q 3-12 months
TG value to treat
>500***
LDL value to treat
>190
ALT
>3x upper limit of normal = contraindicated bc statins are highly metabolized by liver
baseline muscle pain
bc we might attribute it to the statin when it might have been underlying
all med categories
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins)
fibrates
bile acid sequestrants
sterol absorption inhibitor
nicotinic acid
omega-3 ethyl esters
plant sterols/stanols
red yeast Chinese rice
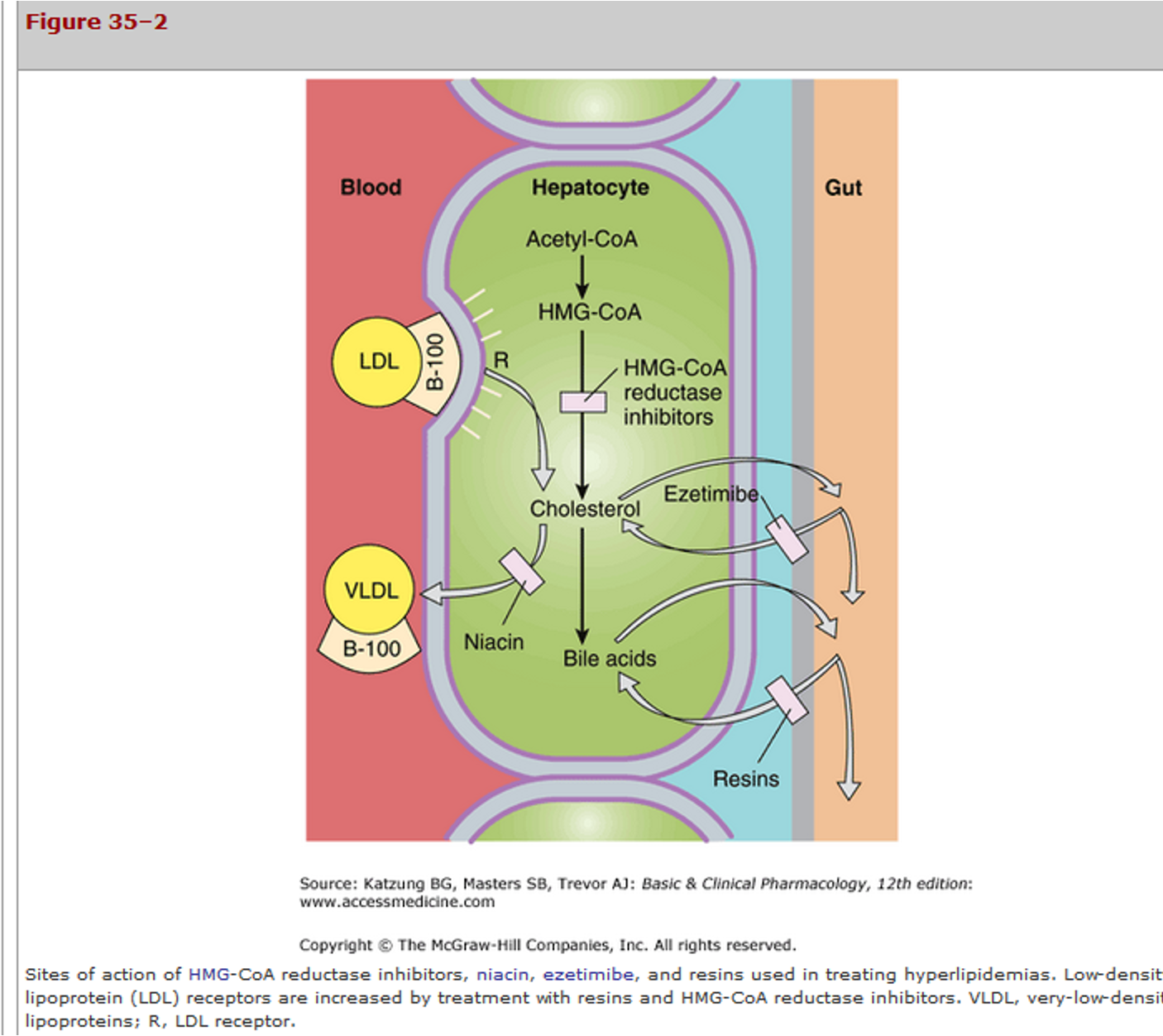
statins MOA
HMG-CoA is converted to cholestererol by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
statins BLOCK this process —> reduces cholesterol synthesis
upregulates LDL receptors on hepatocytes
recycling/removal the LDL already there
ULTIMATELY —> prevents more being made, removing what’s there
statins ADEs
rare confusion state or memory impairment
hepatic dysfunction
avoid in severe hepatic impairment
myopathy
rhabdomyolysis (increased CK)
DM
hemorrhagic stroke potential if plaque ruptures
contraindicated in pregnancy/lactation!!
when are statins most effective?
in the evening because that’s when the most cholesterol is made
who’s at higher risk for adverse effects with statins?
multiple comorbidities (renal/hepatic impairment)
Hx muscle disorders
unexplained ALT >3x ULN
age >75 yrs
genetic factors that decrease statin metab, clearance
drug interaction risk bc lots of CYPs
lipophilic statins vs hydrophilic statins
lipophilic more likely to cross into muscle than hydro
—> proteolysis & apoptosis —> muscle Sx
lipophilic statins
atorvastatin, simvastatin, lovastatin
hydrophilic statins
rosuvastatin, pravastatin
LESS muscle pain!!
if muscle symptoms happen, and if severe, ____
d/c statin; R/O other causes
it SHOULD be reversible else it’s something else
if severe, check CK, creat, UA for myoglobinuria
checking for rhabdo
more likely with lipophilic (atorva, simva, lovas)
mild-moderate muscle Sx: resolve and no contraindications
restart same statin or lower dose
mild-moderate muscle Sx: resolve so statin IS the cause
use low dose of different statin then increase as tolerated
mild-moderate muscle Sx: Sx unresolved after 2 months
identify other causes then restart same statin at same dose
high-intensity statins
atorvastatin (lipitor) and rosuvastatin (crestor— reduce with renal impair)
both are CYPs
<1L grapefruit juice daily
fibrates names
lopid (gemfibrozil)
CYP!!
tricor (fenofibrate)
fibrates MOA
decreases VLDL secretion
increases lipoprotein lipase (breakdown)
increase HDL
fibrates ADEs
dyspepsia, rash
HYPOkalemia
myopathy
hepatic dysfunction
gallstones
rhabdo
AVOID IN RENAL/HEPATIC impairment
avoid in obesity bc inc risk gallstones
avoid using fibrates with statin because ___ unless ____
because increased risk for myopathy, rhabdo (same ADEs)
UNLESS TG >500!! can add to low or moderate intensity statin
ezetimibe MOA
prevents absorption of cholesterol from gut into liver
also inhibits reabsorption of cholesterol and decreases LDL
cholesterol still being made, just won’t be absorbed
in combo with statins
ezetimibe ADEs
rare hepatic dysfunction, myositis
ezetimibe monitoring
baseline LFTs
contraindicated during pregnancy/lactation
use with STATINS!!
bile acid sequestrants names
colestid (colestipol)
questrand (cholestyramine)
welchol (colesevelam)
bile acid sequestrants MOA
sequestering bile acid —> can’t absorb into intestinal lumen —> increase cholesterol breakdown
also breaks down LDL receptors
NEVER LEAVE THE GUT so no systemic SEs
bile acid sequestrants ADEs
constipation, bloating, heartburn, diarrhea, increased VLDL (only local effects)
bile acid sequestrants monitoring
fasting lipid banel at baseline, 3 months, q6-12 months
bile acid sequestrants considerations
avoid in diverticulitis, TG >250 so NOT FOR TGs!!
can impair vit K and folic acid absorption
NEED to take with food
other meds 1 hr before or 2 hours after
niaspan (nicotinic acid) other name + MOA
aka Vitamin B3
MOA
dec VLDL hepatic secretion
inc HDL, dec LDL/TG
nicotinic acid monitoring
start low; titrate up
fasting BG, A1C, LFTs, uric acid
nicotinic acid ADEs
severe flushing so premedicate with ASA 325mg 30min prior to dose
teratogenic!!
also pruritis, rash, dry skin, N, abd discomfort, hyperBG, arrythmias
d/c nicotinic acid/niaspan/vit B3 IF
persistent severe cutaneous Sx
persistent hyperBG
acute gout
unexplained GI Sx
new-onset afib or weight loss
omega-3 ethyl ester name
lovaza aka fish oil!
ONLY for TGS
lovaza MOA
reduce hepatic synth of TGs
lovaza ADEs + monitoring
pruritis, rash, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, constipation, LFTs abnormals
may increase LDLs
monitor for GI changes, skin changes, bleeding
when would we consider adding lovaza?
when TG >500
can use with high-intensity statin (atorvastatin (lipitor) and rosuvastatin (crestor)
both CYPs
PCSK9 Inhibitors names
praluent (alirocumab)
repatha (evolocumab)
only if they failed statin therapy
PCSK9 inhibitors use + ADEs
technically the most effective for lowering LDL but they’re INJECTIONS q2-4weeks! and also very
ADEs
rash, itchy, swelling, pain or bruising at injection site, flu, allergic rxns
which one doesn’t touch TGs?
bile acid sequestrants
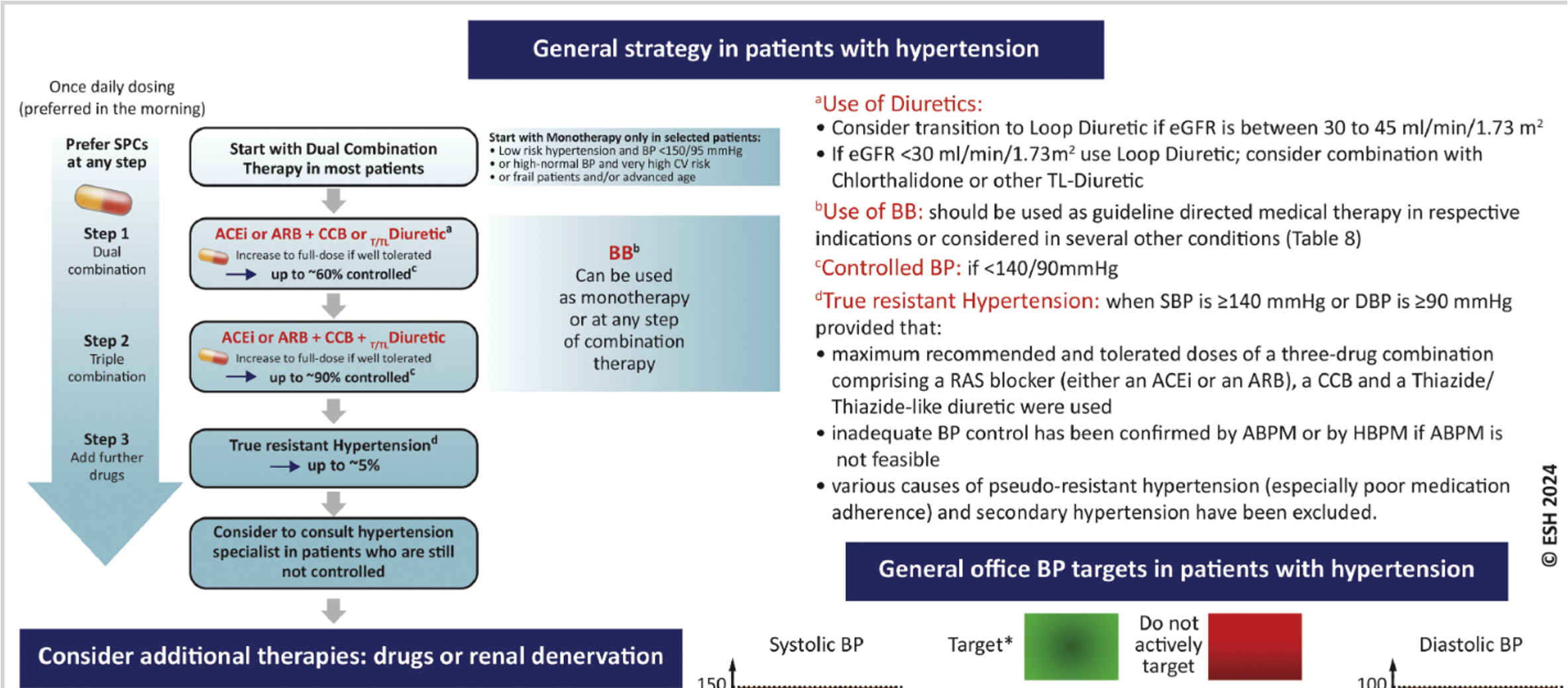
HTN treatment + goals (she will give us this chart)
DUAL therapy— either ACE or ARB + Ca channel blocker or diuretic**
prevents side effects of Ca channel blockers
monotherapy if low risk
can also use beta blockers as second drug or monotherapy
aim for BP control within ____
3 months
HTN drug classes
thiazide/thiazide-like diuretics
Ca channel blockers
ACEi
ARBs
do NOT use __ & __ together
ACEi & ARB because they work on the same RAAS system
thiazide names
hydrochlorothiazide
chlorTHALIDONE
indapamide
metolazone
thiazide MOA
works in distal convoluted tubule for sodium reabsorption
if i block sodium reabsorption and Na stays in urine, water stays in urine —> pee it out —> lowers BP
eventually normalizes CO, decreases SVR
thiazide ADEs
hypoNa
hypoK BOTH low
metab alkalosis
photosensitivity
hyperBG
weakness
monitor lytes, BP, fluid status
thiazides are less effective for who?
renal pts
won’t get to site of action in same amount
it’s so far down the nephron
what’s one way to increase thiazide efficency?
give with a loop diuretic
RAAS general overview
angiotensinogen is converted by renin (from kidneys) —> AG1
AG2 UPs aldosterone —> more salt/water retention —> BP up
how do ACEi work?
stops AG1 —> AG2
how do ARBs work?
block receptor directly
this is also why we can use ONE OR THE OTHER, not both
ACEi names
-prils
ACEi oral formulations
prodrugs so need hepatic activation through hydrolysis NOT CYPs so not a lot of drug interactions
ACEi ADEs
hyperK
dry, hacking cough (can happen anytime)
can switch to ARB or try a different ACEi
angioedema —> never use again!
switch to ARB
rash
dysgeusia
ACEi considerations
avoid in pregnancy! esp 1st trimester
hold in AKIs
but actually helps stabilize CKD (dec proteinuria)
protective effect for neprhon bc vasodilates Efferent arteriole —> reduces pressure IN nephron
enalaprilat
IV formulation of enalapril
ARBs names
-sartans
which ARBs are CYPs?
losartan
irbesartan
ARB MOA
blocks AG receptor
ARB ADEs
fatigue
diarrhea
hyperK
angioedema (not as often)
NO dry cough
contraindicated in pregnancy!
(ACEi/ARB) in volume depleted pts,
hypotensive— monitor BP especially with 1st dose
if angioedema,
life threatening!
stop drug immediately
do ARBs, CCB, or thiazide instead
monitoring hyperkalemia
monitor K 1-2 wks after starting drug and with each titration
know their baseline K
advise about salt substitutes that have high K
CCB: Dihydropyridine names
amlodipine (norvasc)
nisoldipine (sular)
nifedipine
immediate release
nicardipine
clevidipine
only IV, very short acting
all -dipine
all CYPS!!!
CCB: Dihydropyridine MOA
potent peripheral vasodilation
won’t affect HR or output
CCB: Dihydropyridine ADEs
peripheral edema
flushing
h/a
dizzy
which CCB is immediate release?
nifedipine
BLACK BOX WARNING**
avoid using for acute Tx of HTN crisis
increased risk of MI, CVA, death
CCB: Nondihydropyridine names
diltiazem
verpamil
CCB: Nondihydropyridine MOA
work on CC in HEART rather than periphery
reduces HR, conduction rate —> lowers BP
CCB: Nondihydropyridine ADEs
bradycardia**
heart block
higher risk if used with BBs
constipation (main effect)**
peripheral edema
also will inhibit PGP and CYP**
avoid diltiazem/verapamil in ___
HF 2/2 systolic dysfunction rt negative inotropic effects (weakens the force of muscular contractions)
the NONdihydropyridine CCBs are really not for HTN, more for HR**
when do we use “alternative meds”?
mostly for a patient who has another indication to need this med
OR if difficult to treat HTN
add on to 3 drug regimen or might be a substitute if indication
loop diuretic names
alternative med bc don’t have best CV benefit compared to ACEi/ARBs
lasix
bumex
torsemide
CYP
loop diuretics MOA
works in LOOP of Henle
blocks sodium/water reabsorption
better than thiazides for CHF/CKD
loop diuretics ADEs
hypoNa
hypoK
hypoMg
dehydration
ototoxicity (may not be reversible)
photosensitivity
rash
all are sulfas (except edecrin)
K-sparing diuretics names + MOA
amiloride
triamterene
MOA: epithelial sodium channel blocker
K-sparing diuretics ADEs
hyPONa
HYPERK
others bring both down; this brings K up
metab acidosis
dehydration
kidney stones
reduce dose in renal impairment
aldosterone antagonists names
spirinolactone
NOT selective to aldosterone in kidney only, works everywhere (HRT, acne)
can also cause gynecomastia
eplerenone
-one
both also K-sparing!!
aliskiren (Tekturna)
renin inhibitor (renin converts angiotenosigen into AG1)
BUT not very effective bc too far upstream
avoid in pregnancy!
sympathoplegic: central-acting names
clonidine
methyldopa
clonidine
MOA: central alpha-2 agonist —> dec sympathetic
inc PARASYMPH —> reduced peripheral vasc resistance, bradycardia —> reduced CO
ADEs
sedation, depression, xerostomia, confusion, N/V
abrupt withdrawal —> HTN crisis!!!!**
after missing only 1-2 doses
alpha-2 agonists
negative feedback loop
A2 receptors shut DOWN SNS —> reduce BP
methyldopa
central-acting; reduces periph vasc resistance
primarily used during pregnancy
beta blockers MOA
beta 1 ANTAGonists
dec HR, myocardial contractility, periph vasc resistance
reduce renin release
beta blockers ADEs
bradycardia
bronchoconstriction (from beta 2 after losing selectivity)
hypoglycemia unawareness
when you have low BG —> SNS activated; Sx being blocked with beta blockers
sexual dysfunction
depression
caution in depression, asthma pts
abrupt dc —> rebound tachy**
beta 1 receptors vs beta 2; alpha vs beta
1 heart
beta 2 lungs
alpha = constrict
beta = dilate
beta blockers are most effective when
used with a diuretic to combat compensatory mechanisms
alpha blockers names
doxazosin (cardura)
terazosin (Hytrin)
prazosin (minipress)
-azosin
alpha blockers MOA
alpha 1 antag = constrict on heart antag —> directly vasodilates
alpha blockers ADE
orthostatic hypotension**
dizzy
fatigue
h/a
rare priapism