FALL Midterm
1/88
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Alphabetic principle
Letters and letter patterns represent the sounds of spoken language, different from oral language and phonemic awareness.
Letter knowledge
The same letter can look different (Aa), and letters have names related to sounds.
Phonological awareness
The idea that students are aware of phonemes, alphabet letters, and their sounds.
The ability and awareness to work with sounds, ultimately for word reading. (sounding out, blending, word reading)
Print awareness
Understanding the nature and uses of print, recognizing words. Understanding the forms and functions of printed language
Book conventions
Defining characteristics or must-haves of a text; where to start, how it's held, location of the print.
Conventions of print
Awareness of how print works: concepts of words, word boundaries, sentences (separate words with capital letters and punctuation).
Functions of print
Print carries meaning, used for different purposes, and corresponds to speech.
Print referencing
A read-aloud strategy used to direct students' attention to forms, features, and functions of written language. (using finger to track reading)
Continuous Stroke
A way to write letters without lifting the pencil in order to prevent mistakes. Fewer strokes: fewer steps to remember and fewer chances to make mistakes
Letter-Name Idonicity
the names of the letters contain the sound that the letter represents (c=cee) (a= aye) (b=bee)
Letter-Sound Correspondence
THE SOUND A LETTER MAKES. a letter whose name contains it's relevant phoneme is learned more easily than the letter sound correspondence for a letter whose name does not contain it's relevant phoneme.
Lowercase Letters
the shorter, smaller versions of letters
phonological similarity
the number of phonemes that pairs of letter names share in the same position. (p= pē, b=bē)
Uppercase letters
the bigger, taller versions of letters
Onset
all sounds in the syllable that come before the vowel sound (example thr)
Rime
the vowel sound and every other sound that follows the vowel sound in a syllable
Phoneme
the smallest unit of sound in a spoken language
Morpheme
The smallest parts of words that create meaning
Diphthong
A sound formed by the combination of two vowels in one syllable.
Affix
Bound morphemes; an additional element placed at the beginning or end of a root, stem, or word, or in the body of a word, to modify its meaning
R-Controlled Vowels
The letter R affects the sound of the vowel(s) that precedes it. (Ex. er, ir, ur, ar, or)
Syllable
a unit of pronunciation having one vowel sound, with or without surrounding consonants, forming the whole or a part of a word
Vowel Combination
a syllable with a short vowel, long-vowel, or diphthong sound spelled with a vowel combination such as ai, ea, ee, oi, or oo
Root
a single word that cannot be broken into smaller words or word parts in which the prefix and or suffix is attached to form a new word
Consonant le
a final, separate syllable containing a consonant followed by the letters Le.
Digraph
two consonant letters that together stand for a single sound. (Example: gn, kn, ey)
Schwa
the central vowel sound sometimes heard in an unstressed syllable
Stop Sounds
sounds that can be produced for only an instant. Ex. /b/, /d/, /g/, /h/, /j/, /k/, /p/, /t/
Phonogram
Non-Linguistic term for rime.
Suffix
a morpheme added at the end of a word to form a derivative, e.g., -ation, -fy, -ing, -itis. It might change the meaning, tense or form of the root word.
Consonant
complete/partial closure of the voice tract
Continuous Sounds
can be produced for several seconds
Prefix
"fixed" to the beginning of the root word
Sound/spelling
a phoneme/grapheme pairing
Vowel
open, unobstructed speech sounds - not consonants
Vowel-consonant e
VCE words - long vowel sound, consonant, silent "e"
Grapheme
Printed or visual symbol (a letter)
Print Concepts
organization and basic features of print
What is a major source of reading failure?
Ineffective teaching methods
What word describes the brain activation patterns in good and poor readers?
different
What is NOT a defining characteristic of a student with dyslexia?
Poor vocabulary
What could be a cause of the fourth grade slump?
Reading of academic text containing more challenging words and concepts
What is NOT one of the essential components of comprehensive reading instruction?
Silent reading
Which type of reading assessment is appropriate for all students at the beginning of the school year?
Screening
How often should a teacher monitor the progress of students who are reading significantly below the expected level?
Weekly or biweekly
What might be a cause of an adolescents low motivation and interest in reading?
Difficulty in first learning to read
Where are students most likely to encounter new academic vocabulary?
children's books
All of the following statements describe effective reading instruction for ELL's, except which one?
ELL's first language literacy does not affect their literacy development in English
Approximately how many different phonemes are there in spoken American language?
43
What is the difference between a phoneme and a grapheme?
A grapheme is written and a phoneme is spoken
What does it mean for a phenomenon to be voiced?
You can feel it vibrate
What is an example of a continuous sound? (Multiple answers)
/m/ /s/
How are the distinct vowel sounds produced?
By changing the tongue and lip positions
What is a word that has two open syllables? (Multiple answers)
Veto
All of these syllable divisions are correct except which one?
Pap-er
What is the onset in the word "flame?"
Fl
What phrase could you use to describe the word "mailbox?"
A compound word made up a free morphemes
What changes when you add the derivational suffix -ful to the word "care?"
The part of speech
Which three early literacy domains form the foundation of literacy learning?
Print awareness, letter knowledge, and phonological awareness
What statement accurately describe the three early literacy domains?
The domains are interrelated
Which early literacy skills are the foundation of the alphabetic principle?
Letter knowledge and phonological awareness
What is the alphabetic principle?
the relationship between letters or combinations of letters (graphemes) and sounds (phonemes)
What is an example of a book convention?
A left page is read before a right page
All of the following statements describe functions of print, except which one?
Printed words are made up of letters
When a teacher opens a story book and ask, "can you tell me how many words are in the sentence," what print wearing a skill is the teacher assessing?
Sentences and print are made up of separate words
All of the following strategies, promote print awareness, except which one?
Limiting the choice of classroom reading materials
What is the name of a read aloud strategy for teaching print awareness?
print referencing
What print awareness skill should be developed by the end of kindergarten?
Being able to differentiate between letters and words
What are the five pillars of reading?
1. Phonological awareness
2. Phonics
3. Fluency
4. Vocabulary
5. Comprehension.
What are the five pillars of literacy?
1. Reading.
2. Writing.
3. Speaking.
4. Viewing.
5. Listening.
What is the science of reading?
- comprehensive body of research
- Literacy, psychology, neurology
- encompasses years of scientific knowledge under many languages
All of the following are benchmarks of letter knowledge except which one?
Ability to sing the alphabet song
Which lowercase letter shape might be easiest for a student to learn?
u
Which statement describes the concept of letter-name iconicity?
Knowing a letter's name can be used to learn the letter's sound
What is the benefit of teaching letter-name iconicity?
letter names and sounds can be taught together
What is an example of an iconic letter name?
b
What phonologically similar letters are early readers likely to confuse?
d and t
Which phonologically and visually similar letters are early readers likely to confuse?
b/p
Which statement describes children's learning of letter names and sounds?
Children can more easily identify a letter's sound when the sound occurs at the beginning of the letter's name.
Which letter sound correspondence might be easiest for a student to learn?
T /t/
What is the purpose of assessing letter naming fluency?
To measure letter-identification speed and accuracy
Phonemic awareness is comprised of several critical components including all of the following except:
Segmenting words
A subset of a larger category of nonfiction
Informational text
Orthographic mapping
involves the formation of letter-sound connections to bond the spellings, pronunciations, and meanings of specific words in memory. It explains how children learn to read words by sight, to spell words from memory, and to acquire vocabulary words from print
sound categorization
Given a set of three or four words, student recognizes the word that has the "odd"
Segmenting/segmentation
Given a whole word, student separates the word into individual phonemes and says each sound
What is the Science of Reading? Is it a curriculum or not? How can you use it to teach students to read? Use information and examples to support your assertions.
comprehensive body of research
not a curriculum, but is used to better reach students in the way they need in order for them to strategies as a “good reader.”
For example, we should teach our students that good readers see a movie in their head rather than just reading fast
What is structured literacy. Use information and examples to support your assertions.
teaching strategies that highlight all of the important parts of literacy
foundational (decoding, spelling, etc.)
higher literacy skills (reading comprehension)
providing patterns for students instead of just having them memorizing words (pip, dip, lip)
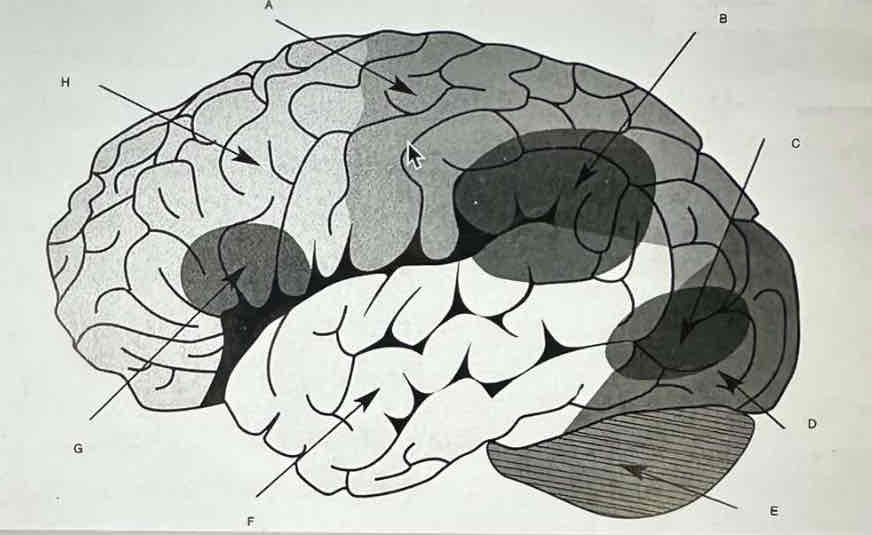
List all the parts of the reading brain
a. Parietal lobe
B. Parieto-temporal area
C. Occipito-temporal area
D. Occipital lobe
E. Cerebellum
F. Temporal lobe
G. Broca’s area
H. Frontal lobe