OPT 329 Wound Repair
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are 2 benefits of eyelid skin being thin?
rapid healing
does not scar much
What affects the speed of recovery in eyelid wounds?
depth
size
microbial contamination
allergies
pt factors = genetics, comorbidities (DM)
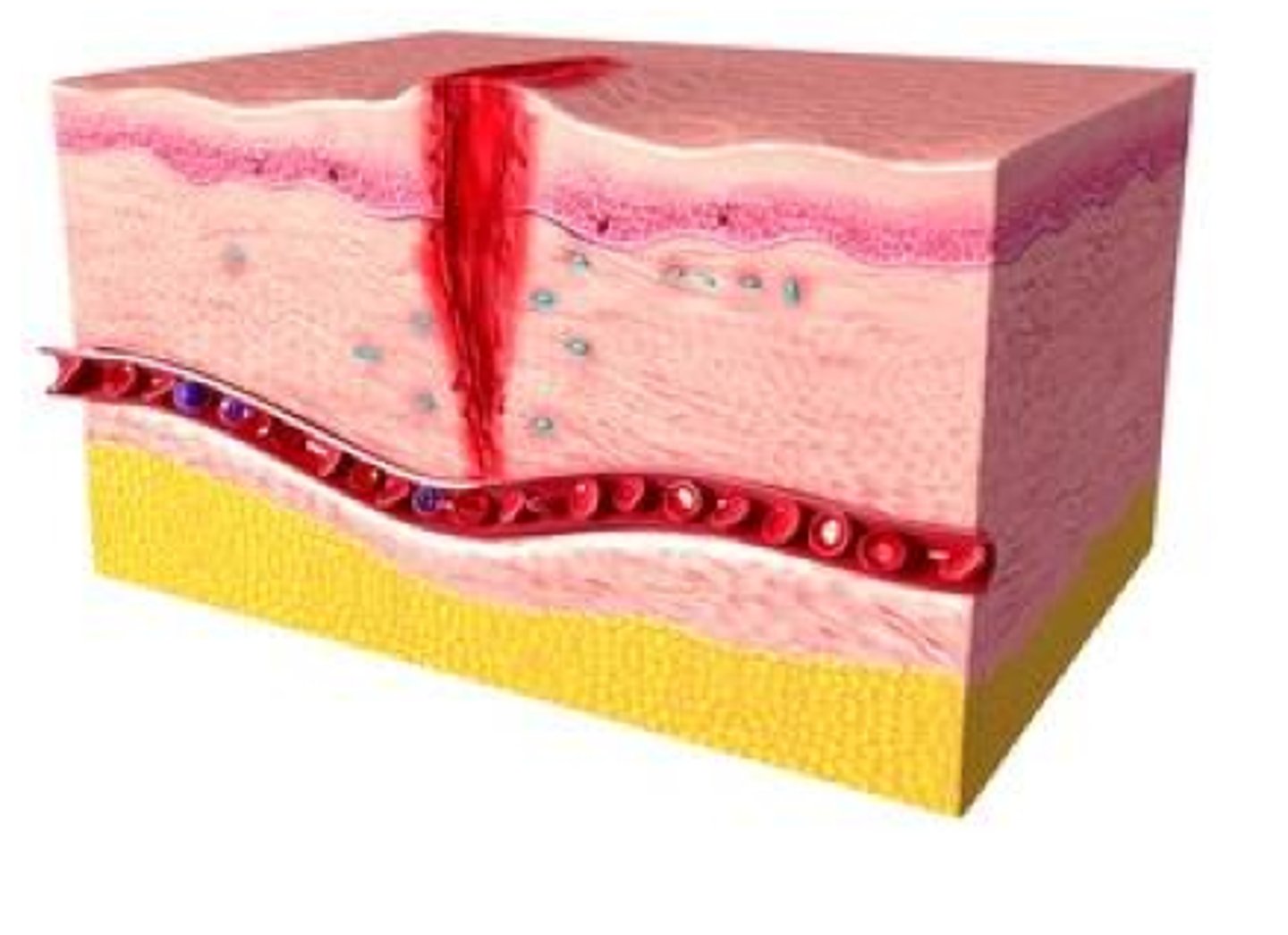
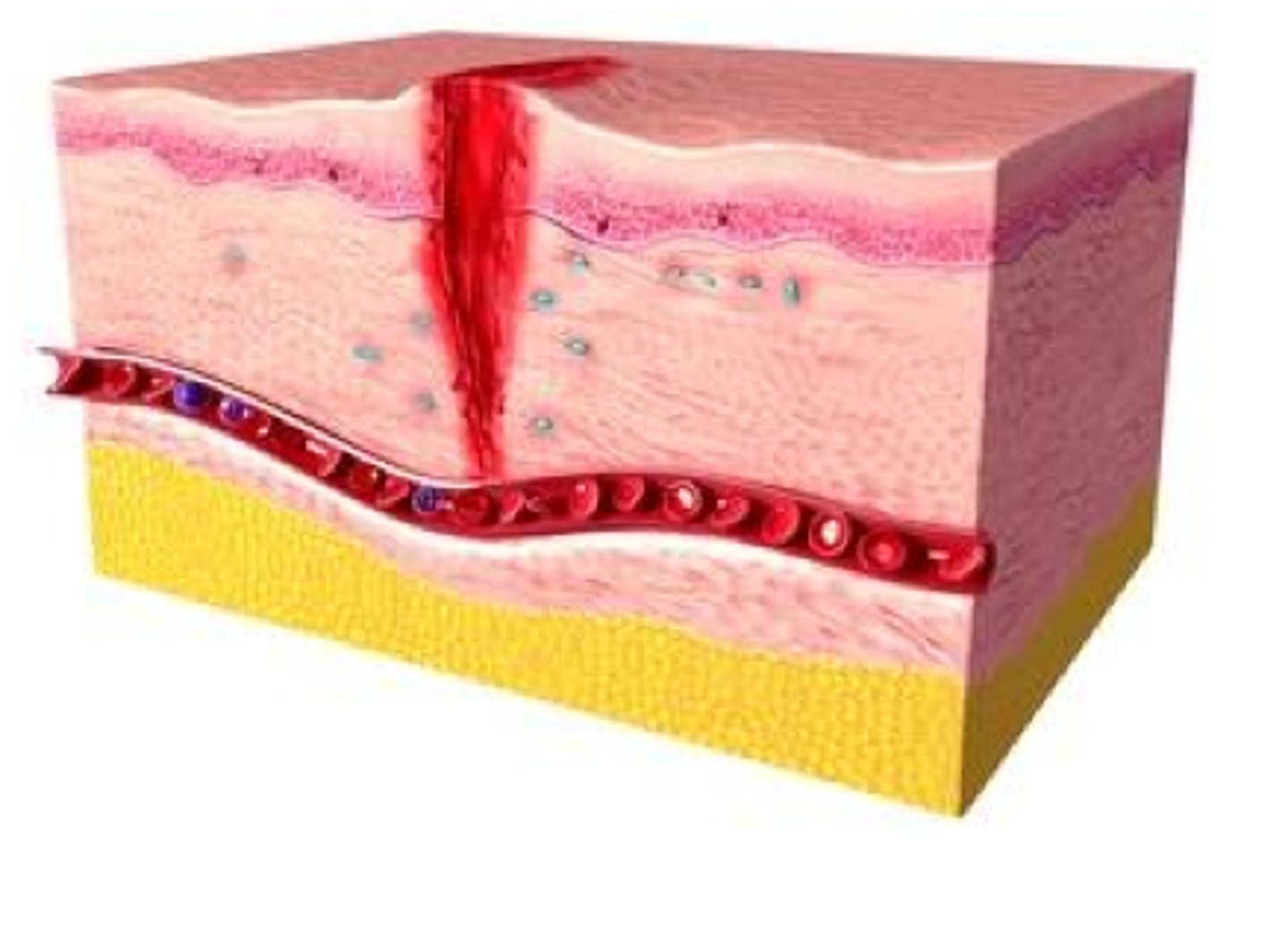
What are the 3 phases of eyelid wound healing?
inflammatory phase
proliferative phase
remodeling phase
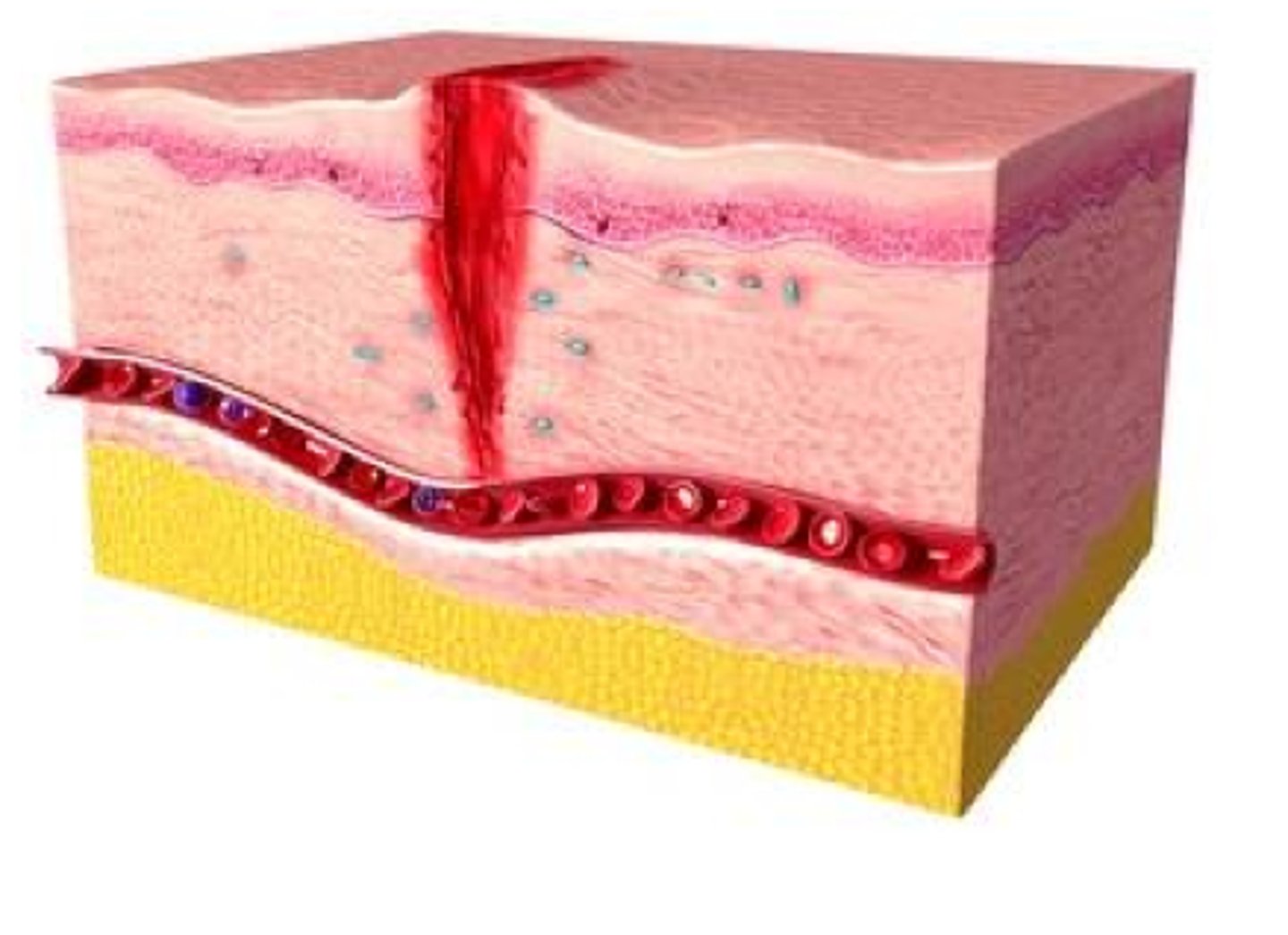
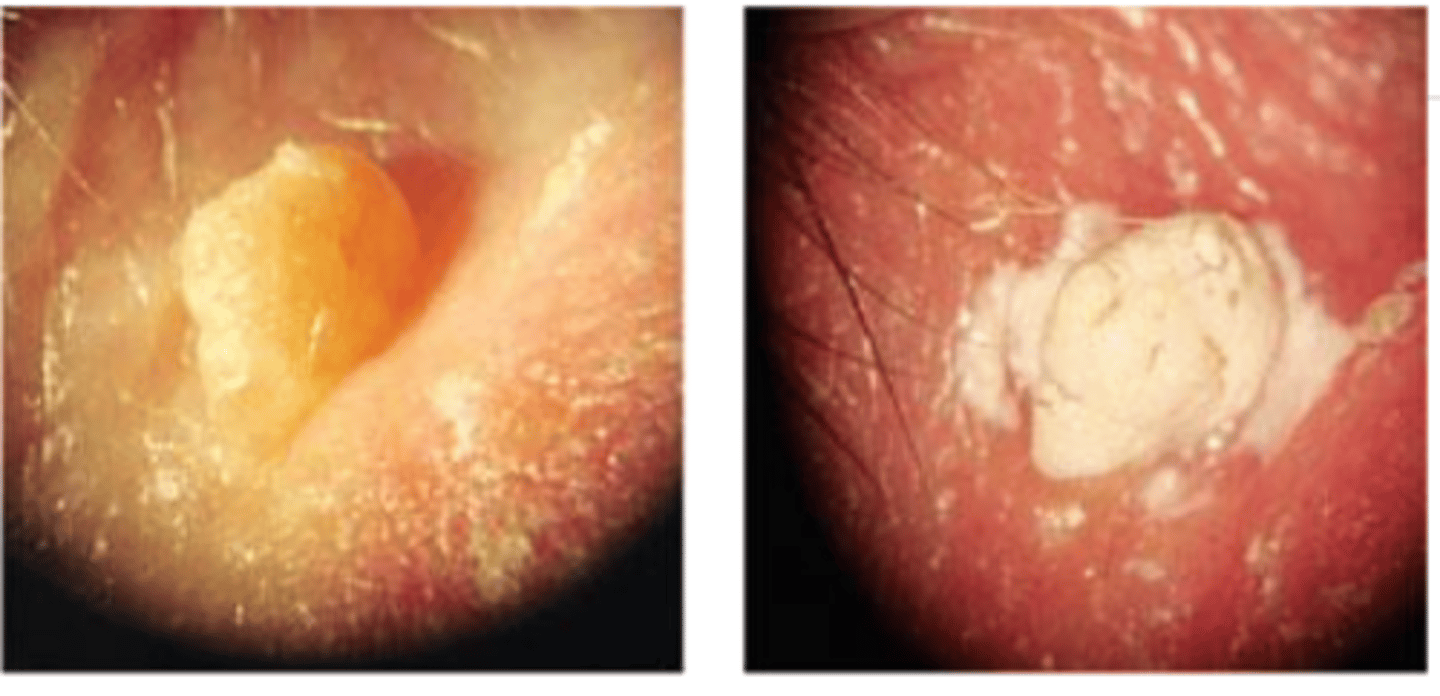
What are the 2 types of fibrosis which are possible complications of healing?
scar = deformity across the joint of the wound
OR
keloid = deformity beyond the joint of the wound
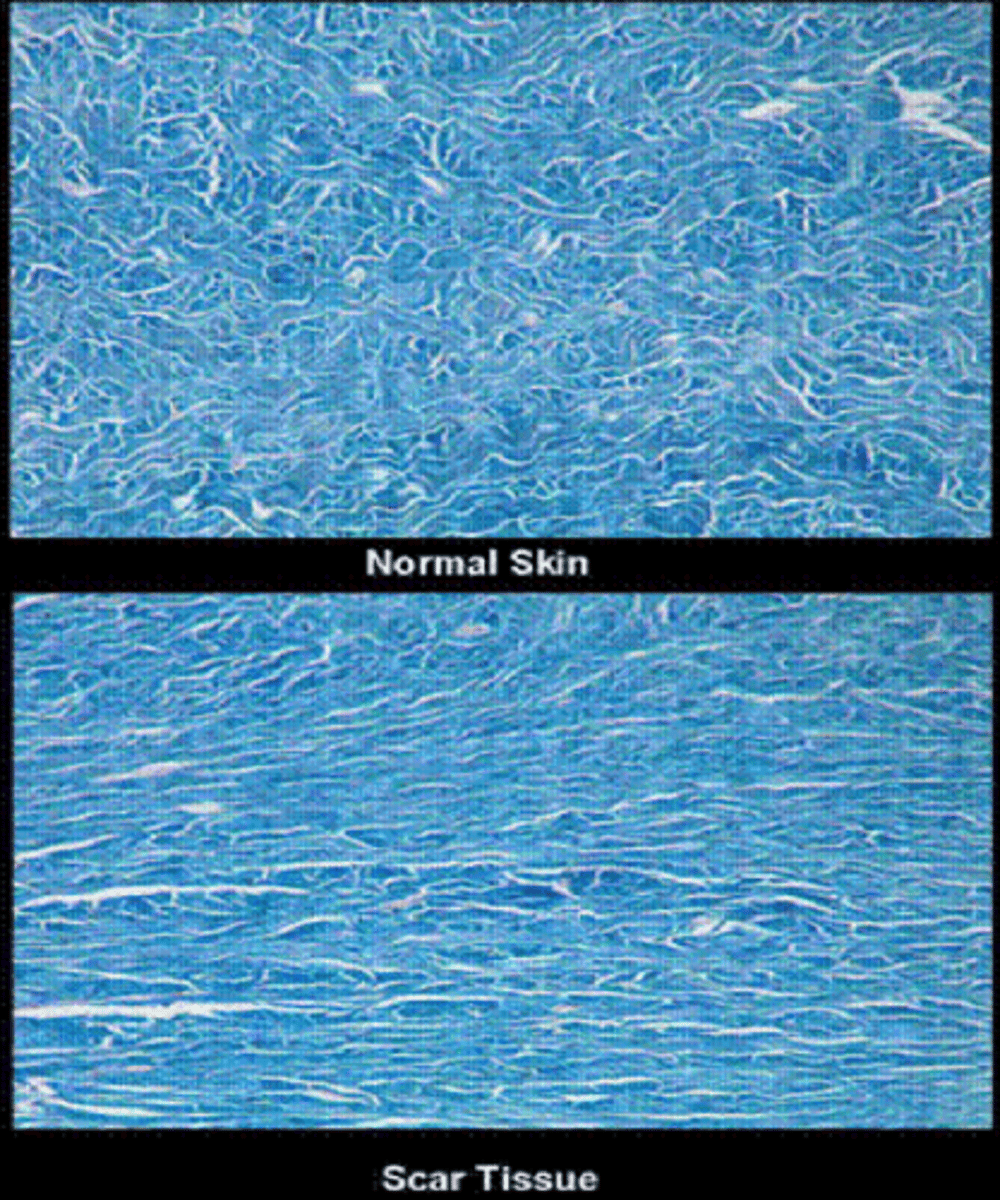
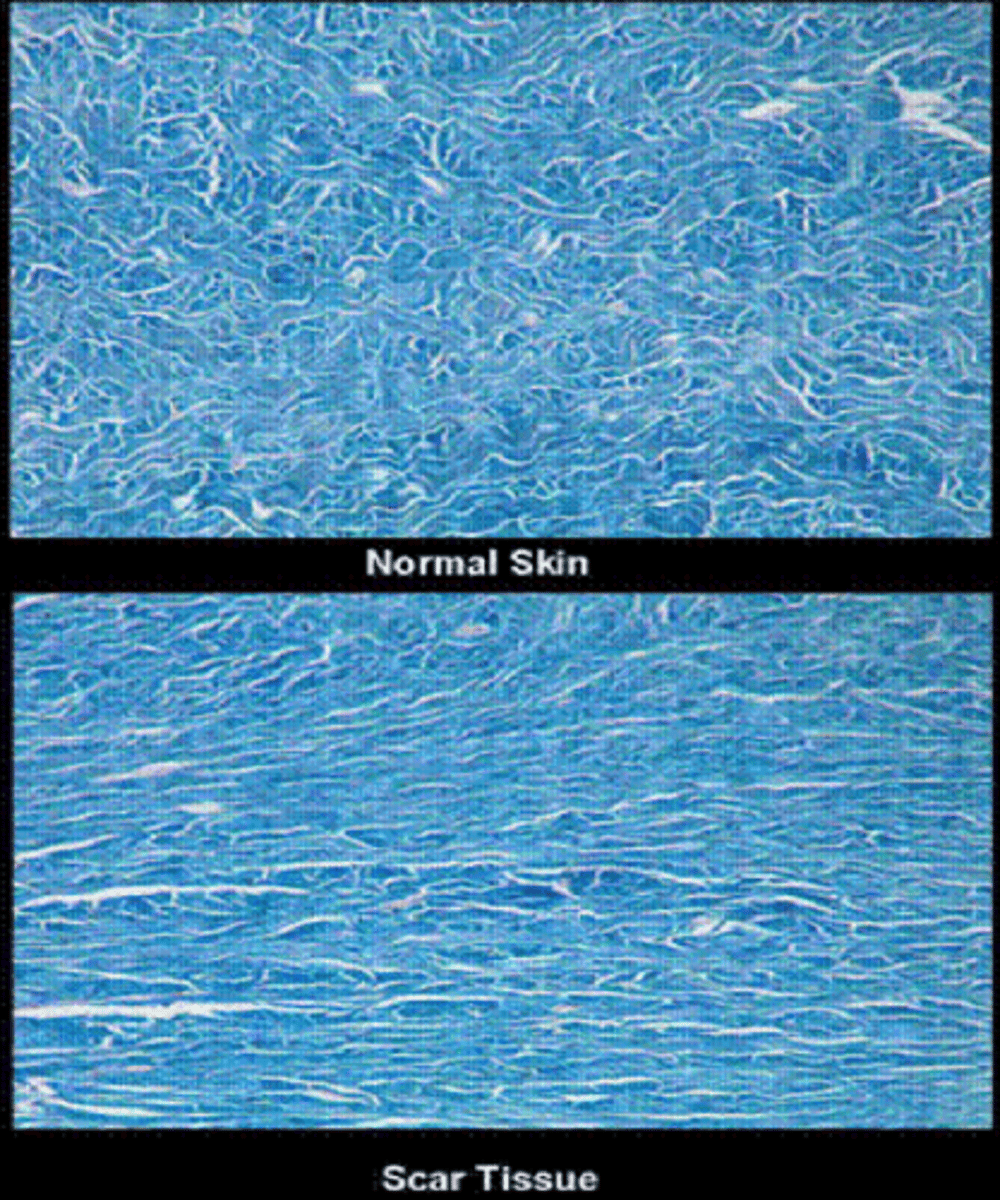
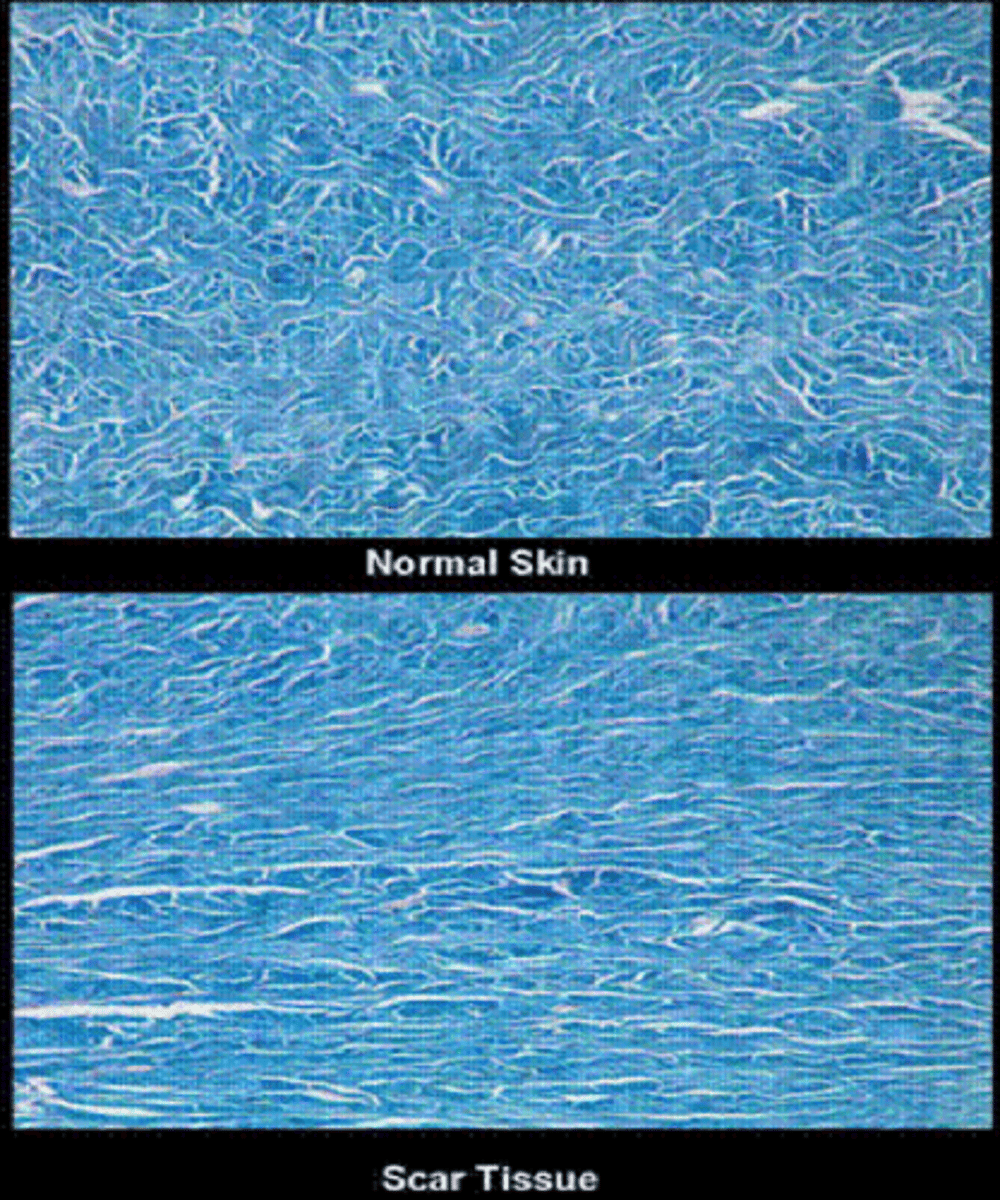
What is a scar?
replacement of original skin tissue (reticular/basket weave collagen) with collagenous tissue = more densely packed parallel collagen = altered appearance, less elasticity
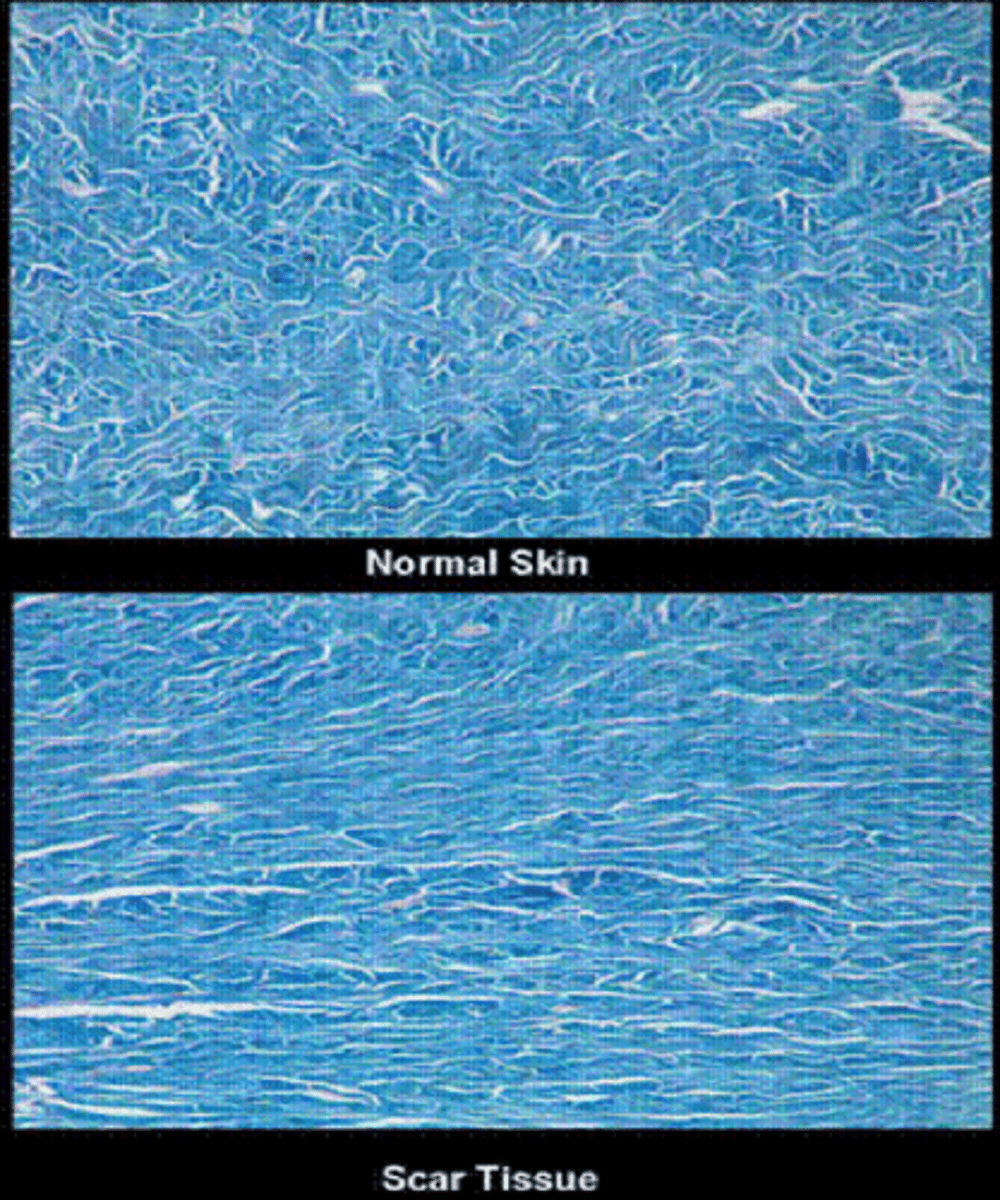
What do scars lack?
dermal appendages such as hair follicles, sebaceous glands
How does the colouration of a scar change over time?
red at first due to high capillary density that will regress
pigmentation increases over time depending on pt pigment
What causes a hypertrophic or keloid scar?
excess inflam mediators due to excess macrophage activity (poor signaling among macropahges, fibroblasts, epithelial and endothelial tissue)
fibrosis due to excess fibroblast activity and overproduction of collagen
excess epithelial mesenchymal transition
chemotactic factors
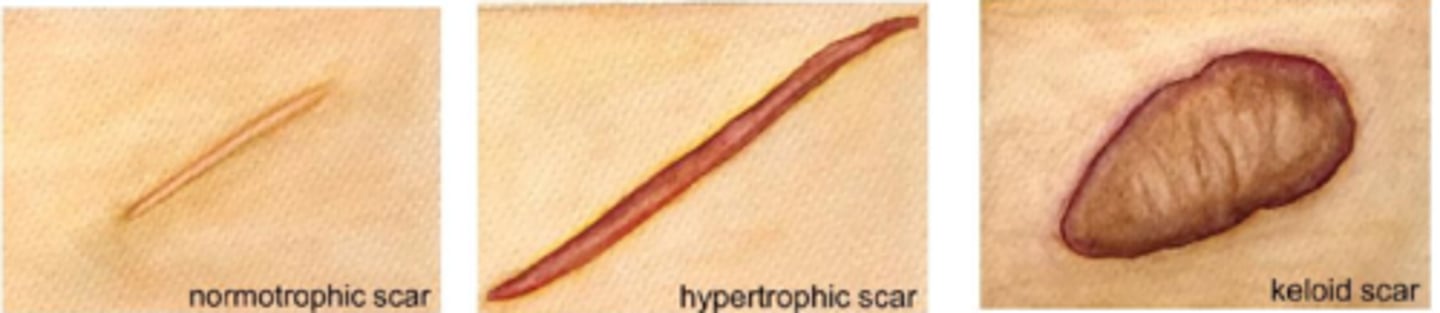
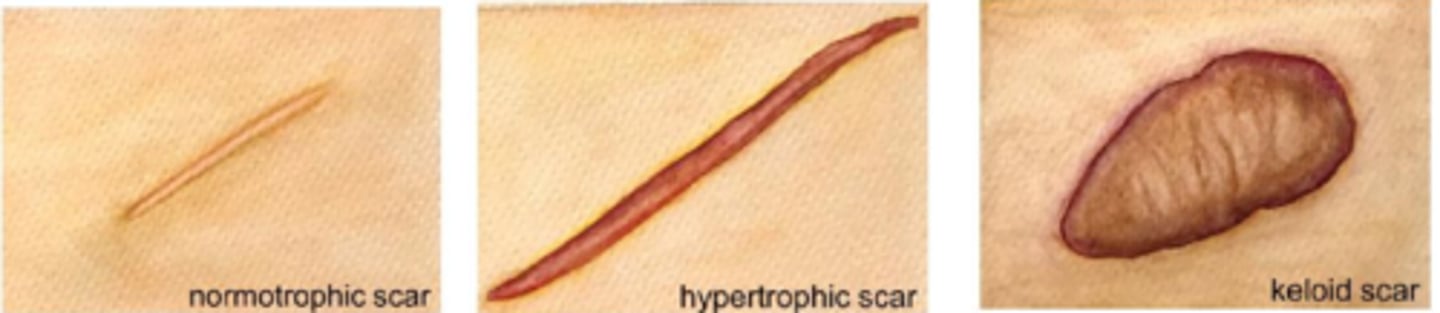
What is a hypertrophic scar?
does not go beyond wound border but is raised, red, itchy from excess tension (esp across joints/tendons) = may fade or flatten over time
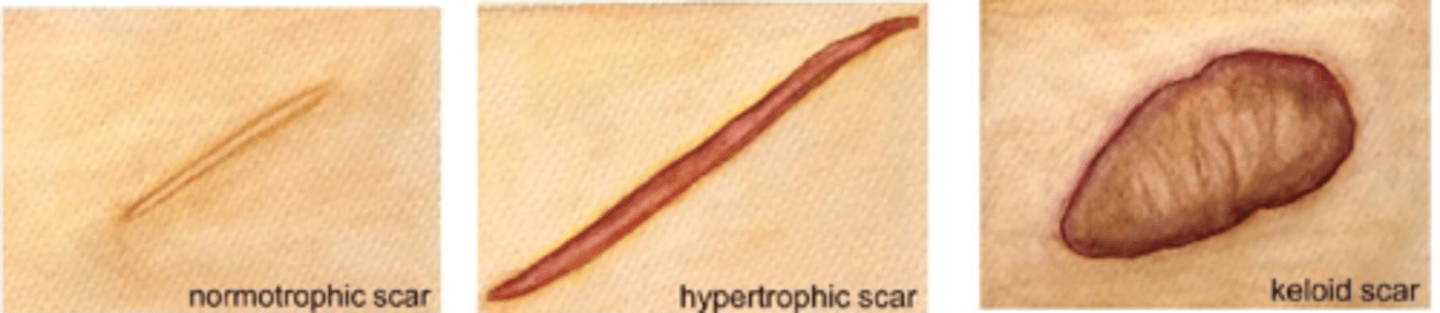
What is a keloid scar?
extends beyond wound border because it infiltrates surrounding tissue
does not regress and may progress or evolve over time
collagen is very disorganized (unlike parallel in a scar)
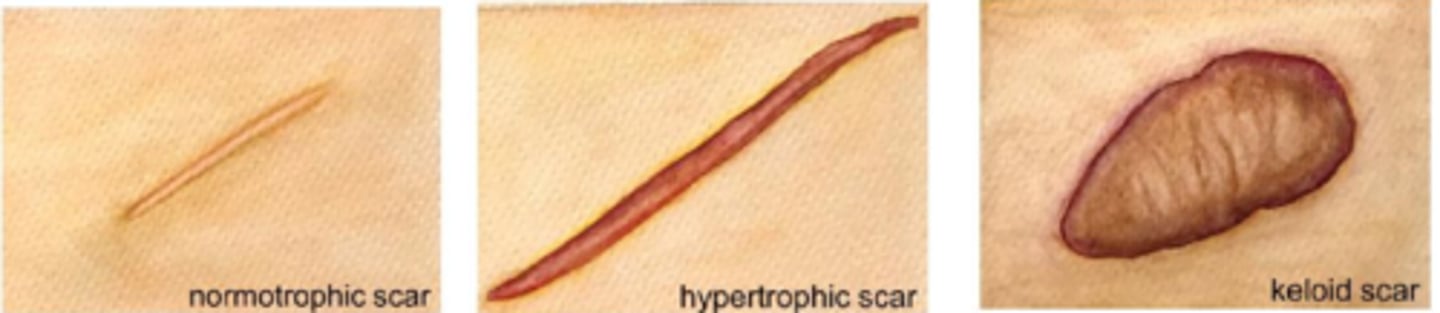
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of onset?
hypertrophic scar = develops soon after surgery
keloid = can develop months after trauma
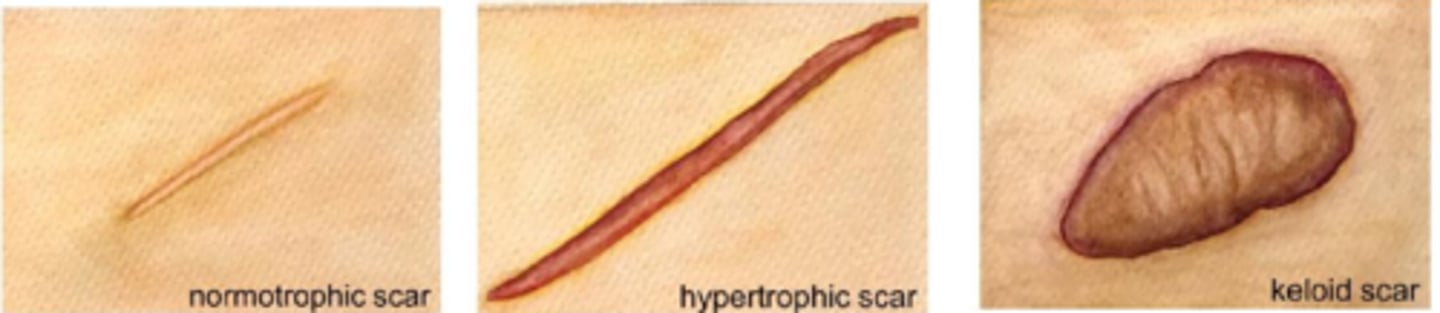
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of improvement over time?
hypertrophic scar = usually improve with time
keloid = rarely improve with time
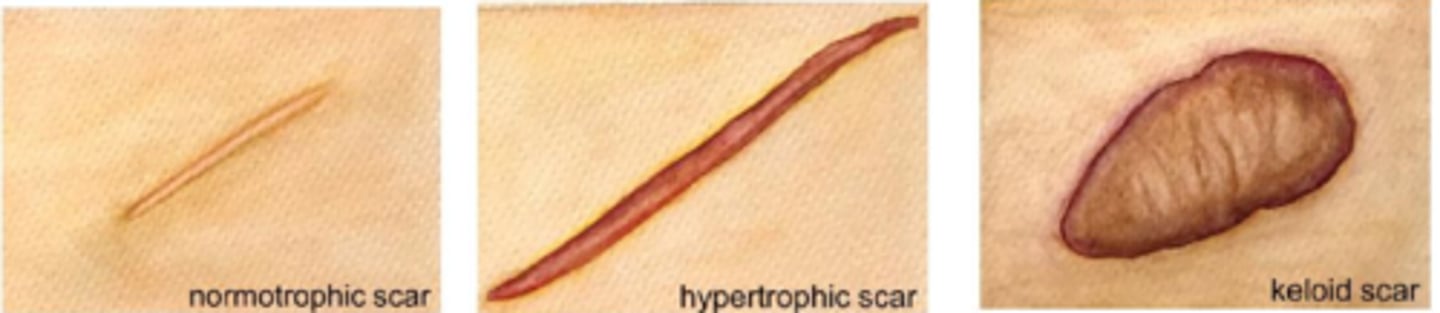
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of boundaries?
hypertrophic scar = remain within confines of wound
keloid = spread outside boundaries of wound
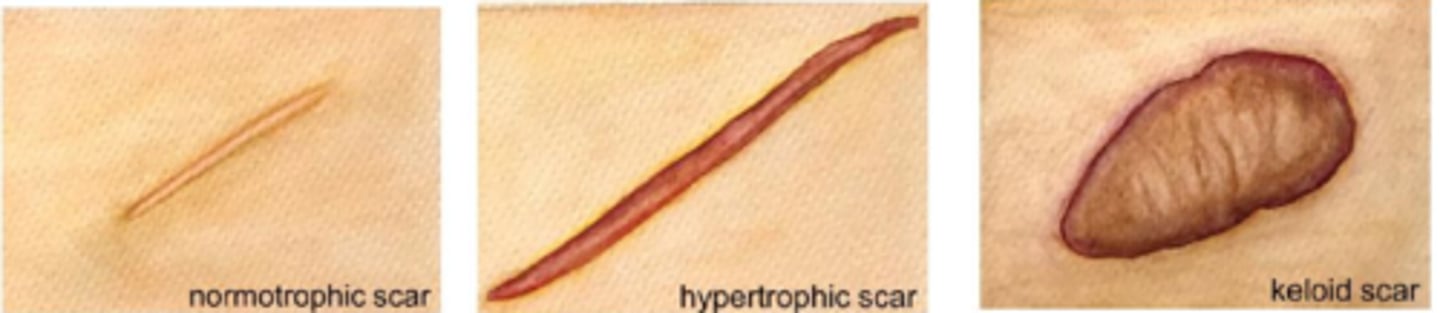
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of body location?
hypertrophic scar = scars over joints, skins creases
keloid = ear lobe, shoulders, sternal notch
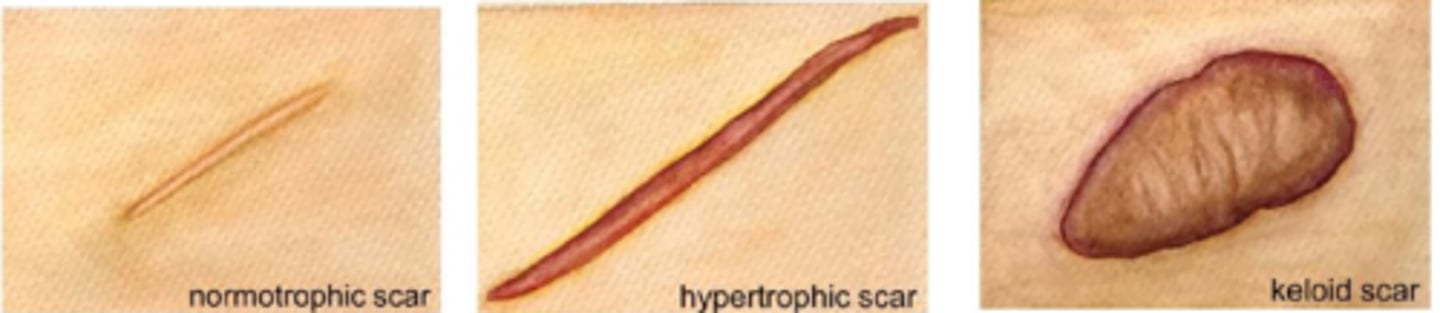
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of improvement after Sx?
hypertrophic scar = improve with surgery
keloid = often worsened by surgery
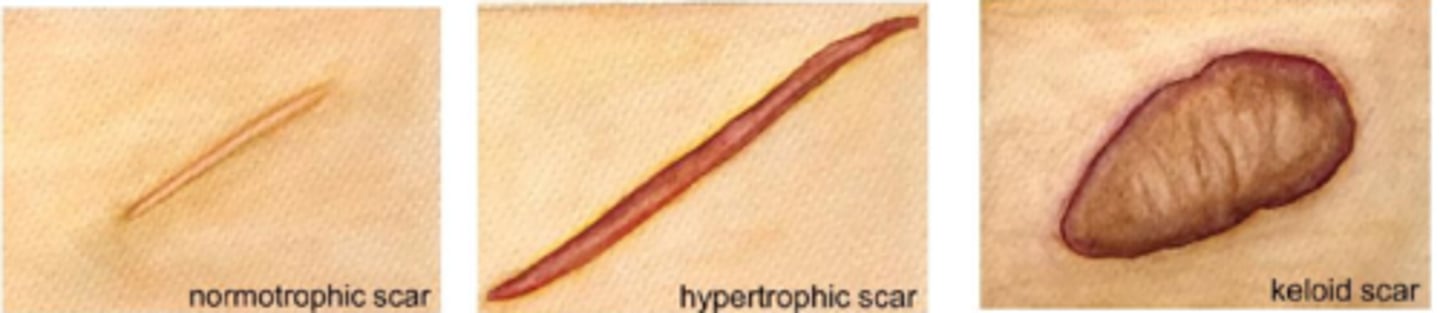
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of rarity?
hypertrophic scar = frequent
keloid = rare
How do hypertrophic and keloid scars differ in terms of skin colour association?
hypertrophic scar = no assocation
keloid = increased risk in darker skin colour
What are some ways to reduce complications like scars?
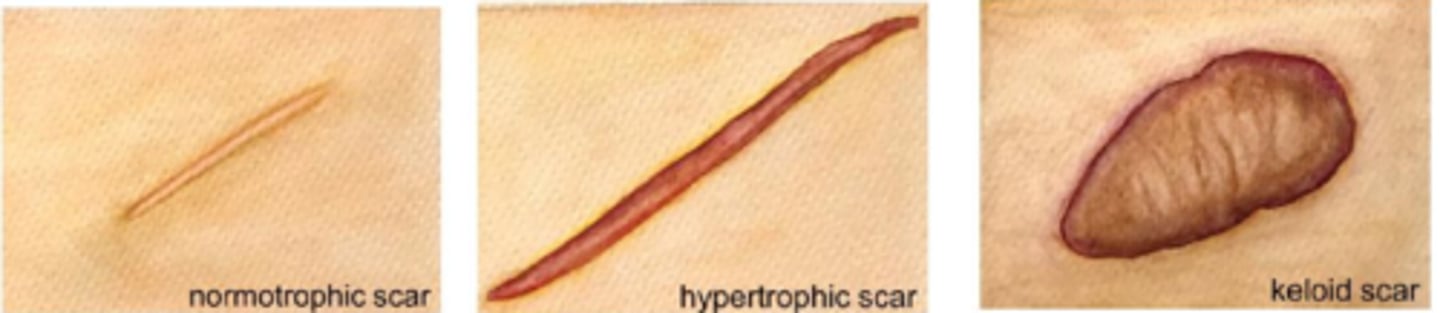
incisions parallel to natural tension (Langer) lines to prevent tension and blend with natural creases
sharply defined, well aligned edges
infection management through asepsis
wound closure with sutures
sun protection
silicone gel sheeting/ointments to hydrate straum corneum
steroid injection for keloids
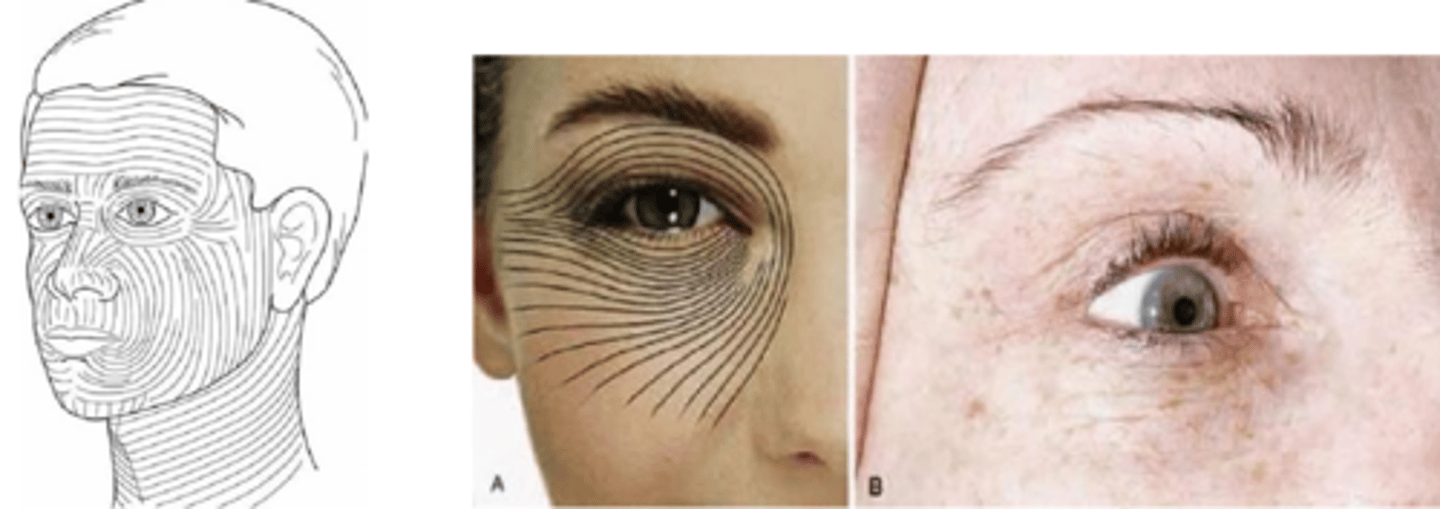
What is this alternative to excisions? Include the 2 MOA's of this tx.
chemical cautery with DCA, TCA (di or tri-chloracetic acid) = keratolytic and cauterant properties break down hyperkeratinized superficial lesions
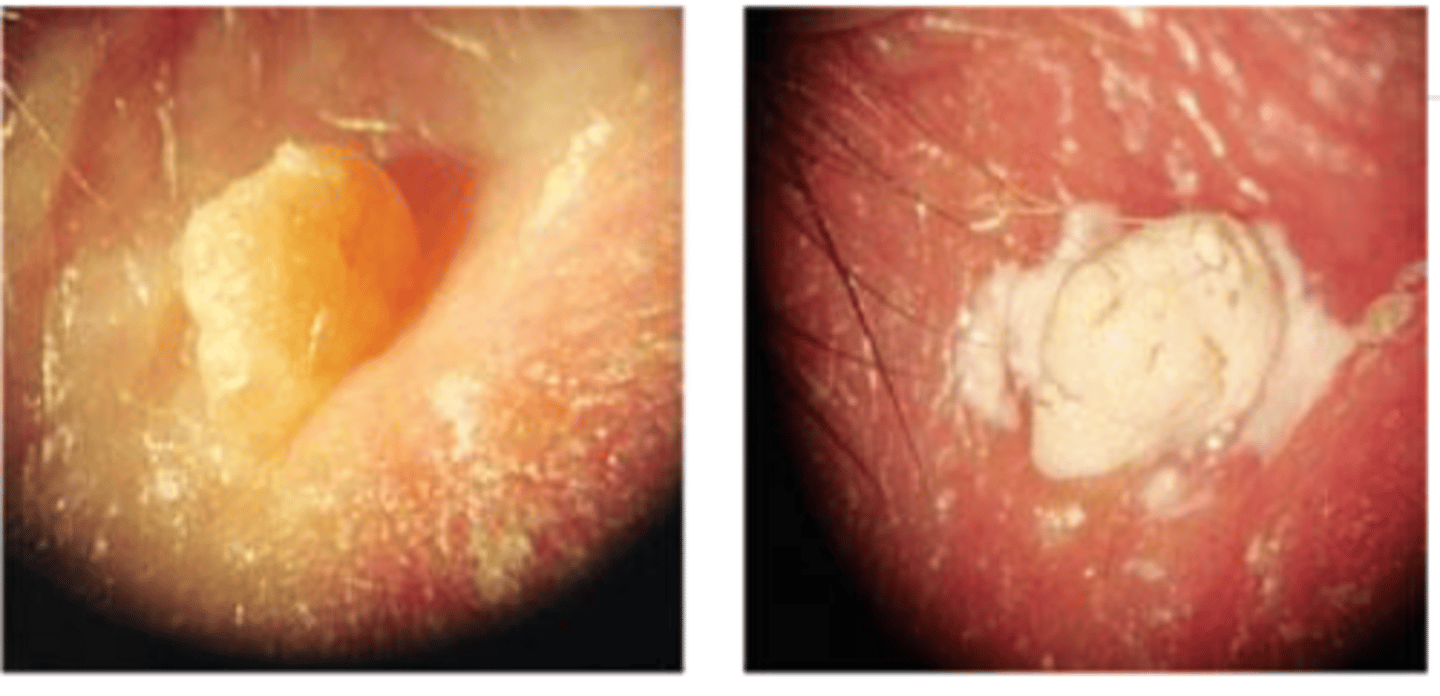
What is the process for chemical cautery?
proparacaine to reduce tearing from fumes
apply petroleum jelly to prevent compounding running to other areas
apply chemical on lesion with an applicator (may burn or sting slightly)
affected tissue turns white and may slough off to leave a small scab
apply abx/steroid ung to scab