DNA translation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Translation
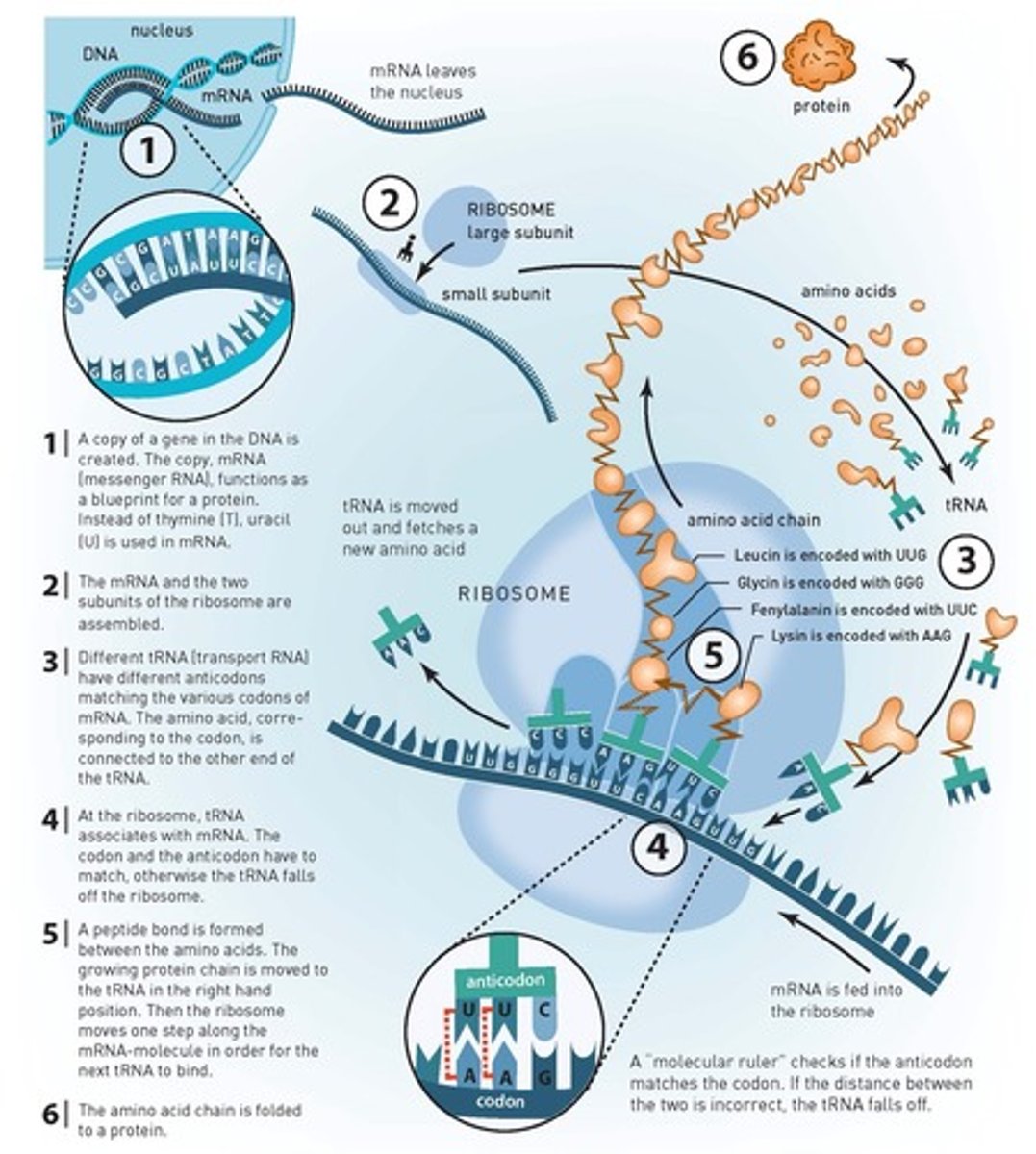
The process by which mature mRNA become the template for protein synthesis
mRNA is "decoded" to build a protein that contains a specific series of amino acids
Translation
Diagram
mRNA instructions for
Building a polypeptide?
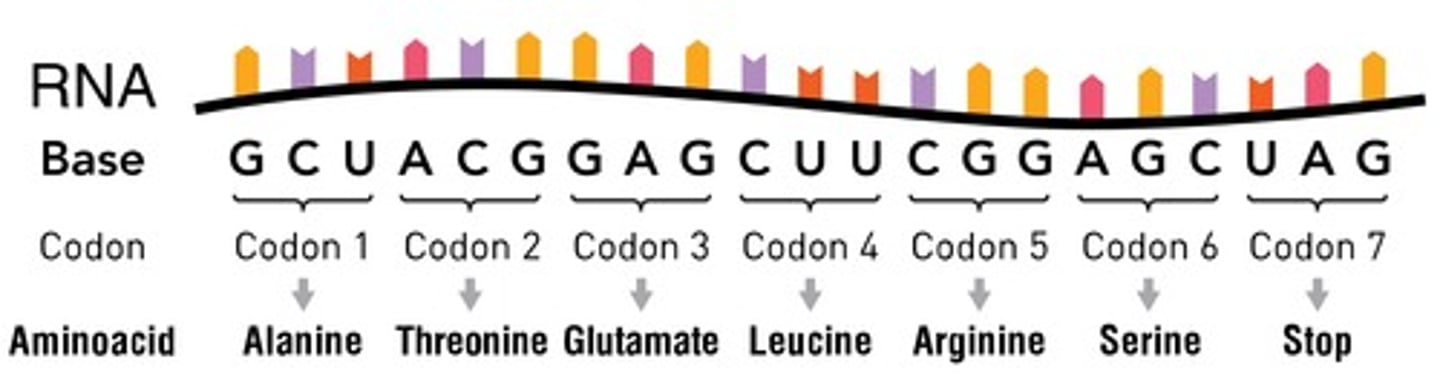
In an mRNA, the instructions for building a polypeptide are RNA nucleotides (As, Us, Cs and Gs) read in groups of 3. These groups of 3 are called CODONS
Codon
Diagram
Codon
Each triplet of nucleotides is a codon and codes for one amino acid
How many triplets for
Amino acids? codons?
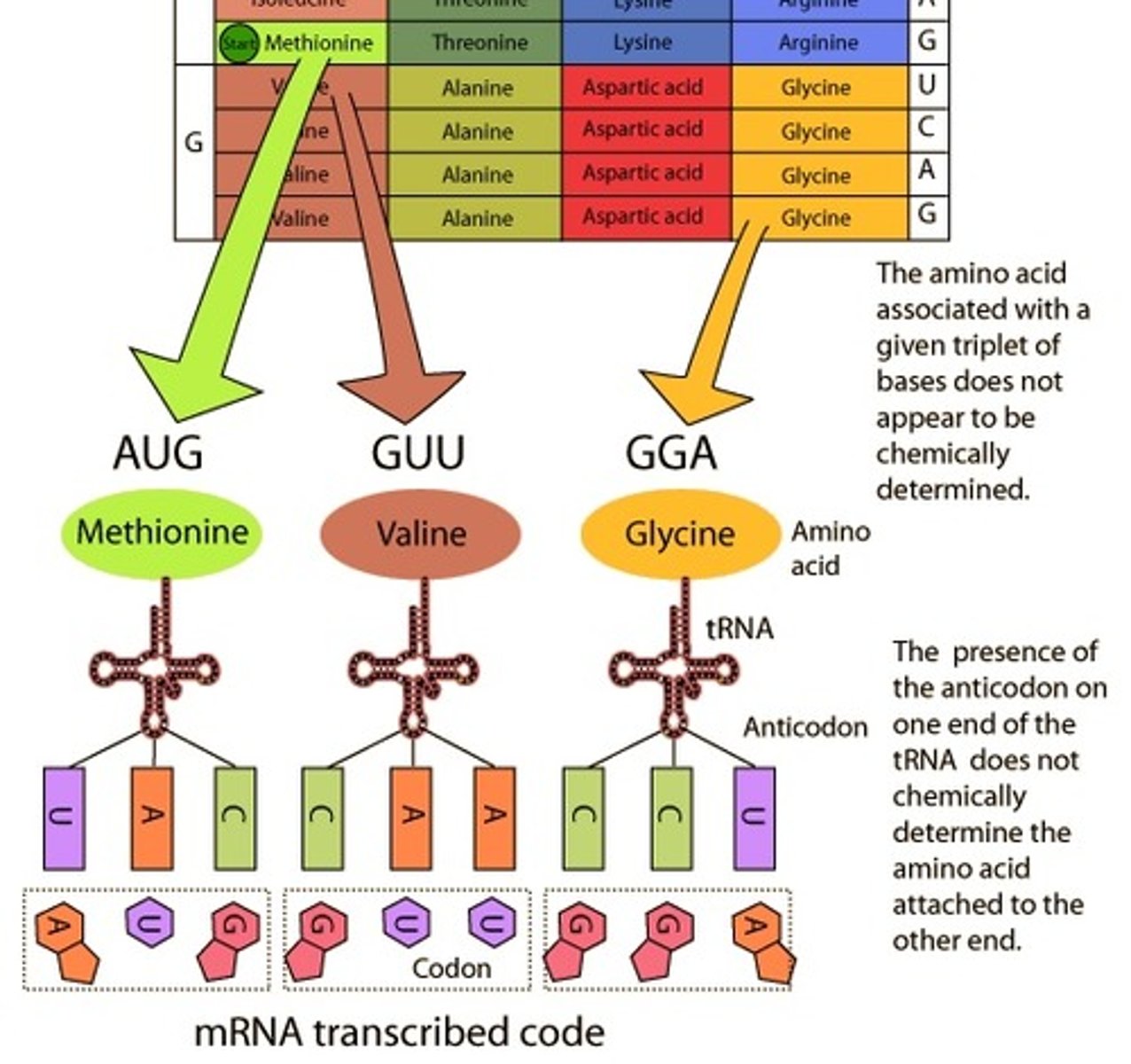
There are 64 triplets (codons)that code for amino acids. Each is 'read' to specify a certain amino acid out of the 20 commonly found in proteins.
Three of these triplets AUA, UAA and UAG are stop codons and do NOT code for any amino acids.
AUG
Start codon, signals the start of protein construction; specifies the amino acid methionine.
Genetic Code
This relationship of codon\amino acids is called the genetic code because it lets cells 'decode' an mRNA into a chain of amino acids.
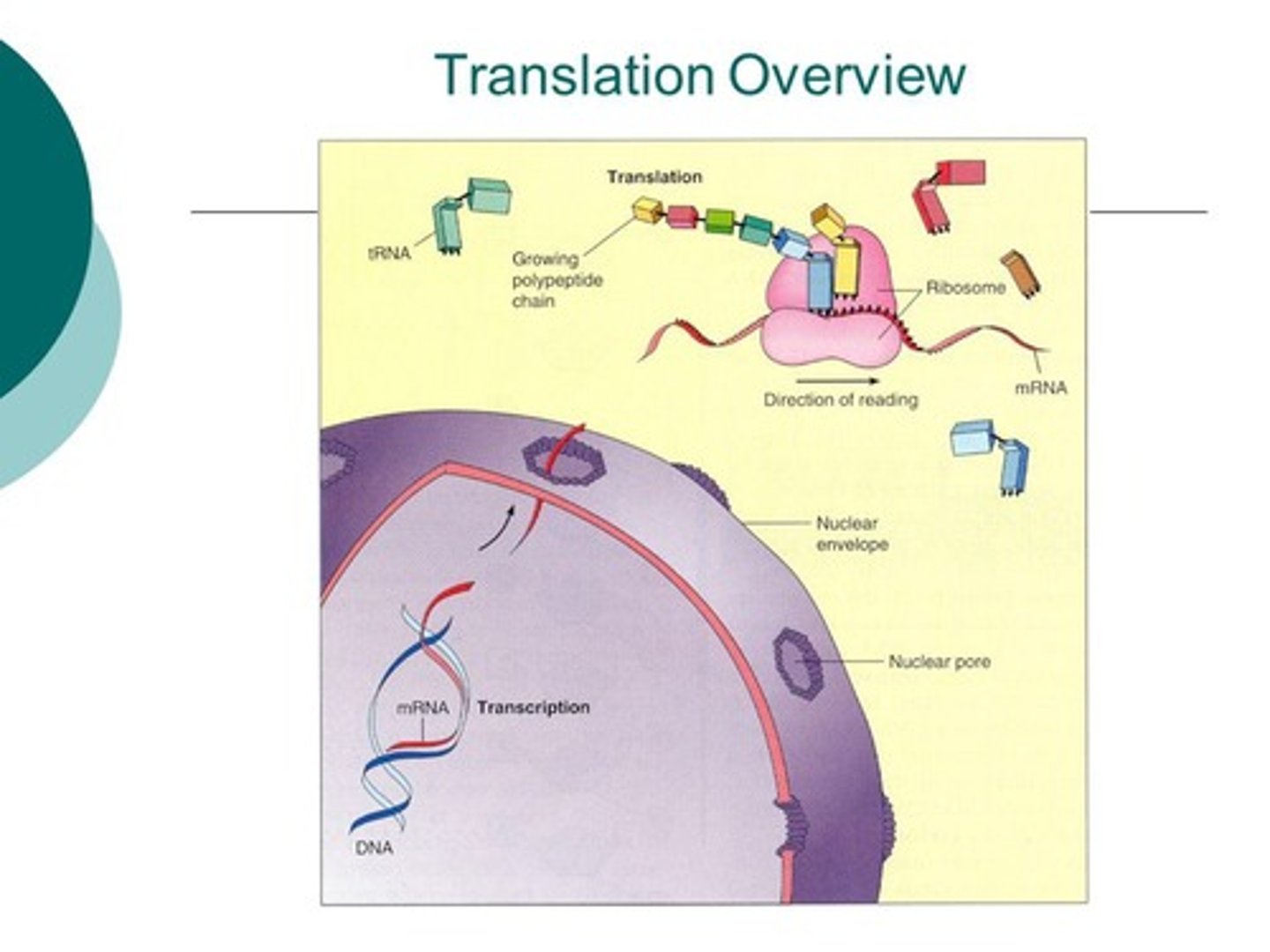
Overview of
Translation
Process of how an mRNA is 'read' to make a polypeptide
2 molecules play key roles in this process: tRNA and ribosomes
Stop Codons
UAA, UAG and UGA. These DO NOT specify amino acids. The stop codons tell the cell when a polypeptide is complete.
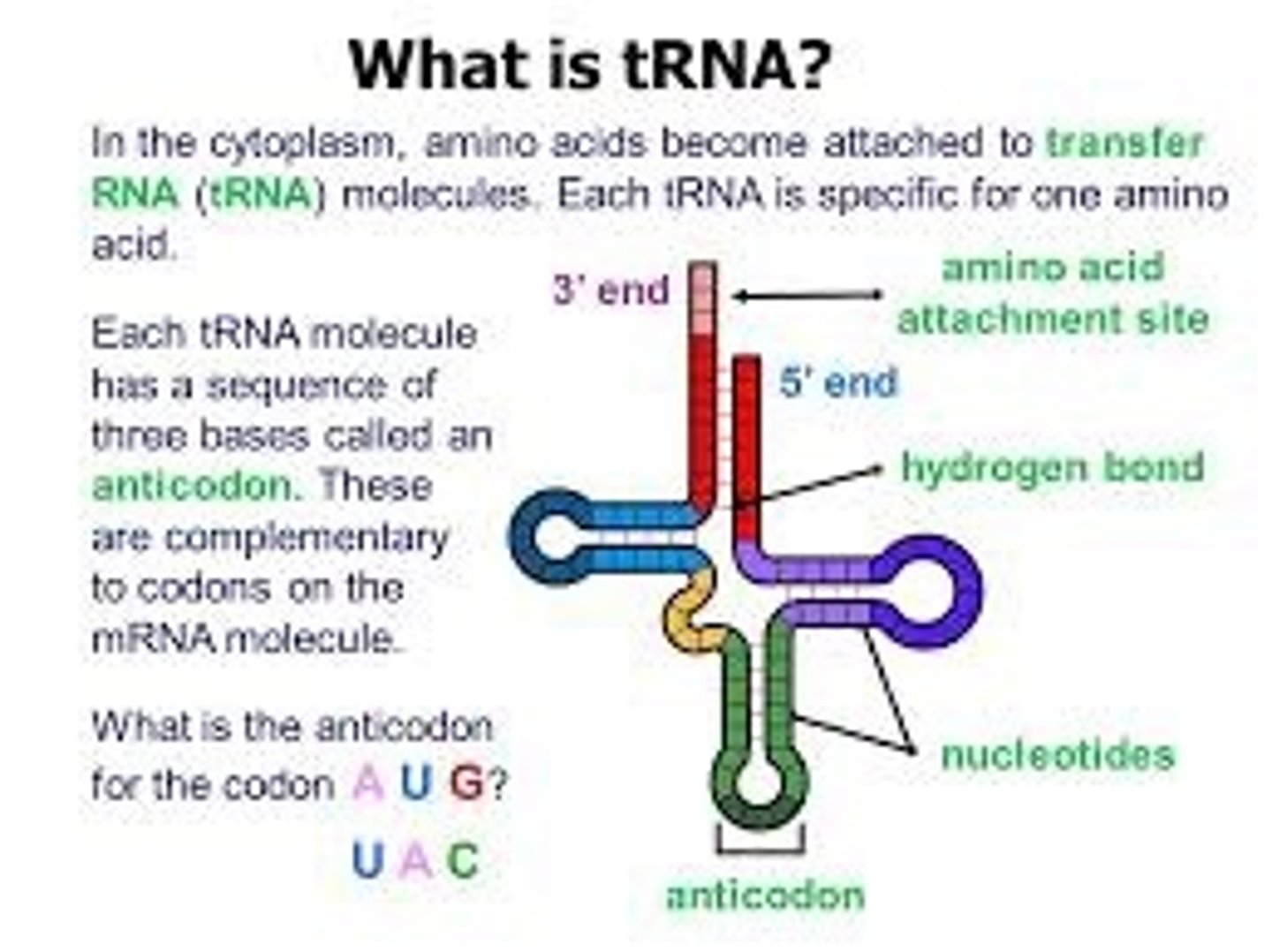
tRNA
Molecular 'bridges' that connect the mRNA codons to the amino acids they encode. One end of each tRNA has a sequence of 3 nucleotides called an anticodon, which can bind to a specified mRNA codons. The other end of the tRNA carries the amino acid specified by the codons.
**there are many different types of tRNAs. Each type reads one or a few codons and brings the right amino acid matching those codons.
Ribosomes
Structures where polypeptides ( proteins) are built. They are made up of protein and RNA(rRNA). Each ribosome has tow subunits, a large one and a small one, which come together around an mRNA.
**kind of like 2 halves of a hamburger bun coming together around the patty.
**made of 2 ribosomal units; a small one and a large, they contain ribosomal RNA and proteins
Aminoacyl -tRNA synthetase
is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its tRNA
Enzymes that bring the tRNA its specific amino acid
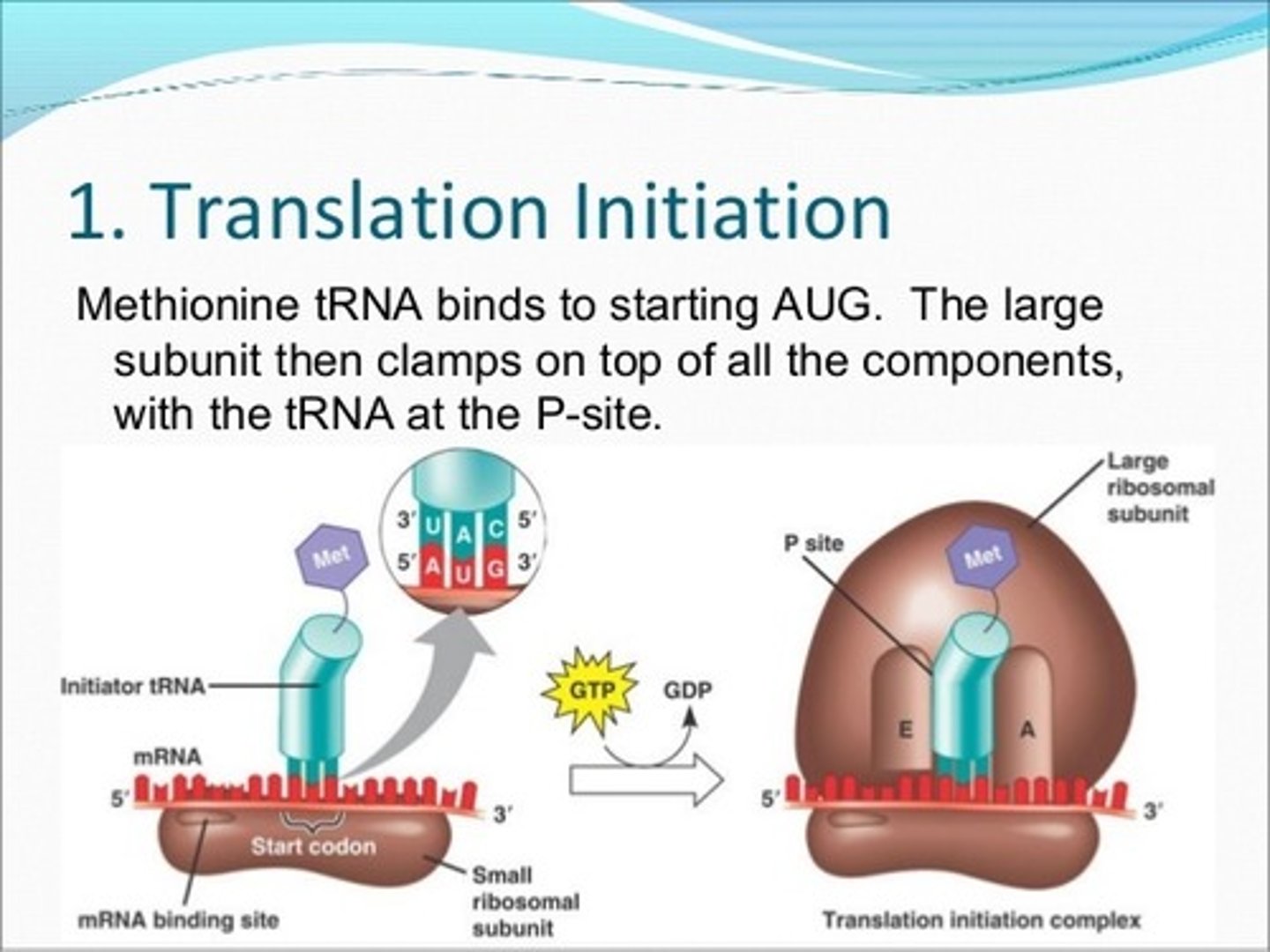
Translation Initiation
1. The ribosome assembles around the mRNA to be read and the first tRNA (carrying the amino acid methionine, which matches the start codon, AUG).
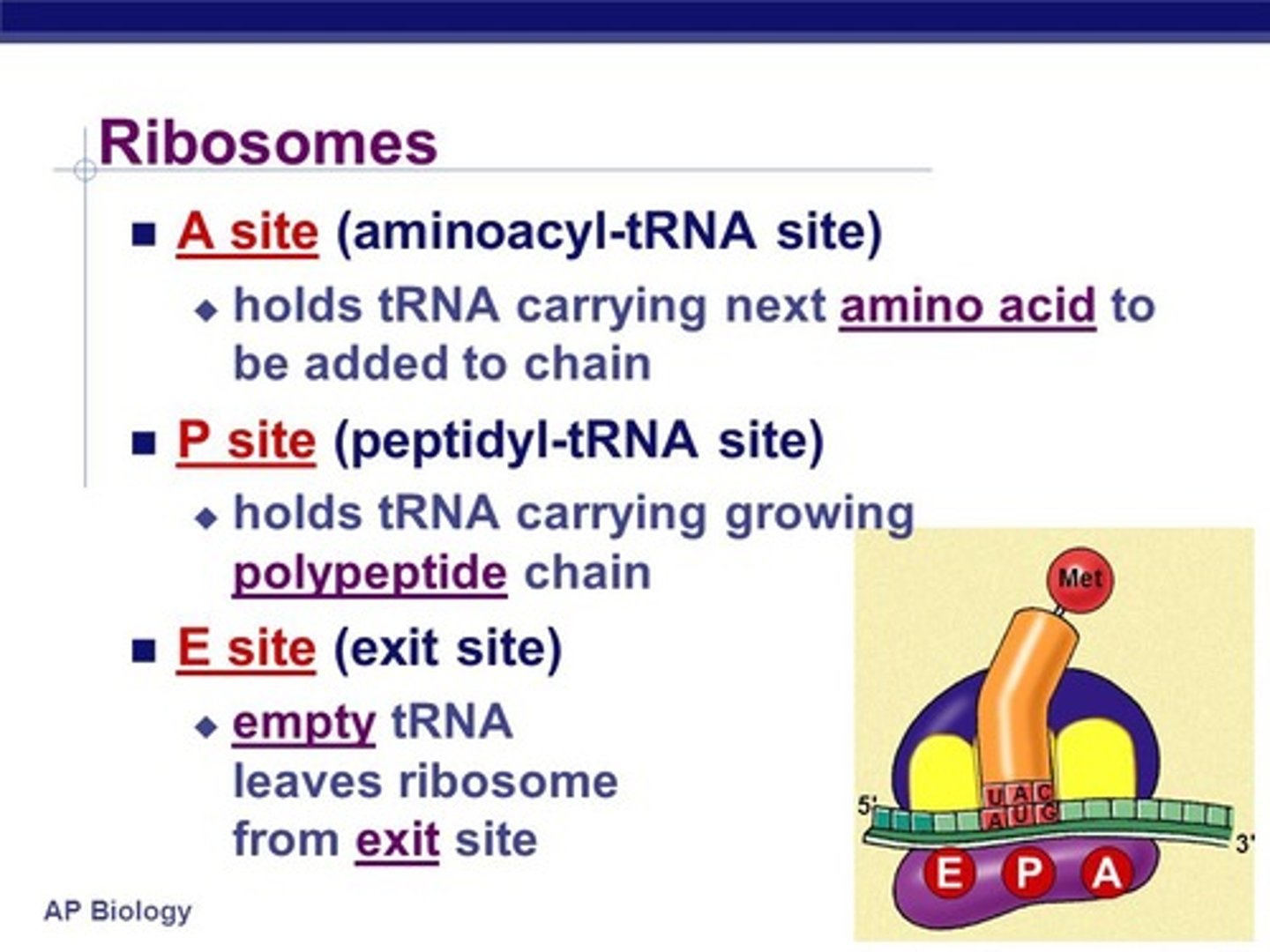
2. A large ribosomal subunit binds to the small one , creating a functional ribosome. The initiator tRNA fits into one of the two tRNA binding sites o the ribosome. This site is called the P SITE and holds the growing polypeptide. The other tRNA binding site is called the A SITE is shown vacant and ready for the next amino acid bearing tRNA.
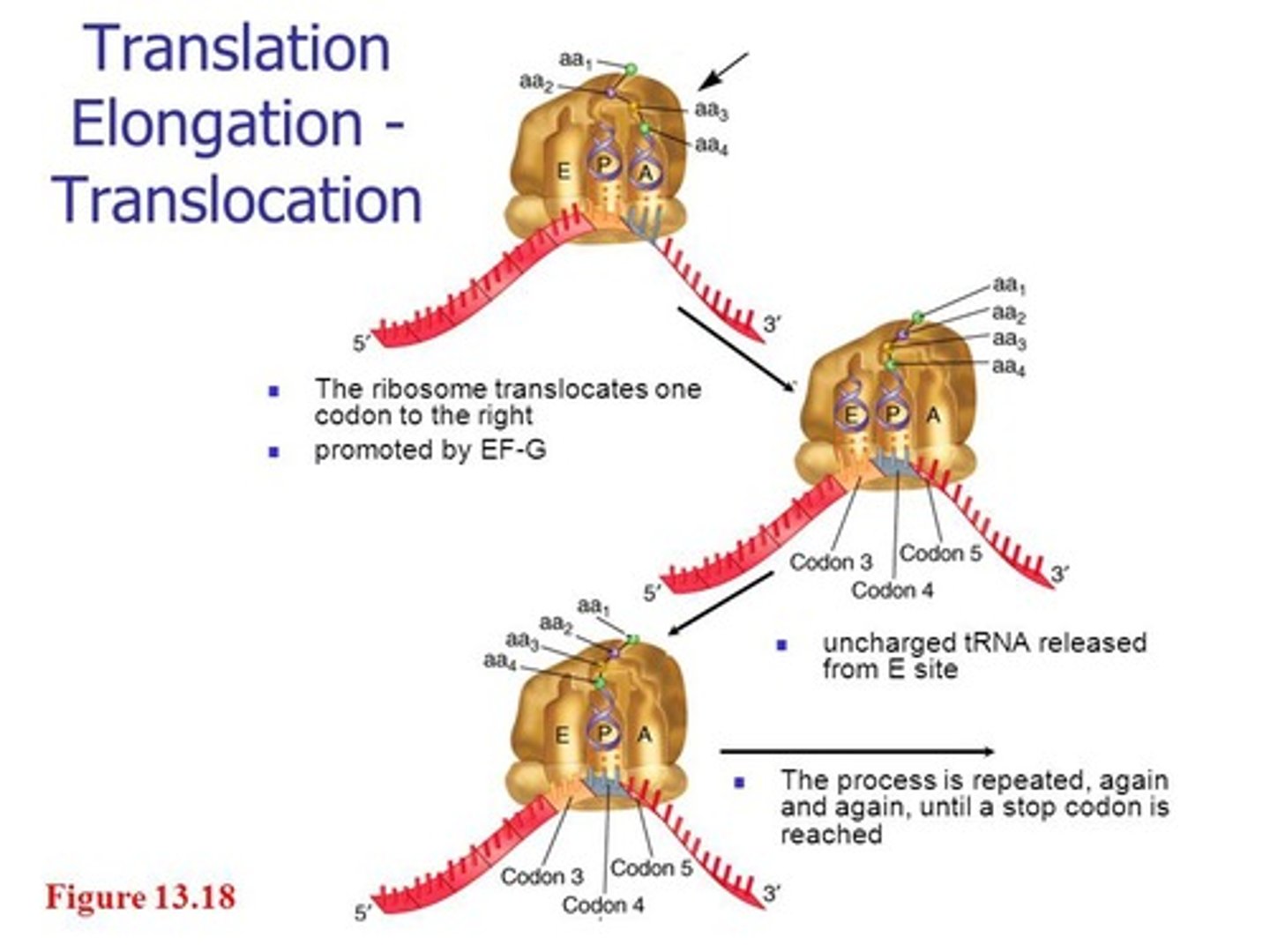
Translation Elongation
The ribosomes move three nucleotides to the right. The new sites are: the previous P becomes E, the previous A becomes P and a new A opens up to receive the new tRNA. That brings another amino acid coded by the next triplet. A peptide bond is formed and now you have 3 amino acids bonded together. The ribosomes move a position to the right (3 nucleotides) and so on and so on.
**tRNA's move through the A, P, and E sites of the ribosome. This process repeats many times as new codons are read and new amino acids are added to the chain.
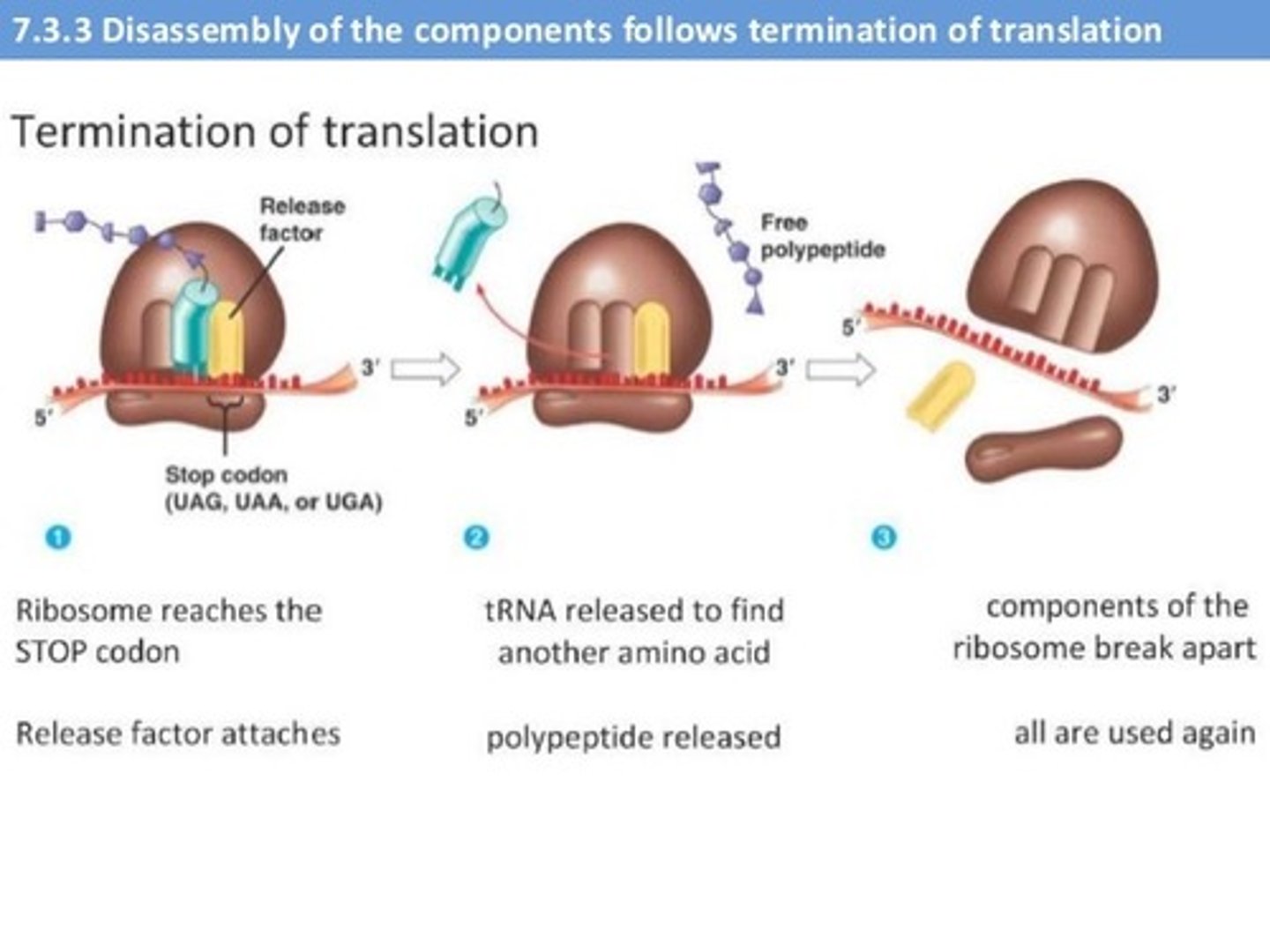
Translation Termination
The finished polypeptide chain is released. A stop codon is reached. UAG, UAA or UGA enters the ribosome, triggering a series of events that separate the chain from its tRNA and allow to drift out of the ribosome. This point a termination factor binds and the complex is dissembled. So you get the ribosomal unit free, the mRNA and your protein
Translation
Initiation
Diagram
Ribosome diagram
Translation
Elongation
Diagram
tRNA diagram
Translation
Termination
Diagram