biology past papers
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
describe how chemiosmosis is involved in the synthesis of ATP
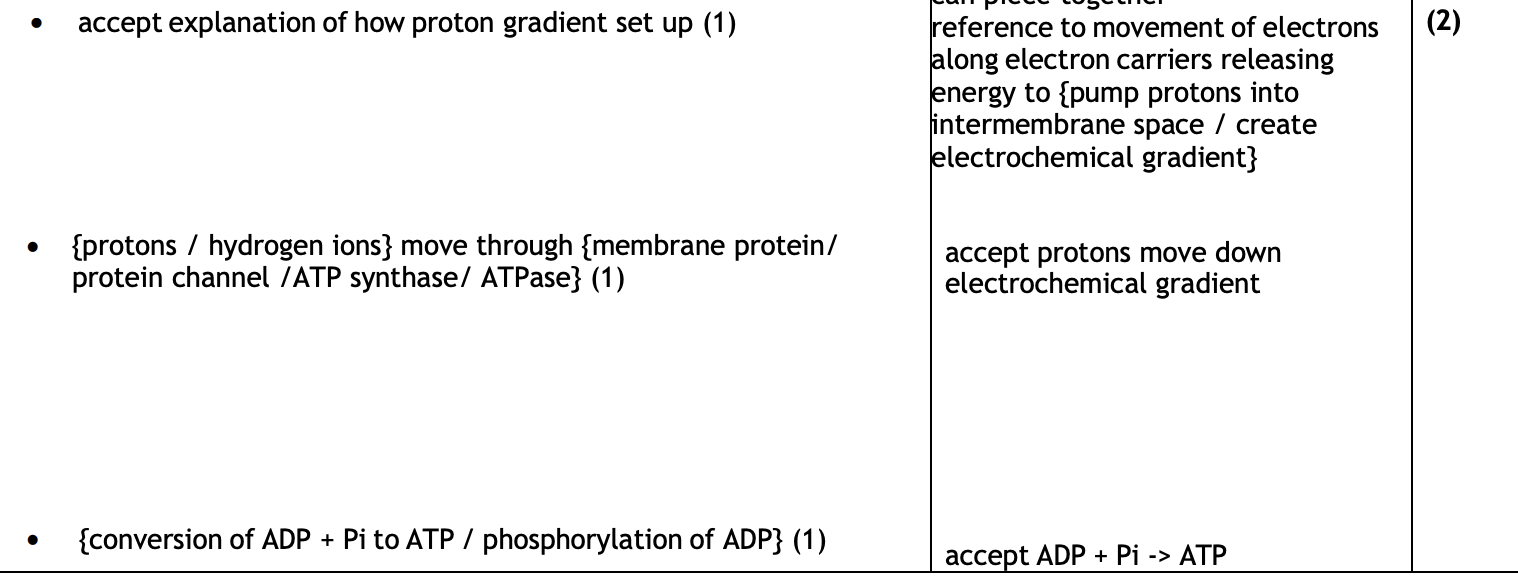
-H ions actively transported into the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane using energy provided s electrons pss along the transport chain, this results in a proton gradient as there is a higher concentration of H ions in membrane space than matrix
-H ions moves through membrane protein through pores on stalked particles/atp synthase channel
-ADP phosphorylated (converted) to ATP
explain how knee joint can be held steady as a giraffe bends down to drink

describe role of atp in sliding filament theory


explain how heart rate increase
last bullet point important!!! (cvc, sympathetic nervous system)
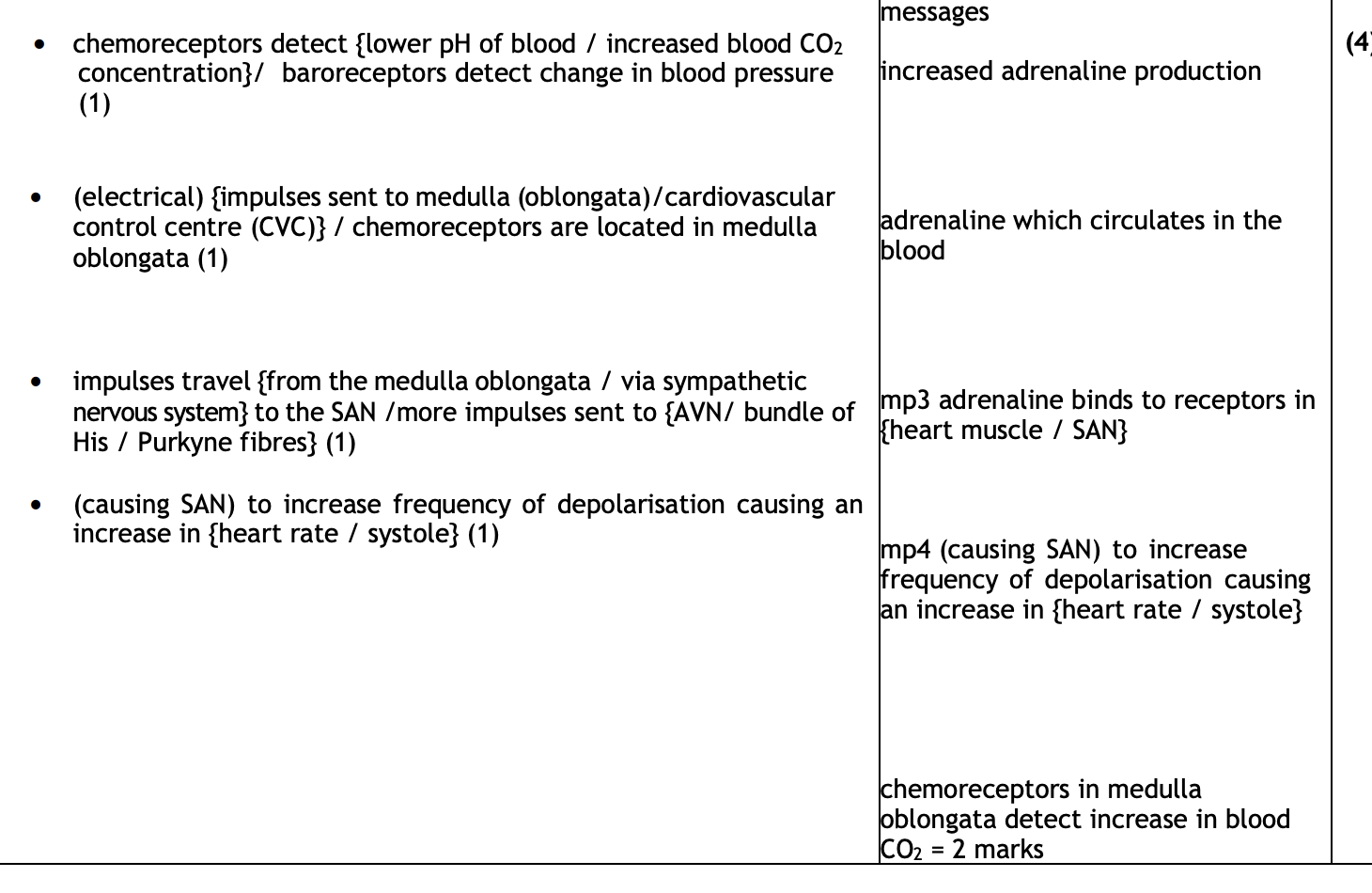
suggest why a cheetah can maintain a high heart rate only for a short period

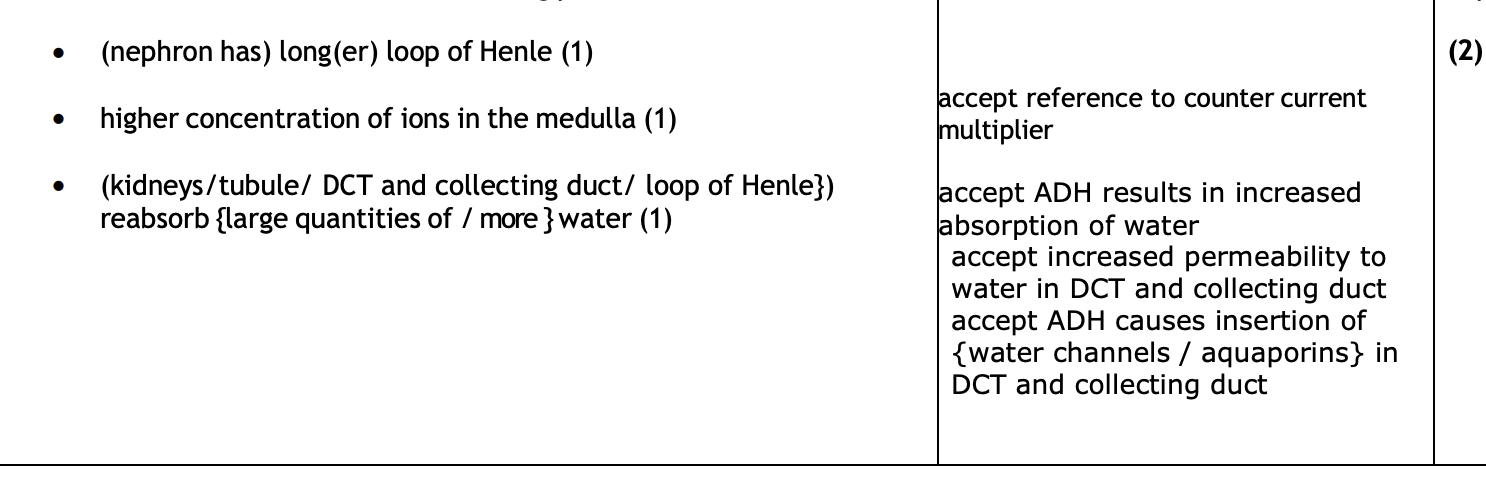
IMPORTANT explain how nephrons in the kidney of the kangaroo rate are able to produce very conc urine
effect of gibberellins- gibberellins regulare starch hydrolysis, how
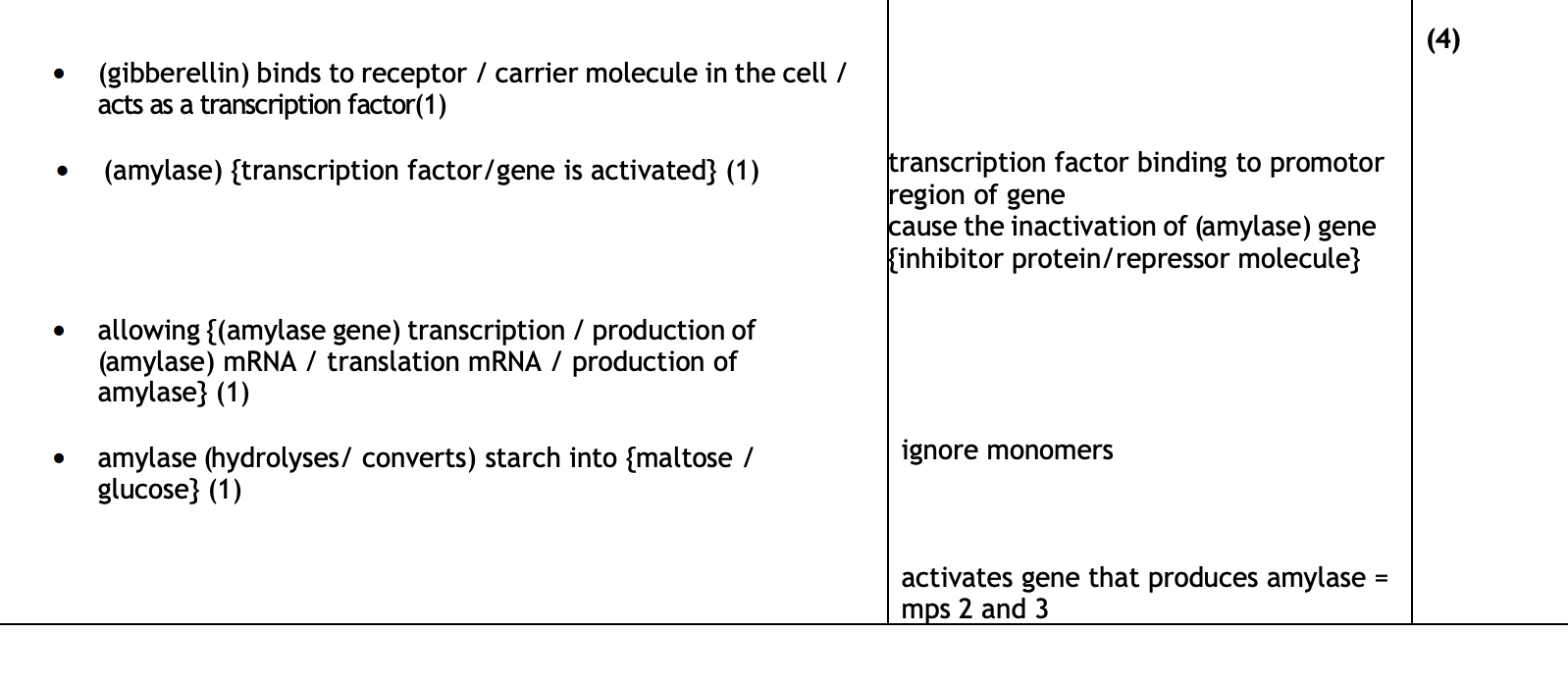
first it enters nucleus!!
important- unit 4
some patients given rHE develop anti rHE antibodies, how are they produced?
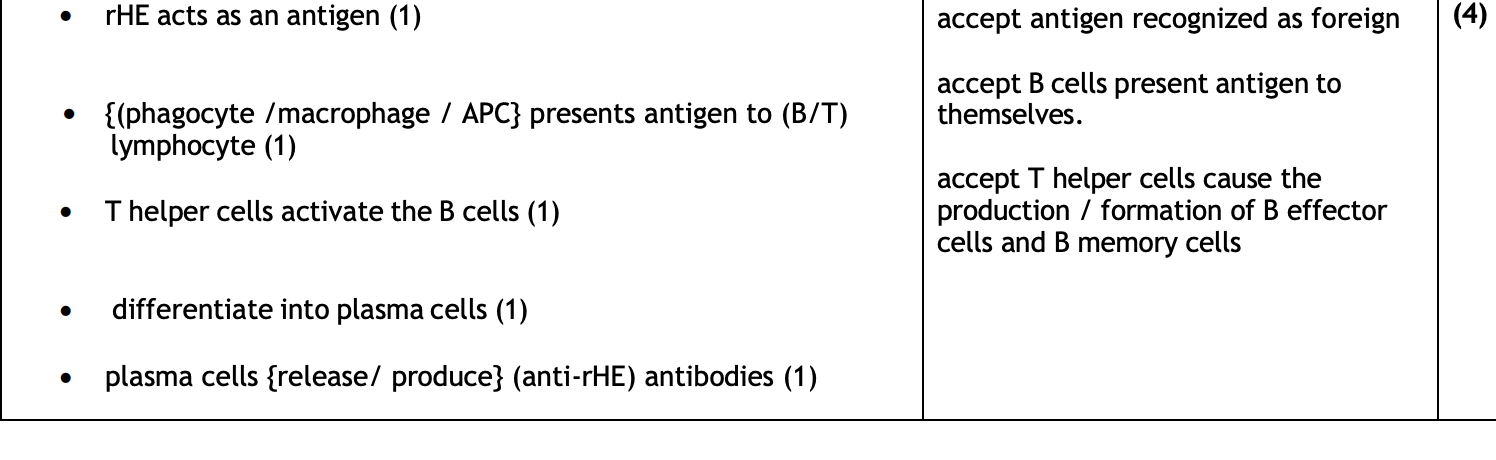
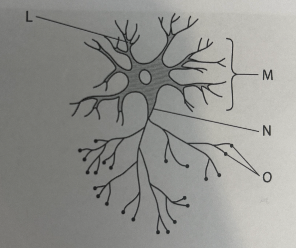
8d- explain how changes in ion channel protein result in nerve impulses in the nervous system
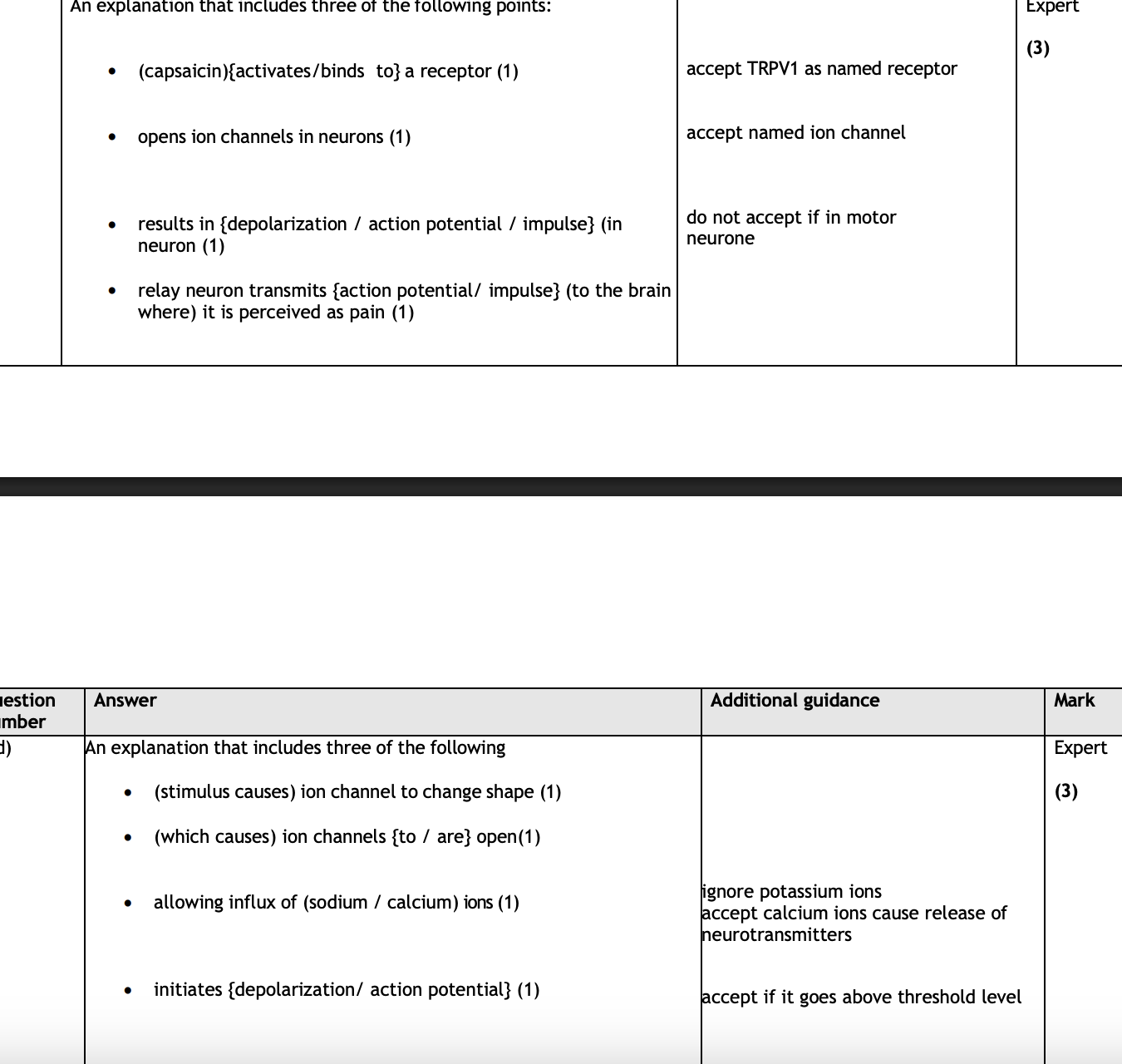
explain how MECHANICAL stimjue converted into electrical signlas

how is creatine filtered from blood in glomerulus?/ how ultrafiltration…


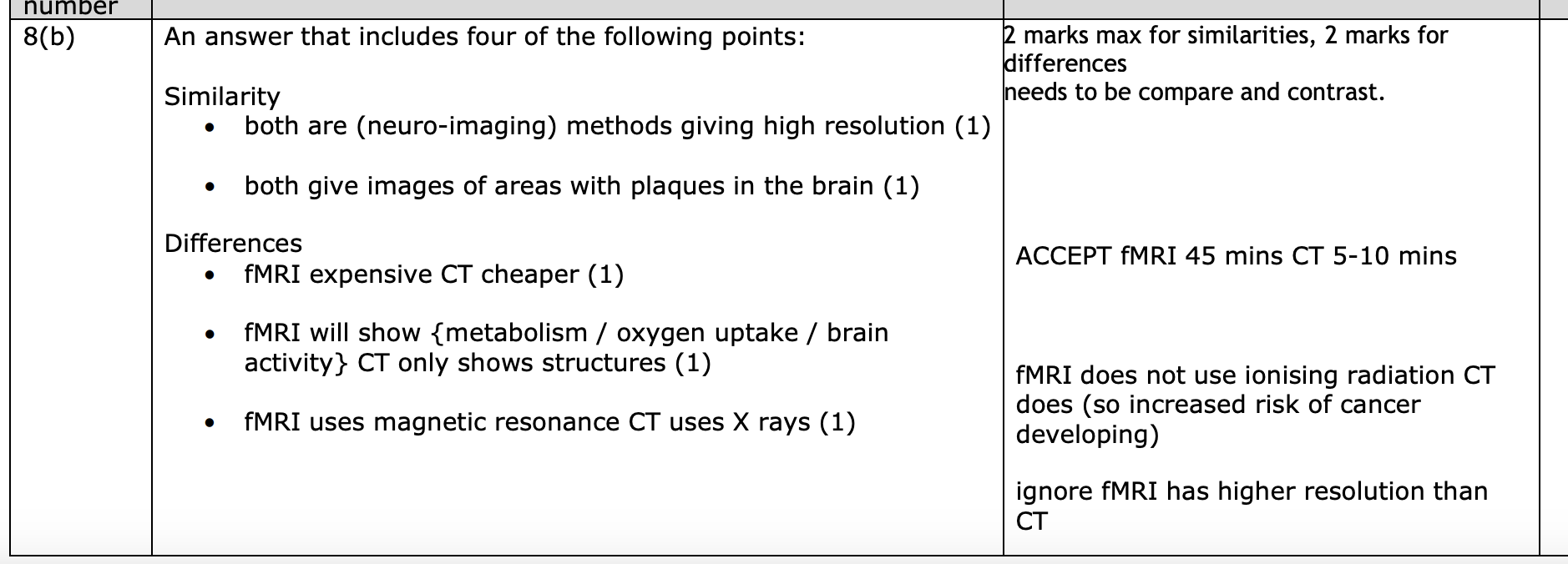
compare ct and fmri
it was found that p.gingivalis in is in cerebral cortex. describe how team could show that this genetic material is active

1st bullet point!!
describe how glucose reabsorption takes place in nephron

where is adh created and secreted
produced- hypothalamus
secreted-pituitary gland
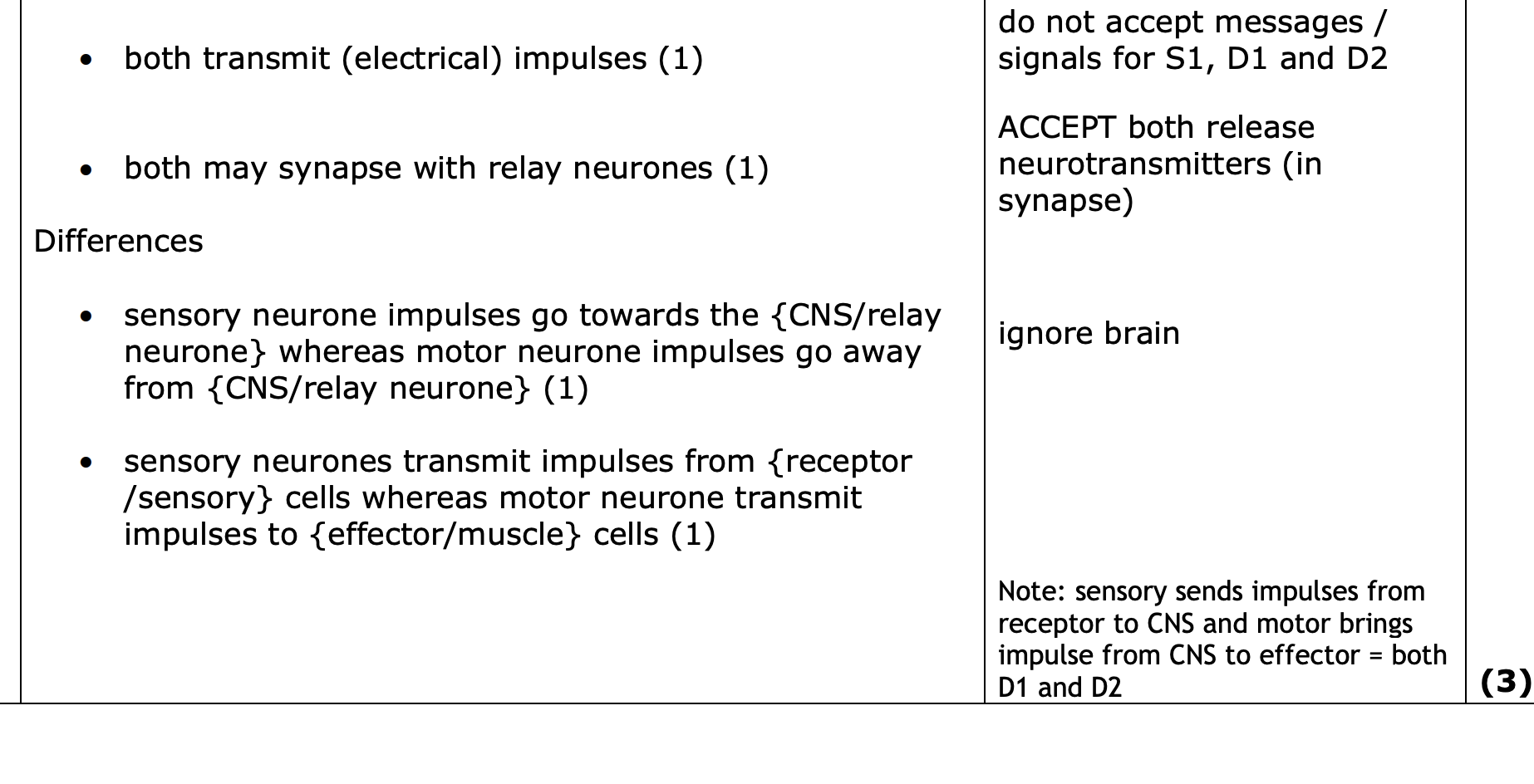
compare function of motor and sensory neurone
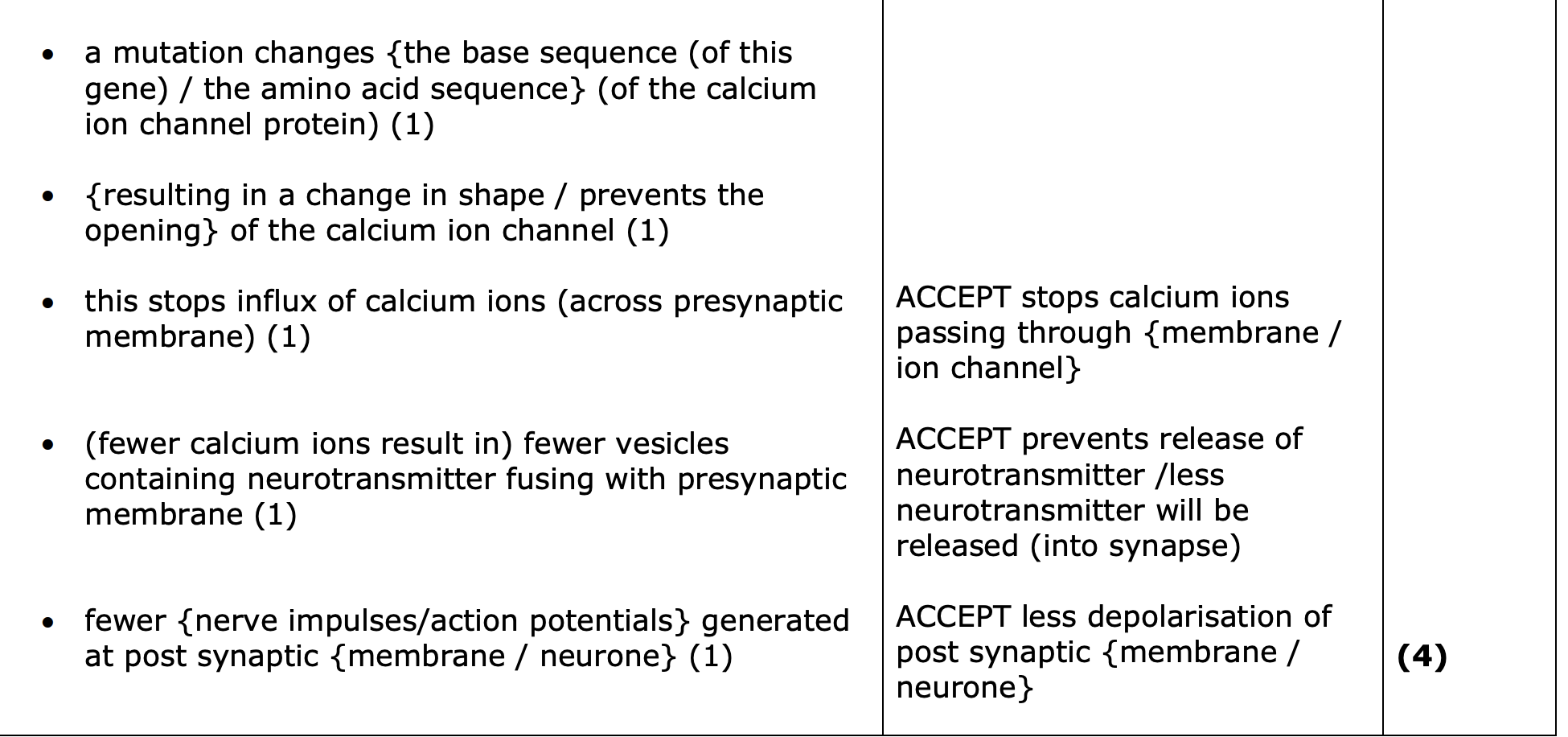
explain how mutations in gene coding for ca2+ channels are linked to neurological conditions
descirbe how autonomic ns regulation breathing rate when person resting

suggest how the activity of sympathetic ns regulates inflammation

explain why maintaining a resting potential requires ATP

important how is pet scan used to identify part of brain involved

ISOPTOPE THAT EMITS POSITRON INCORPORATED INTO GLUCOSW
more active neruones with increased respration will require more glucose supply
POsiTRONS PRODUCE GAMMA RAYS THAT ARE DETECTED AND coNVERTEd TO IMAGE

rpe65 converts transretinal to cisretinal
explain why mutations in rpe65 gene can result in blindness

what is found in fast twitch compared to slow twitch fibre?

mutations in genes can result in blindness
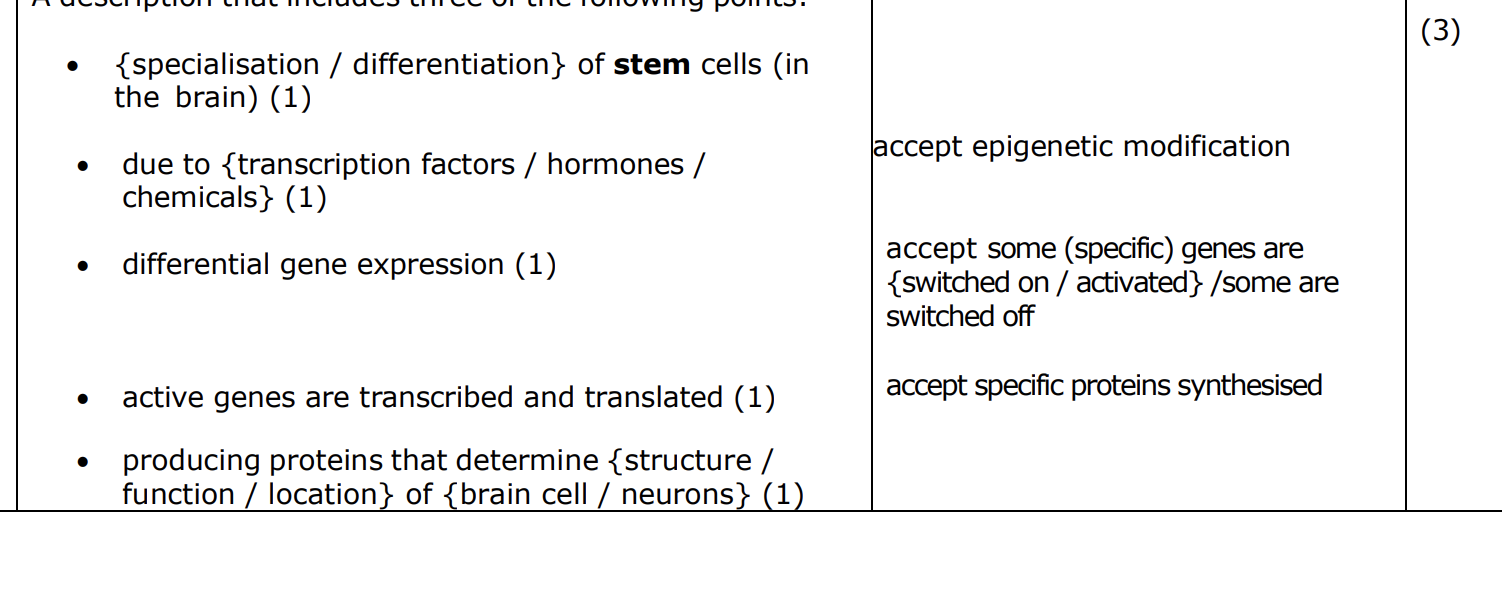
describe how these genes could be identified

How does virus cause internal bleeding

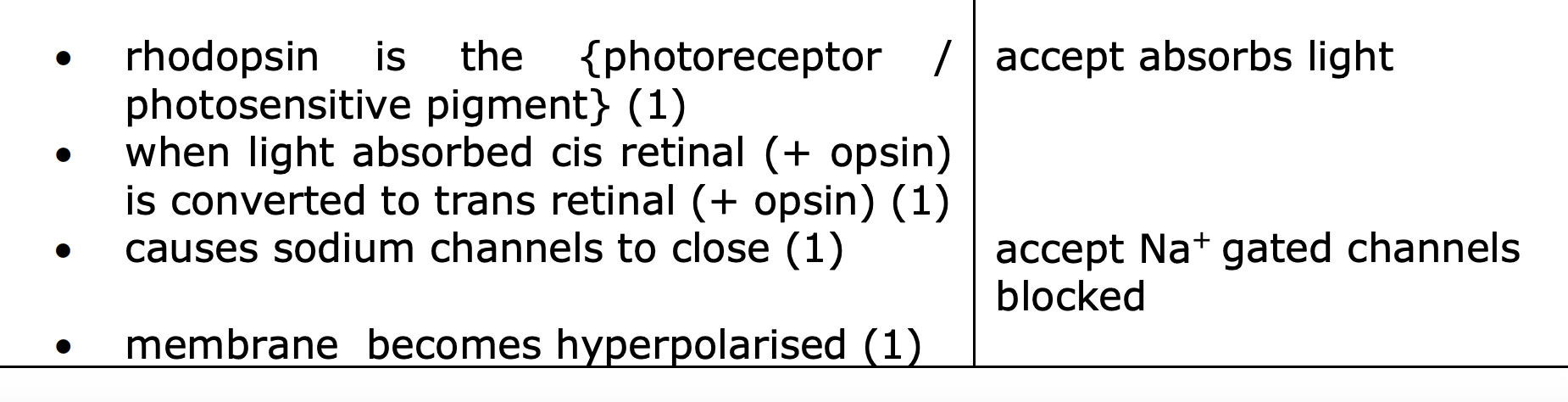
describe how light entering eye causes pupil to respond

define pluripotent stem cells

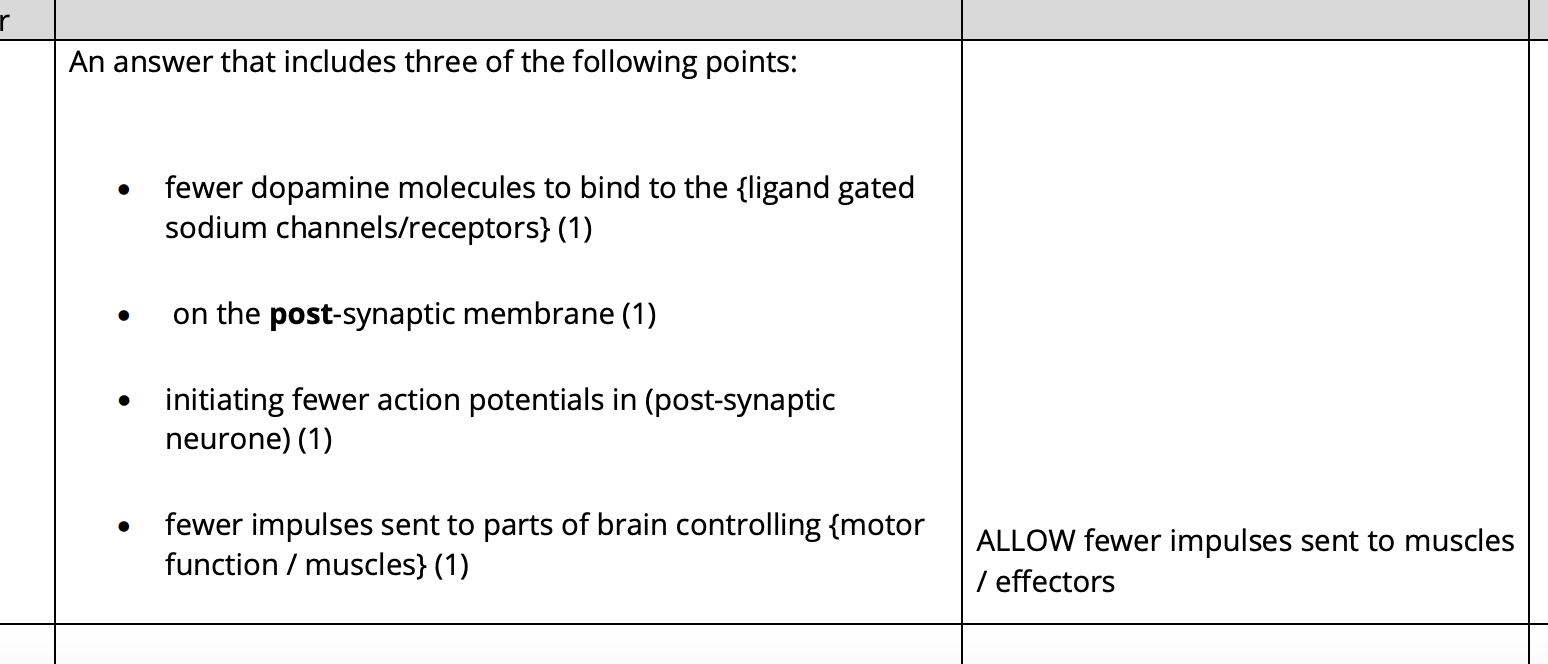
why does the release of less dopamine by presynaptic neurone result in motor symptoms
why is ct scan used for tumours

explain how gene variant that produces defective form of an enzyme reduces effectiveness of clopidogrel

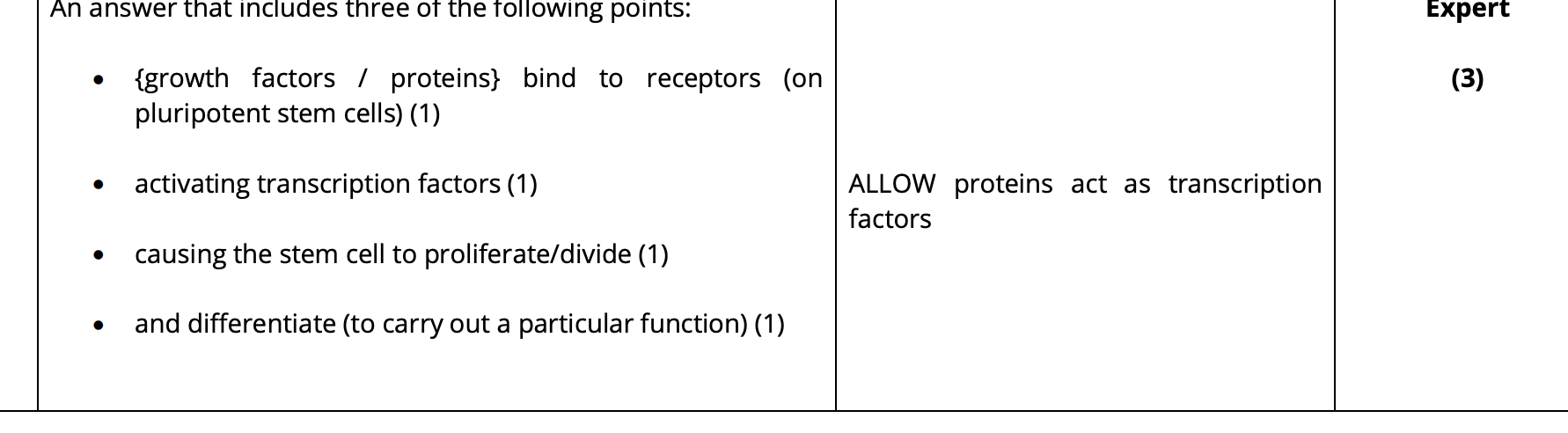
suggest how growth factors and other proteins stimulate induced pluripotent stem cells to produce a functioning tissue
important- how does loop of henle act as countercurrent multiplier

IMportant- rhodopsin role in rods in retina
say causes na 2+ ions to close, photoreceptor
growth substance role

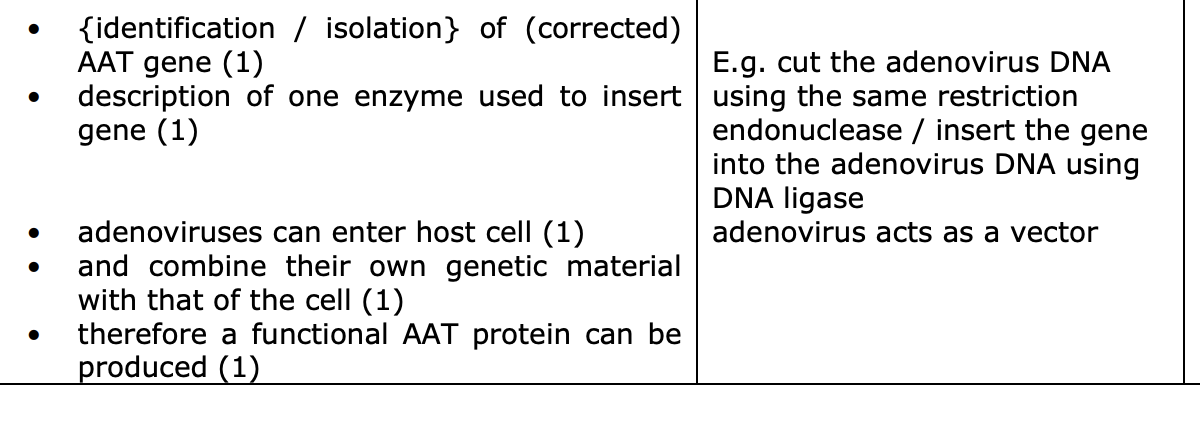
a treatment for aat deficiency uses adenovirus to genetically modify cells in affected person
adenovirus contain double stranded DNA
explain how these viruses can be used to treat AAT deficiency in a person
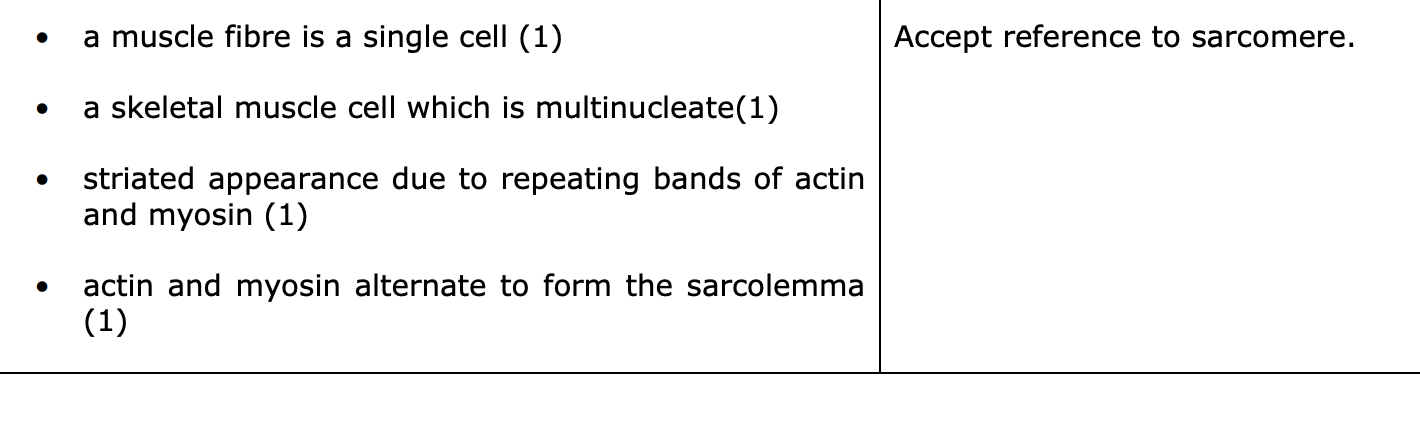
describe structure of skeletal muscle fibre
explain why calcium ions binding to troponin allows contraction of muscle

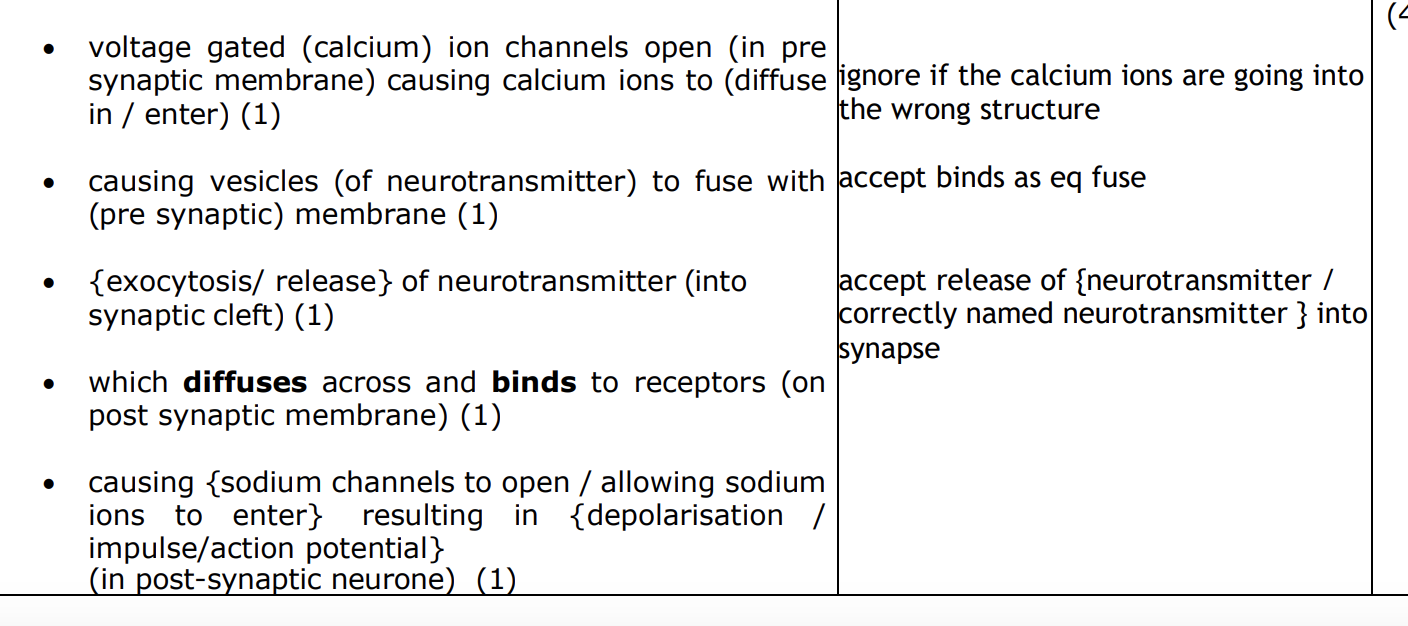
explain how nerve impulse transmitted across synapse
STEROID HORMONE
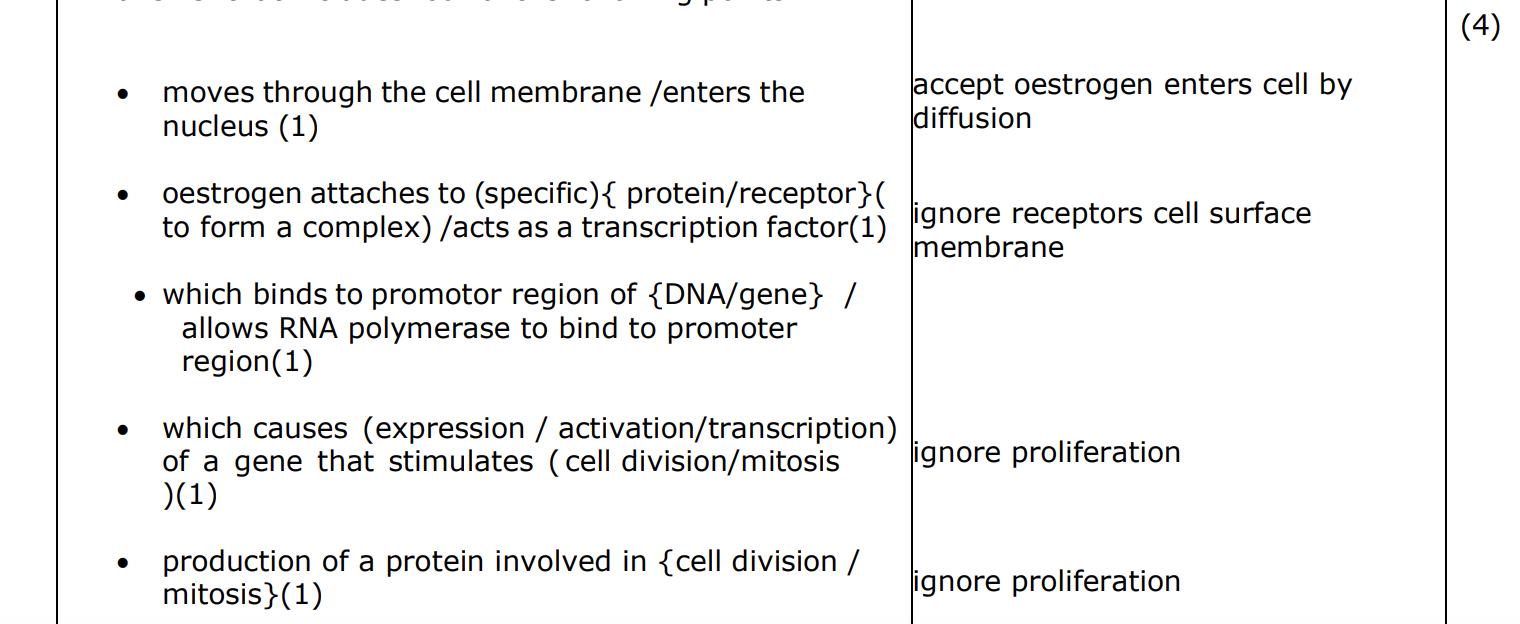
what happens to lactate
taken to liver
converted to pyruvate/glucose
used in link rxn/ krebs


explain what happens during repolarisation