Market failure
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the 4 functions of price
signalling function
incentive function
rationing function
allocative function
What is the signalling function of price
Prices provide information that allows buyers and sellers to plan and coordinate their economic activities
What information does the signalling function of price tell sellers?
For sellers: Rising price suggests high demand/short supply
.Falling price=low demand/excess supply
What information does the signalling function of price tell buyers?
A high price indicates scarcity/greater value
Low prices signals abundance
What is the incentive function?
Prices create incentives for people to alter their economic behaviour
What incentives may firms and consumers have?
Higher prices incentivise firms to produce more as it will be profitable to do so. Lower prices discourage production
Higher prices for consumers, make them more likely to seek substitutes whereas lower prices are deemed attractive
What is the rationing function of price?
Rising prices ration demand for a product
If there is excess demand, prices will be made higher to discourage consumption.
What is the allocative function of prices?
Changing relative prices to allocate resources away from markets with excess supply and into markets in which there is excess demand
What is market failure?
Market failure occurs when the market/price mechanism performs unsatisfactorily or does not perform at all.
What is complete market failure?
When the free market fails to provide a good or service at all.
Also known as a missing market
What is partial market failure?
When a good is provided by the market but it is either under or over provided leading to inefficiently allocated resources
What happens when 1 or more of the 4 functions of price breakdown
Market failure occurs
What are private goods?
They are excludable, meaning nobody can reap the benefits of owning and using the good if they haven’t purchased it.
They are rivalrous, meaning one persons consumption of a good reduces the amount available to others.
What are public good?
Public goods are non-excludable and non-rivalrous
These characteristics can cause market failure
How can a public good such as light house cause market failure?
The beam of light provided by a light house is an essential service as it provides safety
It is non rivalrous as one ship utilising the light provided doesn’t prevent other ships from also using it
But the service is non-excludable as those who haven’t paid for it (free- riders) can use the light provided for free
Because of this it will be impossible for the firm to providing the light house to make enough revenue to cover costs.
The profit incentive disappears so the incentive to provide the service diminishes.
Causing market failure as a necessary service is not provided
What can be done to solve the problem of a missing market?
The government may provide an alternative provision to ensure the good is being produced
What are other examples of public goods?
National defence
Police
Street lighting
Roads
What are quasi public goods?
A good which is not fully non rival or where it is possible to exclude people from consuming the good
Shows charectaristic’s of both a public and private good
Examples of a quasi public good
Roads
Beaches
Parks
How can roads be quasi public goods?
They can be excludable if a toll is charged. Without paying a fee you cant access the road
They can be rivalrous in times where there is mass amounts of congestion. One person using road space can take away the road space available for other drivers
How has technological change impacted the status of roads as a pure public good?
Technological change such as electronic prices makes it more feasible for government to charge all motorists for road use
The price charged can be changed depending on time of day incentivising road users to travel in times of non-rush hour
Making roads more of a quasi public good now
Define an externality
A side effect of production or consumption that affects third parties who are not directly involved in the transaction
Externalities can be positive or negative
Why do externalities arise?
The market fails to fully account for all the costs and benefits for the good
The market price of the good doesn’t reflect the social cost or social benefit
What is a negative externality?
When the production or consumption of a good causes a cost to the third party
Social cost exceeds the private cost
Private cost=costs that consumers or producers pay directly when they make a decision to produce or consume a good
What is a positive externality?
This occurs when the social benefit of the production or consumption of the good exceeds the private benefit
The private benefit= the benefit received by the individual
What is production externality?
An externality that is generated when producing a good/service
Examples of negative production externalities
Pollution
Industrial waste
Acid rain
Explain negative production externalities in terms of a power station producing electricity
A power station may cause pollution when producing electricity
The pollution becomes an external cost which is a part of the true costs of production
This external cost is ignored by firms and passed onto third parties
The cost that consumers pay for the electricity only reflects the money costs of production and not the real cost which includes the external costs
This causes the electricity to be under-priced and over produced- causing a partial market failure
What are consumption externalities?
An externality generated by the consumption of a good or service
Examples of negative consumption externalities
Incorrect disposal of chewing gum- ends up under desks or roads creating displeasure
Alcohol- can cause more drink driving accidents, domestic violence
Using phone at cinema - disrupts someone’s experience
(The private benefit exceeds the social benifit)
What is another way to describe positive/negative externalities?
Negative=External costs
Positive= External benefits
How do positive production externalities effect price and production of a good?
A positive production externality means that third parties are benefiting from the production of a good/service
But these benefits aren’t reflected in the market price.
The good is under produced and under consumed. Price thus being high
(Firms don’t get paid for positive externalities so lowering the price wont be profitable for them)
Define social benefit
The total benefit of an activity including external benefits and private benefits
Social benefit= Private benefit + External benefit
Define social cost
The total cost of an activity including private and external costs
Social cost = Private costs + external costs
Diagram for negative production externalities
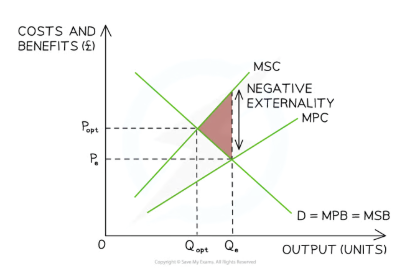
Explain the negative externalities of production diagram
Marginal social benefit(MSB) = Marginal private benefit (MPB) - as the diagram is focusing on production costs
The larger the external costs, the lager the gap between MPC and MSC.
The optimal allocation of resources for society would be when MSB=MSC (Socially optimum equilibrium)
This is depicted by Qopt and and Popt
There is no market failure at this equilibrium
Firms tend to allocate resources at the private optimum (Qe) as they fail to take into account the full social costs- Resulting in a welfare loss
Qe> Qopt shows overproduction
Diagram for negative consumption externalities.
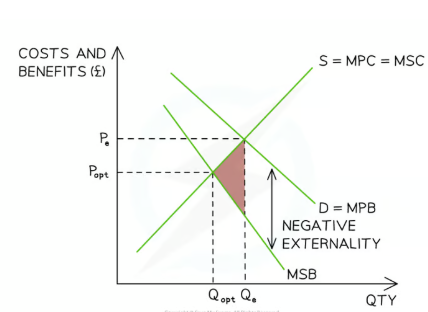
Explain the negative consumption externality diagram
MSC is assumed to eqaul MPC as the diagram is focusing on the benifts
The larger the external costs the larger the gap between the MPB and the MSB
The optimal allocation for society would be when MSB=MSC
This happens at Popt and Qopt no market failure atp
The market allocates resources at the private optimum (Qe) as consumers fail to take into account the negative externalities from consumption that cause welfare loss.
When Qe > Qopt there is over consumption
What is a merit good?
A good such as healthcare for which the social benefits of consumption exceed the private beneifts
Value judgement are involved in deciding that a good is a merit good
What are the differences between a public good and a (de)merit good?
Unlike public goods the market can and does provide merit goods but arguably underprovides
Merit or demerit goods lead to partial market failure
Free market provides merit goods but in the wrong quantity
What does a merit good provide?
Positive externalities of consumption- that benefit third parties
Diagram representing the under consumption of a merit good
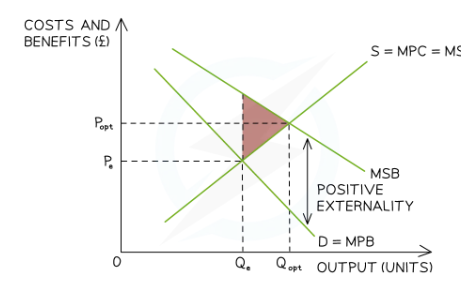
Explain the diagram displaying the underconsumption of a merit good in the free market?
The optimal allocation of resources for the merit good would be where the MSB intersect the MSC
The free market equilibrium for the merit good is at Pe and Qe showing under consumption
This is because the market fails to consider the positive externalities resulting from the consumption
Leading to partial market failure