AP Psych Semester 1 Final
1/633
Earn XP
Description and Tags
History and Perspectives, Science Practices, BBB, BBB2: Sensation, Tranduction, Sleep, and Drugs, Perception, Cognition, Learning and Behaviorism, Developmental
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
634 Terms
Psychology
the study of human behavior, the mind, consciousness
mind
where cognition occurs
Consciousness
our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment
Nature/Nurture Problem
Nature=genes influence behavior, Nurture=environment influences behavior (tabula rasa)
Free Will vs Determinism Problem
FW: Choice and cognition D: fate, Destiny, cause and effect
Perspectives
differing viewpoints of the same thing
approaches
differing ways of investigating an issue
philosophy
study of life’s great questions (ex. why are we here?)
plato
ancient Greek philosopher, foundational thinker of western philosophy
Prisoner’s Cave Analogy
how do we know that what we see as reality, is truly reality
Rene Descartes
All you can know is your here and you can only know what you know
The Mind/Body Problem
issue of understanding connection between mind and body
Mind/Body Dualism
The way of superstition. Non-verifiable, non-scientific
Monism
Early Precursor to the biological perspective
British Empiricism
Knowledge is gained empirically. foundation of science, away from philosophy
psychoanalysis
Freud’s theory of personality that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts
Sigmund Freud
Developed psychoanalysis: Hypnosis, Dream Analysis, Fee association. Oedipus and Electra Complex
psychodynamic
Freud, psychoanalysis, iceberg- more to you than can be seen
Free Association
In psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing
Phobia
an anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation
Defense Mechanism
in psychoanalytic theory, the egos protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality
Repression
In psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts
Unconscious
according to freud, a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories. Information processing of which we are unaware
Id
fully unconscious: pleasure principle, food and sex desire
Ego
Partially Conscious: reality principle
Superego
partially conscious: source of guilt conscience
Object Relations Theory
Psychoanalytic; how internal relationships w/ others shape early attachments and influence future relations
Behaviorism
What we see as “behavior” is a result of responses/adaptations to its environment
Ivan Pavlov
Dogs and Salvation - discovered behavior principles by mistake
Edward Thorndyke
discovered the law of effect
Law of Effect
Responses followed by satisfying consequences are more likely to occur, and the opposite.
John B. Watson
little albert experiments, fear can be learned, applied to marketing
Rosalie Raynor
Watson’s assistant, mistress, lil albert
B.F. Skinner
Skinner box, radical behaviorism, cognition=unimportant
Radical Behaviorism
environment influences mind and explains behaviors
Behavior Modification
therapeutic technique to change behavior w/ positive or negative consequences
Humanism
Third force, answer inside you, emphasis on growth potential
Abraham Moslow
Hierarchy of Human needs
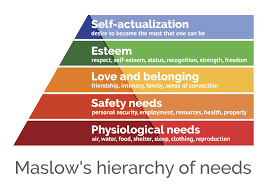
Self-Actualization
Maslow- one of the ultimate psychological needs that arise after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved, the motivation to fulfill ones potential
Personal Growth
grow in areas of life, maslow says to grow everything deltaT must be good
Belongingness
feeling of acceptance and familiarity
positive psychology
The scientific study of human flourishing, with the goals of discovering and promoting strengths and virtues that help individuals and communities thrive
cognitive perspective
mental processes, thinking, language
Gestalt Psychology
The whole is greater than the sum of the parts
Mental Processes
thoughts and actions and tasks that occur in the brain/mind
Cognitive Neuroscience
ask subject to think of something (part of brain lights up)
Biopsychosocial Approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural viewpoints
Socio-Cultural Perspective
How people behave in groups, cultural impacts, social norms affect on behavior, etc.
Culture
the society, region, traditions you grow up with (geographically often)
Social Norms
society’s expectations and common habits (unspoken rules)
Socialization
process where values, behaviors, and attitudes are considered appropriate to culture/society
Cultural Psychology
cultures shape members psych process
Context
background information
individualism
by ones self
collectivism
as a group
biological perspective
studies biological and physical basis of behavior (ex. study brain)
behavioral neuroscience
how nervous system affects behavior and emotions
nervous system
network of nerve cells that allow interaction with environment
behavior genetics
genes and environment affect behavior
neurotransmitter
chemical messengers that allow neurons to communicate with each other and cells. Allow life functions
Endocrine System
network of glands and organs that produce hormones that regulate things such as mood and metabolism
evolutionary psychology
all human behaviors reflect influence of predispositions from ancestors
Darwin
applied natural selection ideas to mind
Domains
specific area
Domain:Biological
biology application to concepts like brain mechanics
Domain: clinical
studies disorders and how to treat them
Domain: cognitive
studies mental abilitys
Domain: counseling
helping others with mental distress
Domain: developmental
studies behavioral and mental development. 0-100
Domain: educational
how people learn and retain information
Domain: experimental
use controlled experiments to study behaviors and functions
Domain: industrial-organizational
in the work place
Domain: personality
big 5 personality traits (openness, extraversion, etc.)
Domain: psychometric
measures attributes like intelligence
Domain: social
how behaviors are influenced by social interactions
Domain: positive
how to encourage acceptance of past and optimism for future
Scientific Method
standardized way of making observations, testing predictions, forming theories, and interpreting results. hoping to avoid bias
Hindsight Bias
“I knew we were the best” after you already won
Applied Research
research that has a specific point (applicable)
basic research
maybe interesting and may add to our knowledge base, but isn’t readily applicable
hypothesis
a testable falsifiable prediction about some phenomenon. (If-then statement)
Independent Variable
variable that we choose to alter
Dependent Variable
variable that changes because of the independent variable change. Result
Confounding Variables
anything besides independent that may skew results
Participant Relevant
Situation Relevant
participant relevant
participants introduce to experiment
situation relevant
environment caused confounding variables
theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
operational definition
translating abstract terms into something observable/empirical and measurable/concrete
validity
the extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what its supposed to
reliability
the extent that a test has consistent results, assessed by retesting, adjustments, and consistency of scores
replication
repeating essence of study, with different people and situations to see whether the basic finding can be reproduced
sampling
the process of selecting the participants for the experiment
sample
a selected group within a population. the larger the sample, the better chance we have of reflecting the characteristics of the population as a whole.
Population
the people who qualify to be in an experiment. anyone or anything who possible could
representative sample
reflects the make-up (characteristics) of the larger population
random sample
statistically random, everyone in population has equal chance of being selected
stratified sample
the sample will be made up of sub-groups that have proportional representation of each significant factor
experimental method
control and experimental groups HAVE causation
laboratory vs field experiments
in lab vs in natural setting (public)
confederate
someone who participates in a study but is not the main focus