DNA Replication
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
importance of DNA
prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes made of this. “blueprint” for proteins.
genome
made of many individual cells
dna copied
so each offspring gets instructions
dna and rna
are nucleic acids that govern cell life
nucleic acids
built from nucleotides
nucleotide parts
phosphate group, sugar (deoxyribose in DNA), and nitrogenous base
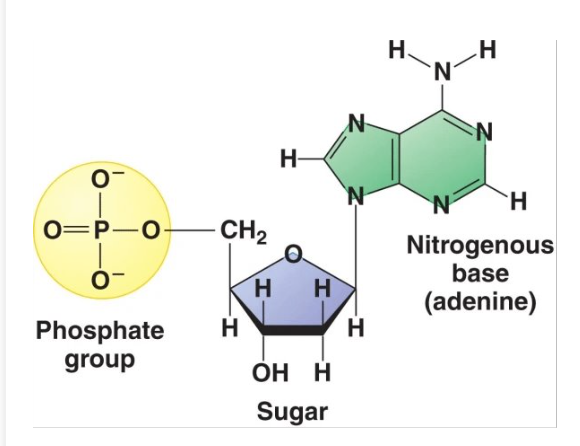
nitrogenous bases
adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
purines
adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
cytosine, uracil, and thymine
double helix
long, double stranded DNA molecule
rungs of dna
consist of nitrogen bases
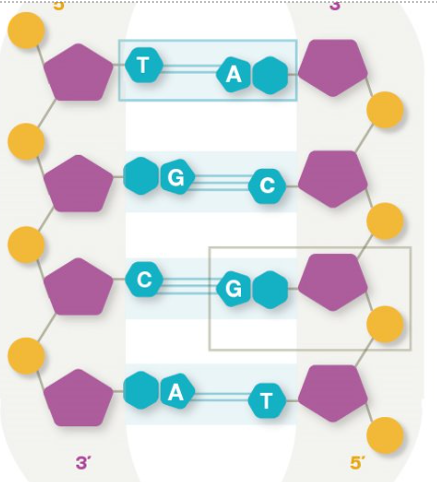
complementary nitrogen bases
A & T, G & C
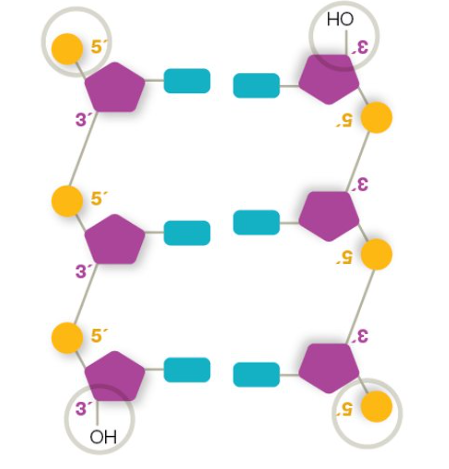
side rails of dna
alternating pattern of sugar and phosphate molecules held together by phosphodiester bonds
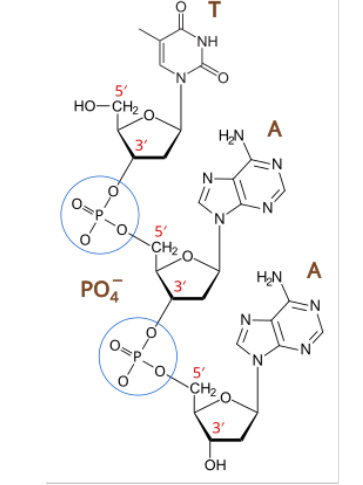
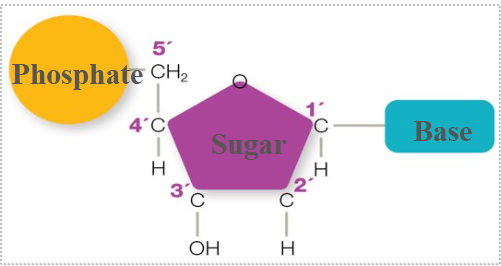
in nucleotides, a base is attached to
1’ carbon of sugar
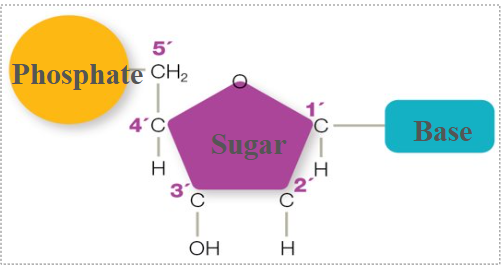
in nucleotides, a hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to
3’ carbon of a sugar
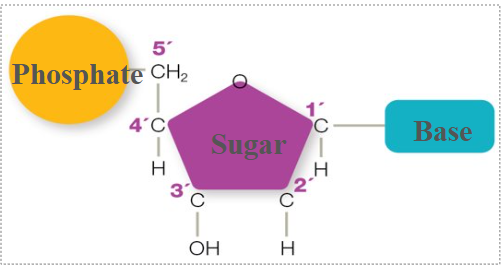
in nucleotides, a phosphate is attached to
5’ carbon of a sugar
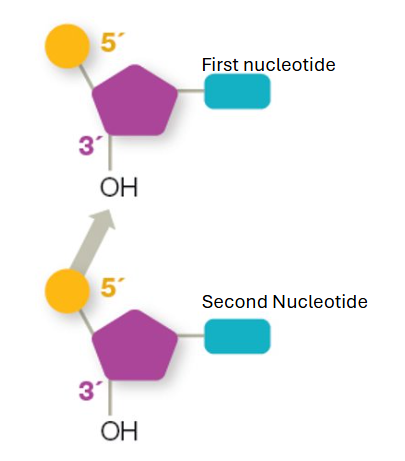
directionality of DNA
5’ phosphate of first nucleotide bonds to 3’ hydroxyl group of next nucleotide
phosphodiester bonds
link nucleotides together to form sugar-phosphate “backbone” of DNA
antiparallel arrangement
one strand runs 5’ to 3’ and the other strand runs 3’ to 5’. allows complementary bases of DNA to bond
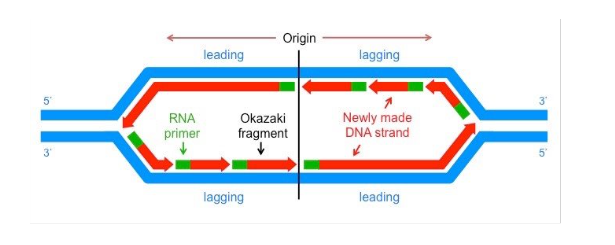
origin of replication
where enzymes collect and form a bubble w/ two replication forks
replisome
contains machinery necessary for replication. binds to origin of replication
seperating genome
DNA is supercoiled in nucleoid, must be separated to replicate
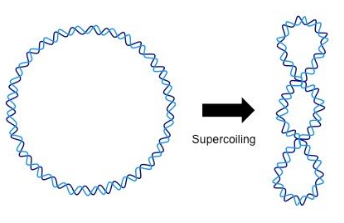
topoisomerases
used to uncoil chromosome
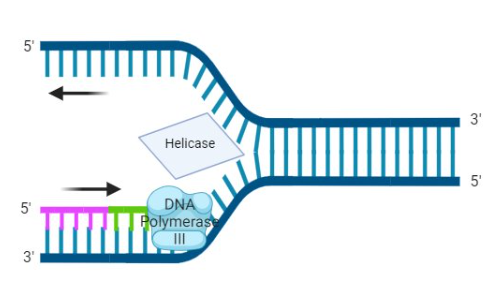
helicase
unzips DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases to separate strands
single strand binding proteins
prevent two strands from rejoining each other to replicate
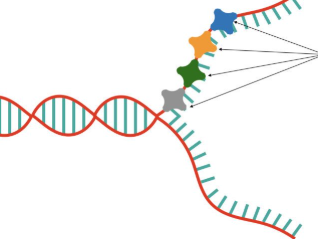
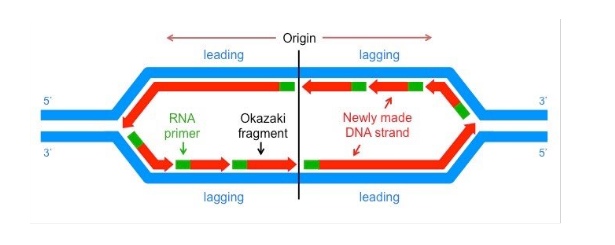
replication fork
two complimentary strands form
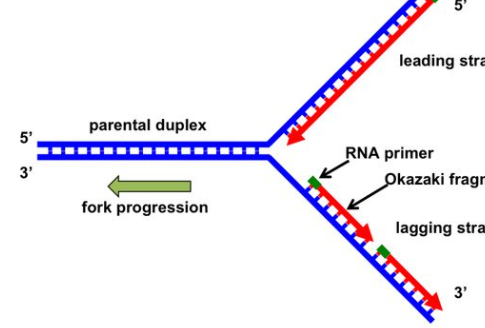
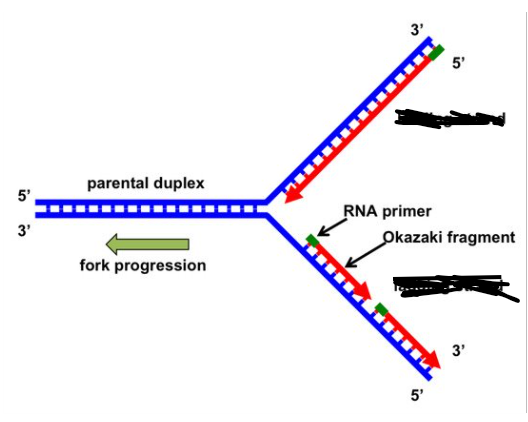
leading strand
replicated in direction fork opens
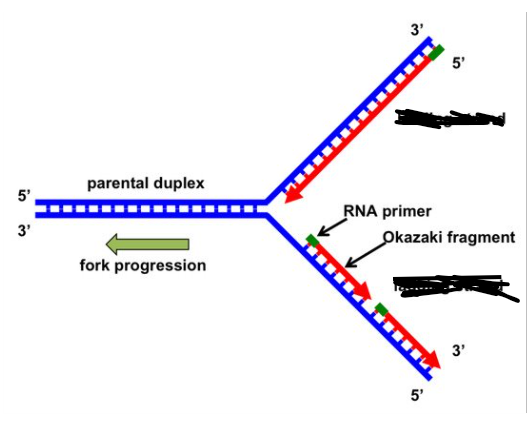
lagging strand
replicated in opposite direction as unwinding helix. replication proceeds away from replication fork
replication bubble
replication proceeds in both directions, forming this at origin of replication
energy to build molecule
provided by formation of phosphodiester bond
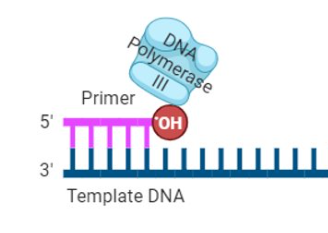
DNA polymerase requires
a 3’ OH to add bases
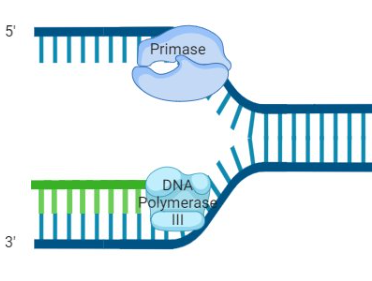
primase
synthesizes primer, makes primer out of RNA
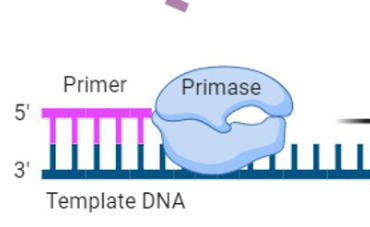
primer
RNA sequence that begins DNA synthesize because it provides the 3’ OH to add bases
DNA polymerase III
binds to the 3’ OH of the primer. adds dNTPs 5’ to 3’
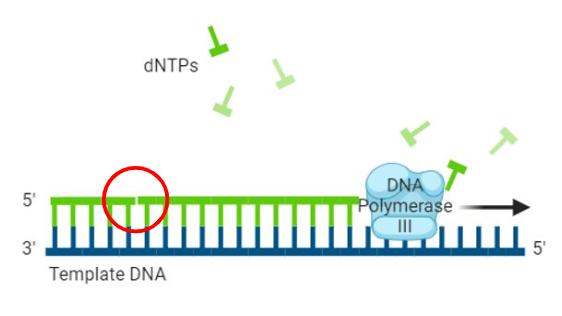
DNA polymerase I
removes RNA primer and replaces it w/ dNTPs
single stranded (SS) break
DNA polymerase I replacing primer leaves this in new DNA
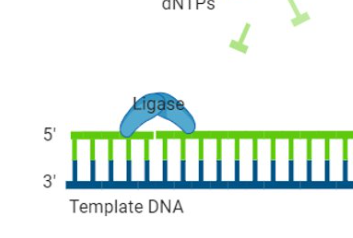
DNA ligase
binds to either side of the single stranded break and glues it back together
leading strand replicates
continuously
primase attaches to lagging strand
when fork opens up enough
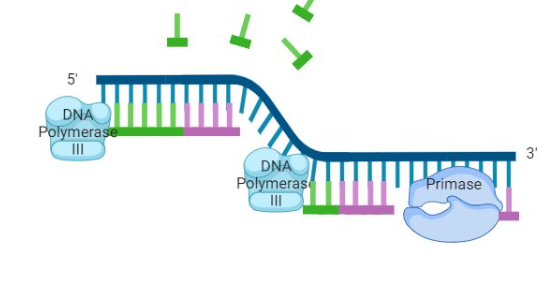
okaski fragments
small fragments of DNA on lagging strand caused by the DNA polymerase repeatedly hitting end of replication fork and waiting for it to open up
concatenated dna
two interlinked dna strand after replication is done due to circular nature of prokaryotic genome
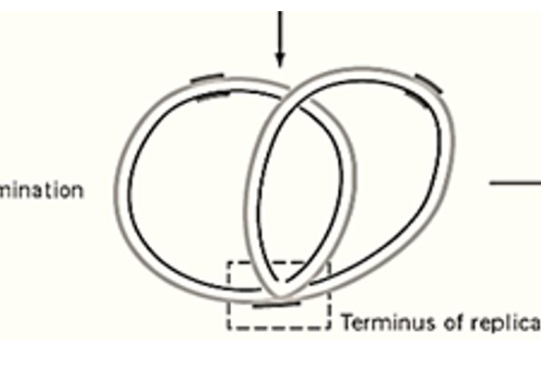
topoisomerase IV after replication
causes double stranded nick and binds single DNA strands back together leaving two chromosomes