anatomy q4 review
1/171
Earn XP
Description and Tags
.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
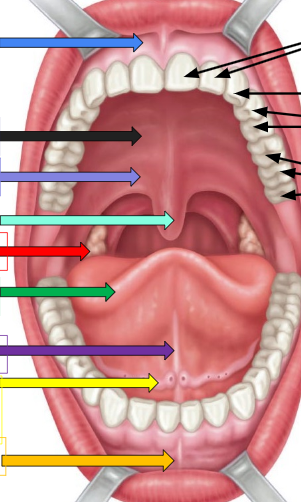
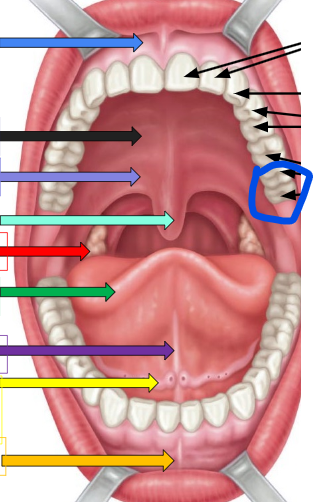
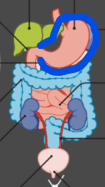
Frenulum
sky blue arrow and orange arrow
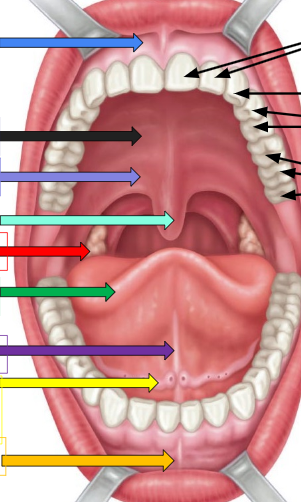
Hard palate
thick black arrow on left
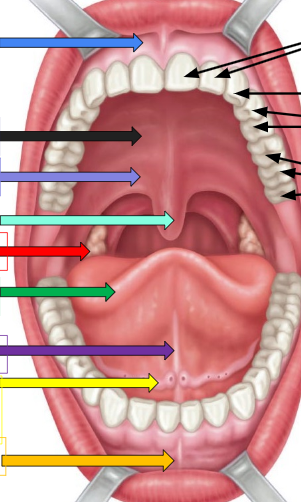
soft palate
lavender arrow
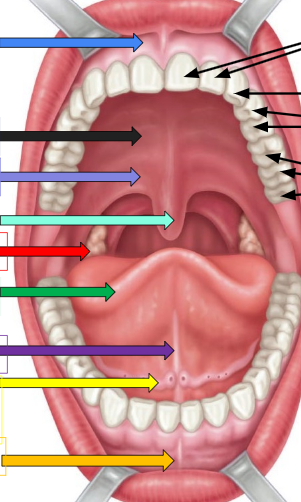
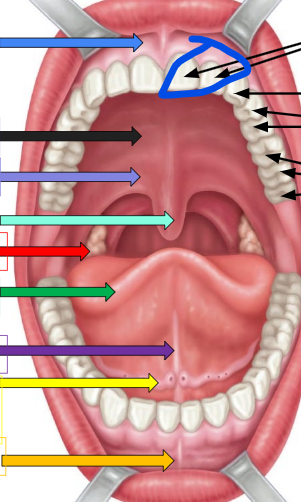
uvula
ivy green palate
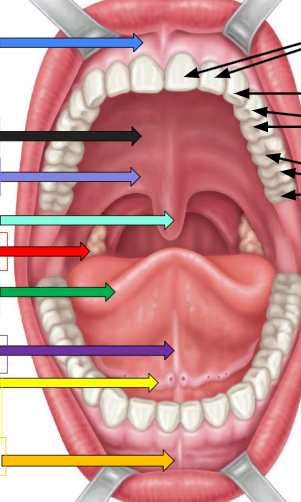
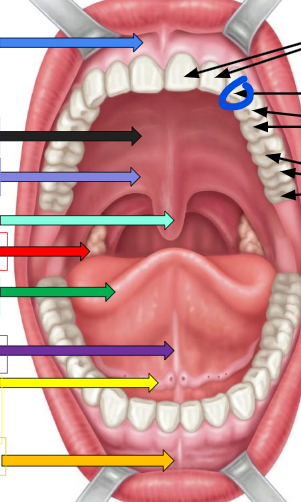
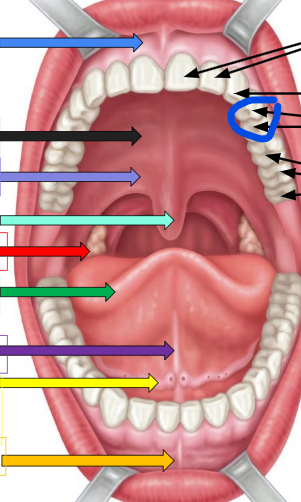
palatine tonsil
red arrow
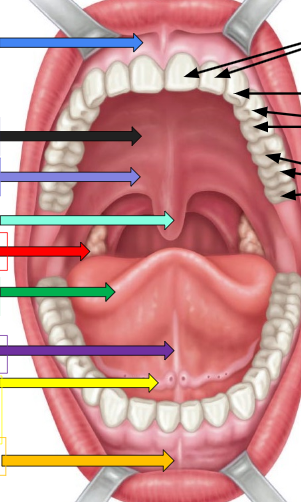
tongue
dark green arrow
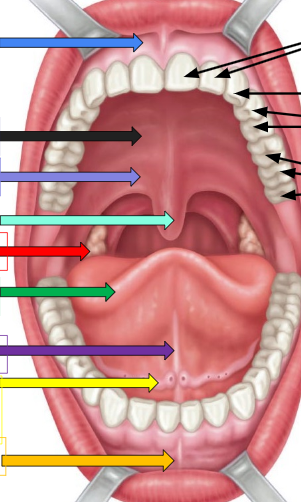
lingual frenulum
dark purple arrow
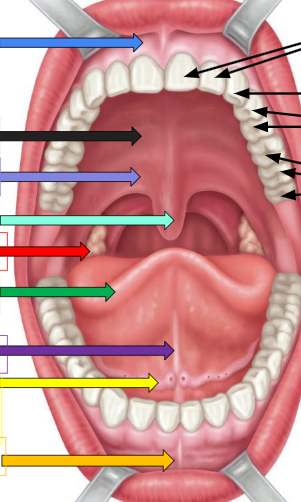
sublingual salivary gland
yellow arrow
incisors
cuspids
bicuspids
molars
mastication
process of chewing
Peristalsis
wave like motion to move food
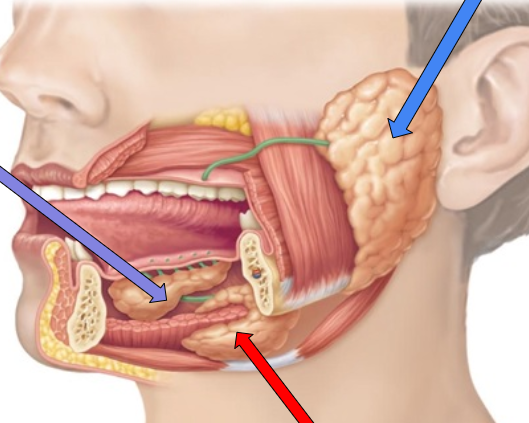
parotid gland
blue arrow
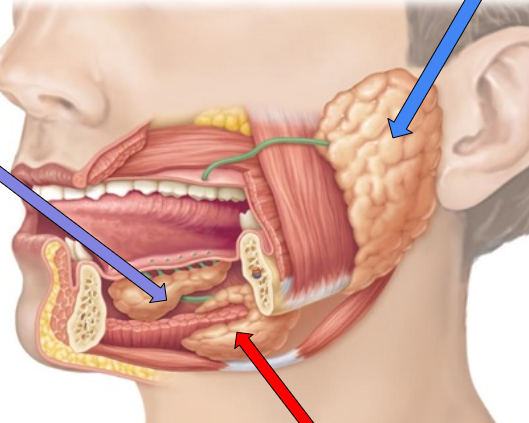
sublingual gland
purple arrow
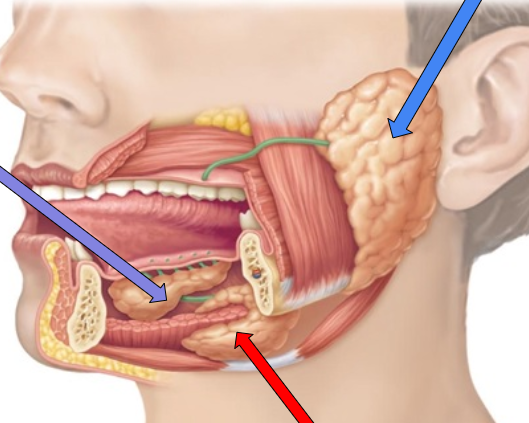
Submandibular gland
red arrow
Duodenum
Small intestine
yellow region
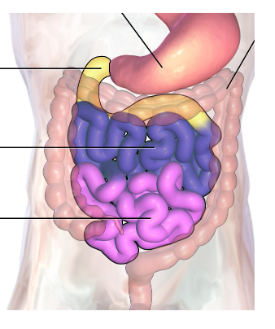
Jejunum
Small intestine
purple region - middle
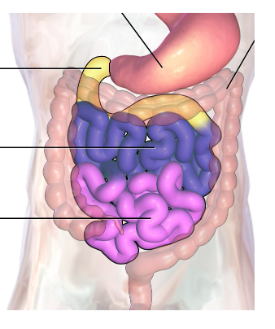
Ileum
Small intestine
pink region
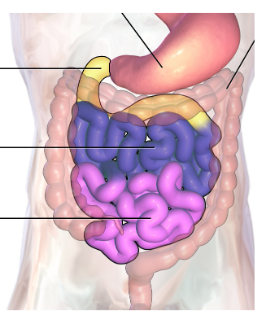
CATDSRA
Large intestine order (letters)
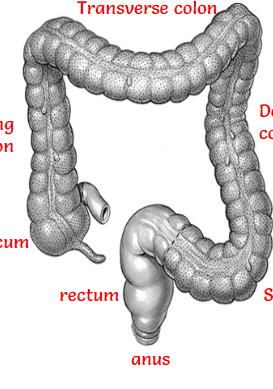
Liver
Gall bladder
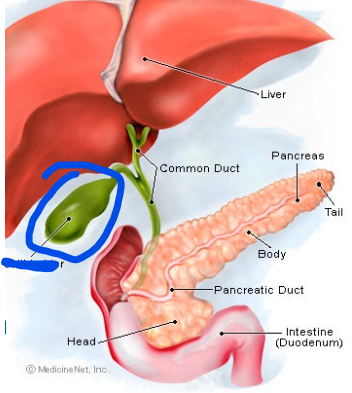
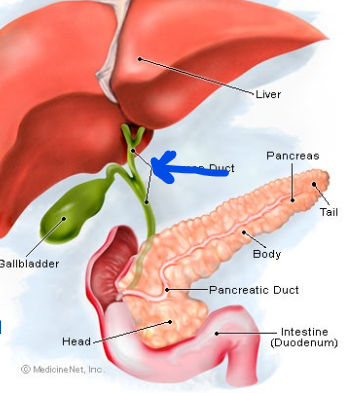
Common bile duct
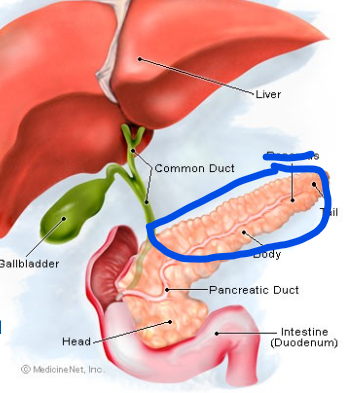
Pancreas
stomach
plasma
55% of blood
Made up of:
Water
Amino acids
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Vitamins
Minerals
Hormones
Electrolytes
Cellular waste
Cell contents
45% of blood
Erythrocytes
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
also known as red blood cells
Leukocytes
defense and immunity
also known as white blood cells
Thrombocytes
blood clotting
also known as platelets

darker
less oxygen causes blood to get _____
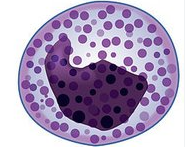
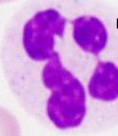
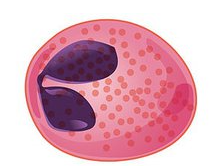
Granulocyte
cells that show granules when stained
basophil
neutrophil
eosinophil
lymphocyte
B when in bones and
T when in thymus gland

Monocyte
largest of leukocytes
Agranulocyte
cells that do NOT have granules when stained
Hemolysis
breakdown of red blood cells
heme → biliverdin → bilrubin → bile
Hemostatis
positive feedback system of blood stoppage
Vasospasm
Stages of Clotting
Smooth muscle spasm to close blood vessels and reduce blood loss
Platelet Plug
Stages of Clotting
Platelets swell
form spiked processes
become stickier
releases chemical messengers
Coagulation
Stages of Clotting
fibrin forms a mesh that traps the red blood cells and platelets, forming the clot
O negative
Universal Blood Donor
AB positive
Universal Blood Acceptor
Ovulation
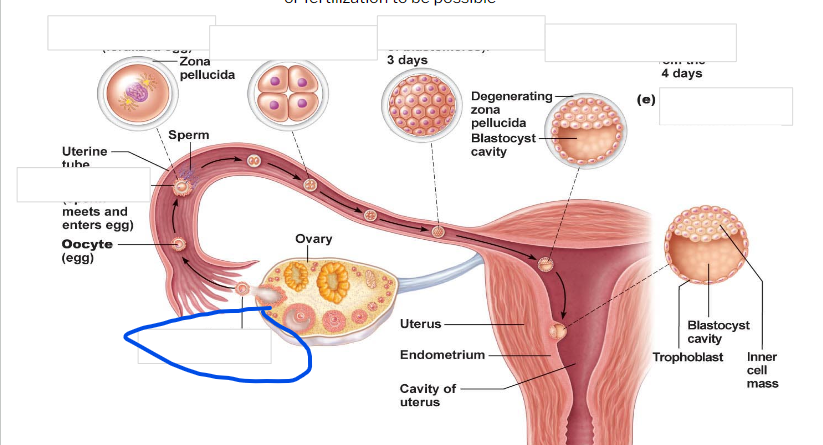
Fertilization
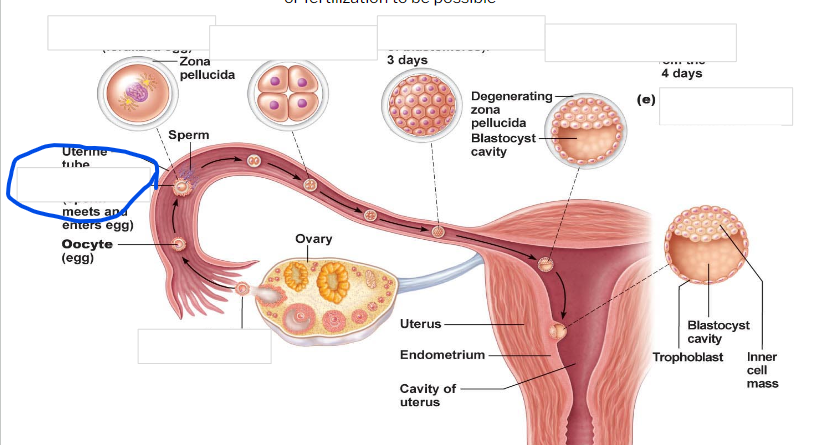
zygote
-First cell of a new individual
-The result of the fusion of DNA from sperm and egg
- begins rapid mitotic cell divisions
-The stage is in the uterine tube, moving toward the uterus
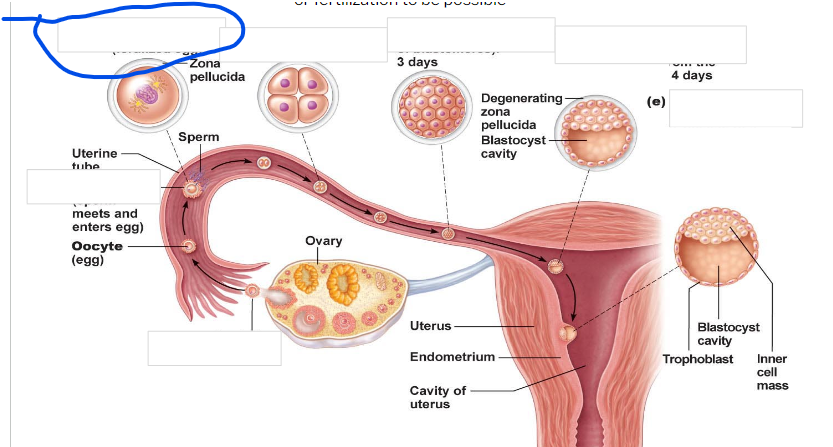
4 cell stage
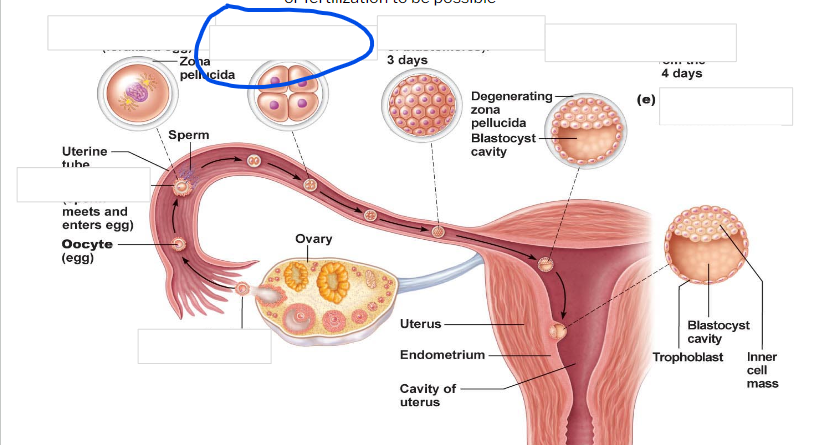
Morula
16 cell stage
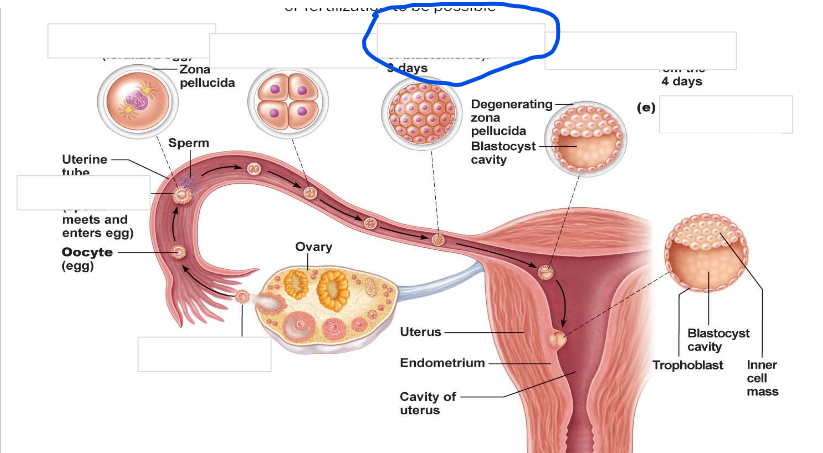
Early blastocyst
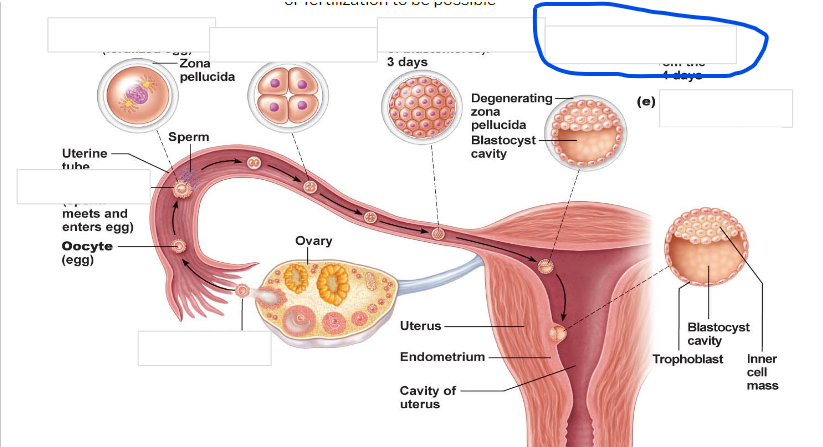
implanting blastocyst
around 100 cells
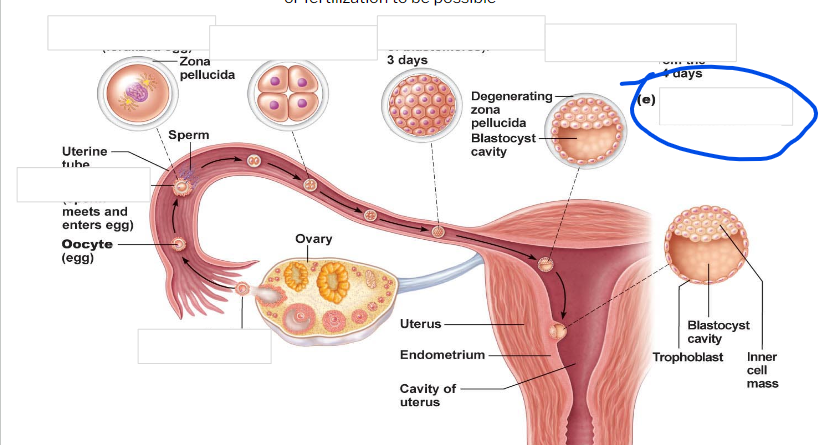
Embryo
developmental stage until 9th week
Ectoderm
Blastocyst outside layer
Mesoderm
blastocyst middle layer
Endoderm
Blastocyst inside layer
fetus
beginning of ninth week
All organ systems are formed by the end of the eighth week
Activities of the ____ are growth and organ specialization
This is a stage of tremendous growth and change in appearance
Labor
the series of events that expel the infant from the uterus
-Rhythmic, expulsive contractions
-Operates by the positive feedback mechanism
False labor
Braxton Hicks take place and are contractions are weak, irregular uterine contractions
Dilation
Stages of Labor
first stage
Uterine contractions begin and increase
Cervix softens and effaces (thins)
The amnion ruptures (“breaking the water”)
Longest stage at 6–12 hours
Expulsion
Stages of labor
second stage
Infant passes through the cervix and vagina
Can last as long as 2 hours, but typically is 50 minutes
in the first birth and 20 minutes in subsequent births
Normal delivery is head first (vertex position)
Breech presentation is buttocks-first
Placental Stage
Stages of Labor
Last stage
Delivery of the placenta
Usually accomplished within 15 minutes after birth of infant
Afterbirth—placenta and attached fetal membranes
All placental fragments should be removed to avoid postpartum bleeding
Menopause
full year without menstruation
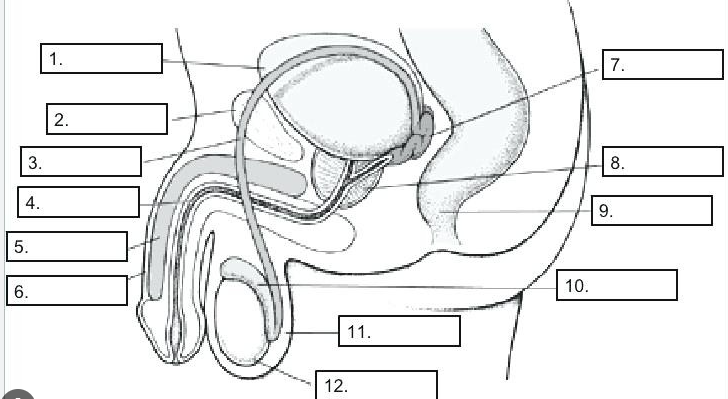
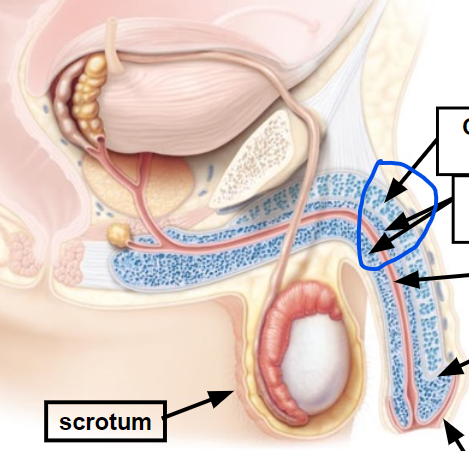
vas deferens
Conveys sperm cells to ejaculatory duct
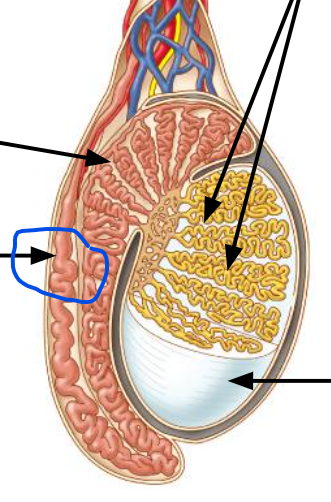
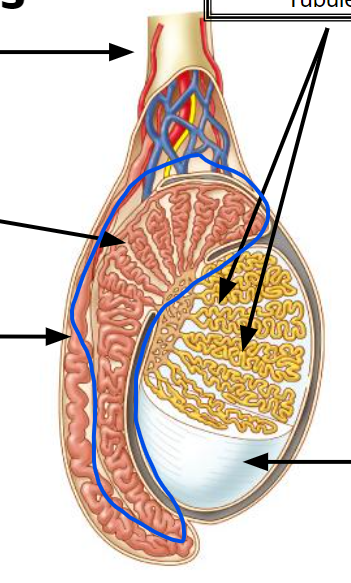
testes
12, Produce sperm
spermatic cord
contains vas deferens
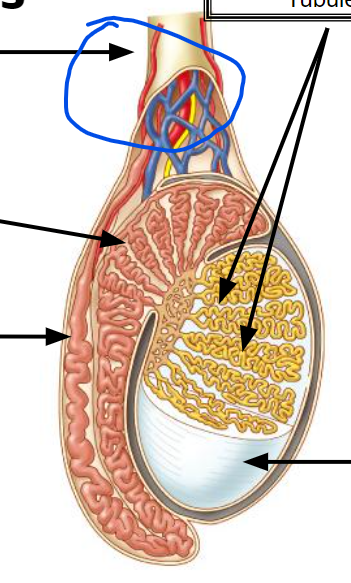
seminiferous tubules
Produce sperm
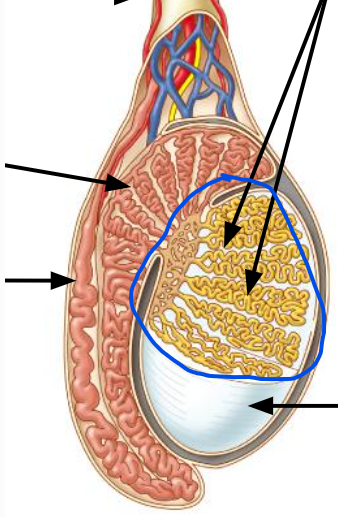
epididymis
Stores & maturation of sperm cells; 🡪 vas deferens
scrotum
11, Encloses, protect & regulates temperature of testes
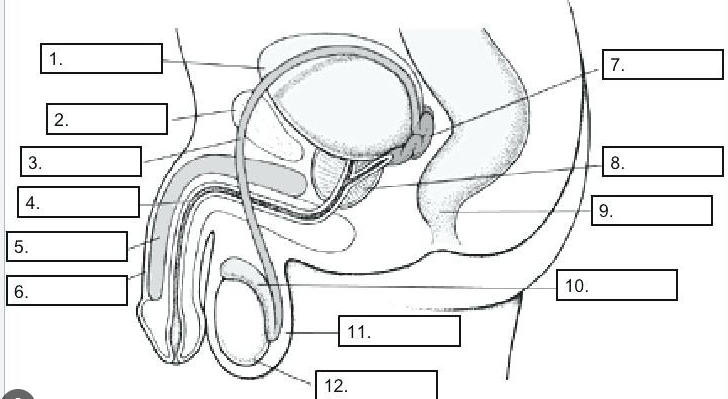
prepuce
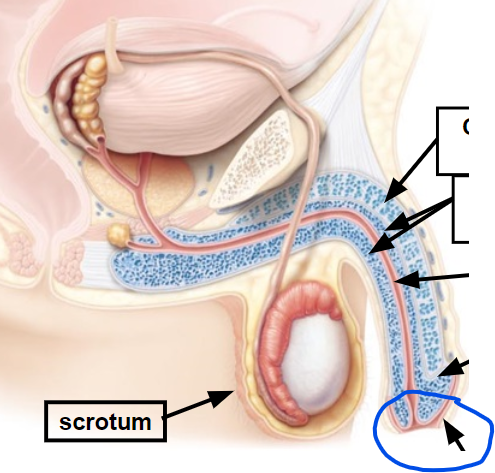
urethra
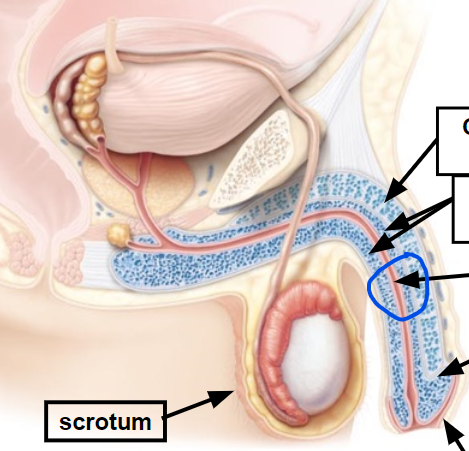
penis
Conveys urine & semen to outside of body; inserted into vagina during sexual intercourse
glans penis
richly supplied with sensory nerve endings associated with feeling of pleasure during sexual stimulation.
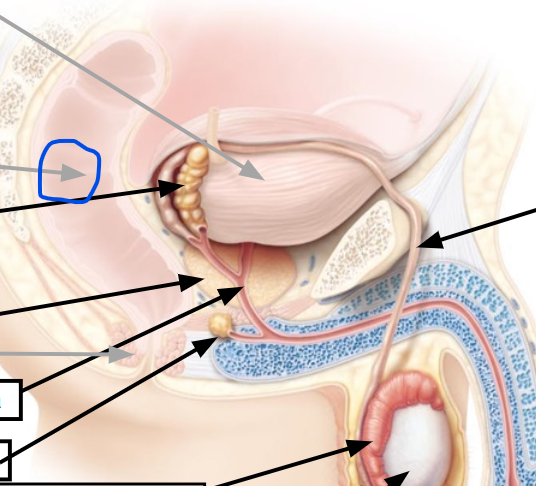
urinary bladder
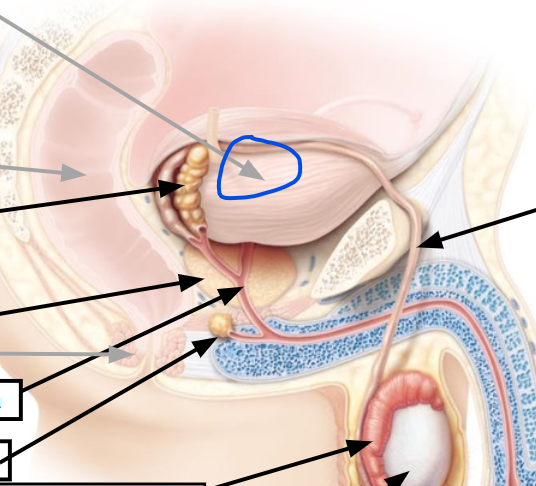
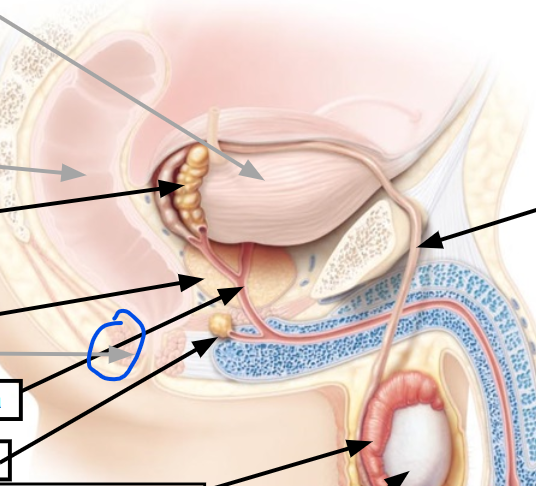
seminal vesicles
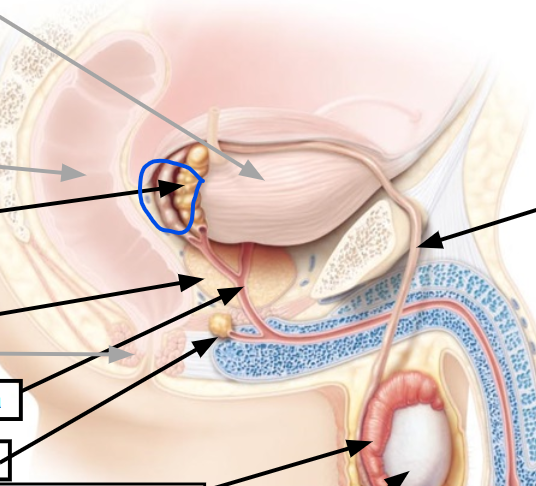
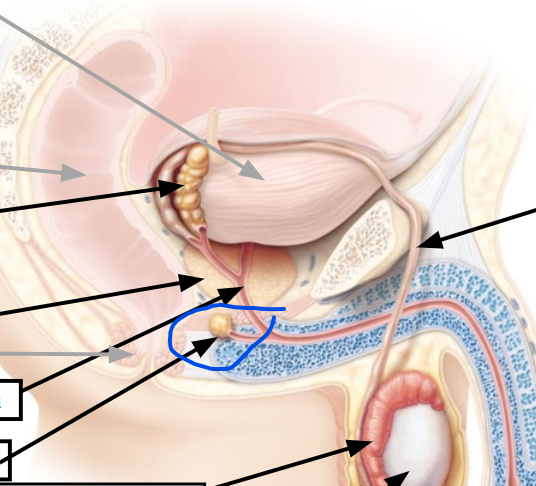
prostate gland
viscous alkaline fluid containing fructose, ascorbic acid, coagulating enzyme (vesiculase), and prostaglandins
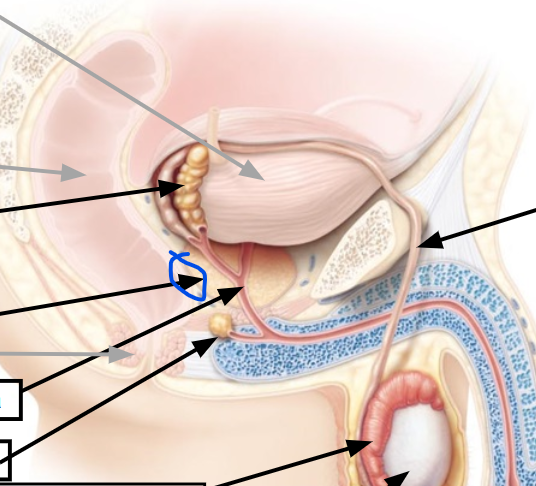
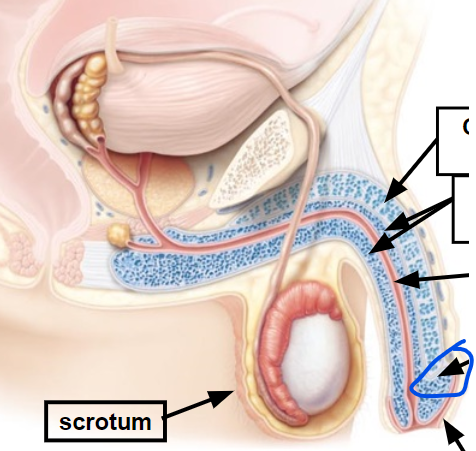
bulbourethra
Secretes fluid that lubricates end of the penis
anus
rectum
20
Below this sperm count is infertile (millions)
60%
what percent sperm should have normal shapes(morphology)
2-5
how many ml volume is normal
Liquefaction
Within a few minutes after ejac. Sperm should coagulate and then liquify again after 15-30 min.
60%
What percent of sperm should have moving flagella?(motility)
relaxin
this hormone enhances sperm motility
seminalplasmin
antibiotic chemical that destroys certain bacteria
fibrinolysin
liquefies the sticky mass
alkaline
found in semen, neutralizes the acid environment found in the male urethra and female vagina
infertility
unable to reproduce or get pregnant , may cause irregular periods or hormone problems, hair, and function.
meiosis
a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information
ejaculation
the semen is expelled by strong spasmodic contractions of the bulbocavernosus muscle
Fertilization
occurs when a sperm and an oocyte (egg) combine and their nuclei fuse
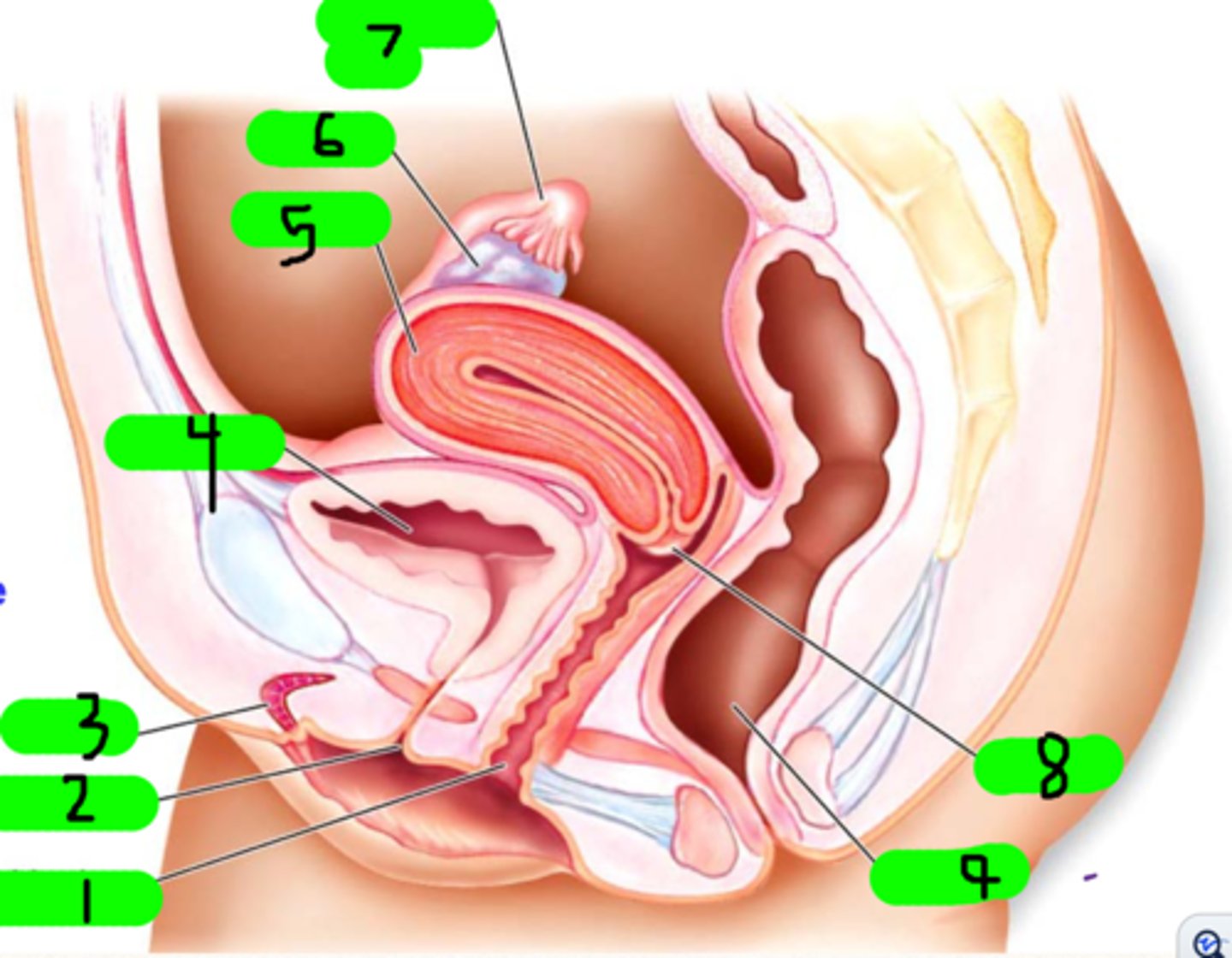
vagina
What is 1?
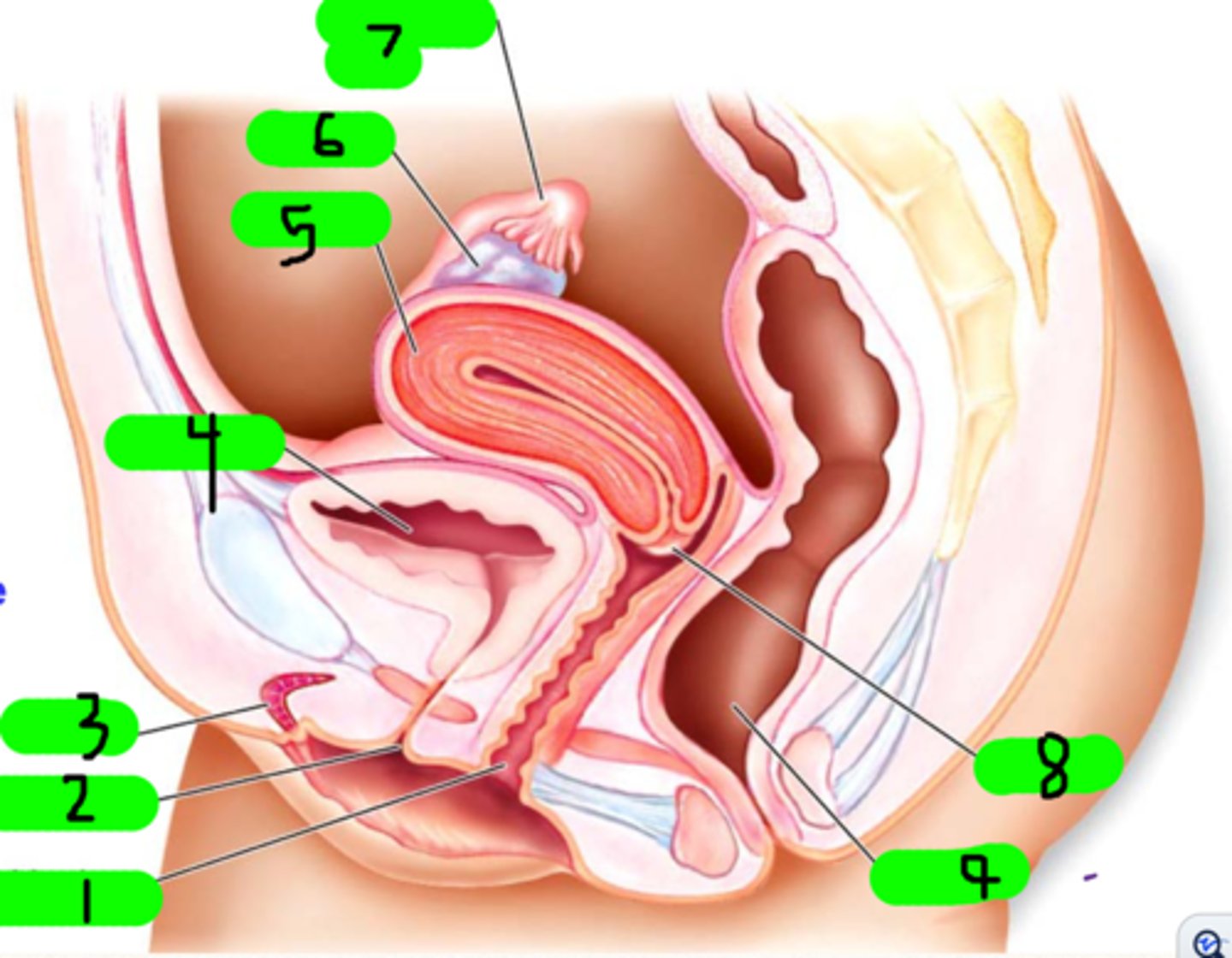
fimbrae
Small strands near number 7 (not number 7 itself)
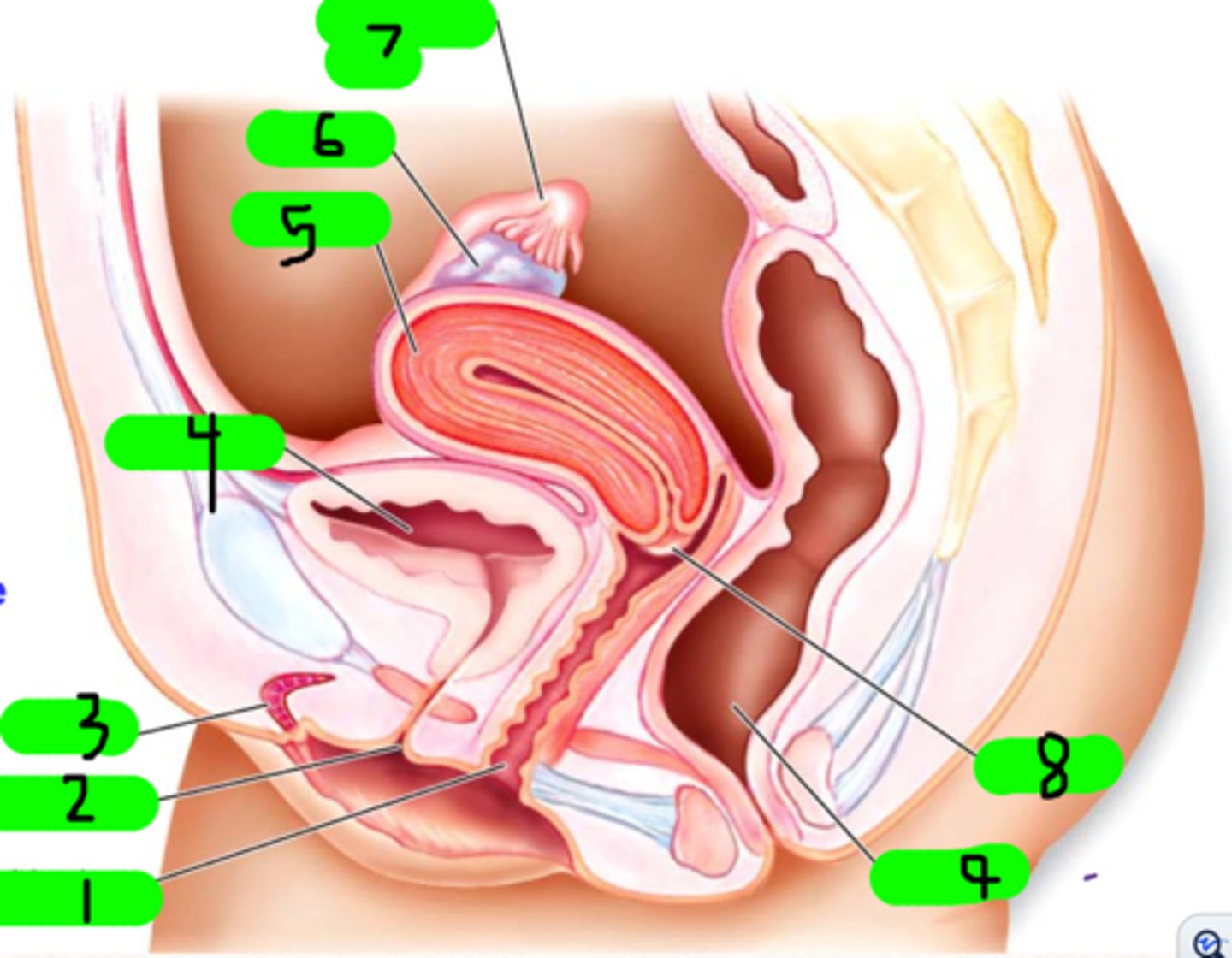
clitoris
What is 3?
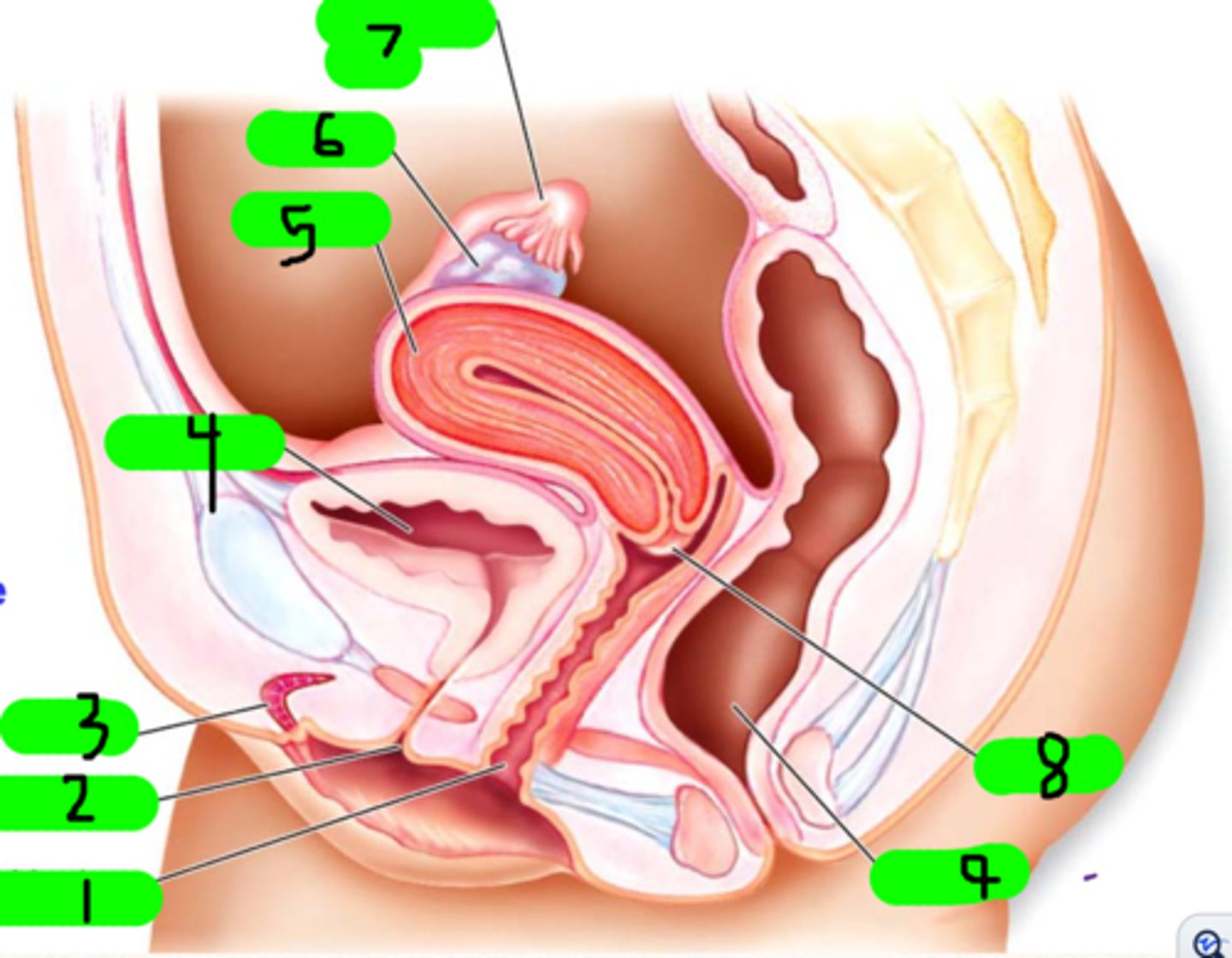
urinary bladder
What is 4?
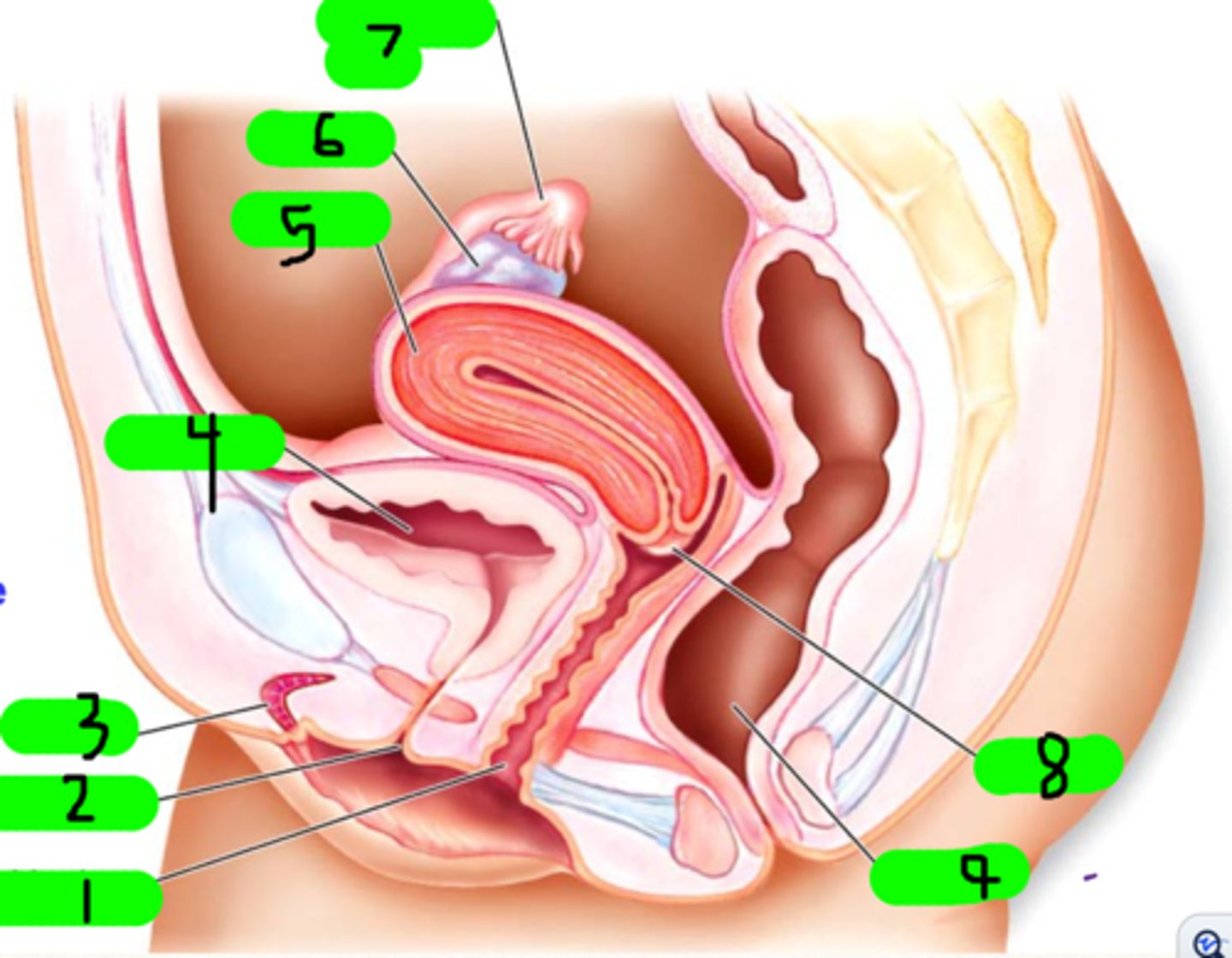
uterus
What is 5?
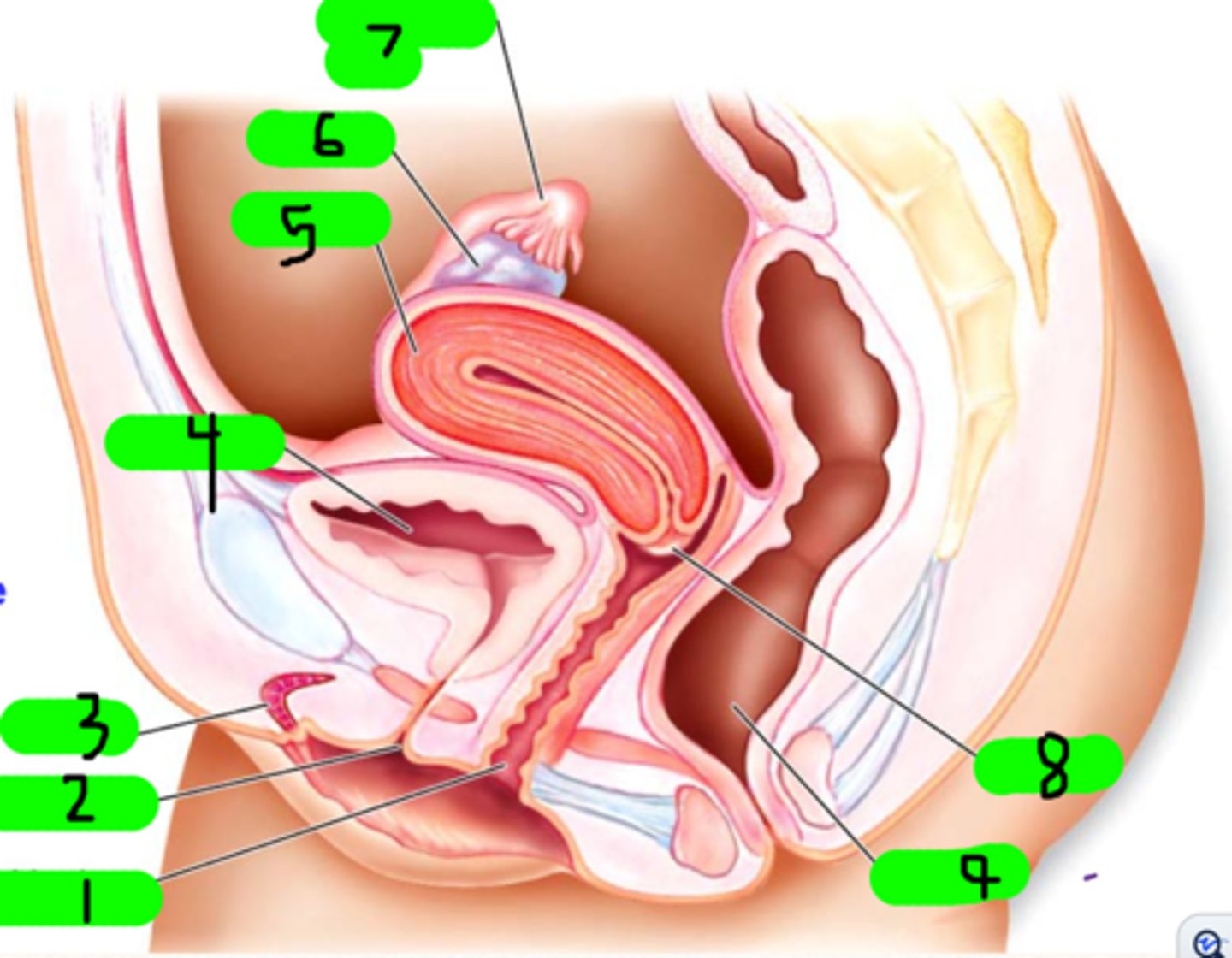
ovary
What is 6?
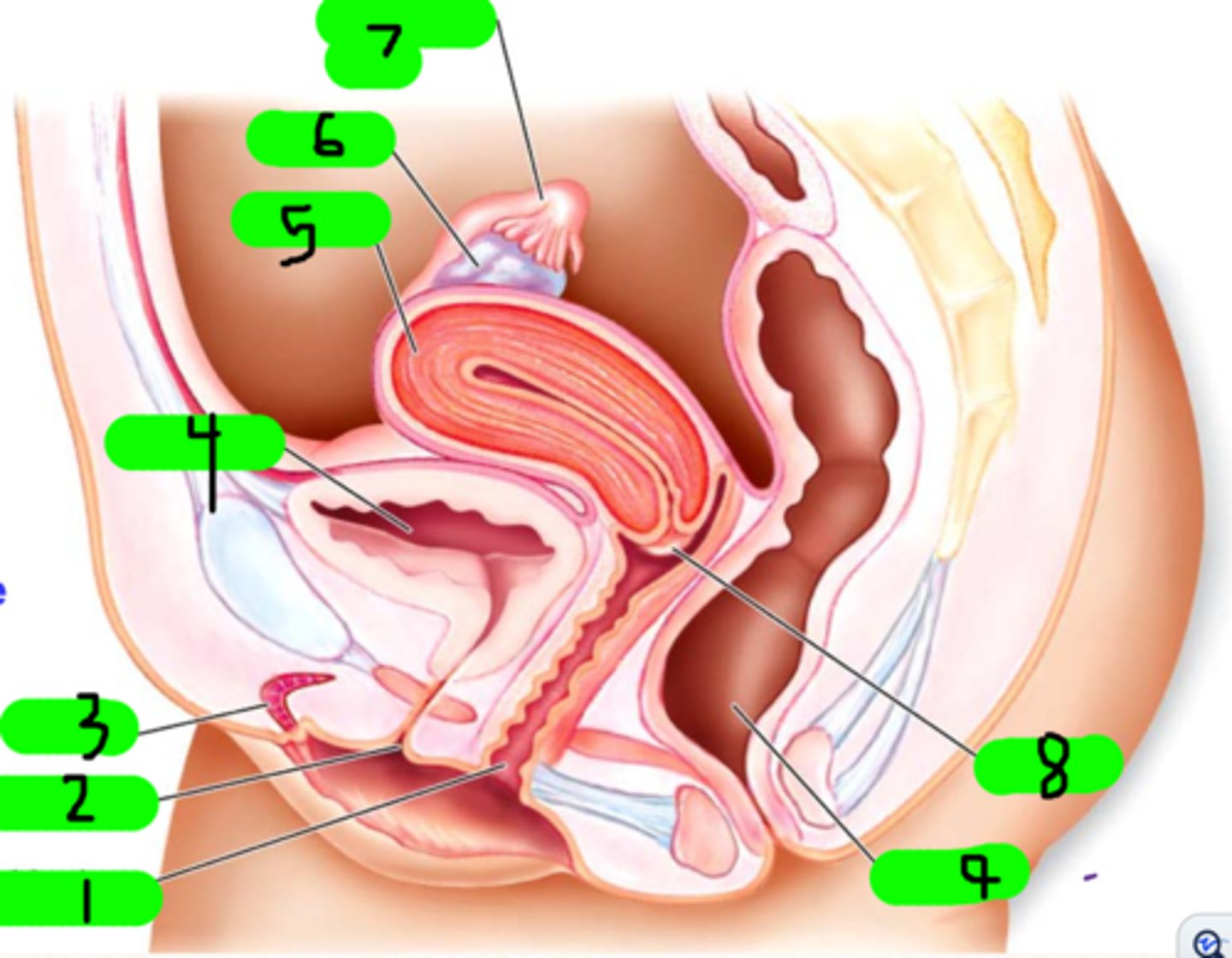
fallopian tube
What is 7?