IMED1004 - Genome Damage, Cancer and Smoking (L28)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
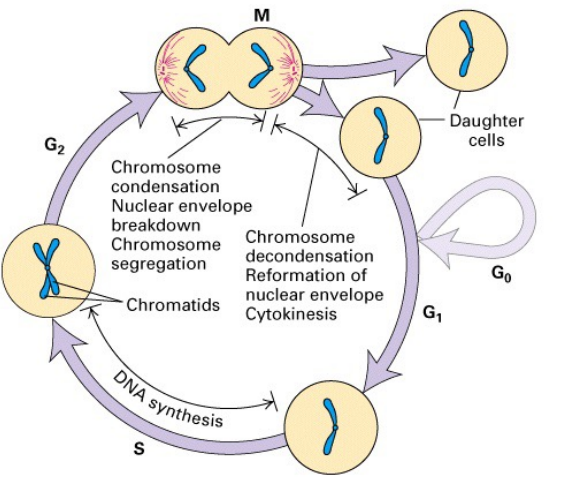
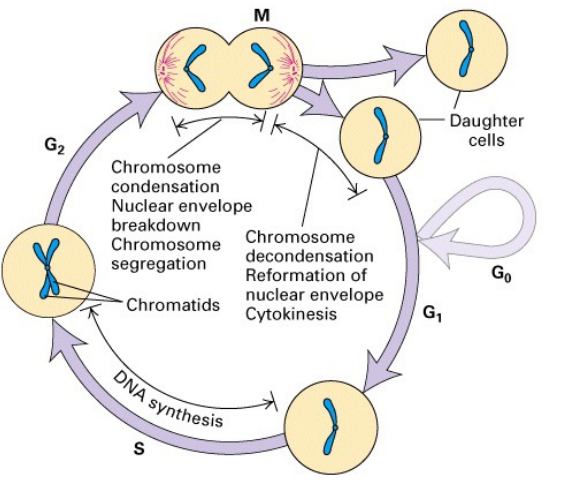
Cell Cycle
Note: The Gaps (G1 and G2) are not simply time delays, allow time for cell to monitor internal and external environment
- ensure conditions are suitable and preparations are complete before cell undertakes major processes of S (and M) phase
- G1 is especially important, its length can vary considerably depending on external conditions and extracellular signals
- Therefore if conditions are unfavourable, cells delay their progress through G1 and do not enter S
Overview
- in humans, cell survival and proliferation are highly regulated by integrated controls that continually evaluate the state of the cell and its environment
- normal cell proliferation is modulated by tight and appropriate control of the cell cycle
- apoptosis eliminates damaged cells and cells needed only temporarily during development
- the accumulation of mutations in cancer cells allows them to escape apoptosis and proliferation controls
Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death)
- in multicellular organisms, systems have evolved to eliminate damaged cells = self destruct mechanisms
- can be activated under many different circumstances e.g cells that are no longer needed for development
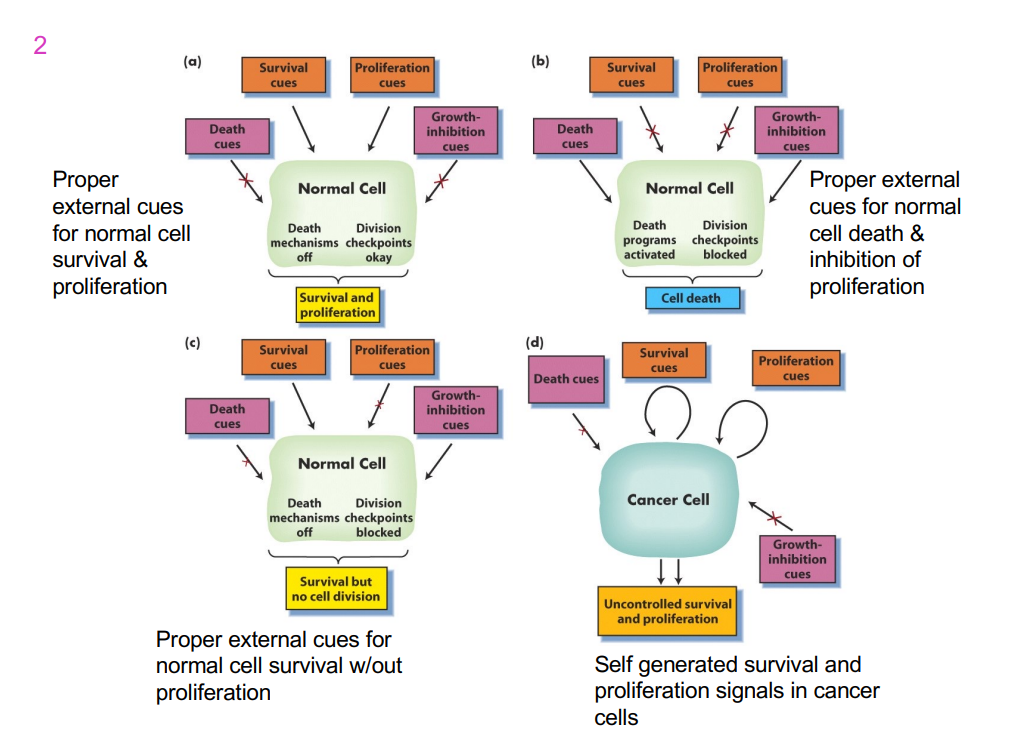
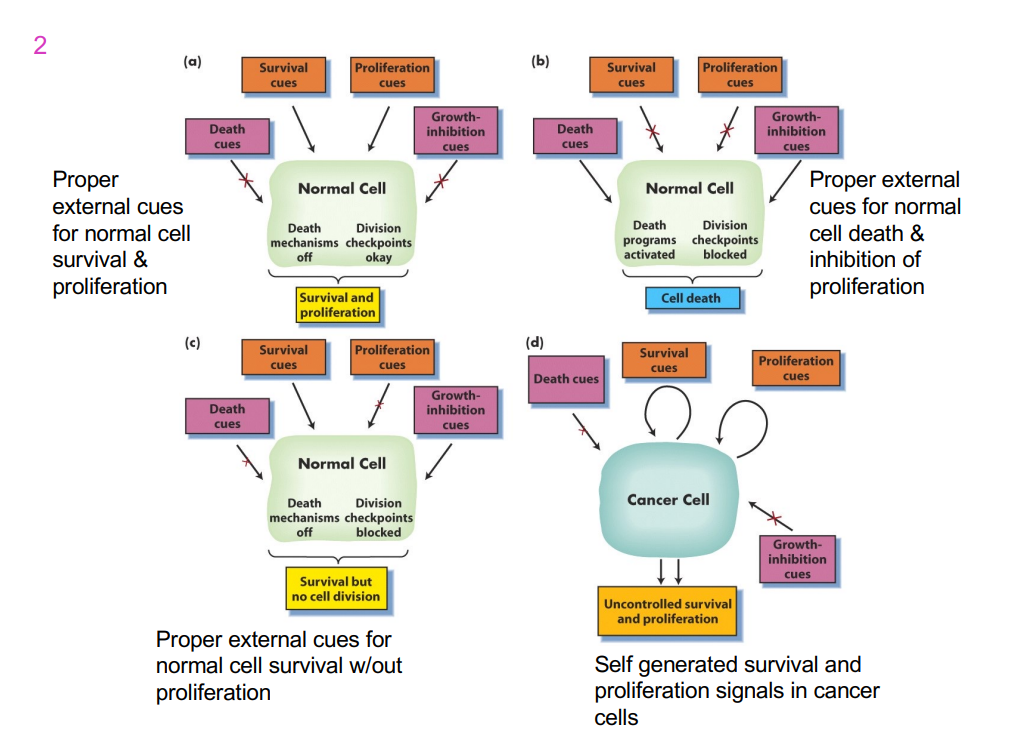
4 different types of cells: 3 normal cells and one cancer cell
- first cell is receieivng proper external cues for normal cell survival and proliferation
- second cell is receieivng proper external cues for normal cell death and inhibition of proliferation
- 3rd cell is receieving proper external cues for normal cell survival without proliferation
- 4th cell is self generated survival and proliferation signals in cancer cells
Origins of Mutations
INDUCED:
- presence of mutagen
- mutagens cause mutations - greater dose = more mutations
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 7 (diagram is for induced)
.
SPONTANEOUS:
- absence of mutation
- spontaneous mutations are ultimate source of genetic variation
- Rate is low: 1 cell per 10^5-10^8
- lots of repair mechanisms to keep mutation rate low, but sometimes they fail
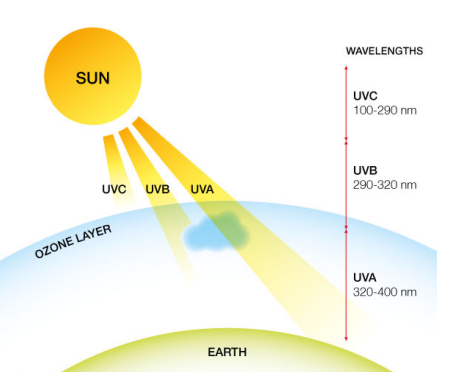
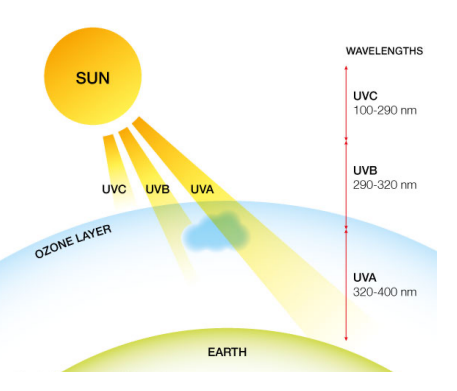
Ultraviolet Radiation Damage
One important DNA damage response is triggered by exposure to UV light
- Only UV-A and UV-B radiation able to penetrate earth's atmosphere (depleting ozone layer -> higher levels)
- UV radation -> 2 classes of DNA lesions (pyrimidine dimers and 6-4 photoproducts (6-4PPs)
- Both distort DNA's structure, impeding trasncription and replication
- relatively flexible areas of DNA double helix are most susceptible to damage
- one "hot spot for UV-induced damage is within the p53 gene. p53 protein suppresses tumour formation
Viral Infection: DNA tumour viruses target cell cycle
- Retinoblastoma (Rb) and p53 are tumour suppressor proteins
.
Proteins of the Human Papilloma Virus: (dont need to remember thse proteins)
- E7 binds and inhibits Rb
- E6 binds and inhibits p53
- E5 causes sustained activation of a specific growth factor receptor
- sufficient to induce loss of cell cycle control
.
- proteins of the large monkey SV40 papova virus "large T" binds and inhibits Rb and p53 (aropund 15% of cancers have osme link to infection)
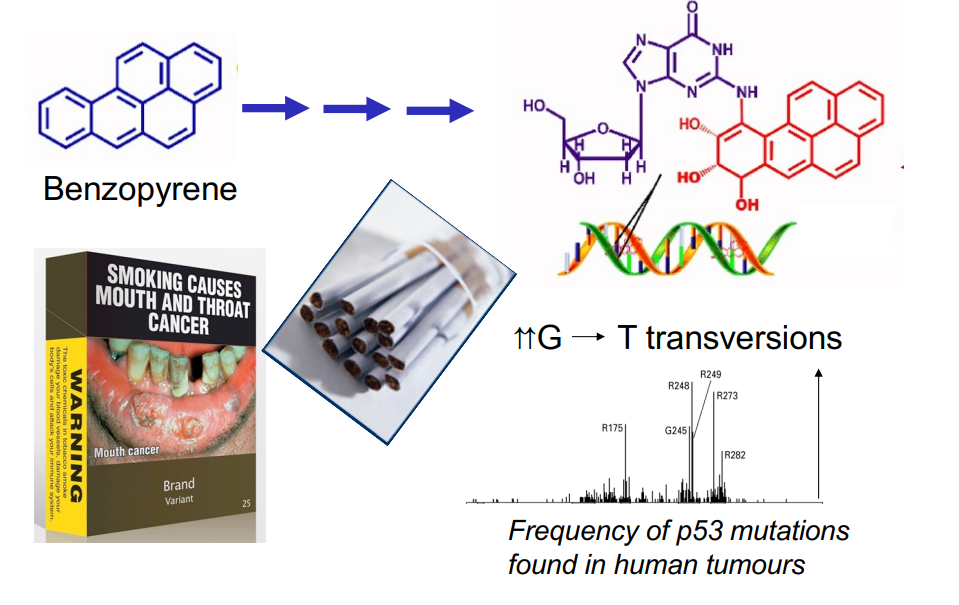
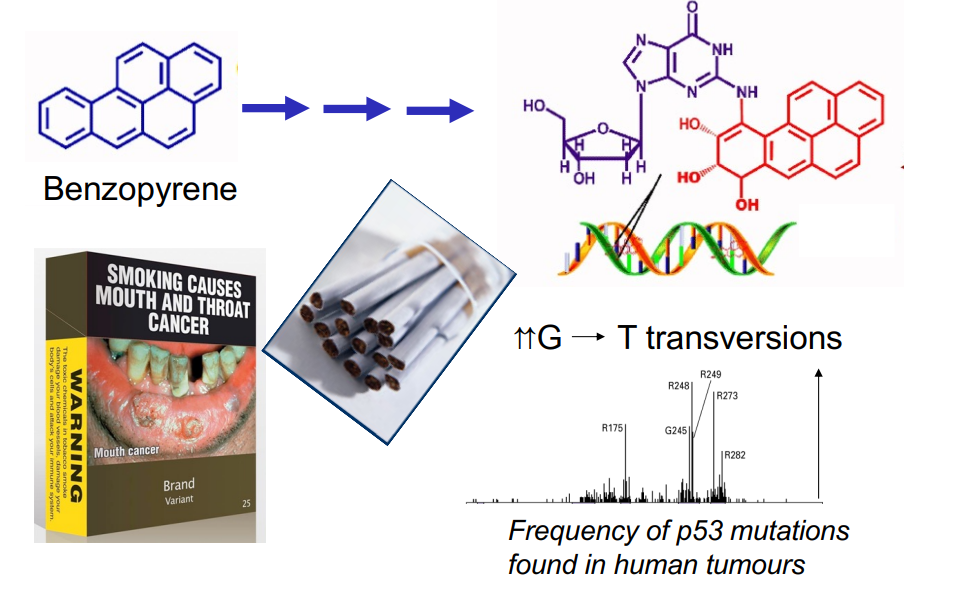
Lifestyle Choices e.g tobacco smoking
60% of human lung cancers have mutant p53