Oral mucosa and periodontium
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:46 AM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 4 main functions of oral mucosa?
* Protection
* Sensation
* Secretion
* Mastication, speech and swallowing
* Sensation
* Secretion
* Mastication, speech and swallowing
2
New cards
Type of epithelium in the oral cavity
Stratified squamous epithelium to resist abrasion
3
New cards
Types of oral epithelium
Masticatory
Lining
Specialised
Lining
Specialised
4
New cards
What type of oral epithelium is found on the hard palate, gingivae, dorsal surface of tongue
masticatory oral epithelium
5
New cards
What type of oral epithelium is found on the labial mucosa, buccal mucosa, alveolar mucosa, ventral tongue, floor of mouth, soft palate
lining oral epithelium
6
New cards
What type of oral epithelium is found on the gustatory mucosa of the tongue, vermillion zone/border between skin and oral mucosa
specialised oral epithelium (papillae)
7
New cards
Masticatory vs lining oral epithelium
Masticatory is keratinised to withstand forces generated during mastication
Lining is non-keratinised as it’s not subject to such high forces the the structures are elastic tissues which move out of the way
Lining is non-keratinised as it’s not subject to such high forces the the structures are elastic tissues which move out of the way
8
New cards
Label the 4 structures below the epithelium
1. Stratified squamous epithelium
2. Lamina propria (connective tissue)
3. Submucosa
4. Periosteum (only if over bone)
5. Bone/muscle
9
New cards
When is periosteum present
if over bone
10
New cards
What is found in the submucosa
fat deposits, glands, blood vessels
11
New cards
Name the 4 layers of keratinised oral epithelium from most to least matured
1. Keratinised cell layer – stratum corneum
2. Granular cell layer – stratum granulosum
3. Prickle cell layer – stratum spinosum
4. Basal cell layer – stratum basale
12
New cards
Name the 4 layers of non-keratinised epithelium
1. Superficial cell layer – stratum superficiale
2. Intermediate cell layer – stratum intermedium
3. Prickle cell layer – stratum spinosum
4. Basal cell layer – stratum basale
13
New cards
orthokeratinised vs parakeratinised
Orthokeratinised - no nuclei in keratinised layer
Parakeratinised - nuclei retained within keratinocytes
Parakeratinised - nuclei retained within keratinocytes
14
New cards
Function of basement membrane
* Connection between epithelium and lamina propria
* Site of metabolic exchange
* Controls biological behaviour of epithelial cells
* Site of metabolic exchange
* Controls biological behaviour of epithelial cells
15
New cards
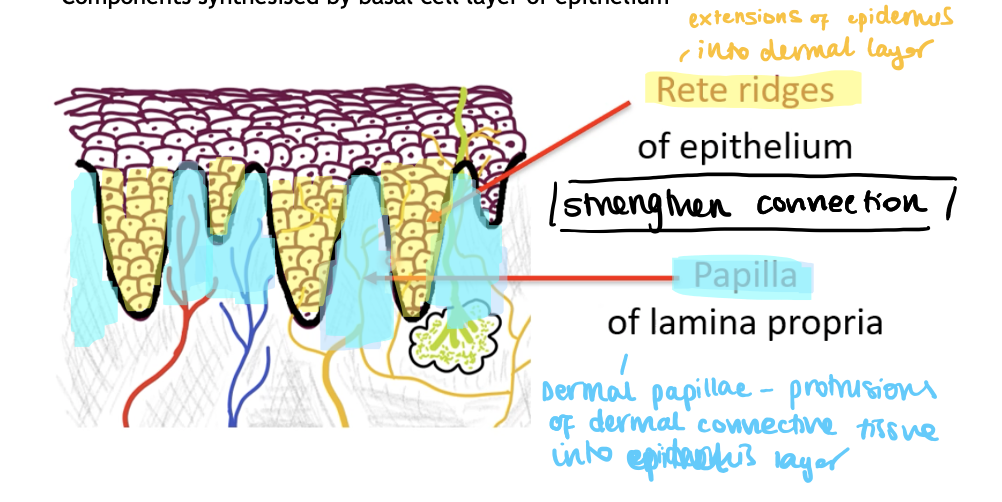
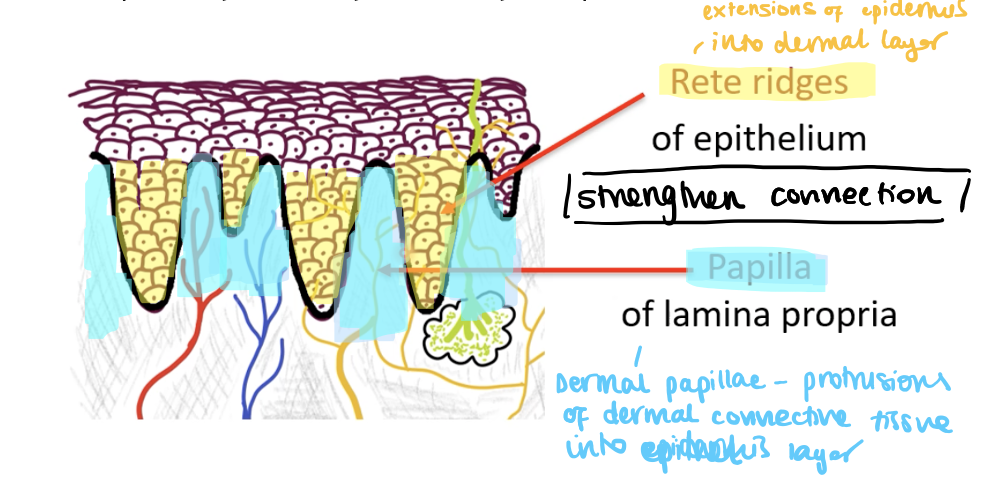
What are rete ridges of the epithelium
Extensions of the epithelial layer into the dermal layer
16
New cards
What are papilla of the lamina propia
Protrusions of the dermal connective tissue into the epithelial layer
17
New cards
What are the layers of lamina propria
1. Papillary layer between epithelial rete ridges – thin, loose collagen fibres
2. Deeper reticular layer – thick, parallel bundles collagen fibres
18
New cards
Function of lamina propia
Provides mechanical support and nutrition for epithelium
19
New cards
What is found in submucosa
* Contains minor salivary glands, fat cells, blood vessels, nerves
20
New cards
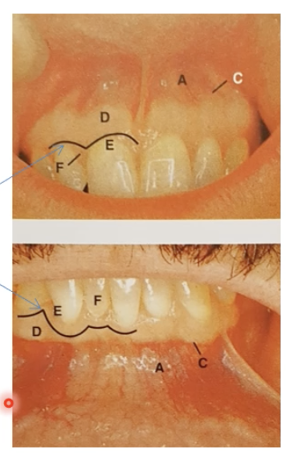
Label A - F
A - Alveolar mucosa
C - Mucogingival junction
D - Attached gingivae
E - Free gingiva
F - Interdental papilla
C - Mucogingival junction
D - Attached gingivae
E - Free gingiva
F - Interdental papilla
21
New cards
Texture of free vs attached gingiva
Free - smooth
Attached - textured
Attached - textured
22
New cards
Keratinisation of gingiva vs alveolar mucosa
Gingiva - keratinised
Alveolar - non-keratinised
Alveolar - non-keratinised
23
New cards
Type of mucosa on the attached gingiva
masticatory mucosa
24
New cards
How is attached gingiva bound to bone
directly via mucoperiosteum
25
New cards
Where is interdental papilla and col found?
Triangles of the gums between teeth

26
New cards
how large is a healthy crevicular epithelium
0-2mm
27
New cards
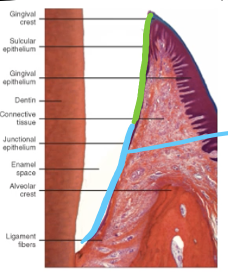
Where is crevicular epithelium found
Unattached region between pre-gingiva and tooth (green line)
28
New cards
Where is junction epithelium found?
When the gingiva is connected to enamel
29
New cards
Why do the dark triangles appear in periodontal disease?
Interdental papilla lost
30
New cards
Crevicular vs junction epithelium
* Crevicular has more folding at interface with underlying tissue
* Crevicular has different site of keratin profile
* Crevicular has different site of keratin profile
31
New cards
Dentogingival junction
* Region where oral mucosa meets tooth surface
* Principal seal between oral cavity and underlying periodontal tissues
* Junction epithelium forms an epithelial collar around tooth from the cementoenamel junction to the base of the gingival sulcus
* Principal seal between oral cavity and underlying periodontal tissues
* Junction epithelium forms an epithelial collar around tooth from the cementoenamel junction to the base of the gingival sulcus
32
New cards
Thickness of crevicular vs junction epithelium
crevicular - 30 cells thick
junction - 1 cell thick
junction - 1 cell thick
33
New cards
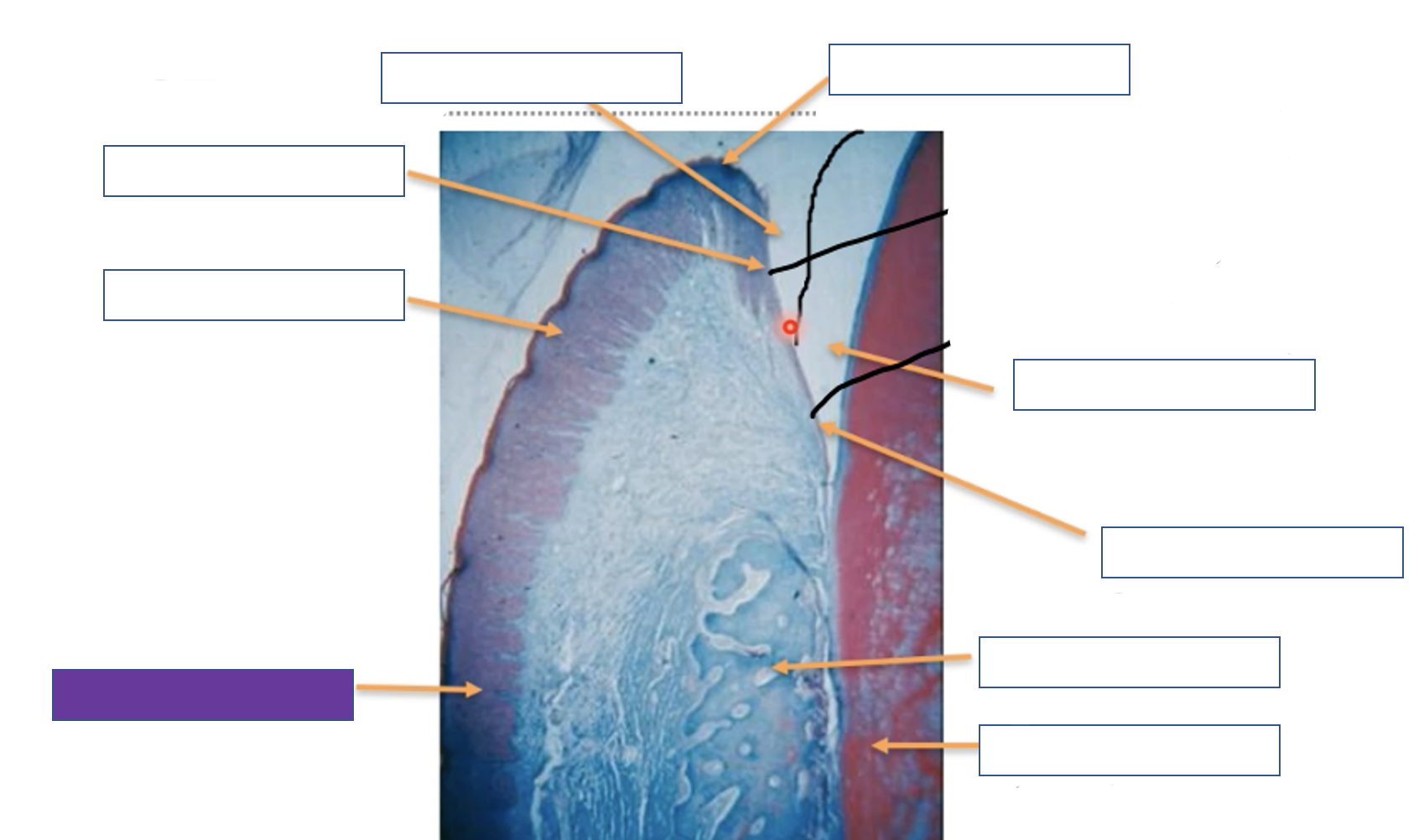
Attached gingiva
34
New cards
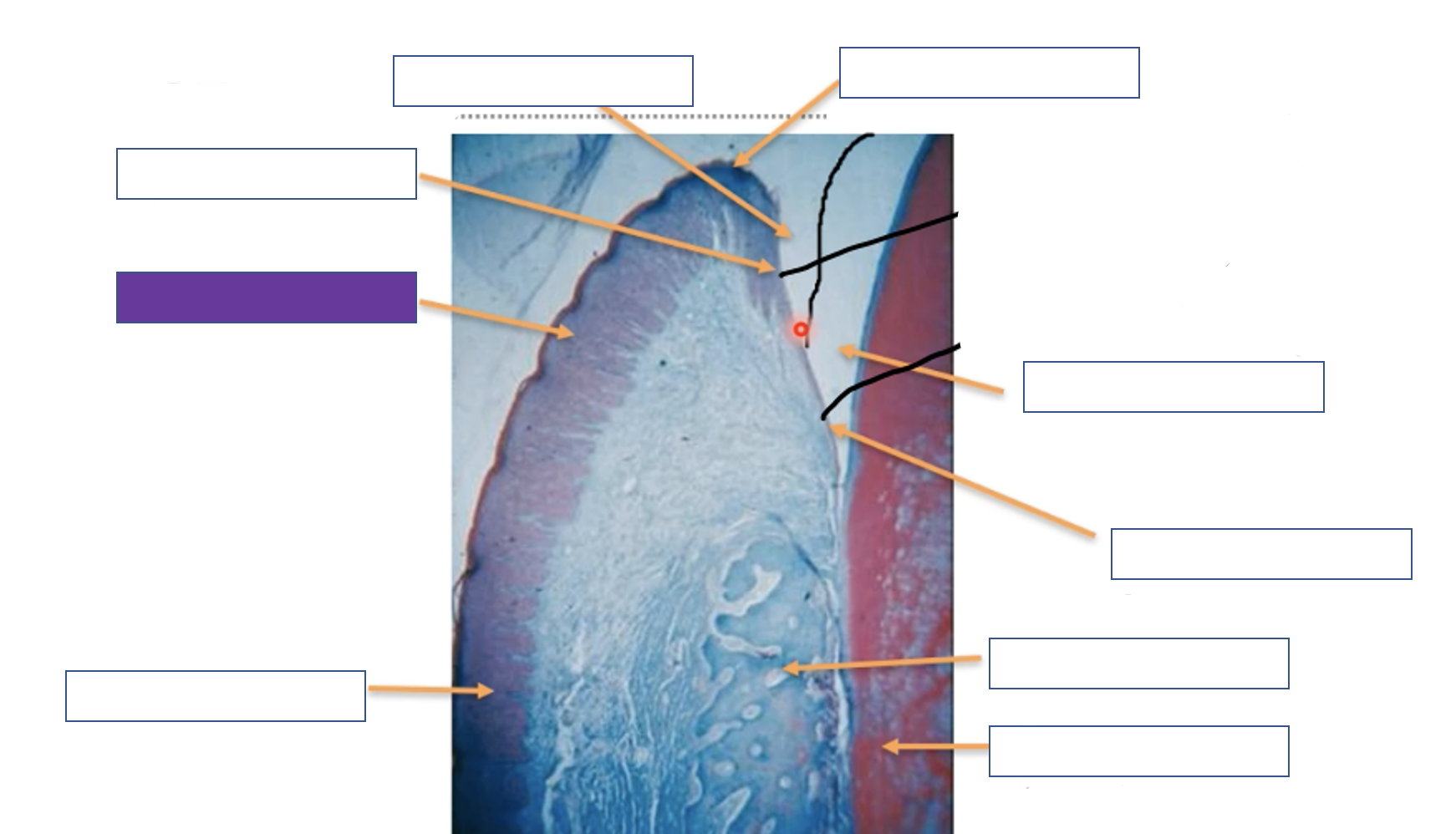
Free gingiva
35
New cards
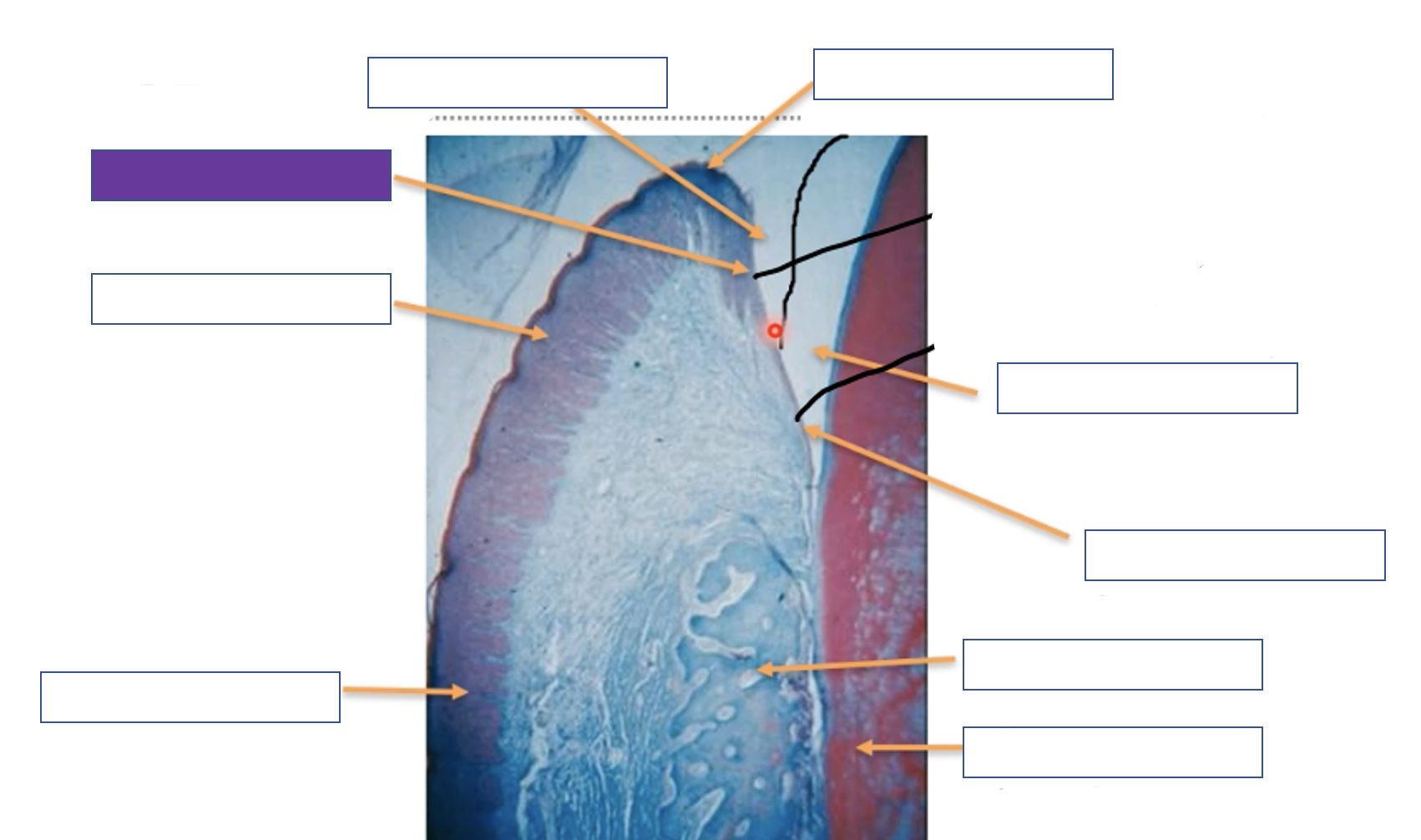
Crevicular epithelium
36
New cards
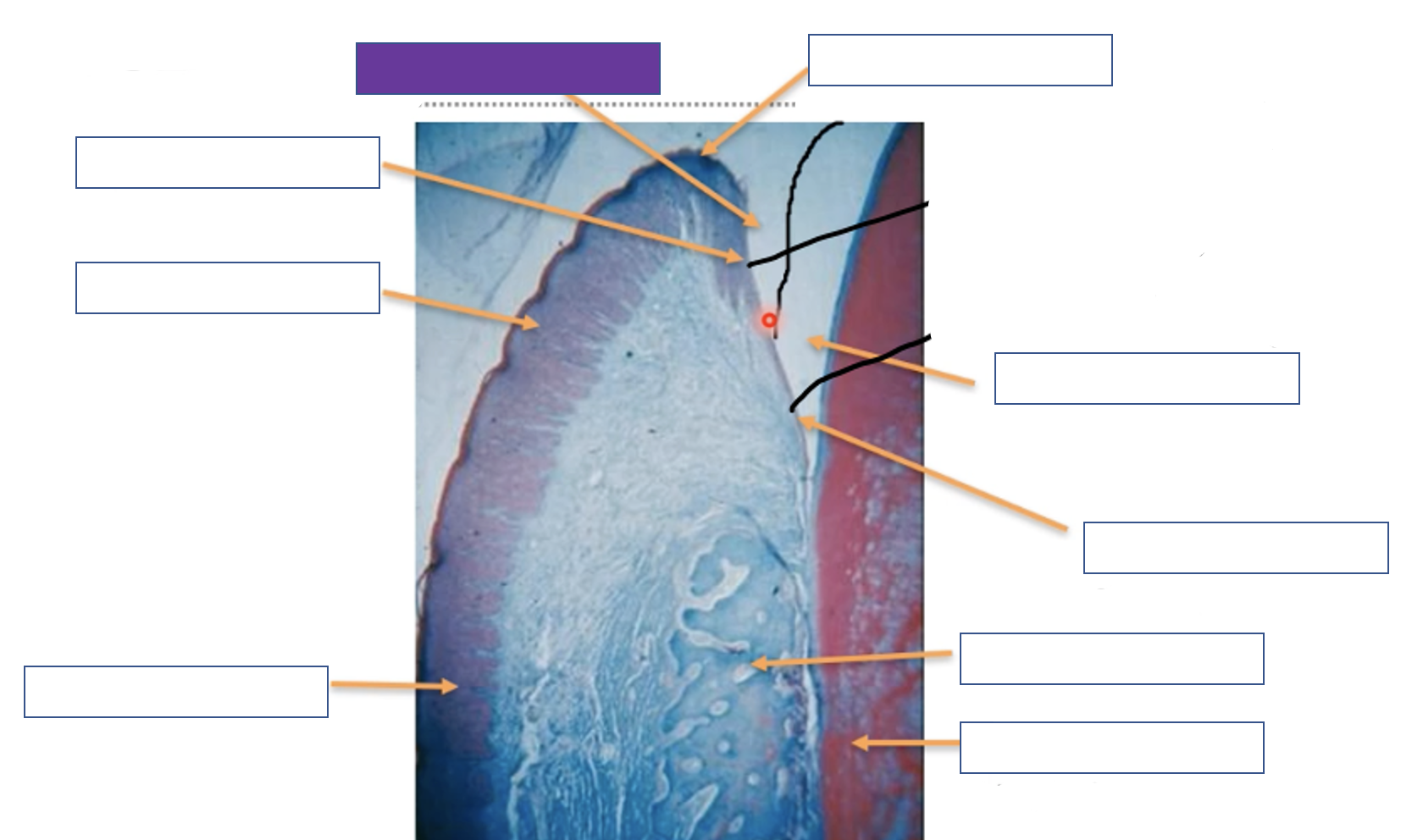
Gingival sulcus
37
New cards
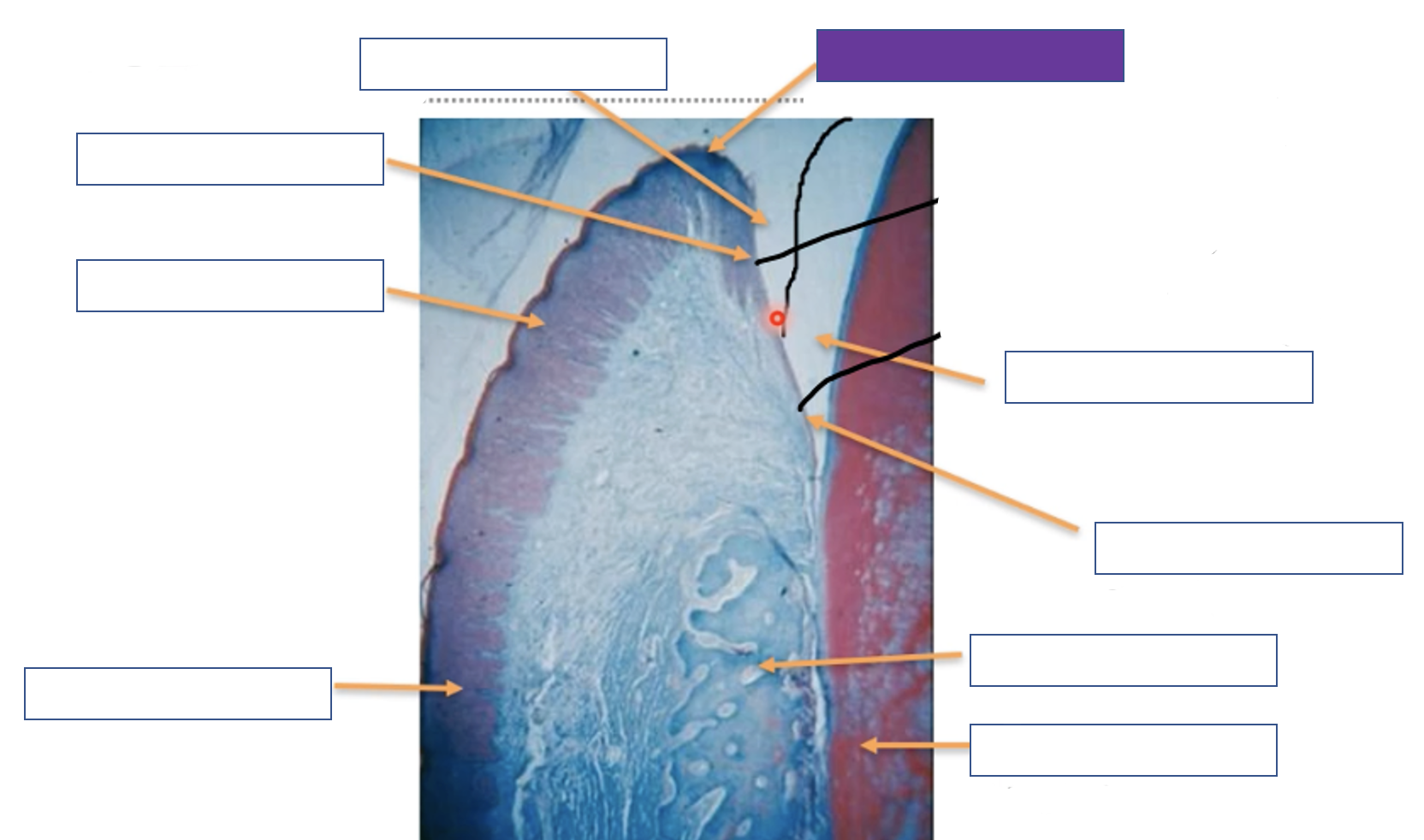
Gingival margin
38
New cards
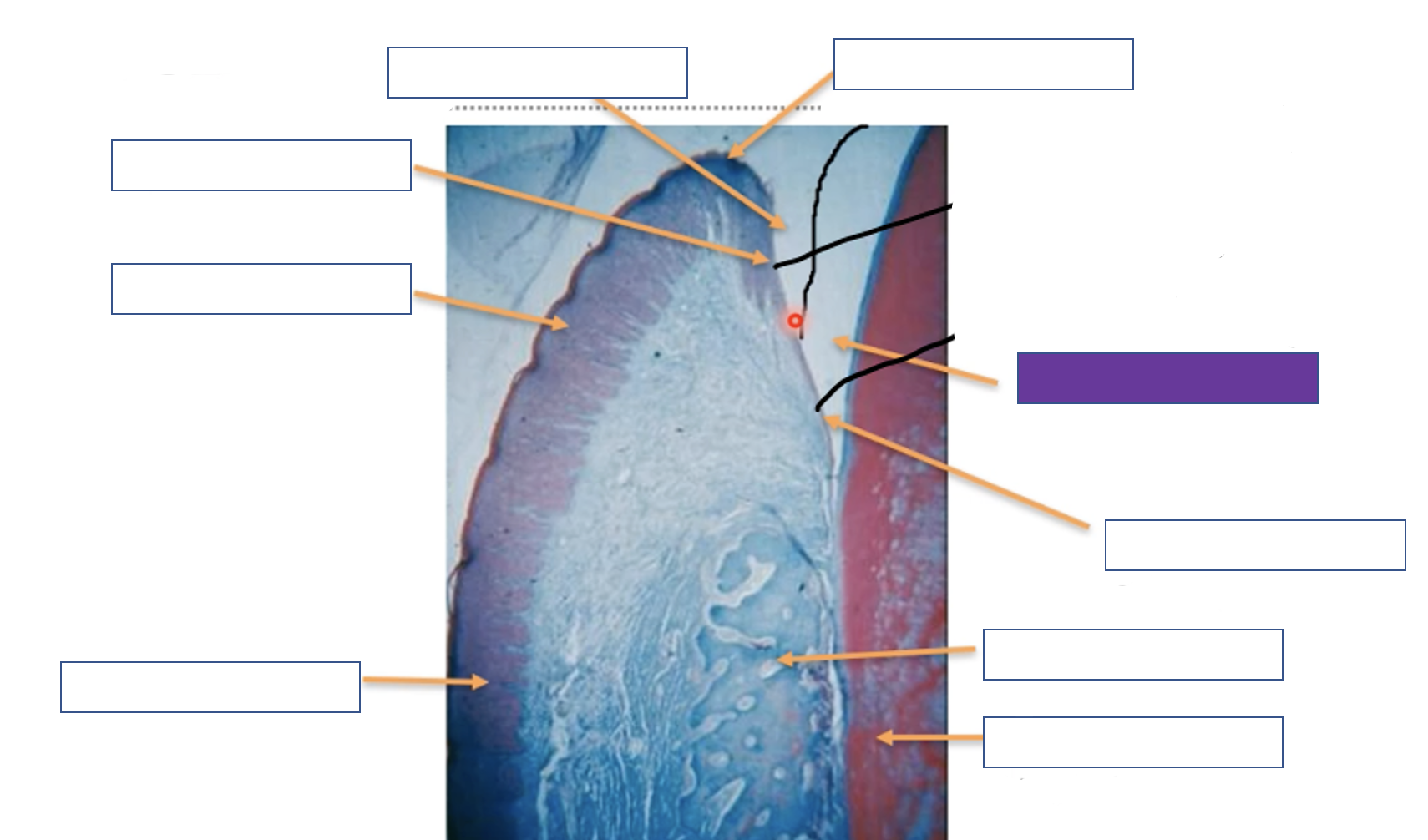
Enamel space
39
New cards
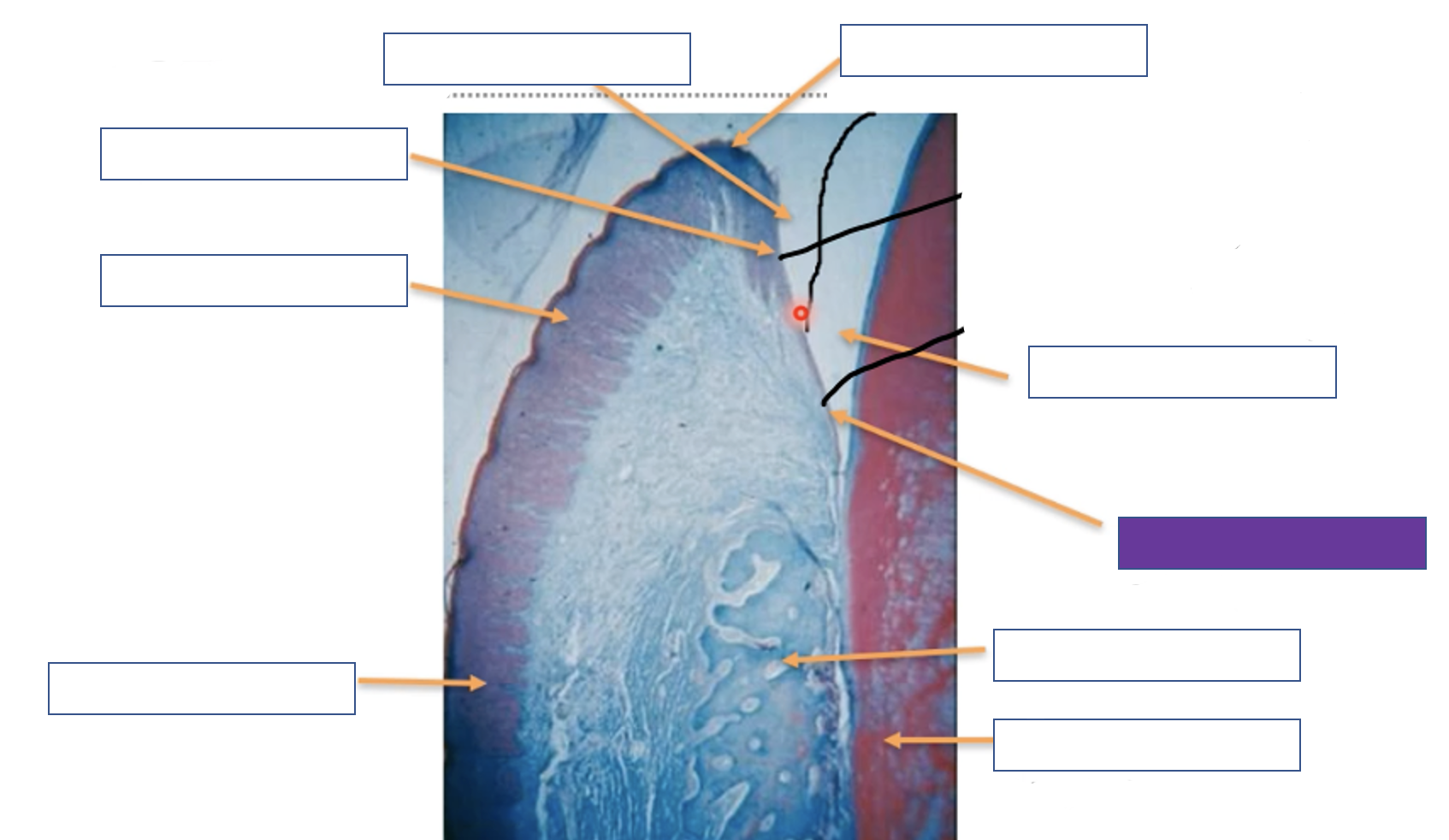
Junction epithelium
40
New cards
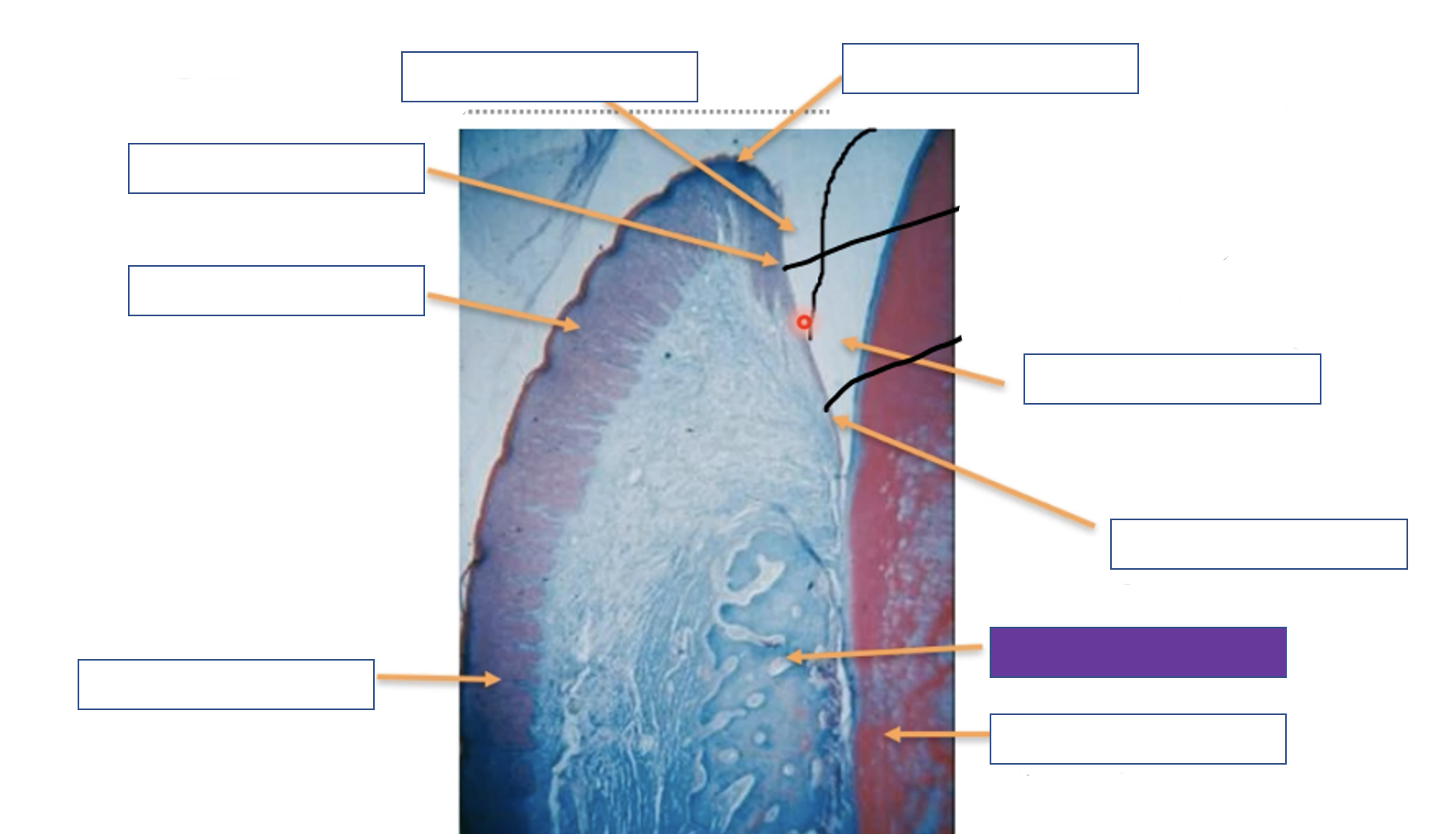
Alveolar bone
41
New cards
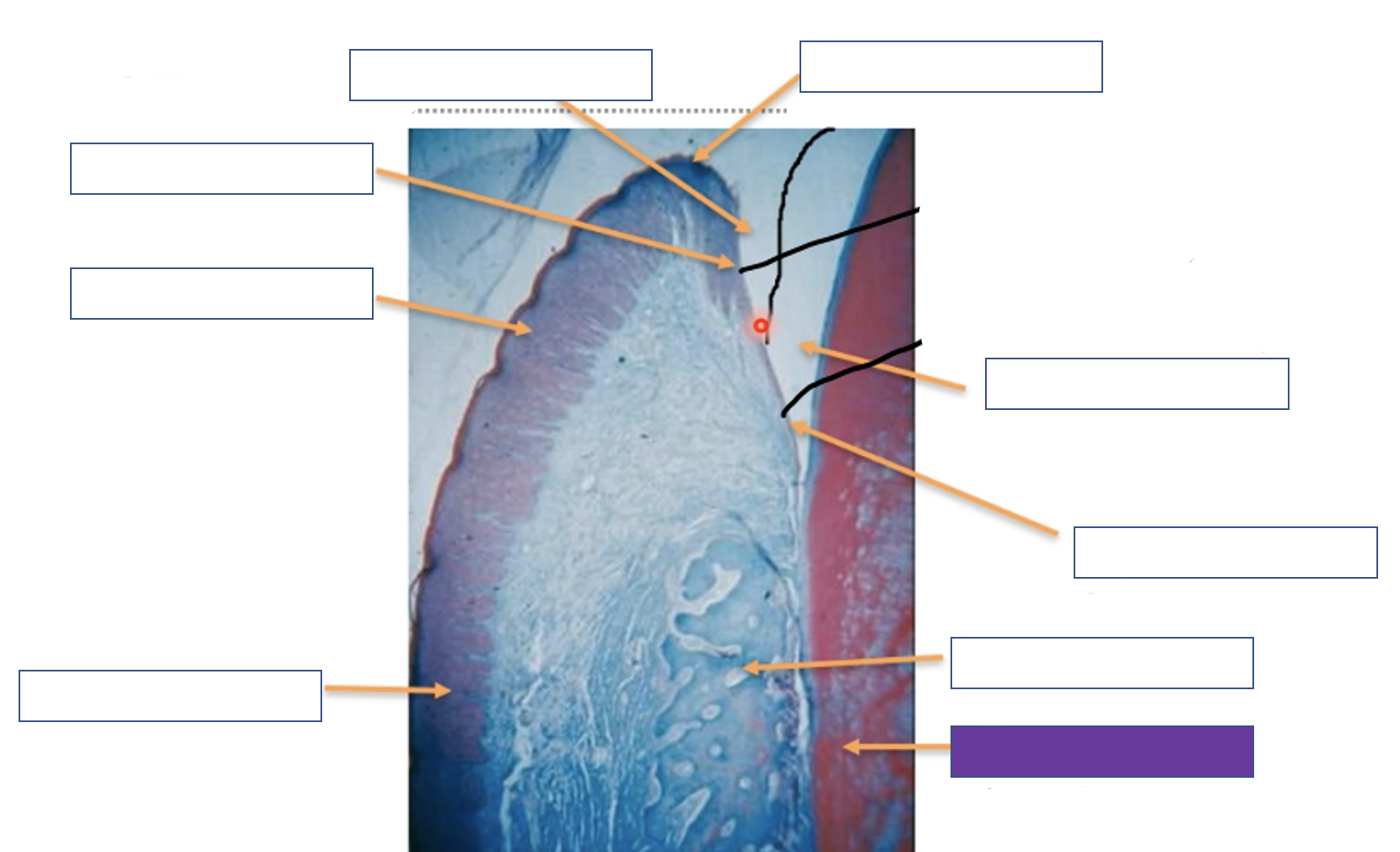
Tooth (dentine)