7 Heredity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Heredity
the passing of traits to offspring from its parents
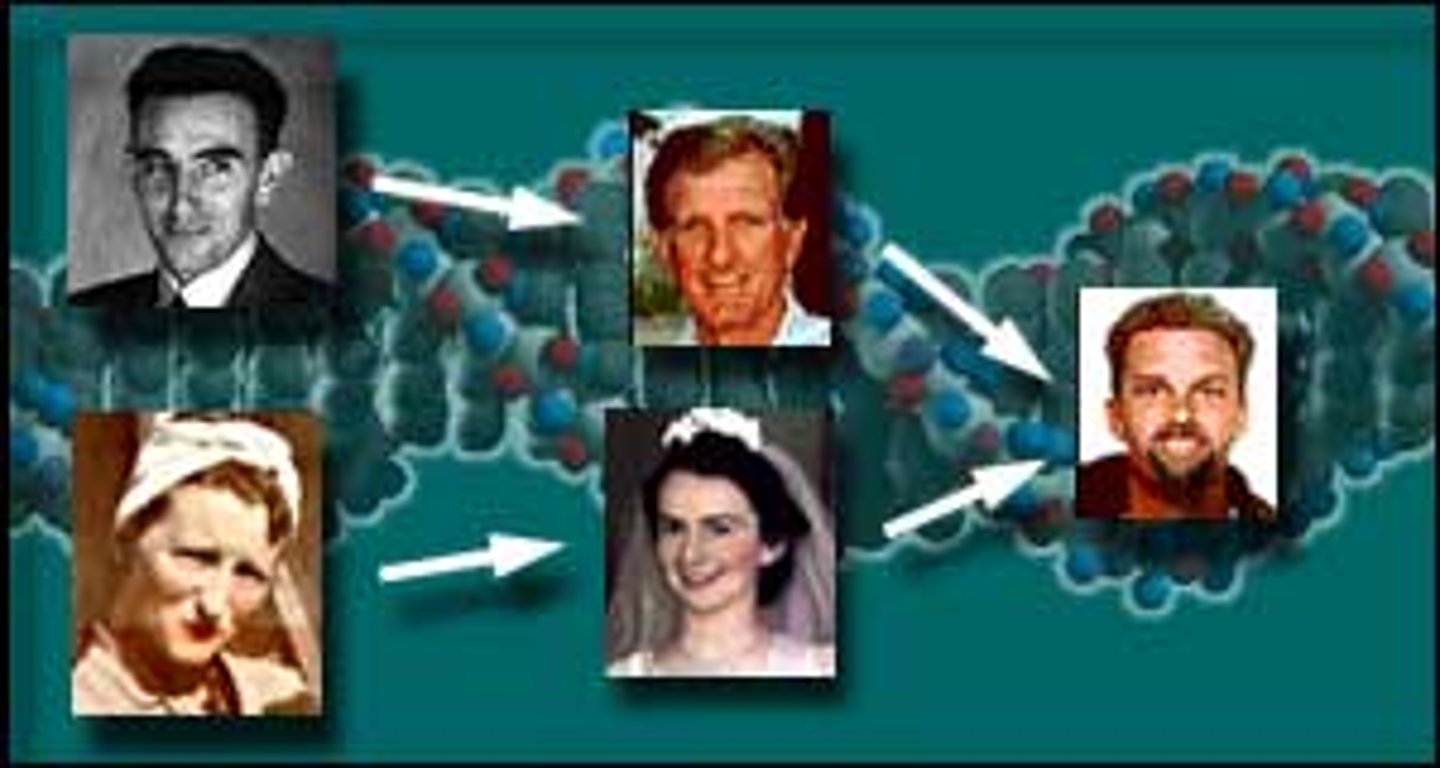
Genetics
science or study of heredity
Genes
the molecular unit of heredity, segments of DNA found in chromosomes that give instructions for producing a certain characteristic
Traits
a distinguishing quality or characteristic
DNA
molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of ALL living organisms, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells

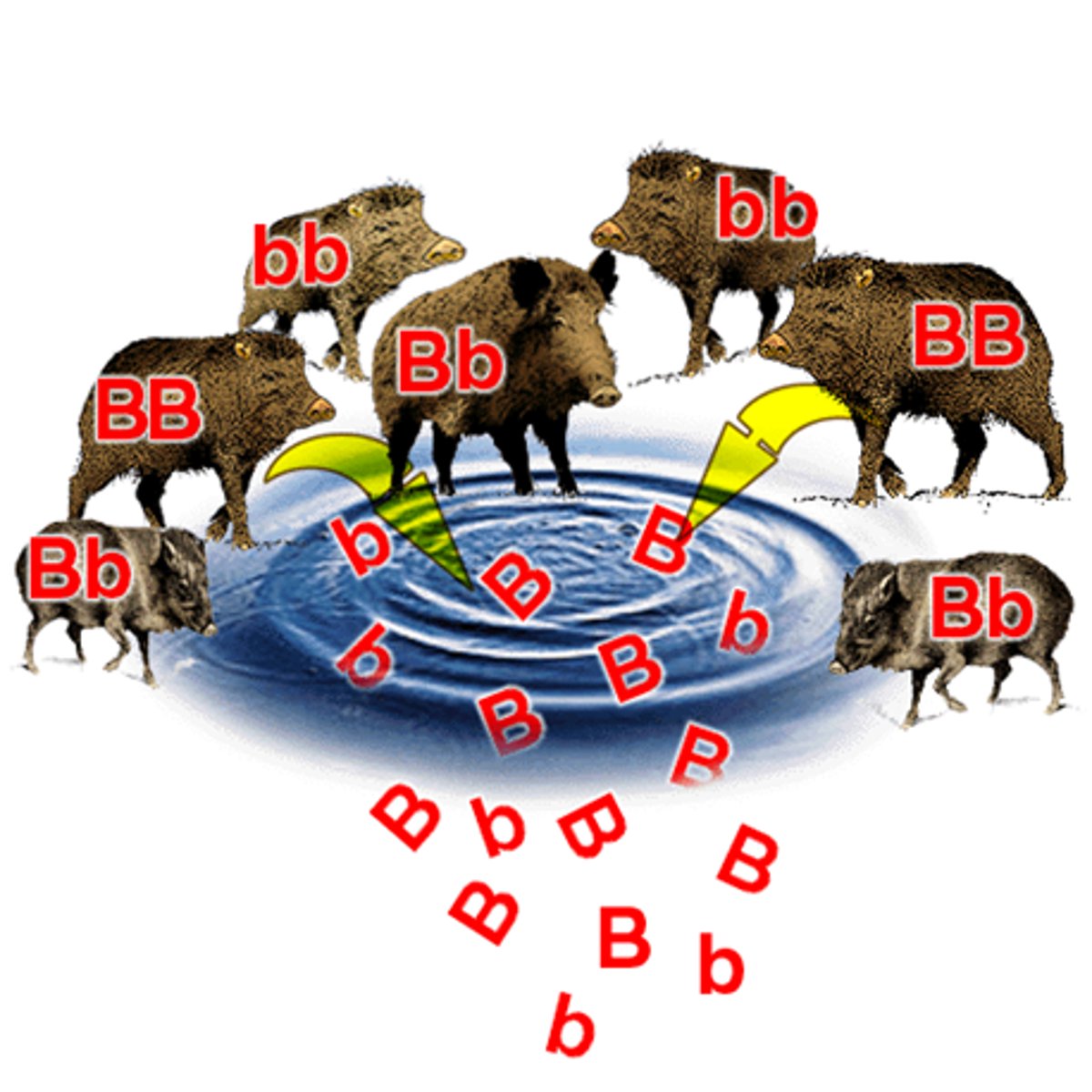
Genotype
combination of alleles that you inherit from your parents (Two letter code! AA, Aa, aa)
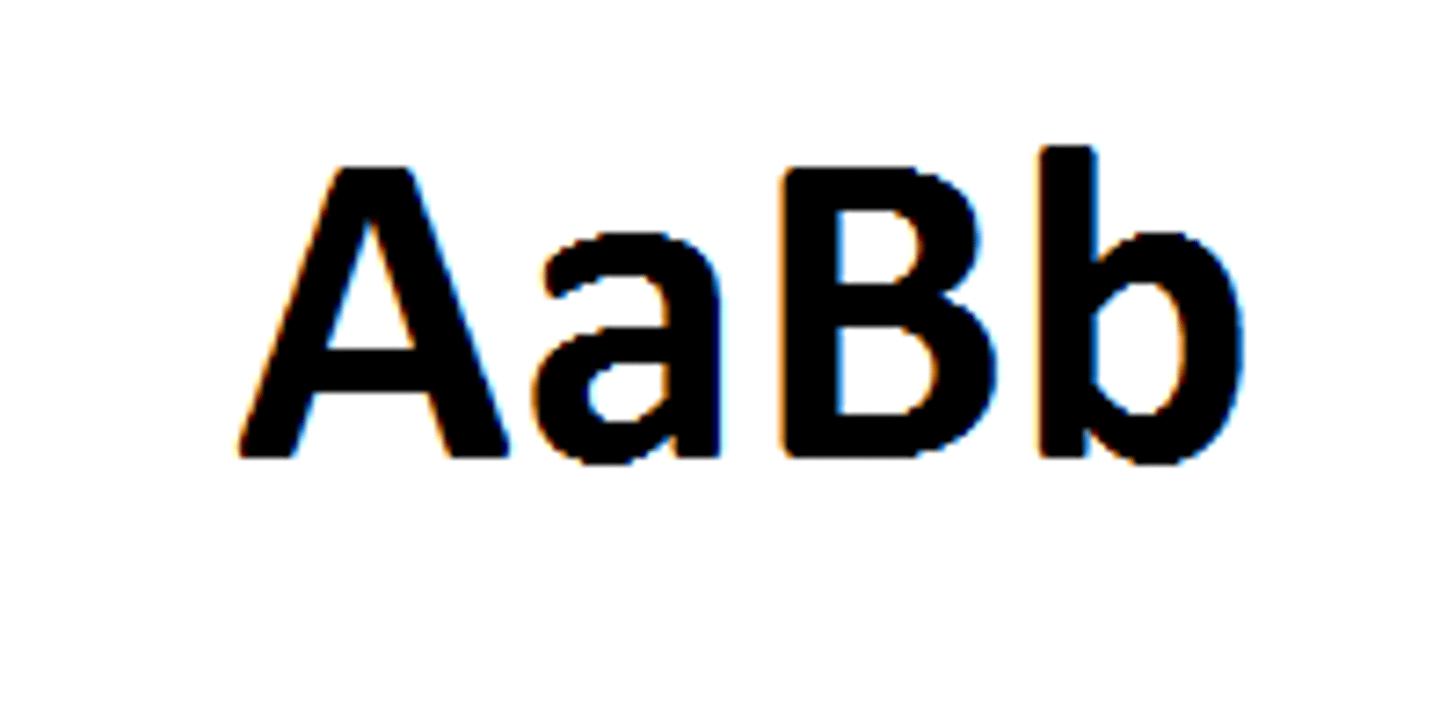
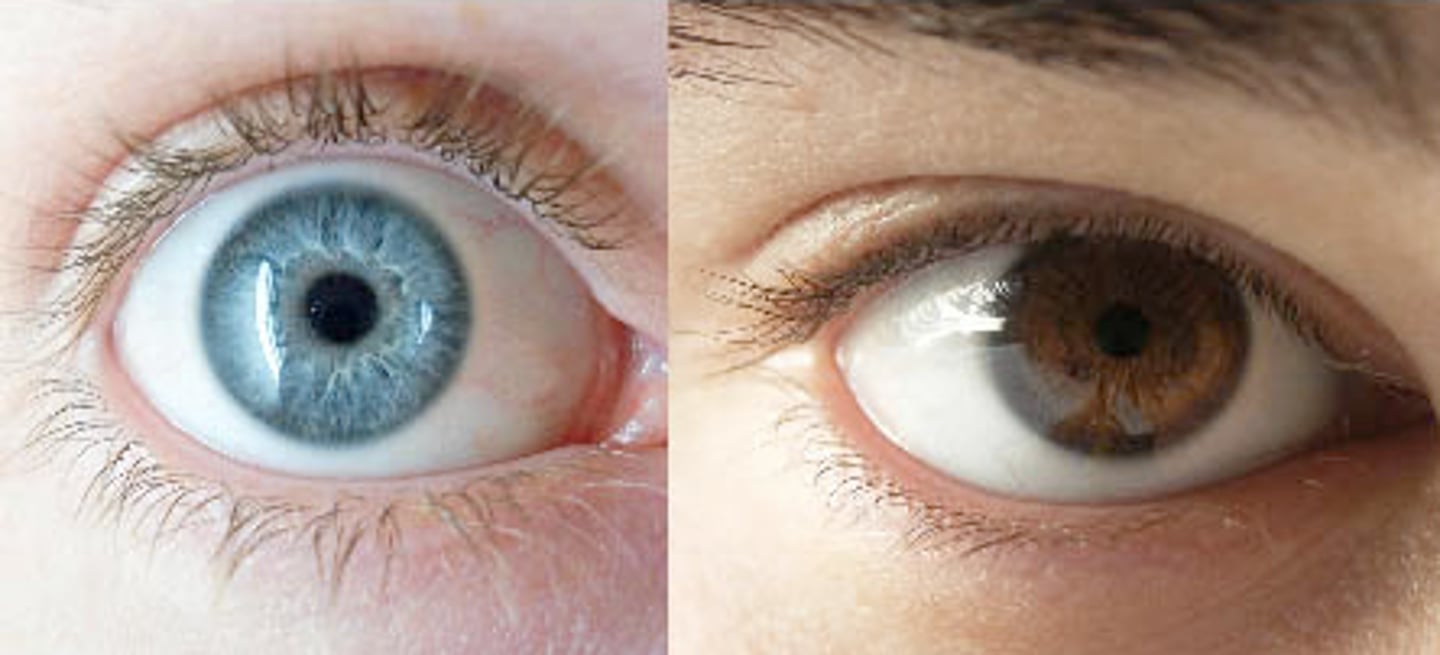
Phenotype
observable traits (What you see! Blue eyes or Brown eyes)
Dominant Trait
phenotype shows if 1 or 2 copies are present in the genotype. Capital letter! (BB, Bb)

Recessive Trait
phenotype ONLY shows when 2 copies are present. Lowercase letters. (bb)
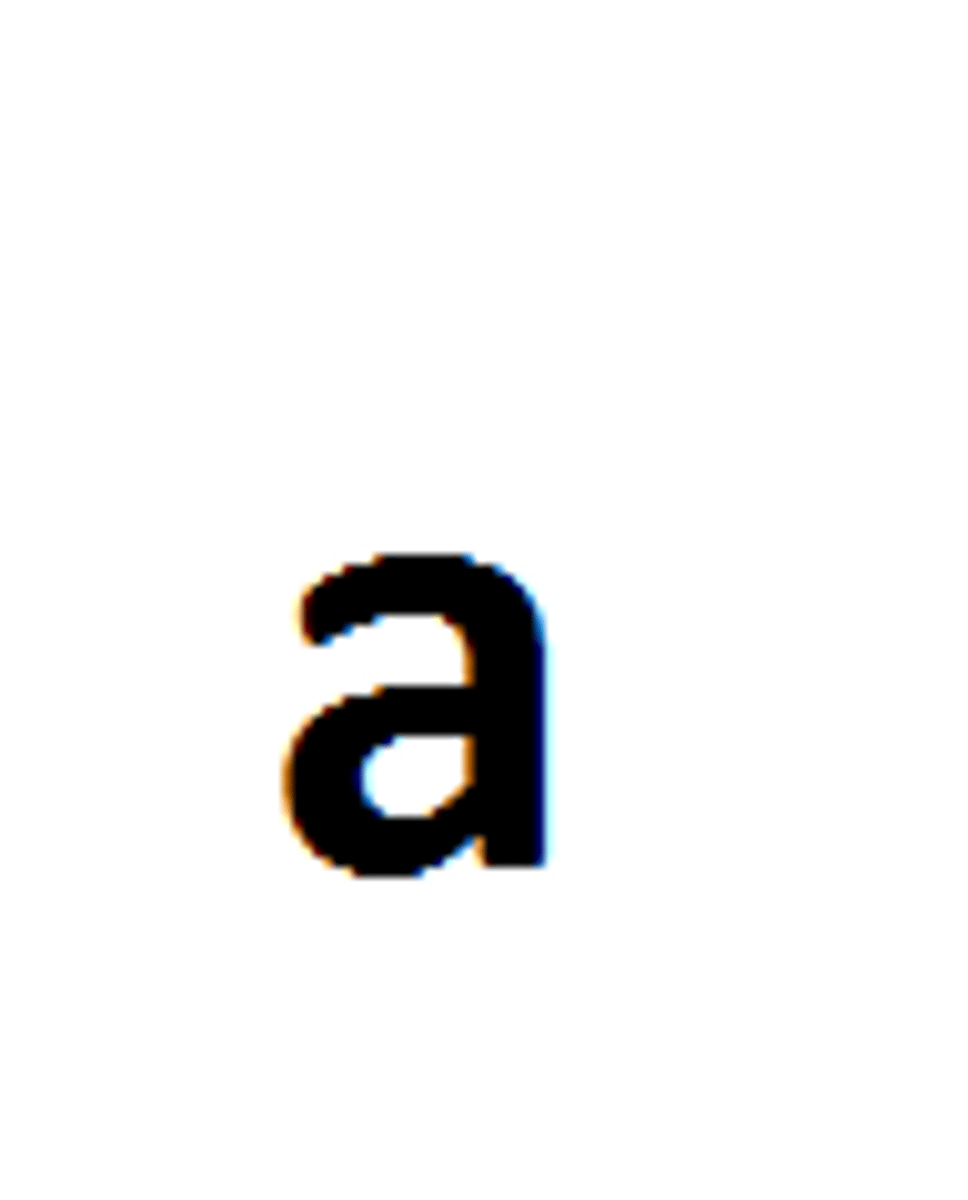
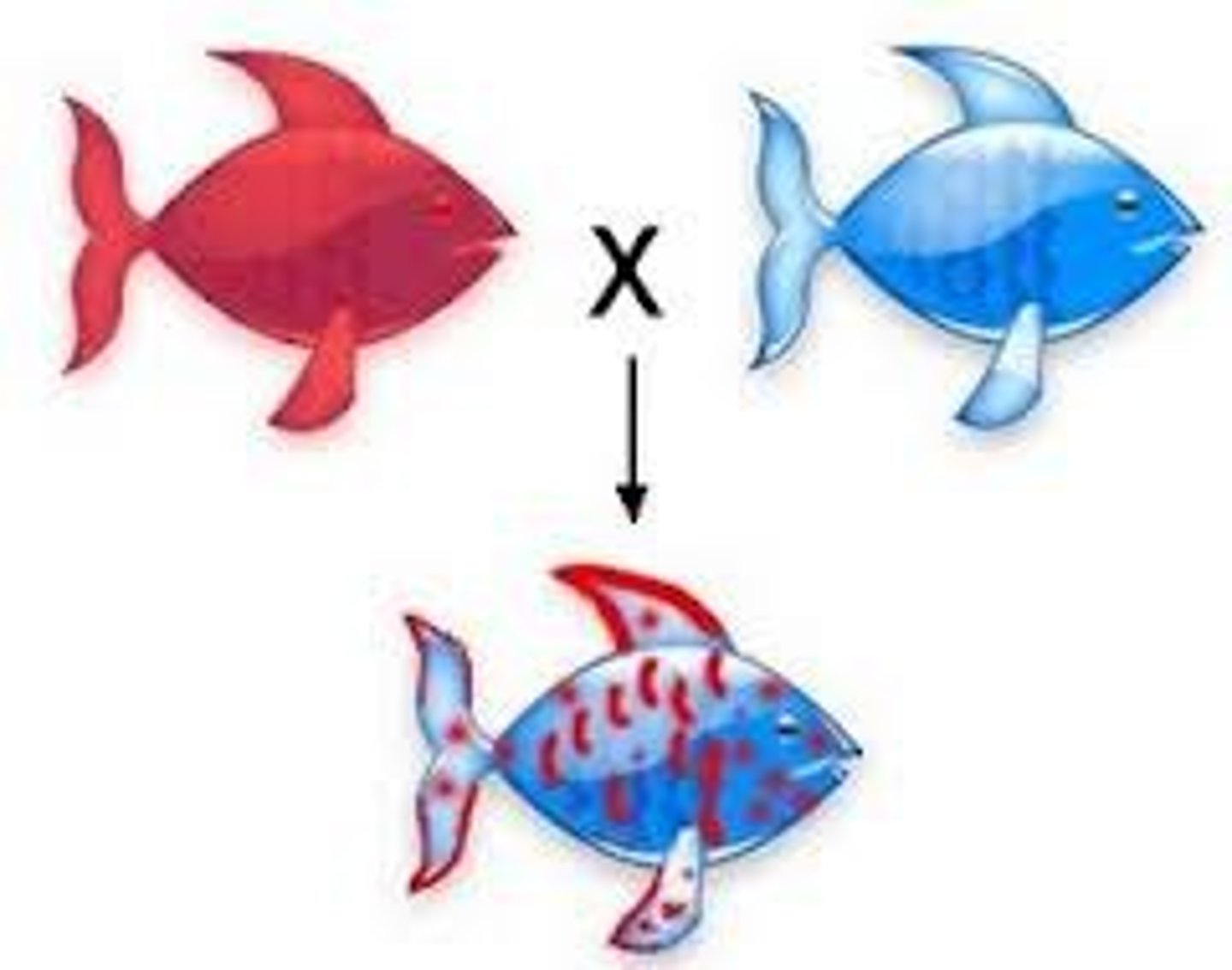
Codominant
both alleles in the heterozygous individual contribute to the phenotype. (A and B make AB)
Allele
different versions of the same gene
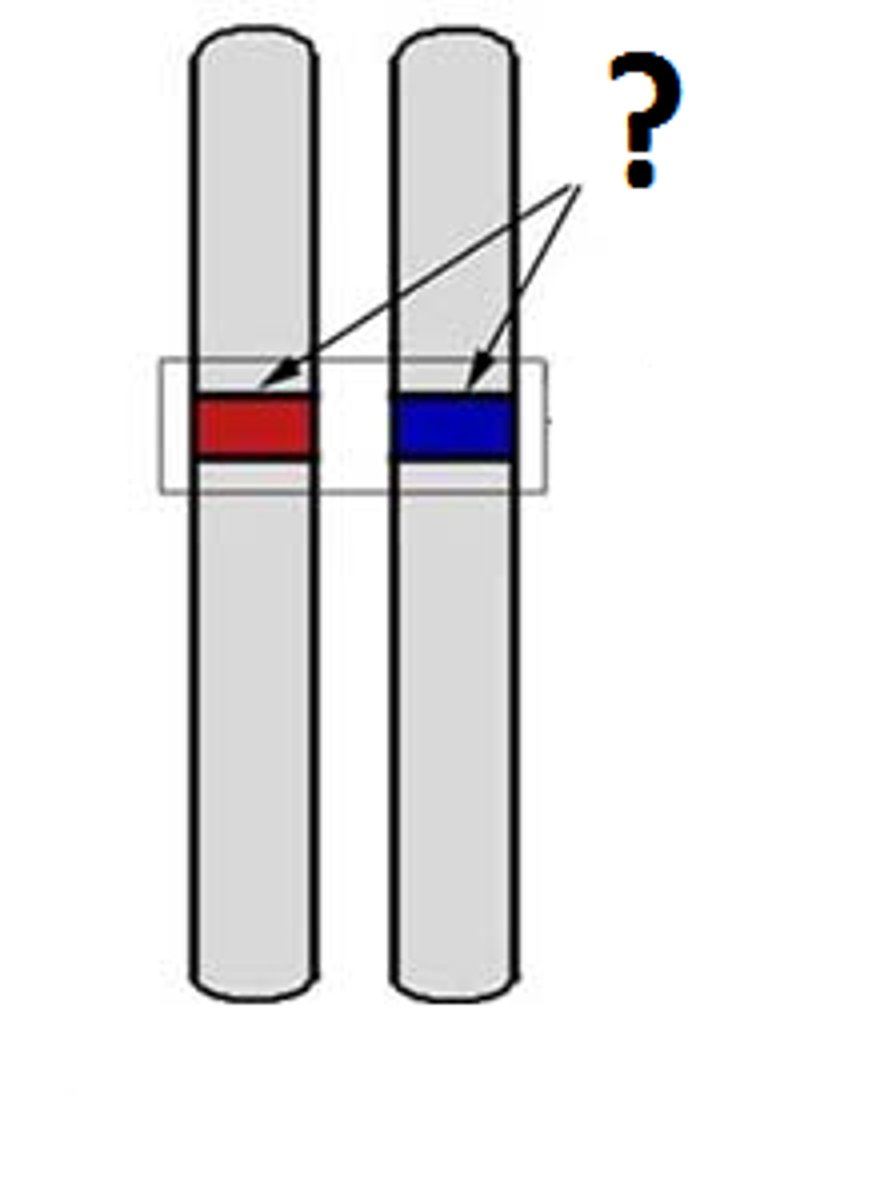
Homozygous
same (AA or aa)
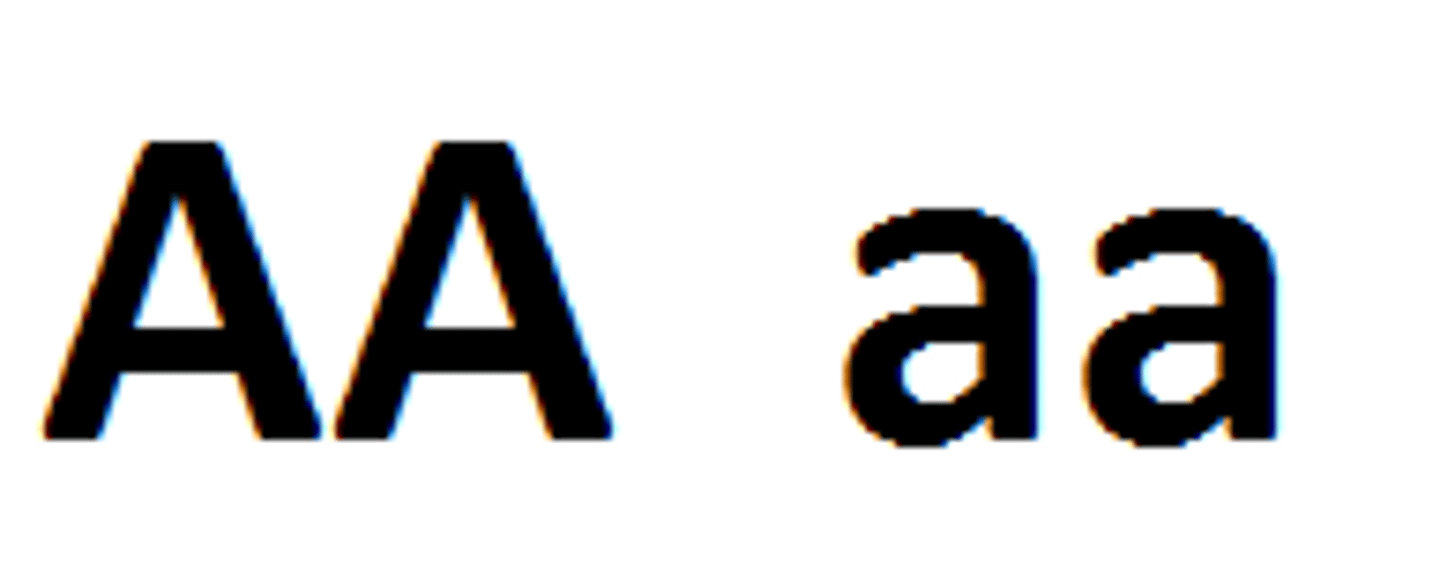
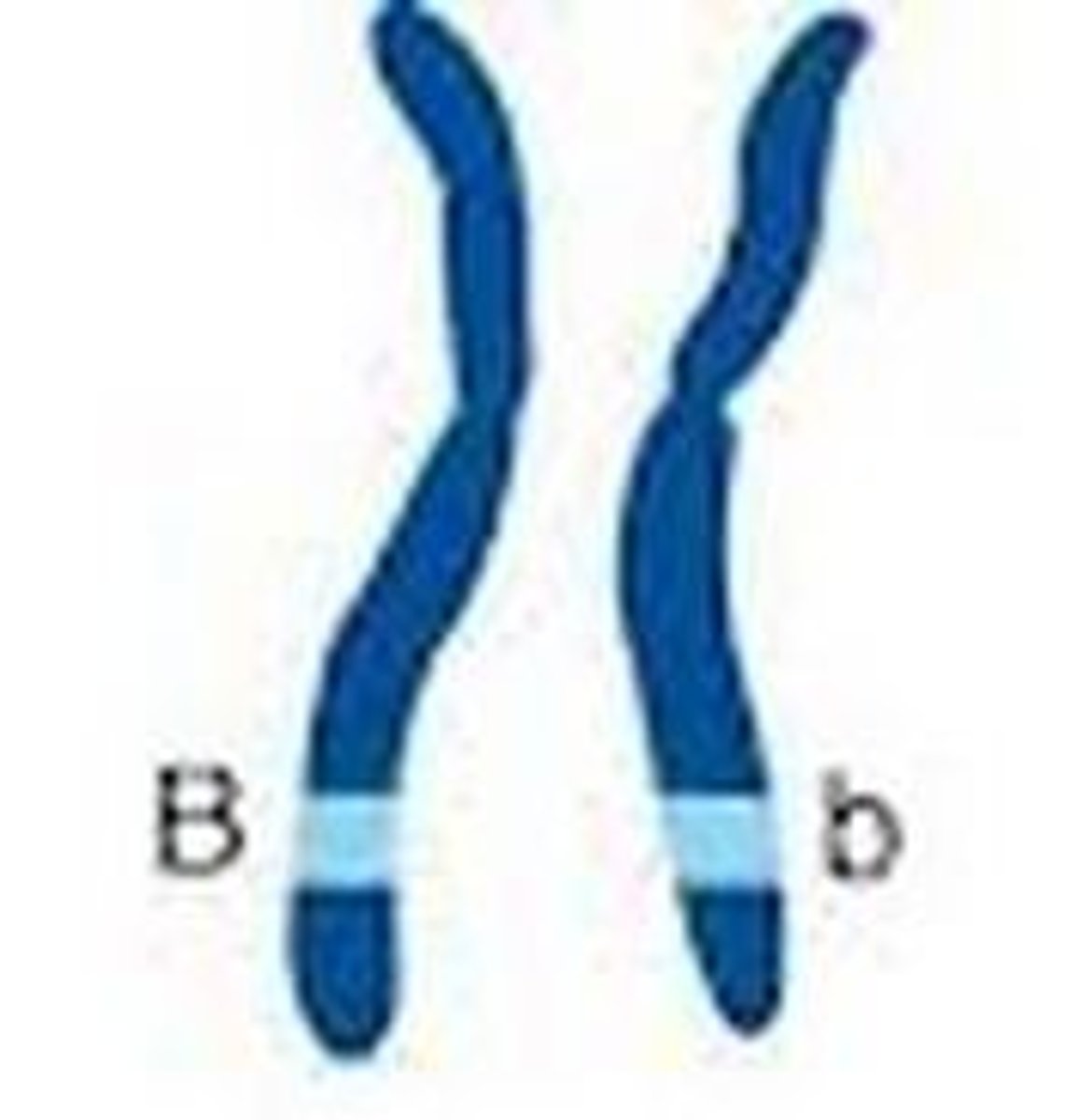
Heterozygous
different (Aa)
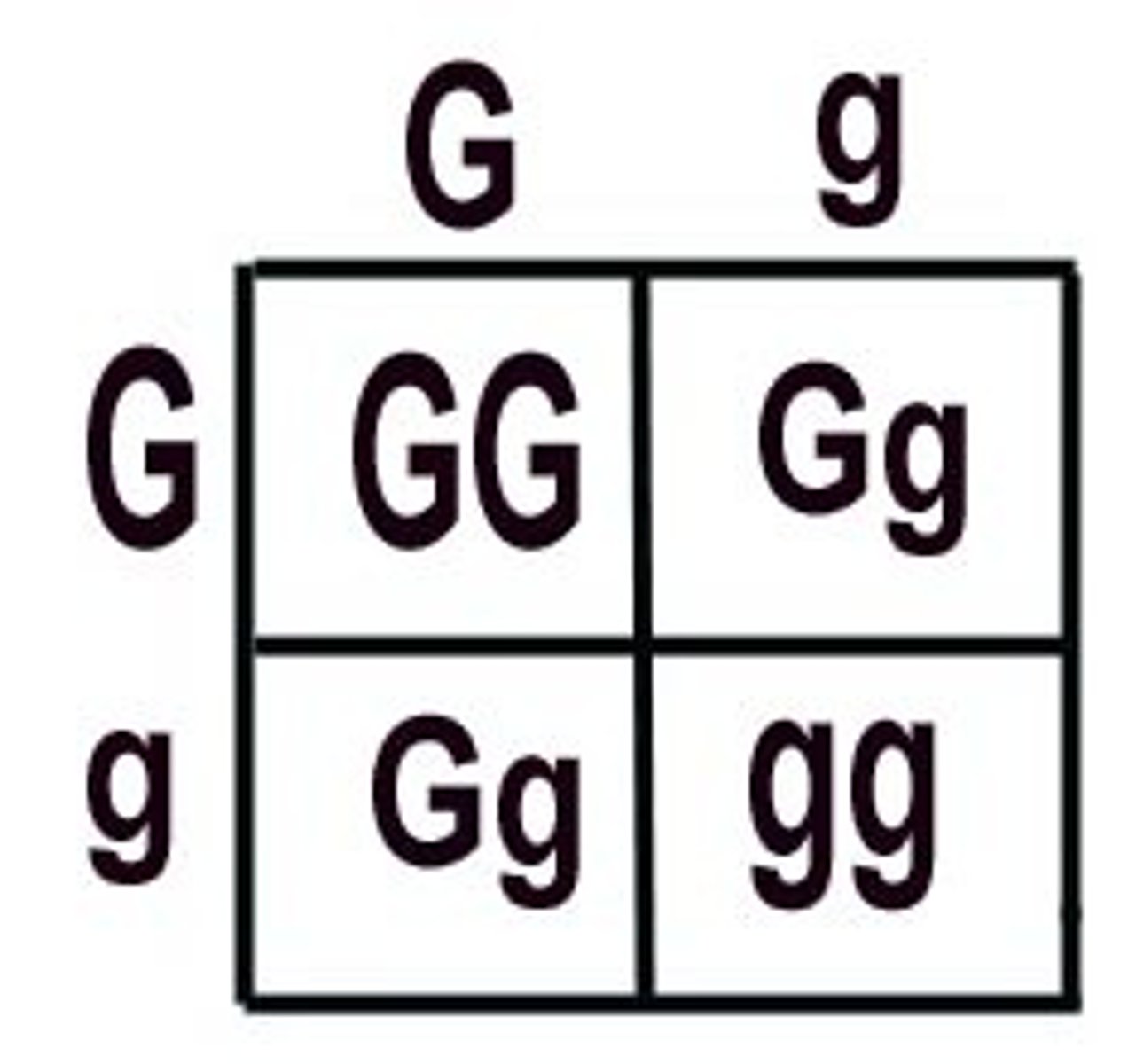
Punnett Square
shows possible combinations of offspring, and the probability these combinations will occur
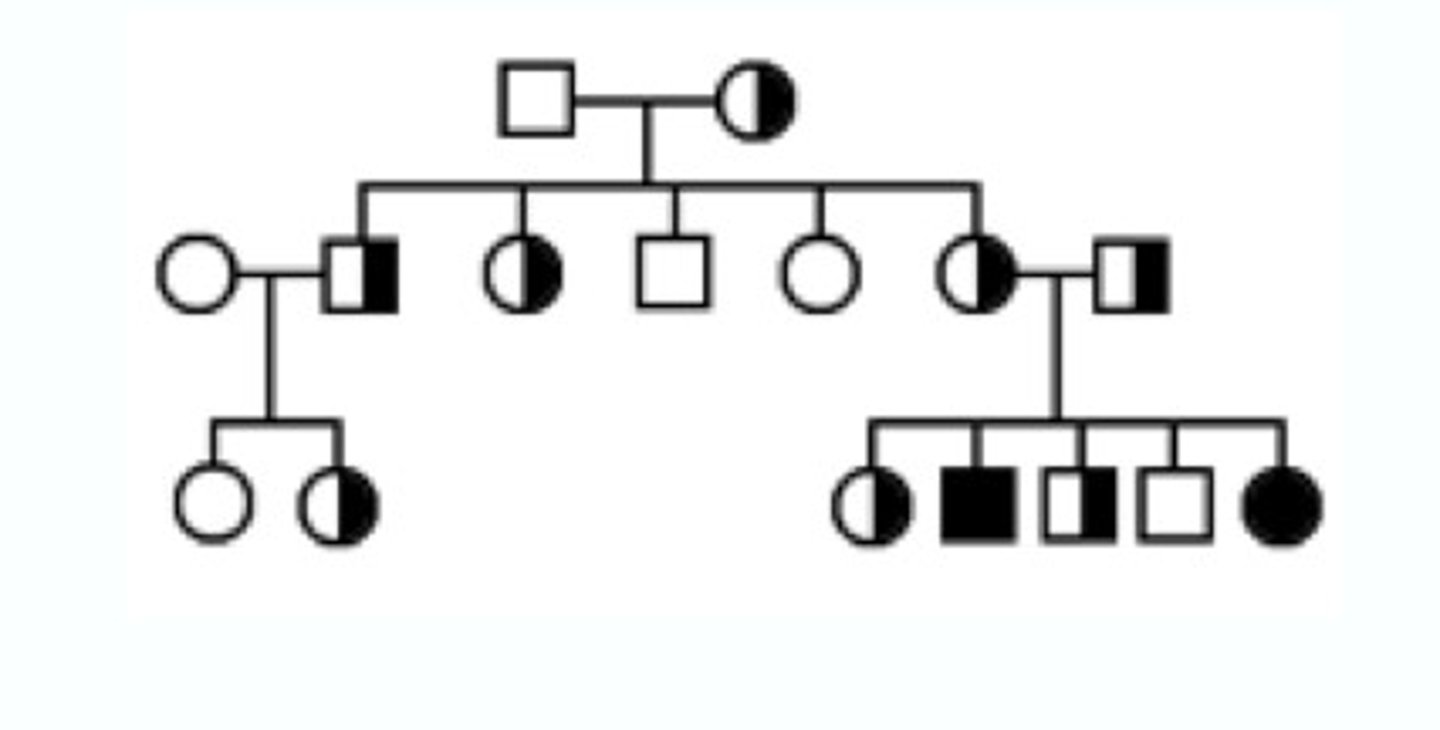
Pedigree
shows a family tree there traits can be tracked from parent to offspring
Complete Dominance
one allele is dominant, one allele is recessive
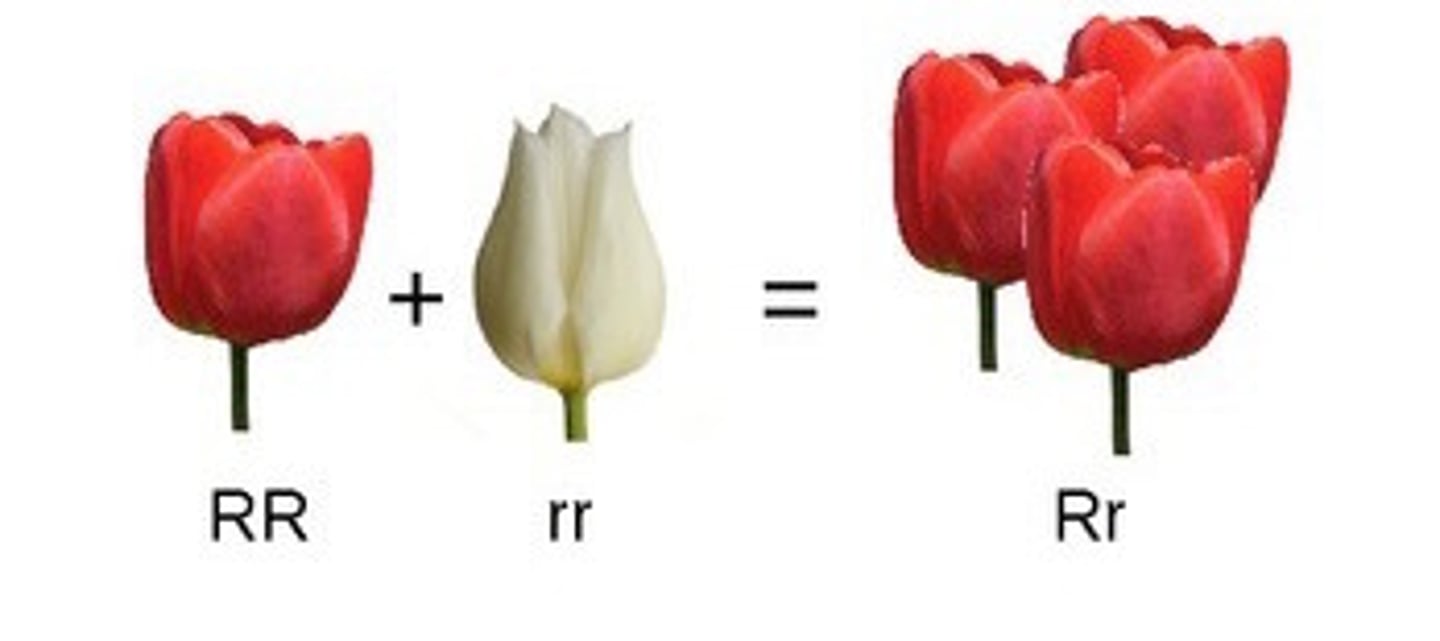
Hybrid
Another way to say heterozygous (Aa)
Pure
Another way to say homozygous (AA or aa)
Carrier
Someone how has the allele for a trait that they do not show. (Heterozygous - they have the recessive trait but you don't see it in the phenotype, you only see the dominant variation)