Biochemistry, Enzymes, and Digestion
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons
2
New cards
Electronegativity
measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound
3
New cards
Nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
4
New cards
Polar covalent
a type of bond that forms when electrons are not shared equally
5
New cards
Ionic Bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
6
New cards
Hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
7
New cards
van der Waal interactions
weak intermolecular forces that only occur when the olecules are close together
8
New cards
reactants
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
9
New cards
products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
10
New cards
cohesion
an attraction between molecules of the same substance
11
New cards
adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
12
New cards
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
13
New cards
kinetic energy
energy due to motion
14
New cards
heat
The energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures
15
New cards
specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
16
New cards
heat of vaporization
The amount of energy required for the liquid at its boiling point to become a gas
17
New cards
evaporative cooling
The process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation, a result of the molecules with the greatest kinetic energy changing from the liquid to the gaseous state.
18
New cards
solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
19
New cards
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
20
New cards
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
21
New cards
hydration shell
the sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion
22
New cards
acid PH
below 7
23
New cards
base PH
above 7 pH
24
New cards
organic compound
a covalently bonded compound that contains carbon, excluding carbonates and oxides
25
New cards
hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
26
New cards
functional groups
A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions.
27
New cards
monomer
one unit
28
New cards
polymer
many monomers
29
New cards
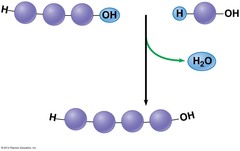
dehydration reaction
occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule
30
New cards
carbohydrates
sugar, quick energy
31
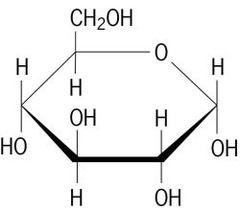
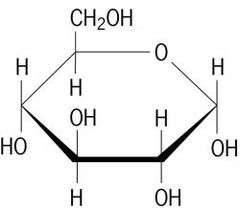
New cards
monosaccharides
one sugar
32
New cards
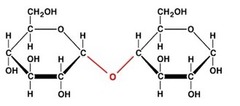
disaccharide
two sugars
33
New cards
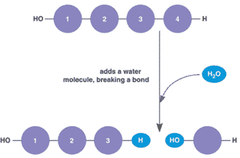
hydrolysis
occurs when water is added to split large molecules
34
New cards
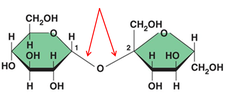
glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
35
New cards
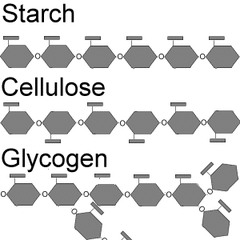
Polysaccharides
many sugars
36
New cards
starch
energy storage in plants, rice potatoes, wheat, and corn
37
New cards
glycogen
short term energy storage in animals
38
New cards
cellulose
makes up plant cell walls
39
New cards
chitin
makes up insect exoskeletons and fungal cell walls
40
New cards
lipids
functions are: long-term energy storage, insulation, communication, cell membranes
hydrophobic and non-polar
hydrophobic and non-polar
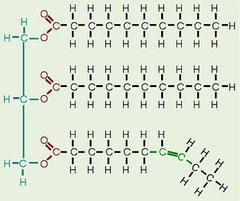
41
New cards
fat
triglyceride
42
New cards
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain often bonded to glycerol in a lipid
43
New cards
triacylglycerol
Three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule; also called a fat or a triglyceride
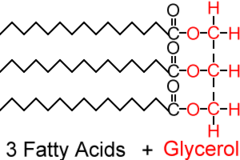
44
New cards
saturated fatty acid
contains the maximum number of hydrogen atoms and no double bonds
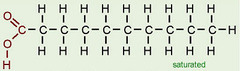
45
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
contains one or bent double bonds, bent
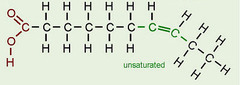
46
New cards
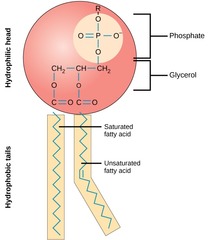
Phosopholipids
two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol
47
New cards
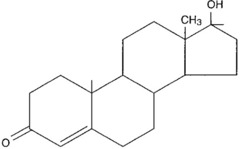
steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
48
New cards
cholesterol
component of animal cell membranes
49
New cards
catalysts
Chemical agents that selectively speed up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction.
50
New cards
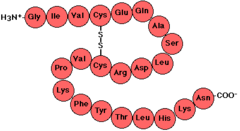
polypeptides
unbranched polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
51
New cards
protein
polymer, biologically function molecule that consist of one or more polypeptides
contains a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups
contains a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups
52
New cards
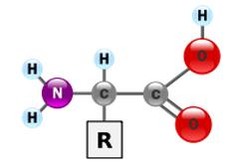
amino acids
monomers of proteins
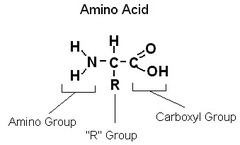
53
New cards
functions of proteins
defense, storage, transport, cellular communication, movement, and structural support
54
New cards
peptide bond
bonds between amino acids
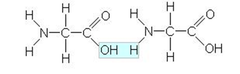
55
New cards
4 levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
56
New cards
primary structure
unique sequence of amino acids held by peptide bonds

57
New cards
secondary structure
consists of alpha helix and beta sheets due to hydrogen bonds
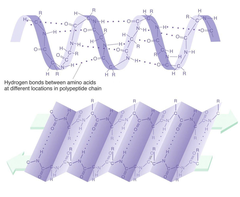
58
New cards
tertirary structure
3D globular structure due to interactions among R groups
held by ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges, and van der waals interactions
held by ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges, and van der waals interactions
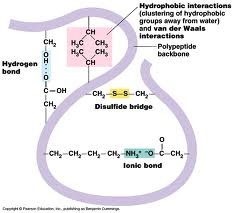
59
New cards
denaturation
loss of a protein's native structure, biologically inactive
60
New cards
chaperones
oversees the structure of proteins
61
New cards
nucleic acids
store, transmit, and help express hereditary information
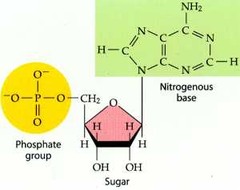
62
New cards
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
gives directions for its own replication and directs the synthesis of rNA, and through this controls protein synthesis ; double-stranded
63
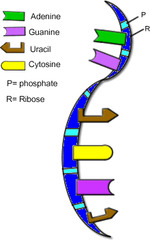
New cards
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses.
64
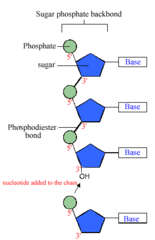
New cards
polynucleotides
polymers of nucleic acids
65
New cards
nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids
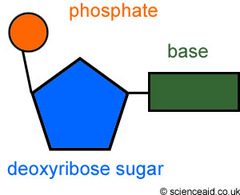
66
New cards
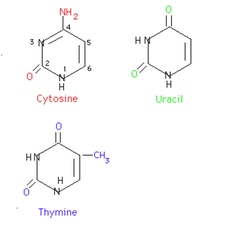
pyrimidine
single-ring nitrogenous base, cytosine, thymine, uracil
67
New cards
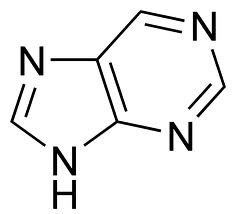
purines
two-ring nitrogenous base, adenine and guanine
68
New cards
ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
69
New cards
dexoyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
70
New cards
Hydroxyl group
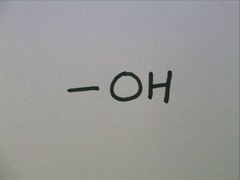
71
New cards
Carbonyl group
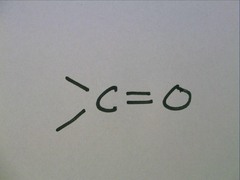
72
New cards
Carboxyl group
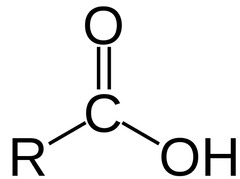
73
New cards
Amino group
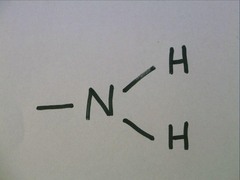
74
New cards
Sulfhydryl group
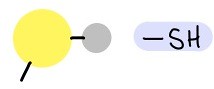
75
New cards
Phosphate group
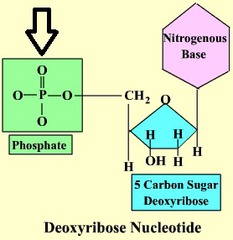
76
New cards
Methyl group
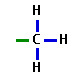
77
New cards
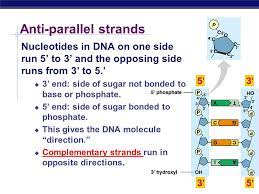
antiparallel
The strands each run from 5' to 3' and run in antiparallel, or opposite, directions from one another.