The Chemistry of Life (Midterm Review)
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
Atom
basic unit of matter - make up living things
Atoms are made up of:
even smaller particles that make up atoms (subatomic particles)
What are those subatomic particles:
Protons, Nuetrons, Electrons
Center of an atom:
Nucleus
Nucleus contains:
protons and neutrons
Proton has a ___ charge and a neutron has a ___ charge:
positive, neutral/no charge
An electron is:
negatively charged particle (-), smaller than a proton, and found surrounding the nucleus in shells
Electrons are always in
motion
First shell:
2 electrons
Second shell:
8 electrons
Third shell:
18 electrons
Atoms are as _ cancel out.
neutral - positive and negative charges
Element:
pure substance consisting of ONE type of atom
An element is often represented by
one or two letter symbols (ex: C = carbon, CL = chlorine, 0= = oxygen)
Atomic Number:
total number of protons in an element
What can the atomic number tell us?
This can tell you the # of the rest of the particles in the atom
Atomic mass/mass number:
total number of protons + neutrons
A valence shell is:
The outermost shell of an atom
What does the valence shell want
8 electrons
Life on earth is called
carbon based
Organic compounds ALL have
carbon + hydrogen
6 major elements to life: CHONPS
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfuir
Isotope
atoms that are the same element but differ in the number of neutrons only
In nature, elements combine with each other to
form compounds
Compound:
substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements
Most abundant compound in living things
water
Compounds are written in terms of
a chemical formula
What does a chemical formula show us?
what elements are in the compound and how many of each there are
How to read chemical formulas:
fixc this later (ex- H20 = 2 hydrogens and 1 oxygen)
To make compounds, elements must
bond together through one of two main types - ionic or covalent bonding
Ionic bonds
bond formed when one or more electrons are TRANSFERRED from one atom to another
Ions
atoms that have lost or gained an electron
*Lose an electron
positive charge ion (cation)
*Gain an electron
negative charged ion (anion)
Covalent Bond:
bond formed when one or more electrons are SHARED by elements
4 major organic molecules:
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids
(Covalent Bond) Sharing two electrons =
single bond
(Covalent Bond) Sharing four electrons =
double bond
(Covalent Bond) Sharing six electrons =
triple bond
When atoms join together ____, we call these ____ - smallest unit of most compounds
covalently, molecules
On top of the strong bonds (ionic and covalent) ____ interactions are just as important between ___ and _____.
weak, atoms, molecules
Van der Waals forces provide ___ attractions between ____ when they are very close together.
slight, molecules
_____ is also an example of weak interactions/Van der Waals forces.
Hydrogen bonding
Carbon: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, PNE
6, 12.011, 6, 6, 6
Hydrogen: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, PNE
1, 1.00794, 1, 0, 1
Oxygen: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, PNE
8, 15.994, 8, 8, 8
Nitrogen: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, PNE
7, 14.0067, 7, 7, 7
Phosphorus: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, PNE
15, 30.97376, 15, 16, 15
Sulfur: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, PNE
16, 32.06, 16, 16, 16
Carbon bonds with other elements but it will also form bonds with
other carbon atoms
These combinations of carbons are called
hydrocarbons (H3-CH2-CH2-CH2…)
These bonds can be __________ with other carbons which produces carbon chains or can even from rings
single, double,or triple bonds
Due to the bonding nature of carbon, we can form large organic molecules called
macromolecules
small units of a macromolecules
monomers
monomers that joined together
polymers
process of building larger molecules from smaller ones
polymerization
Carbohydrates are made up of
CHO, ratio 1:2:1 (example - C6H12O6)
Short term storage and release energy
Carbohydrate function (1)
Major energy source for body
Carbohydrate function (2)
Structural support
Carbohydrate function (3)
Protection
Carbohydrate function (4)
Monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharide (glucose, galactose, fructose)
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides together (sucrose, maltose, lactose)
Breaking down sugars creates
energy immediately for cells
Many organisms will store energy in the form of
starches
Starches are ____, and contain ___
complex, multiple monomers
Polymer of carbohydrates is
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide (how many, and example)
3 or more monosaccharides combined (glycogen, starch, cellulose)
In plants, polysaccharide equals
starch (how plants store excess sugars)
In animals, polysaccharide equals
glycogen
When sugar is low, we break down glycogen ______
to get energy
Each time a monosaccharide combined with another one, a
water molecule is released
When bonds are formed,
energy will be stored
Dehydration Synthesis
process in which two molecules combine and water is released
how dehydration synthesis occurs
-OH from one monosaccharide removed and an -H removed from the other, creates water (which is why water is released during process)
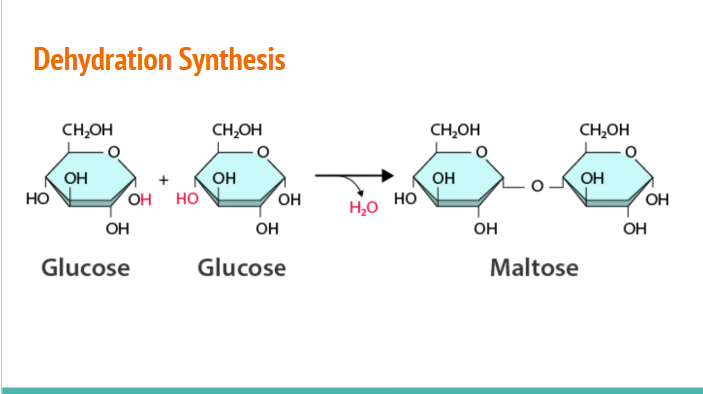
(Hydrolosis) When bonds are broken,
energy is released
Hydrolysis
chemical reaction where water is ADDED and a compound is broken apart
Lipids
a group of macromolecules that are generally not soluble in water
What do Lipids contain?
CHO mainly C and H
compounds for Lipids we know as
fats, oils, and waxes
3 types of lipids
triglyceride, phospholipids, sterols/steroids
Lipids don't have true
monomers or polymers
Lipids are made up of
a glycerol molecule and fatty acids
Triglyceride is made up of
glycerol and 3 fatty acid tails
Saturated Fatty Acid
carbon chain is all single bonds and saturated with hydrogens
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
one or more carbons are double bonded together creating a bend
Saturated fatty acids are usually ____ at room temperature
solid - stack on top of each other (ex. butter)
Unsaturated fatty acids are usually ____ at room temperature
liquid - double bonds create a bend that prevent these from stacking (ex. oils)
Monounsaturated =
one double bond
Polyunsaturated =
2 or more double bonds
Cell membranes are made up of
phospholipids
2 parts of a phospholipid
Hydrophilic head, Hydrophobic tails
The tails part of a phospholipid face
towards each other in the center, where heads face exterior
The heads of the phospholipids form _____ protecting the
a bilayer, water fearing tails
Long term energy storage - energy stored in fatty acids
Lipid function (1)
Play a role in cell membranes - phospholipids
Lipid function (2)
Waterproof coverings
Lipid function (3)
Steroid hormones - chemical messengers
Lipid function (4)
What are nucleic acids made up of
CHONP
Monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides