Kidney and Osmoregulation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the amount of water lost in urine controlled by?
ADH (anti diuretic hormone) in a negative feedback system
Where is ADH produced and stored
Produced: hypothalamus
Stored and secreted from: posterior pituitary gland
When is ADH released?
When stimulated by neurones from osmoreceptors
What does ADH do to parts of the kidney?
Increases permeability of DCT and collecting duct to water
How does ADH act on cells?
Binds to receptors on cell membrane of tubule cells
Mechanism of ADH action
Binds to receptors on cell membrane of DCT, collecting duct
Triggers formation of cAMP as 2nd messenger in cell
Second messenger
Molecule which relays signals received at a cell surface receptors to molecules inside cell
What is the cascade of events cAMP causes?
Vesicles in cells lining CD fuse w. cell surface membranes on side of cell in contact w. tissue fluid of medulla
Vesicle contains aquaporins
Membrane has increased aquaporins, making it more permeable to water
More water able to move out of tubule cells into medulla’s tissue and into blood capillaries by osmosis
= increased water reabsorption , small conc. urine, maintains water potential of blud
What happens when ADH levels fall?
Levels of cAMP fall
Aquaporins removed from tubule cell membranes & re-enclosed in vesicles (endocytosis)
CD becomes impermeable to water (can’t leave)
Large amount of v. dilute urine
Water potential of blood and tissue fluid maintained
osmoreceptors
Monitors water potential of blood
Are sensitive to conc. of inorganic ions in blood
Linked to release of ADH
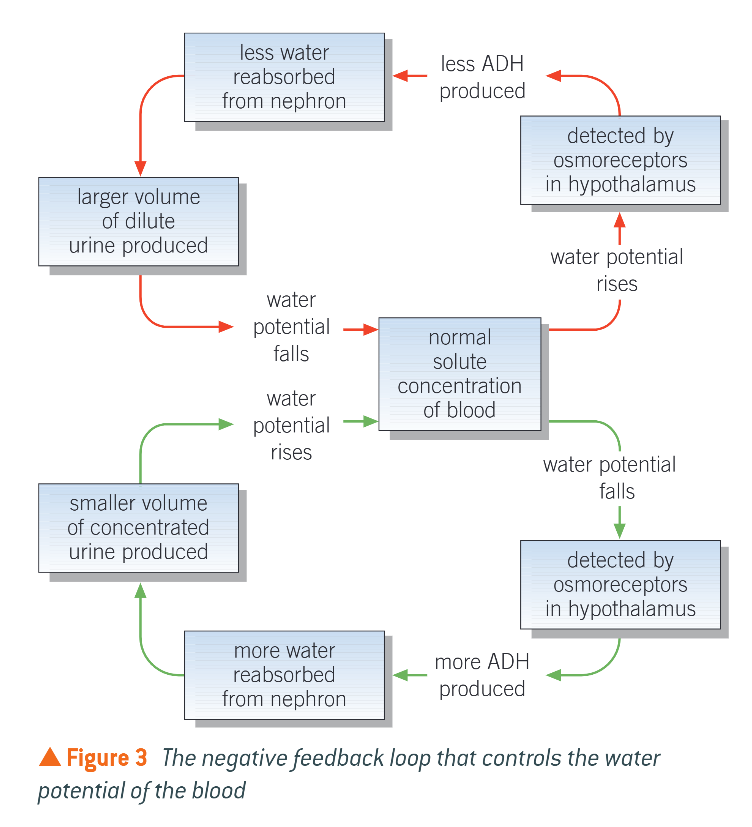
What happens when body in short supply of water?
Blood water potential drops
Detected by osmoreceptors which send nerve impulses to posterior pituitary
Releases more ADH into blood
Binds to receptors in cells of CD, and increases the permeability of the tubules to water
More water reabsorbed from nephron
Small vol. of conc. urine produced
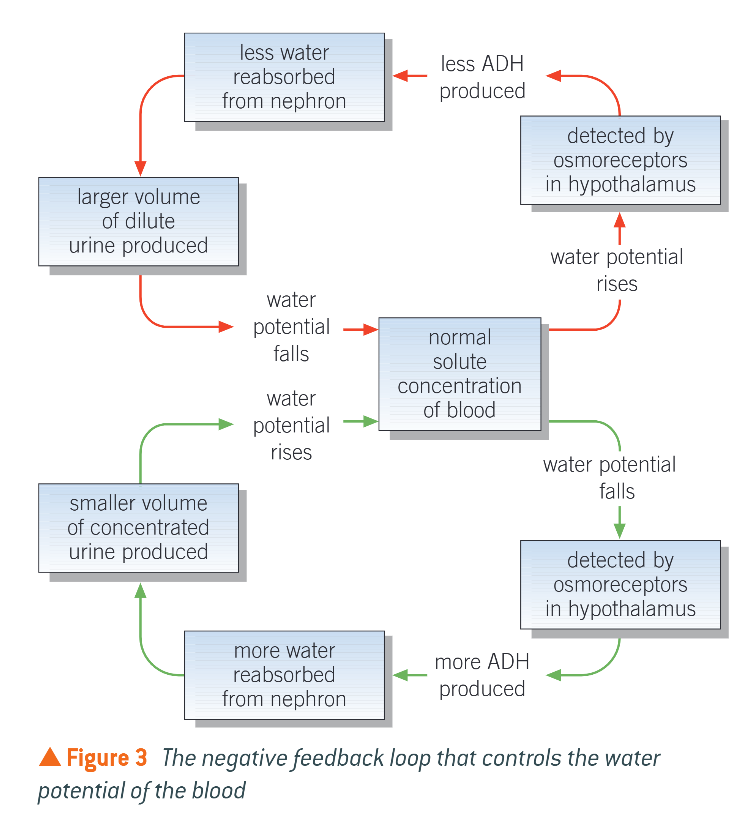
What happens when body has excess of water?
Water potential of blood rises
Detected by stretched osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
Nerve impulses to p.p. are reduced or stopped, so less ADH released or is inhibited
Less water reabsorbed from nephron
Endocytosis of aquaporins
Large vol. of dilute urine produced