IB Chemistry: Organic chemistry
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
homologous series
group of organic species, all containing the same functional group and varying only by carbon-chain length
( number of CH2)
functional groups
reactive parts of the molecules
contains elements like oxygen and nitrogen
What is the difference between unsaturated and saturated bonds?
Saturated: single bonds only
Unsaturated: contains double or triple bonds
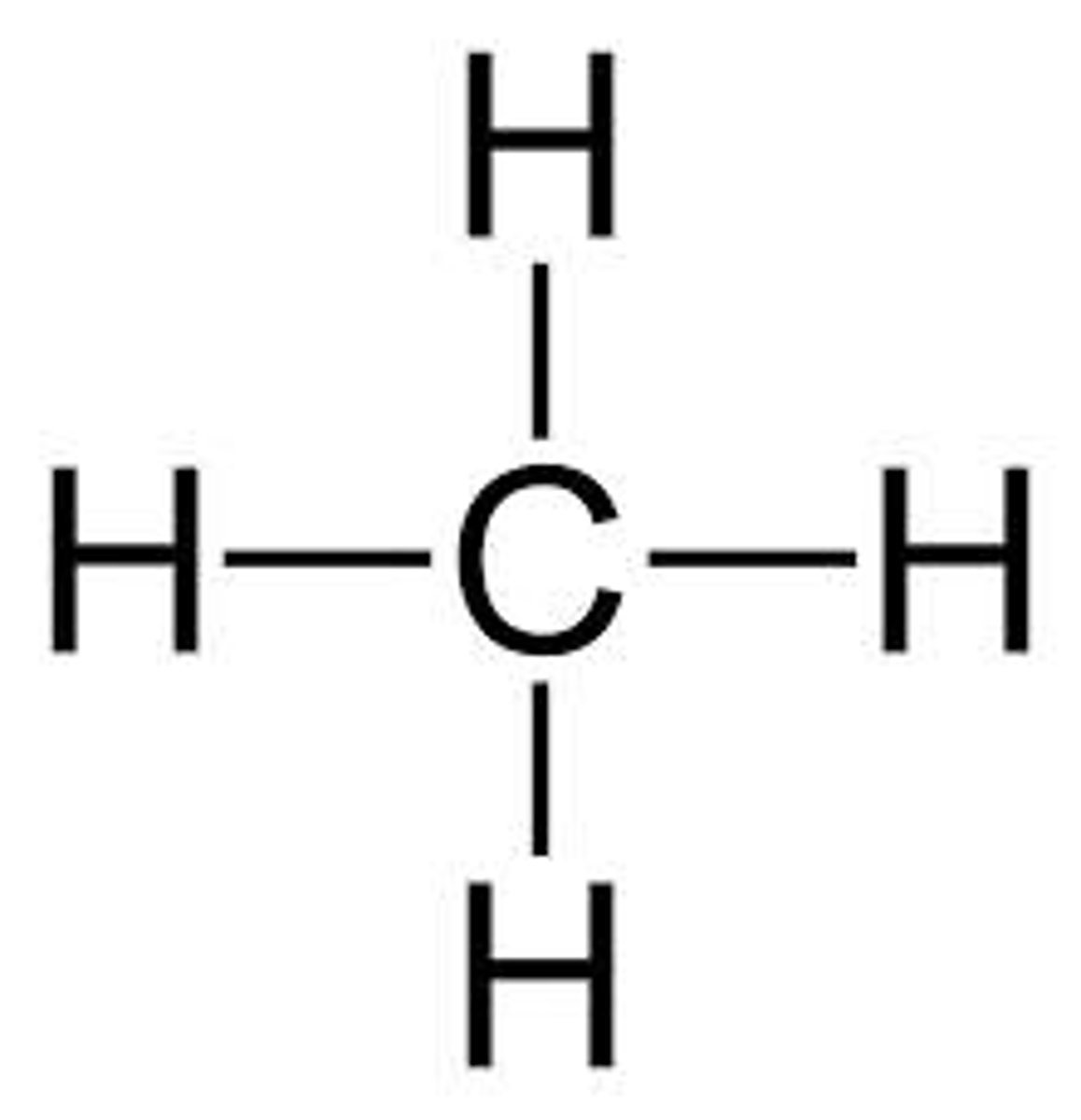
Show the formula, condensed structural formula, and structural formula for methane.
Formula:: Ch4
Condensed: Ch4
Structural:
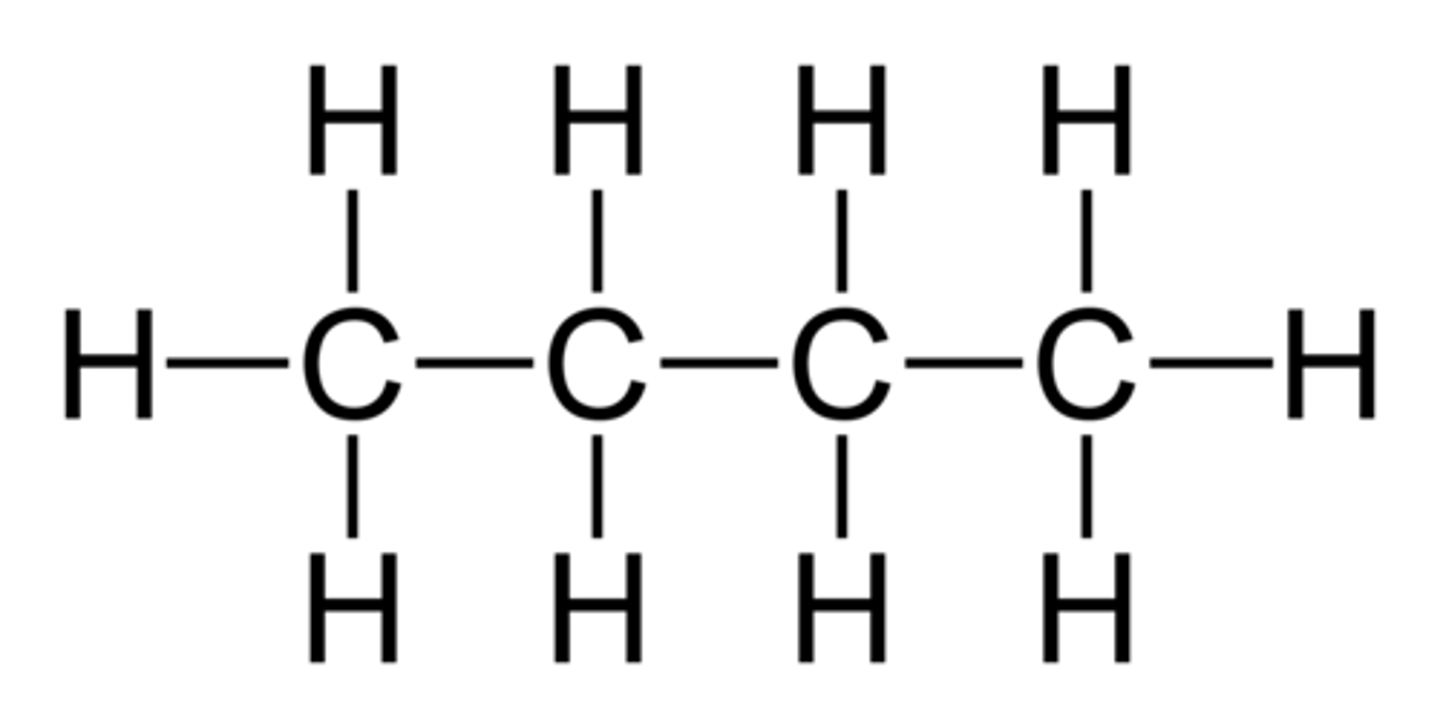
Show the formula, condensed structural formula, and structural formula for butane.
Formula: C3H6
Condensed: Ch3Ch2CH2Ch3
Structural
General formula for alcohols
C(n)H(2n+1)OH
General formula for aldehydes
C(n)H(2n)O
General formula for ketones
C(n)H(2n)O
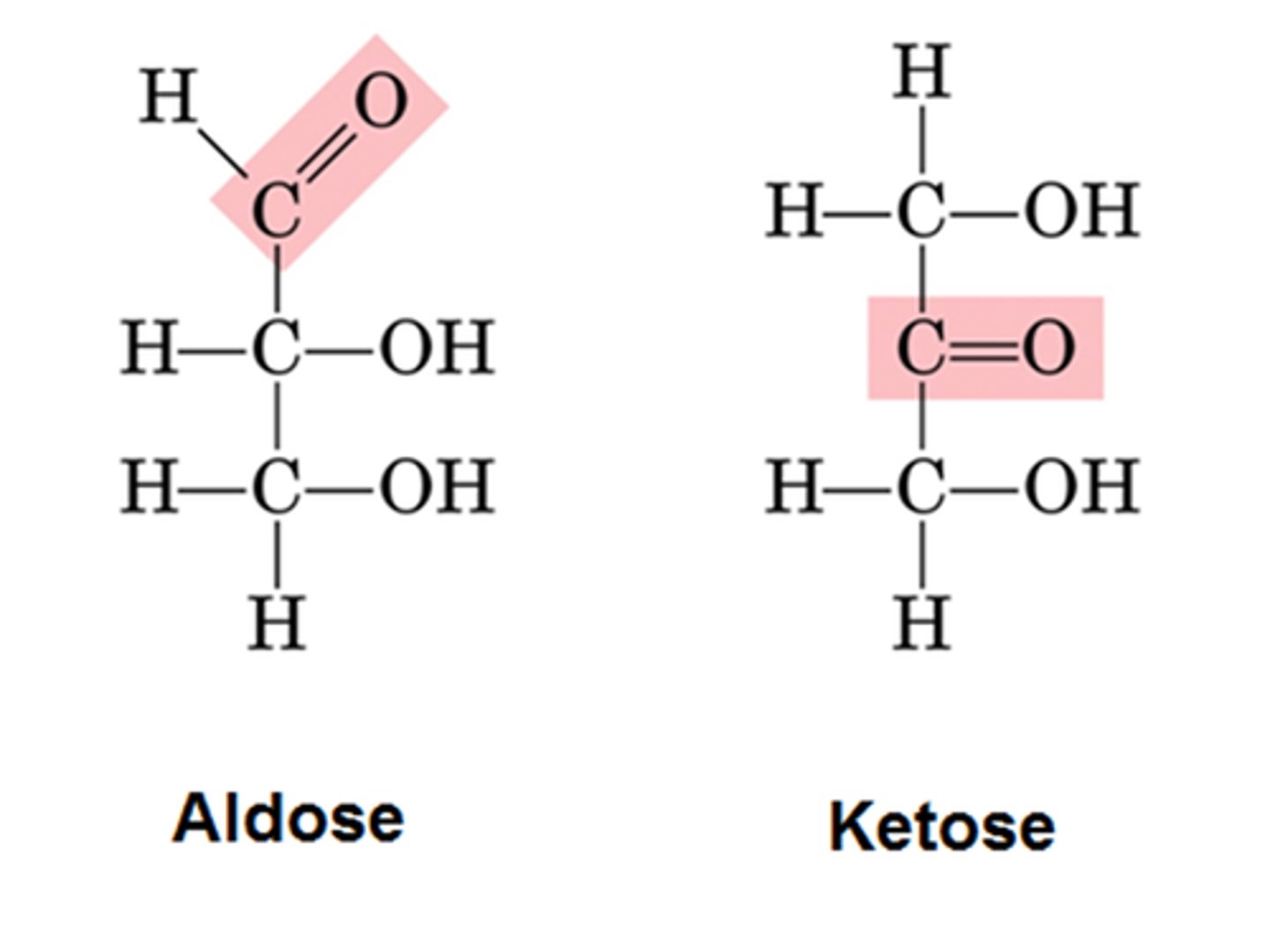
what is the difference between aldehydes and ketones
aldehydes: hydrogen is attached to the C=O on end of the chain
Ketones: no hydrogen and C=O in middle of chain (not at end)
What happens to the the physical properties of homologous series as the carbon chain increases?
boiling point increases
What is fractional disillation
physical separation process that uses differences in boiling points to separate the mixture
What is benzene?
aromatic, unsaturated hydrocarbon
What are hydrocarbons?
Compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen
characteristics of successive members of a homologous series
differ by a CH2 group; same general formula; gradual change in physical properties; similar chemical properties
empirical formula
the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms the molecule contains
molecular formula
the actual number of atoms of each element present in the molecule
skeletal formula
most basic form: each corner means a carbon and each carbon has hydrogen atoms connected that are not shown
Propane:

structural formula
a representation of the molecule showing how the atoms are bonded to each other
-ane
alkane
alkane general formula
C(n)H(2n+2)
-ene
alkene
-yne
alkyne
-anol
alcohol
-anal
aldehyde
-anone
ketone
-anoic acid
carboxylic acid
-anoate
ester
structural isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of the atoms
primary carbon atom
carbon atom in an organic molecule that is attached to the functional group and at least two hydrogen atoms
secondary carbon atom
carbon atom in an organic molecule that is attached to the functional group, one hydrogen atom and two alkyl groups
tertiary carbon atom
carbon atom in an organic molecule that is attached to the functional group and three alkyl groups
Alkenyl
Functional group of alkenes
Alkynyl
Functional group of alkynes
Phenyl
Functional group of Arenes
Hydroxyl
Functional group of alcohols
Aldehyde
Functional Group of Aldehyde
Carbonyl
Functional group of ketones
Carboxyl
Functional group of carboxylic acids
Ester
Functional group of esters
Ether
Functional group of ethers
Amino
Functional group of amines
Amido
Functional group of amides
Cyano
Functional group of nitriles
Saturated
All carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds
Unsaturated
One or more carbon-carbon bonds are double or triple bonds
Aliphatic Compounds vs Aromatic Compounds
Aliphatic compounds can have saturated or unsaturated carbon chains but the bonds are localized between two carbon atoms. Aromatic have delocalized electrons that circulate around a ring.