Static Charge
5.0(7)Studied by 101 people
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Last updated 4:26 AM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
What does static charge mean?
Static charge refers to electric charge that can be held in one place (aka static electricity)
2
New cards
What are examples of static electricity?
* A lightning strike
* Dusters that attract dust
* Crackles when combing hair
* Plastic wrap sticking to your hands
* Dust being attracted to television screens
* Clothes clinging to each other in a dryer
* Getting a shock after rubbing your feet on a carpet and then touching a metal object
* Dusters that attract dust
* Crackles when combing hair
* Plastic wrap sticking to your hands
* Dust being attracted to television screens
* Clothes clinging to each other in a dryer
* Getting a shock after rubbing your feet on a carpet and then touching a metal object
3
New cards
Where does static charge come from?
All materials are made of atoms, which contain electric charges
There are electrons around the atom, which are negative
There are protons in the centre of an atom, which are positive
An atom has an equal amounts of positive and negative charges, so the atom had no overall charge
__Electrons do not always stay attached to atoms and can sometimes be removed by rubbing__
There are electrons around the atom, which are negative
There are protons in the centre of an atom, which are positive
An atom has an equal amounts of positive and negative charges, so the atom had no overall charge
__Electrons do not always stay attached to atoms and can sometimes be removed by rubbing__
4
New cards
How does static charge build up?
It can build up when two insulating materials are rubbed together, such as a plastic comb moving through hair
5
New cards
What causes electrons to be transferred from one material to another?
Friction
6
New cards
When you rub two insulators together, what happens to the charges of the two insulators?
One material ends up with more electrons, so it has an overall negative charge
One material ends up with fewer electrons, so it has an overall positive charge
One material ends up with fewer electrons, so it has an overall positive charge
7
New cards
What are electrical insulators?
Materials that do not allow charges to move easily
8
New cards
What happens if you rub a neutral plastic rod with a paper towel?
The end of the plastic rod that was rubbed would become charged and the other end would remain neutral, meaning the plastic rod is an electrical insulator (the charges on one end did not transfer to the other end
9
New cards
What are examples of electrical insulators?
* Glass
* Dry wood
* Ceramics
* Plastics
* Rubber
* Dry wood
* Ceramics
* Plastics
* Rubber
10
New cards
What are electrical conductors?
Materials that allow electrons to move freely
11
New cards
Why are metals good conductors?
Metal atoms have at least one valence e- that can be easily transferred
Free electrons are the electron(s) in metals that are free to move throughout the conductor
Free electrons are the electron(s) in metals that are free to move throughout the conductor
12
New cards
Which of the two: insulators or conductors, can retain static charge?
Insulators can retain static charge
Conductors cannot retain static charge
Conductors cannot retain static charge
13
New cards
What is the unit of electric charge?
Coulomb (C)
14
New cards
How many electrons need to be transferred to produce one coulomb?
It takes the addition/removal of 6.25 x 10 to the 18 electrons to produce 1C of charge
15
New cards
How do you measure static charge?
With an electroscope
16
New cards
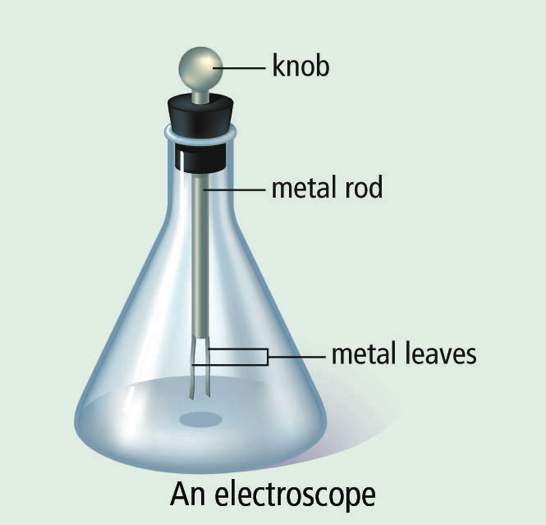
How does an electroscope work?
* An object with a suspected static electric charge is brought near the metal knob
* Electrical charged move to the metal and down to the foils
* Since each foil (a thin metal leaf) has the same charge (positive or negative), they repel each other and separate
* Electrical charged move to the metal and down to the foils
* Since each foil (a thin metal leaf) has the same charge (positive or negative), they repel each other and separate
17
New cards
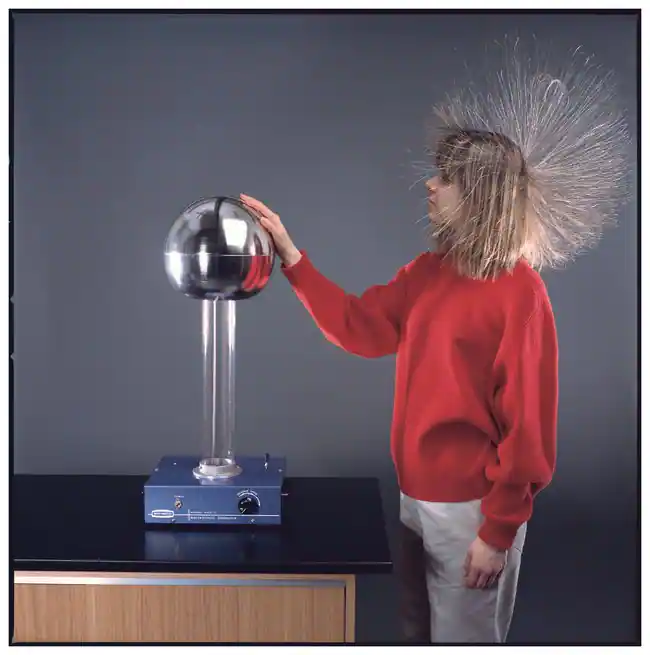
What is a Van de Graaff generator?
It is a machine that uses friction to produce a large static charge on a metal dome

18
New cards
What is lightning?
The result of a buildup of static charge in clouds due to friction created as hot air rises rapidly and ribs against ice crystals and dust particles in cloud banks
19
New cards
How do we use static electricity?
We use it for plastic wrap, to make it so the plastic wrap clings to whatever is is covering
We use it to decrease air pollution (devices in chimneys attract particles of dust and smoke)
Paint used to paint cars is given an electric charge, charged paint particles stick to the metal
We use it to decrease air pollution (devices in chimneys attract particles of dust and smoke)
Paint used to paint cars is given an electric charge, charged paint particles stick to the metal
20
New cards
What is grounding?
The process of the process of allowing charge to flow into the earths surface
A lightning rod is placed on top of a building, so if lightning comes near, the charge will pass through the rod into the ground, rather than through the building, which can be dangerous
A lightning rod is placed on top of a building, so if lightning comes near, the charge will pass through the rod into the ground, rather than through the building, which can be dangerous