Chapter 1: Introduction to System Analysis and Design
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Information Technology
refers to the combination of hardware, software and services that people use to manage, communicate, and share information
It is driving the rise of a new digital economy powered by advancements in hardware, software, and connectivity
How does Systems Analysis and Design influence Future Accounting Professionals?
Be active participants in system development
Evaluate and Improve systems
Ensure Data Accuracy and Reliability
Adapt to technology-driven accounting
SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN (SAD)
Step-by-step process for developing high-quality information systems
Information System
Combines technology, people, and data to provide support for business functions such as order processing, inventory control, human resources, accounting, and many more
System Analysts
Plan, develop, Maintain IS
Plan and process in maintaining - yung mga need sa maintenance “lead sa grupo”
System
Set of related components that produce specific results
Data (Unprocessed)
consists of basic facts that are the system’s raw material
Information (Processed)
is data that has been transformed into output that is valuable to users.
Mission-Critical System
one that is vital to company’s operation
Hardware
Tangible; consists of everything in physical layer of the information system
Software
Intangible; refers to the program that controls the hardware and produces the desired information or results.
System Softwares
supports system of the business process
Application Softwares
Enterprise applications
Horizontal system
Vertical system
Processes
define the tasks and business functions
People
those that interact with the information system
Business today is being shaped by three major trends:
Rapidly increasing globalization
Technology integration for seamless information access
rapid growth of cloud-based computing and software services
Internet based-system
involve various hardware and software designs, but a typical model is a series of webpages that provides a user interface which communicates with database management software and a web-based data server
B2C (Business to Consumer)
Consumers can go online to purchase an enormous variety of products and services. This new shopping environment allows customers to do research, compare prices and features, check availability, arrange delivery, and choose payment methods in a single convenient session.
B2B (Business-to-Business)
Although the business-to-consumer (B2C) sector is more familiar to retailer customers, the volume of business-to-business transactions is many times greater
Mga wholesale
Modeling Business Operations
Systems analysts use modeling to represent company operations and information needs. Business process modeling involves a business profile and a set of models that document business operations
Business profile
is an overview of a company’s mission, functions, organization, products, services, customers, suppliers, competitors, constraints, and future direction
Business Processes Model (BPM)
Graphically displays one or more business processes, such as handling an airline reservation, filling a product order, or updating a customer account
Office System
Administrative StaffO
Operational System
Operational People
Decision Support System
Middle Managers
Executive Information Systems
Top Manager
Enterprise computing systems
Refers to IS that support company-wider operations and data management requirements
The main objective is to integrate a company’s primary functions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and help managers make decisions
In many large companies, applications called enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems provide cost-effective support for users and managers throughout the company.
Transaction Processing Systems
Process data generated by day-to-day business operations
Examples of TP systems include customer order processing, accounts receivable, and warranty claim processing.
Business support system
Provide job-related information to users at all levels of a company
Management information systems
Radio frequency identification (RFID)
Knowledge Management system
Called expert system
Use a large database called a knowledge base that allows users to find information by entering keywords or questions in normal
English phrases
Uses inference rules, which are logical rules that identify data patterns and relationships.
Top Managers
Develop strategic plans
(long-term goals, company directions)
Middle Managers & Knowledge Workers
Oversee departments and analyze data for decision-making
Supervisors & Team Leaders
Monitor daily operations and ensure work is done efficiently
Operational Employees
Perform routine tasks in production, sales, accounting, etc.
User productivity systems
Technology that improves productivity such as email, voice mail, and web conferencing, word processing, automated calendars, database management, spreadsheets, desktop publishing, presentation graphics, company intranets, and integrated mobile computing systems
Prototype
first version (initial version of your software) when it meets basic requirements
feedback is usually obtained from prototypes
Systems Development Life Cycle
(SDLC)
Uses a set of process models to describe a system graphically
A process model shows the data that flows in and out of the system process. Inside each process, input data is transformed by business rules that generate the output.
Business rules are specific rules that each company has.
5 steps of SDLC model
systems planning
systems analysis
systems design
system implementation
systems support and security.
Objec-toriented analysis
This combines data & processes into objects. — Properties are inherited
Object is a member of a class
Objects process properties
Methods change on object’s properties
A message requests specific behavior or information from another object.
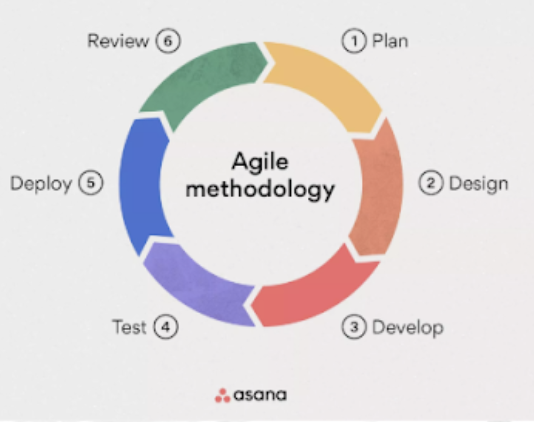
Agile Methods
Attempt to develop a system incrementally, by building a series of prototypes and constantly adjusting them to user requirements.
emphasizes continuous feedback, and each incremental step is affected by what was learned in the prior steps. Example: Scrum, Kanban, Extreme Programming (XP)
Joint Application Development & Rapid Application Development