Introduction to Psychotherapy
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Psychodynamic Therapy
The first therapy developed by Freund and later honed by Jung, Adler, and Klein
Freund conceptualized he could help change patterns of behavior by helping clients understand the unconscious reasons for their origin
Clinician is neutral and non-reactive
Emphasis on how past and present life events and relationships affect current feelings, relationships, and choices
Emphasis on unconsciousness
Id: impulsivity/pleasure seeking
Ego: realism, decision making, mediates between id and superego
Superego: moralizing, judgement,
Goal
Help clients find self awareness and understand the influence of the past on one’s behavior
Helps to recover repressed memories
Popular treatment for people with depression and trauma
Pillars
Free association
Given stimulus and client speaks/draws freely
Processing transference (projection of unconscious feelings onto others) projection (putting one’s own biases onto another person/group), resistance (resisting repressed unconscious feelings or drives to be brought into conscious analysis)
Dream analysis
Early childhood influences and family of origin
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Theorized by Dr. Albert Ellis rational emotional therapy
Founded on premise that thoughts control behaviors
Found that people with depression have a very negative thought pattern
Very structured and time limited
Recognize cognitive distortions or thinking traps
Clinician is neutral and non-reactive
Lots of worksheets
Pillars
Core belief: a person grows up in a home with a very negative attitude (always told that they are stupid) and the child grows up believing the negative comments that were made to them
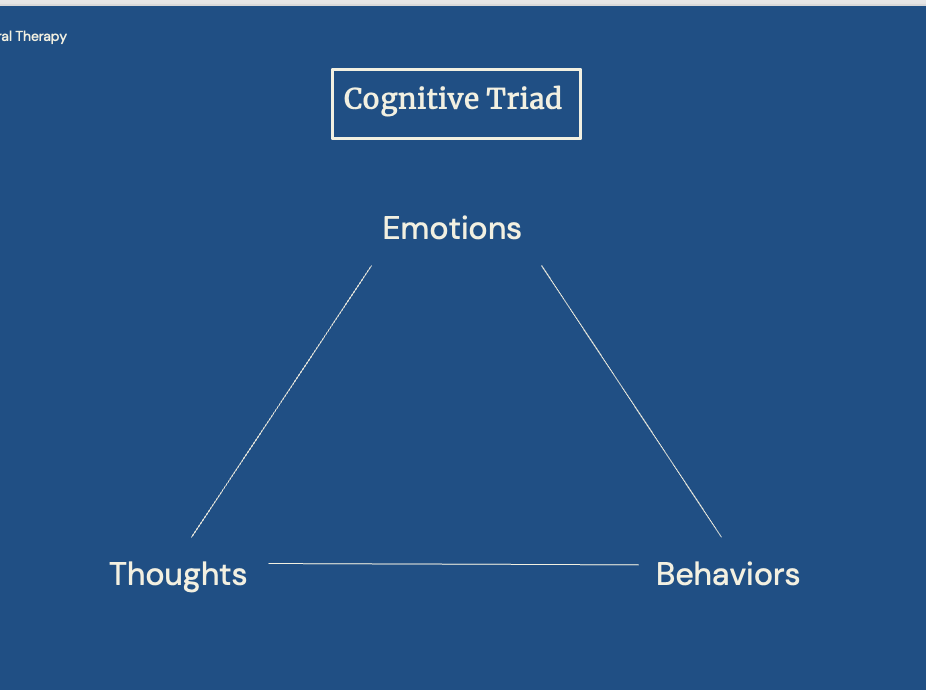
Cognitive triad
Cognitive distortions and restructuring (resetting your mind, challenging distortions, modifying your negative belief system through very concrete modeled coping skill bhevaiors)
Catastrophization
Should statements
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
Form of CBT that aims to give people skills to regulate emotions, improve relationships, handle stress, and live mindfully
First used to treat people with borderline personality disorder
Primary principle
Teach that experiences are real but radical acceptance, coping skills, and mindfulness can help handle negative feelings, interpersonal conflict, and impulsive tendencies
Hallmark of people who benefit from DBT is people with big feelings, or people who use maladaptive coping like substance use, etc…
Clients can’t fail
Pillars
Mindfulness: being aware of the moment
Distress tolerance
Emotional regulation: getting through a negative feeling in a healthy way
Interpersonal effectiveness: getting needs met in a relationship appropriately
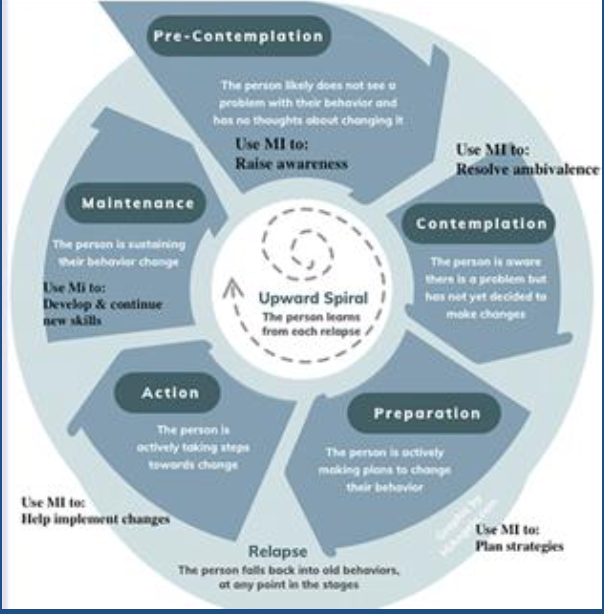
Motivational Interviewing
Developed by Dr. William Miller and Dr. Stephen Rollnick
Developed to manage ambivalence in clients (substance use and smoking cessation): utilized to encourage clients to connect to the part of themselves that wants to change by giving them the opportunity to express themselves in a non-judgemental setting
Teaches the clinical to use open ended questions and validation
Important factors
Eliciting change talk from the client
Pillars are achieving a therapeutic alliance
Examples of open ended questions
What are the positives about your drinking? What are the negatives?
What have other people told you about your substance use?
Interpersonal Therapy
Developed by Dr. Gerald Klerman and Dr. Myrna Weissman to treat depression
Short term 12-16 weeks
Focuses on relieving symptoms by improving interpersonal functioning
Addresses current problems and relationships versus childhood or developmental issues
Therapist is active and not neutral
Goal: improve quality of client’s interpersonal relationships and social functioning to help reduce overall distress
Explores current relationships
Addresses maladaptive thoughts and behaviors only as they apply to interpersonal relationships
Aims to change relationship patterns and difficulties rather then target depressive symptoms
Overall less direction than CBT
Process
Evaluation
Identification of problem
Exploration of patterns
Development of coping skills
Termination and follow up
Supportive Psychotherapy
Developed after psychoanalysis
Typically used when other forms of therapy are not suitable
Integrative approach, can use a variety of schools of thought
Includes empathy, reassurance, psychoeducation, and support (combination of all other methods)
Therapist is active and not neutral
Community Resources: Enhanced care clinics
Most of them have walk appointments for initial intake
Can go with any insurance or no insurance
Cons
Long wait time to meet a therapist
Must show commitment before med management
Community Resources: PsychologyToday.com
Good option for patients with insurance
Online phonebook for psychiatric professionals
Can be filtered based on city, specialty, insurance
Community Resources: Mobile crisis (211)
Can call in a crisis
Can send someone over for a check if needed
Community Resources: CCAR
Connecticut Community for Addiction Recovery
Can aid in referrals and finding treatment for alcohol or substance abuse
Community Resources: ACT (assertive community treatment)
Multidisciplinary team
Allows chronically ill people to live in the community
Come to the client
Community Resources: Suicidal Hotline (988)
24/7 can call for suicide crisis
Can also test
Principles of Treatment
Patient-provider relationship
Shared decision making
Maintain attention to the biopsychosocial picture/causation
Is this is a psychological or more biological problem
Most purely psychological issues not responsive to medications
Most are going to be more than one intervention (combination of therapy and/or medications)
Ultimate goal: control, provide level of function, remission, strategies to mitigate
Psychopharmacotherapy: the drugs
Most psychotropic medications are lipophilic
Rapid absorption
Cross BBB
Avoids first pass metabolism in the liver
Act on neurotransmitters or their binding site
Quick action but for some longer onset of therapeutic benefits
Side effects
Toxicity
Side effects
Many require ongoing monitoring
Many have specific side effect profiled based on the neurotransmitter affected
Can’t abruptly use → discontinuation syndrome
Lithium and GABA not metabolized by the liver: rest have to go through the liver to have effects on the body (need functioning liver to have an effect)
Psychopharmacotherapy Considerations
Risk to benefit ratio
Many side effects
Drug-drug interactions
Coexisting conditions (chronic health conditions)
Dealing with side effects
Open discussion with patients prior to starting
Patient priorities, which may change
Medical conditions that can be caused by meds
Need for monitoring and other evaluations (EKGs, medication and other chemistries)
Use of drugs or alcohol while in medications
Life ambitions/events
Pregnancy: effects on fetal development, mother’s ability to get pregnant, risk for preterm labor
Serotonin
Too little: anxiety, depression, constipation
Too much:
N/V (have receptors in the gut)
Diarrhea
Decrease sex drive
Serotonin syndrome (life threatening)
GI
Dopamine
Action
Mesolimbic tract (ventral trigeminal area): addiction/reward pathway
Mesocorticol tract (prefrontal cortex): mania, psychosis, cognitive, motivation
Nigostratial path: Parkinson’s
Anything with muscular: think dopamine
Too little:
Parkinsonism (symptom that makes it look like PD)
Disinhibition of prolactin secretion
Decreased sex drive
Too much
Psychosis
Tics
Skin picking
Aggression
Anxiety
Hyperkinesia
NE
Action
Neurotransmitter of the sympathetic fight or flight response
Increase sympathetic and decrease parasympathetic
Too much:
Weakfulness
Anxiety
Hyperfocus
Defense mechanisms
Increased cognition
Too little:
Orthostasis
Sedation
Bradycardia
Depression
Lack of motivation
Increased parasympathetic
GABA
Actions
Inhibitory neurotransmitter part of the down regulation pathway, reducing neuronal activity
Too much:
Increased sedation/lethargy
Weakfulness
Confusion
Blurry vision
Ataxia
Too little (think about what too much alcohol would do):
Seizure
Death
Anxiety
Increased or hyper-neuronal transmissions
Formication
Psychosis
HAs
Nausea
Tremors
Hemodynamic instability
Acetylcholine
Actions
Muscle contraction
Memory processing
Autonomic nervous system
Wakefulness
Too little:
Dry mouth
Constipation
Urinary retention
Cognitive impairment
Delirium
Muscle weakness
Too much
Increased salivation
Lacrimation
Increased activity
Constricted pupils
Perspiration
Muscle tremors
Diarrhea
Emesis
SLUDGE
Histamine
Actions
Immune cascade
Promotes wakefulness and cognition
Found in brain and the gut
Too little
Sedation
Weight gain
Decreased cognition
Has downstream effect on acetylcholine: anti-histamine eventually has downstream effect as an anti-cholinergic
Similar to anti-cholinergic effects
Antidepressants
Subclasses
SSRIs
SNRIs
Tricyclic antidepressant: hit dopamine, serotonin, and NE receptors
MAO-I
Atypicals
Bupropion (Wellbutrin)
Mirtazapine
Trazodone
Nefazodone
Vortioxetine (Trentelllix)
Works on serotonin receptors
Pros: has minimal weight gain and less side effects
Anxiety disorder first line → SSRI
Most require annual EKG (QT prolongation), as well as renal and/or liver functional tests
Some have slower onset: 6-8 weeks before major improvements
Cannot be abruptly stopped nor have others added on to
SSRIs and SNRIs worry the most about
Atypicals do not have to worry about as much: so broad that the withdrawal syndrome does not feel as bad as something that is very specific like to serotonin
Most side effects in first 1-2 weeks: can try to mitigate
Watch for drug-drug interactions
Antipsychotics/Neuroleptics
First generation: dopamine antagonists
Lot of EPS
Some hyperprolactinemia
Second generation: dopamine serotonin antagonists
Generally lower risk of movement disorders
More metabolic syndrome symptoms coming from dual action between dopamine and serotonin
Indications
Schizophrenia
Acute mania
Major depressive disorder
Delusional disorder
Severe agitation/Tourette’s syndrome
Borderline personality disorder (treating symptoms)
Dementia and delirium (not FDA approved: medications used more for symptoms coming from something else)
Psychosis from substance use disorder (treating symptoms)
Monitoring: therapeutic ranges
Monitor Clozaril (Clozapine) serum levels
EPS Side effects
Pseudoparkinsonism
Stooped posture
Shuffling gait
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Tremors at rest
Acute dystonia
Facial grimacing
Involuntary upward eye movement
Muscle spasms of the tongue, face, neck, and back
Laryngeal spasms
Life threatening
Akathisia
Restless
Trouble standing still
Paces the floor
Feet in constant motion
Tardive Dyskinesia: classic EPS example
Protrusion and rolling of the tongue
Sucking and smacking movements of the lips
Chewing motion
Mood stabilizers
Medications to treat bipolar disorder
Most are anti-seizure medications
Mechanism of action
Inhibit inositol uptake process resulting in its depletion → lithium
GABA inhibition → divalporex (Valproic acid)
cAMP and GABA inhibition → Carbamazepine
Reducing the frequency of excitatory postsynaptic currents, increase glutamate, and enhance GABA release → Lamotrigine
Monitoring
Thyroid
Calcium
Renal functions
LFTs
Urine
EKG
Depakote: metabolized in the liver: need serum level to see therapeutic range but the window is very broad
Lithium:
Not metabolized and straight up excreted from the kidneys: if there is insufficient renal function, lithium just continues to build up and deposit in the brain, thyroid, bone and kidneys
Has a very narrow therapeutic window of serum concentration
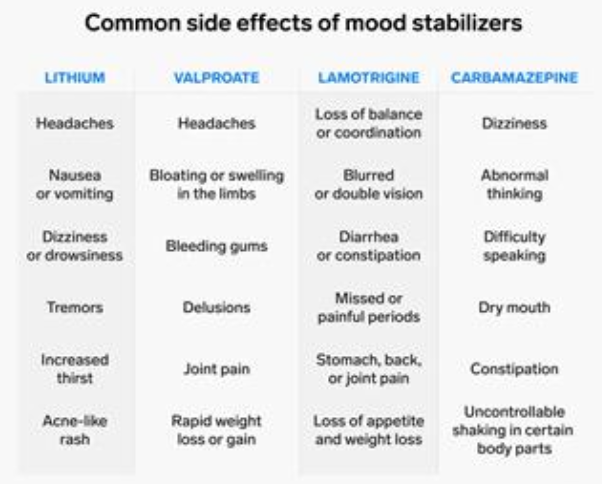
Common side effects
Lithium → tremors and increase in thirst
Lamotrigine: SJS
Anxiolytics
Work by inhibiting the sympathetic hormones released by the amygdala and enhancing GABA
Medications
Benzodiazepines
Z-drugs
Anticonvulsants (Neurontin) and Pregabalin (Lyrica)
Propranolol
Buspirone (Buspar)
Hydroxyzine (Atarax)
Treat people with panic disorder, generalized anxiety, sleep disorders
Common side effects
Cognitive disorder: very common (mostly with benzodiazepines)
Memory impairment
Weight gain
Excessive drowsiness
Increased appetite
Abnormal coordination
Instability
Hyperhidrosis
Nasal congestion
Decreased libido
Withdrawal can have seizures and death