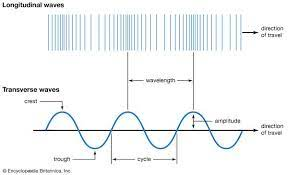
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
Waves transfer energy in the direction they are travelling
When waves travel through a medium, the particles of the medium oscillate and transfer energy between each other. BUT overall, the particles stay in the same place-only energy is transferred
For example, if you drop a twig into a calm pool of water, ripples form on the water’s surface. The ripples don’t carry the water away with them
- The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of a point on the wave from kits undistrubed position
- The wavelength is the distance between the same point on two adjacent waves
- Frequency is the number if complete waves passing a certain point per second. Frequency is measured in hertz. 1Hz is 1 wave per second
- From the frequency, you can find the period of a wave using: T=1/f
- All waves are either transverse or longitudinal
Transverse waves are sideways vibration
In transverse waves, the oscillation ate perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer. Most waves are transverse including:
- All electromagnetic waves, e.g. light
- Ripples and waves in water
- A wave on a string

Longitudinal waves have parallel vibrations
In longitudinal waves, the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Examples are:
Sound waves in air, e.g. ultrasound
Shock waves, e.g. some seismic waves
Wave speed = frequency x wavelength
The wave speed is the speed at which energy is being transferred. The wave equation applies to all waves:
v=fa, wave speed = frequency x wavelength