Module 2A - Units 1-3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Define elastography.
Quantifying and imaging the elastic properties of tissue and masses using U/S.
Elastography measures changes in the ______ of the tissue based on its ______ when a ______ is applied.
Strain, stiffness, stress.
List some tissue characterizations obtained from B-mode imaging.
Echotexture
Echogenicity
Size
Shape
List some tissue characteristics obtained from Doppler modalities.
Presence and direction of blood
Type of flow
Velocity
Name and describe the two techniques for applying stress to tissue for elastography.
Axial strain - hand compression on tissue
Shear wave - transverse waves applied to tissue
Elastography shows soft tissue displaces ______ when compression is applied, whereas stiff tissue displaces _____.
more, less
In elastography, RF data is used to…
Compare information from the same depth/location both pre and post compression.
Define strain.
Rate of displacement.
Why would a clinician prefer shear wave elastography over axial strain?
Shear wave gives a quantifiable value of stiffness.
Provide an example of when elastography would be used in cardiac sonography.
Speckle tracking (stain imaging) is used in GLS to assess myocardial mechanics.
EFOV is also called…
Panoramic imaging.
List some advantages to EFOV.
Directly visualize and image spatial relationships within the body
Accurately measure large structures and/or pathologies
Interpret images easily
What is the first model with EFOV technology?
Static B-scan.
Describe how current EFOV technology uses a transducer with a small FOV to create a large image.
Translation of the transducer along the same axis. The machine stitches the images together.
List and Describe the two techniques for EFOV.
EFOV generated in real time
Acquired frames in memory (Cineloop) are processed, then displayed as a panoramic image
Which EFOV technique is preferred by sonographers? Why?
Real time EFOV because there is less risk of error.
List 2 techniques for extending FOV.
Vector scan
EFOV (panoramic imaging)
Explain the two concepts used by the computer processing to accurately stitch the images together in EFOV.
Image registration - sequential order the frame is acquired
Feature matching - identification of common features in sequential frames that allow for overlap
List some limitations to EFOV.
Tissue motion (patient)
Off plane transducer rotation (sonographer)
List some limitations to imaging blood with Doppler.
Angle dependent
Long SPL → poor axial resolution
Booming and bleeding artifact
Aliasing
Decreased temporal resolution
Name 2 technologies for imaging blood.
Doppler modalities
B-flow imaging
List some advantages of B-flow imaging.
No aliasing
No blooming
Angle independent
Flow direction indicated
Tissue and B-flow displayed simultaneously
High axial and temporal resolution
Explain the physics concepts behind B-flow.
Extended BW resolution and high frame rate detects the Rayleigh scatter and displays the position and amplitude.
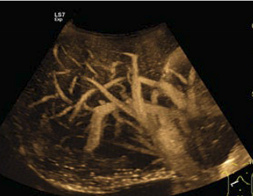
What modality is used in this image?
B-flow
List some clinical applications of B-flow imaging.
Blood vessel wall or plaque irregularities
Residual lumen from a stenosis measurement
Thyroid nodule activity assessment
Kidney perfusion
Vascular disease after transfemoral catheterization
Liver and spleen vasculature
Neonatal head vessels
Explain the computing process behind B-flow imaging.
Coded excitation - each pulse has a long PD and is composed of a code of mini pulses. The pattern of mini pulses is decrypted during processing to create the image.
Name the two factors the binary code is based on in B-flow imaging.
Timing of all the mini pulses
Amplitude of each mini pulse
Define deconvolution (also known as matched filtering).
Decoding binary code through mathematical analysis.
List some advantages to B-flow encoding the pulses.
↑PD → ↑signal intensity → ↑SNR → enhance visualization of weak reflectors
Post-professing filtering can suppress tissue echoes and enhance Rayleigh scatter → blood appears brighter than tissue