Ch. 2 Microscopy
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio 3340
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Microorganism
organism not visible to naked eye
Electron microscope
It was possible to view viruses only after the invention of the electron microscope because they are too small to be seen with a light microscope
Light
refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another
Refractive index
bends the path of light and slows the velocity of light. Air < Glass
Focal point (F)
Focus light rays at a specific place
Focal length (f)
Distance between center of lens and focal point is the f.
Confocal Microscope
creates sharp composite 3D image of specimens by using laser beam
Staining of specimens
Staining allows for better visibility of specimen
Increases visibility of specimen
Accentuates specific morphological features
Preserves specimens
Fixation
Preserves internal and external structures and fixes them in position, Organisms usually killed and firmly attached to microscope slide
Heat fixation
routinely used with bacteria and archaea
Preserves overall morphology but not internal structures
Chemical fixation
often used for eukaryotes, but also bacteria and archaea, particularly with the use of electron microscopy
techniques
Protects fine cellular substructure and morphology
Dyes
Make internal and external structures of cell more visible by
increasing contrast with background
Basic dyes
ex: Methylene blue, basic fuchsin, crystal violet, safranin, malachite green
Have positively charged groups;
bind to negatively charged
molecules such as nucleic acids,
many proteins, and the surfaces
of bacterial and archaeal cells
Simple staining
•Ionizable dyes have charged
groups
•Basic dyes have positive charges
•Acid dyes have negative charges
•Simple stains
•A single stain is used
•Use can determine size, shape, and
arrangement of bacteria
Differential staining
• Divides microorganisms
into groups based staining
properties
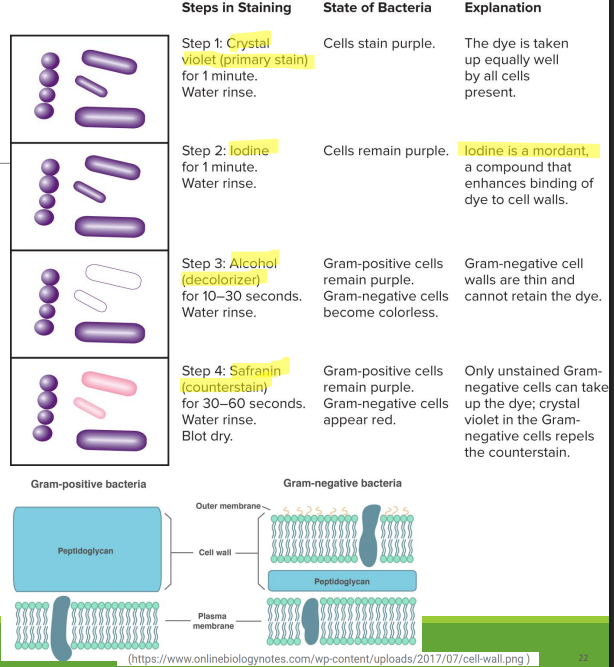
• Gram stain
• Acid-fast stain
• Detect presence or absence
of structures
• Capsules
• Flagella
Gram staining
•Most widely used •Divides bacteria into two groups
• Gram-positive (purple)
• Gram-negative (pink)
• Based on differences in cell wall structure (peptidoglycan)
Electron microscopy
Electrons replace light as ‘illuminating’ beam
• Wavelength of electron beam much shorter than light resulting in higher resolution
• Allows for study of microbial morphology and intracellular structures in great detail
• Analogous to procedures used for light microscopy
• For transmission electron microscopy, specimens must be cut very thin
• Specimens are chemically fixed and stained with electron dense materials, such as heavy metals, that differentially scatter electron
Transmission Electron Microscope
Electrons scatter when they pass through thin sections of a specimen
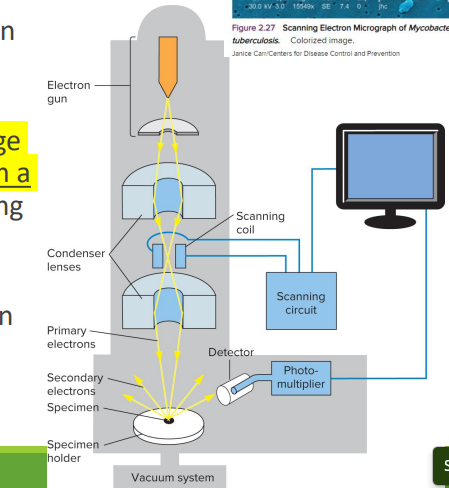
Scanning Electron Microscope
•Scans a narrow electron beam back and forth over the specimen
•Produces a realistic 3-D image from electrons released from a specimen’s surface, visualizing the features in great detail