neuroscience of personality
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Eyesenck’s PEN model
theory of extraversion
introverts had greater cortical arousal than extroverts
RAS(reticular activation system) transmits signals from limbic system and hypothalamus to cortex
introverts higher in baseline arousal, act more restrained and inhibited
extroverts low in baseline arousal, seek more stimulating and unrestrained behaviors
brain scans show no difference between groups at rest
Extraversion
differences between arousability and sensory reactivity
study of I/E groups learning rules of word pairs while listening to white noise
control group: white noise matched to group and could be personally adjusted in volume
no control matched: could not adjust volume but matched to group type
no control unmatched: could not adjust volume and was matched to opposite group type
results: arousal
I/E showed similar measures of arousal in matched condition and choiced condition
opposite condition showed greater arousal for introverts and lower arousal for extroverts
results: performance
choice and match conditions performed similarly
opposite condition requried more learning trials
worse for introverts than extroverts
Neuroticism
Eysenck thought stability of sympathetic nervous system was responsible for neuroticism
sends warning signals for things most people deem unimportant
high neuroticism linked to increased heart rate to intense stimuli and increased startle reflex
high sensitivity to negative emotions
sympathetic responses widely vary however…
Reinforcement sensitivity theory (RST)
3 overarching systems that interact with personality and biology, which play into how we interact with our environment
Fight-Flight-Freeze system (FFS):
emotion of fear, gets us to respond to aversive stimuli
Behavioral Approach System (BAS):
responses to “appetitive stimulus” or things that are rewarding
makes a person more sensitive to reward
Behavioral Inhibition System (BIS):
helps resolve conflicts within one of the other systems
may cause anxiety, worry, vigilance
may clinically lead to OCD or GAD
RST
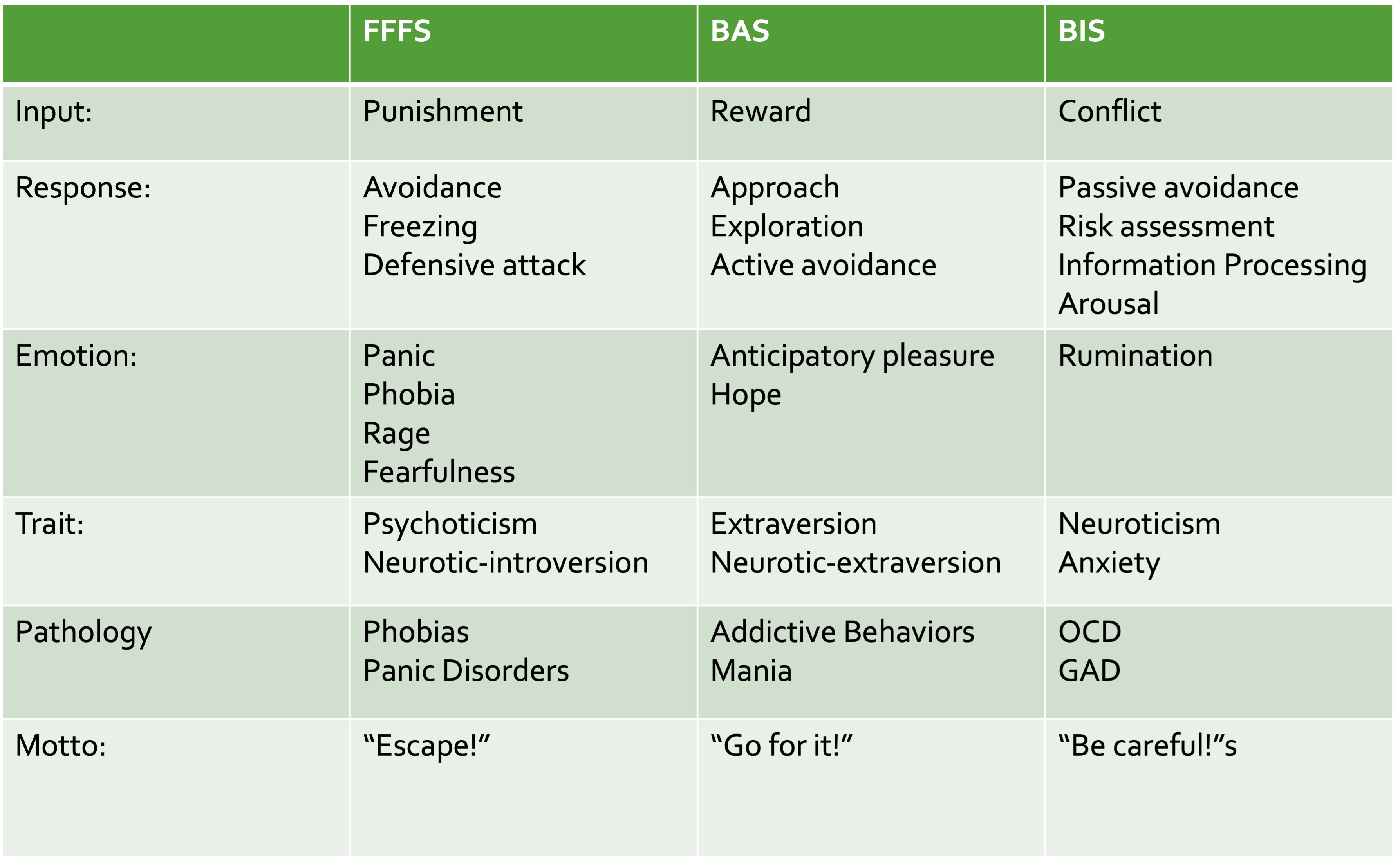
RST the research
support for theory
brain areas related to reward: ventral striatum, amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex, ventral pallidum, midbrain
BAS scored high in the difference between appealing foods and gross foods
strongest reaction when looking at areas related to food regulation
people learn through:
Strong BAS = reward sensitive learning
learn more quickly by going for it
Strong BIS = punishment sentitive learning
trying to avoid punishment
uneven spread in award/conflict/punishment sensitivity
Neurological correlates
two main areas in relation to extroversion and neuroticism: frontal/prefrontal cortex and amygdala
cortex:
greater right cortex cortical thickness in introverts than extroverts(less inhibition)
extroverts may have more efficient processing in that case
neuroticism negatively correlated with left cortex
higher meant less grey matter compared to low neuroticism
stronger in males than females
amygdala:
extroverts have higher gray matter in left amygdala compared to introverts
higher neuroticism had lower concentration of gray matter in right amygdala than low neuroticim
fear and negative-base emotions cause more activation in this area
Left-right asymmetry
Right and left hemisphere are specialized
left = linguistic processes for most people
right = spatial processes for most people
cortex responds to emotions differently
right frontal and prefrontal cortex is more active than left during negative emotions
people differ in how large the relative differences are
right asymmetry = shy, inhibited children and depressed adults
extroverts = more positive emotions at rest and in response
meditation = greater left brain symmetry at rest and response
Neuroscience is…?
The study of both structure and function of the nervous system and brain.
How do we study it?
we have:
neurons
nerves (pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, etc.)
glands
hormones
physiological responses
psychological responses
study via:
brain activity
brain structure
biochemical reactions
body reactions
Body reactions
typically measuring the downstream effects of a biological x physiological interaction
e.g. fear, anger, reactivity, serenity, etc.
measurments:
heart rate
GSR galvanic skin response
measures how quickly a slight electrical current passes through two points on the skin
EMG electromyography
estimates electrical impulses of muscles during contraction and relaxation
Brain structure
looking at structural features of the brain
size of certain areas
computerized tomography
x-ray for brain
detects abnormalities through brain “slices”
Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI
strong magnetic field and radio frequency used to measure electromagnetic energy given off by hydrogen atoms
Electroencephalography EEG
electrodes placed on scalp, monitor electrical activity in the brain
Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI
monitors brain activity over time
measures blood oxygen levels, more oxygen used up = greater color difference
idea on a specific area of the brain being used during certain activities
Positron Emission Tomography PET
radioactive glucose is injected and person placed in CT scanner
amount of metabolism is changed to different colors, showing where work is getting done