Particle Model of Matter Key Definitions and Model Answers
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Internal Energy
The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all the particles in a system
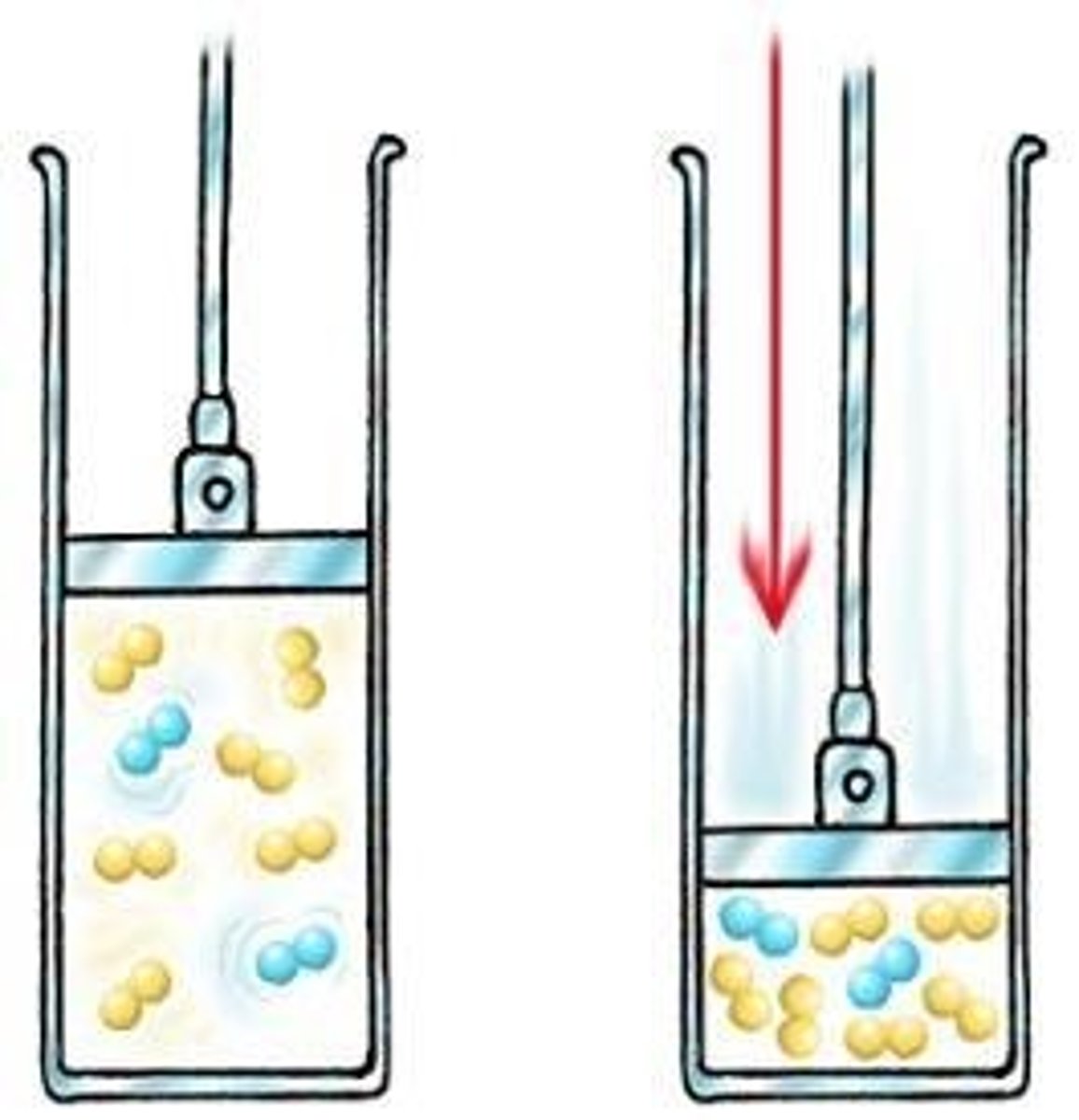
Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation
The energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance from liquid to gas at a constant temperature.
It is released during condensation and taken in during boiling

Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
The energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance from solid to liquid at a constant temperature.
It is released during freezing and taken in when melting
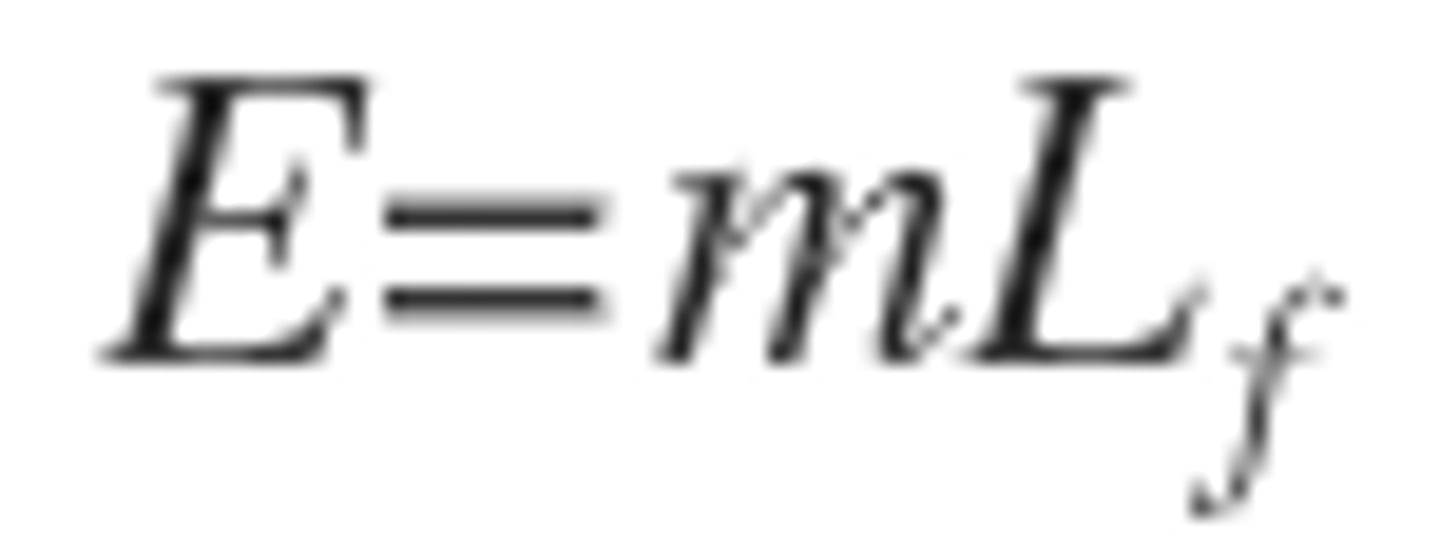
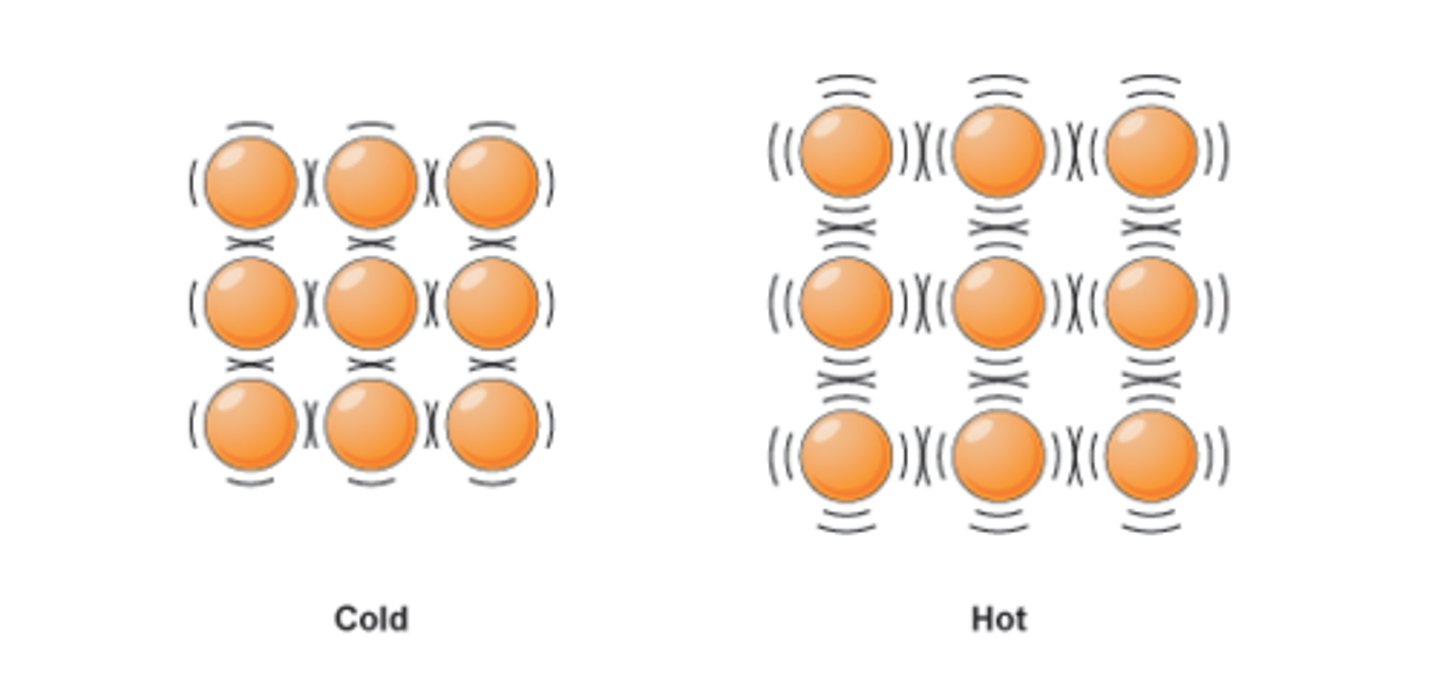
Specific Heat Capacity
The energy required to increase the temperature 1kg of a substance by 1oC

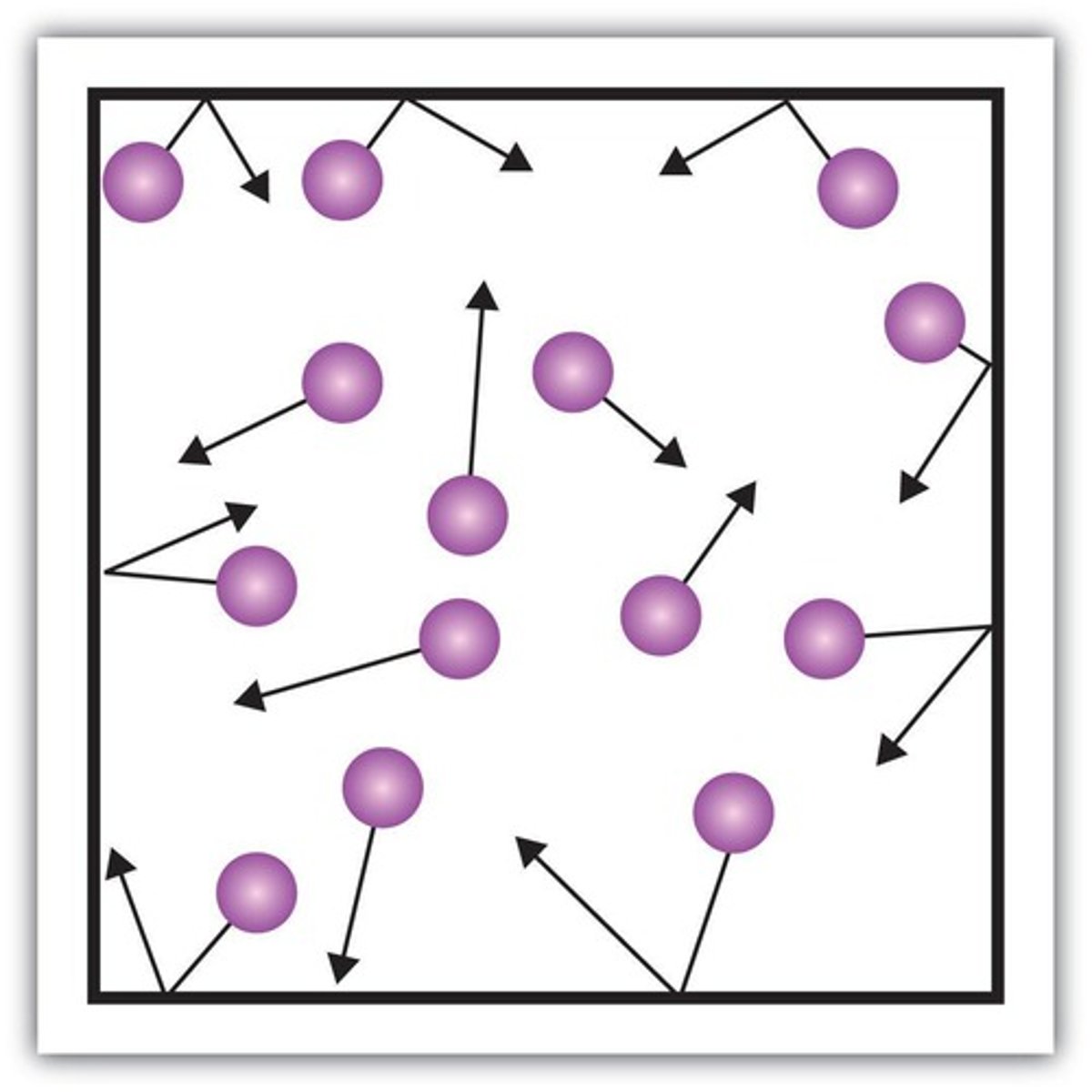
Model Answer: Pressure in a Gas
Gas particles collide with the walls of the container
Pressure in a gas Each collision exerts a force
The force is at right angles to the surface
The pressure is the total force applied over the area of the container in a given time
P=F/A
Model Answer: Pressure in a gas, increasing the temperature
Increasing the temperature increases the speed of gas molecules
There are more frequent collisions with the walls of the container
Each collision exerts a larger force
The total force across the area of the container in a given time increases
So the pressure increases
Model Answer: Pressure in a gas, decreasing the volume TEMPERATURE CONSTANT
There are more frequent collisions with the walls of the container
The total force across the area of the container in a given time increases
So the pressure increases
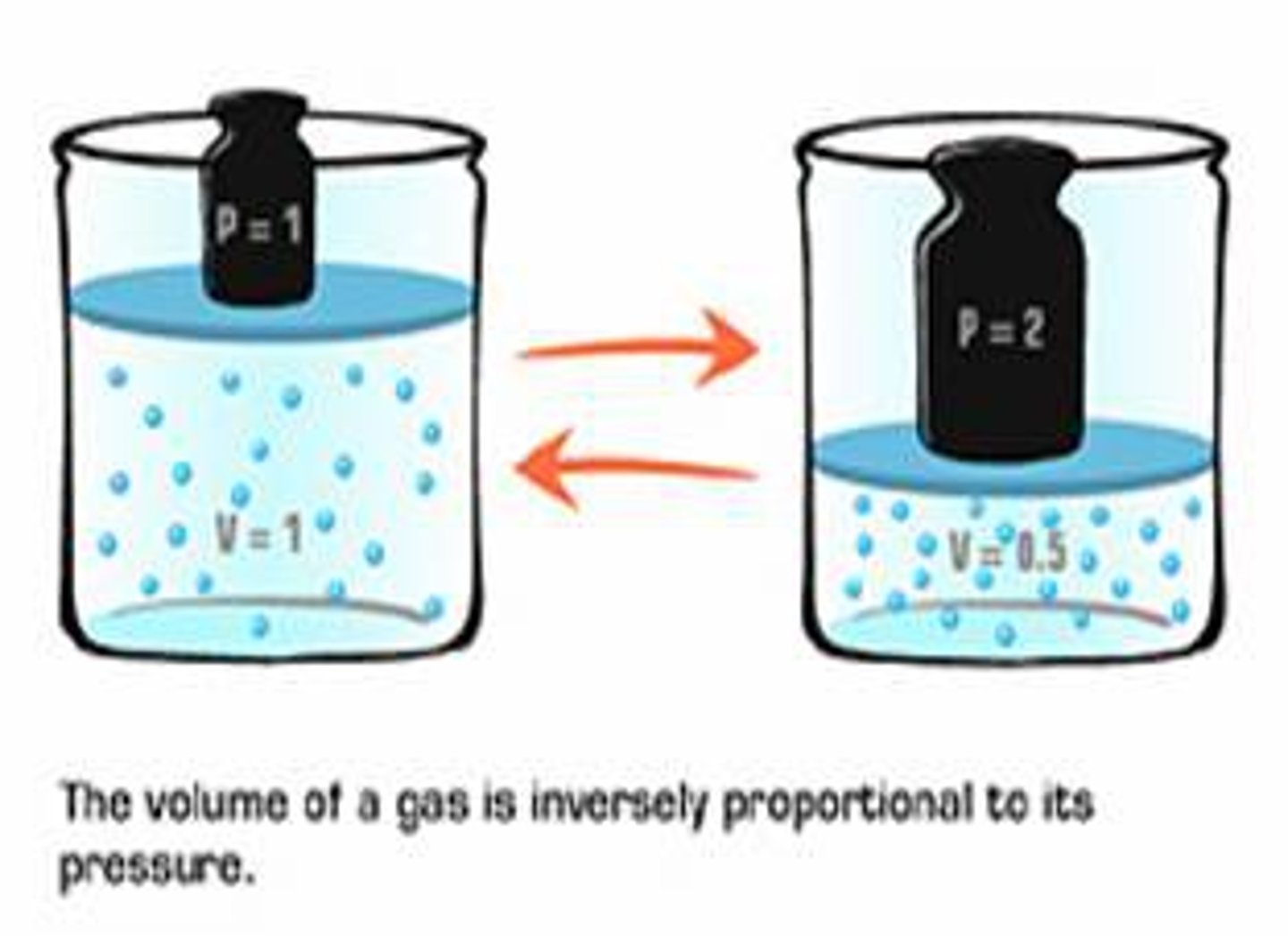
Boyle's Law
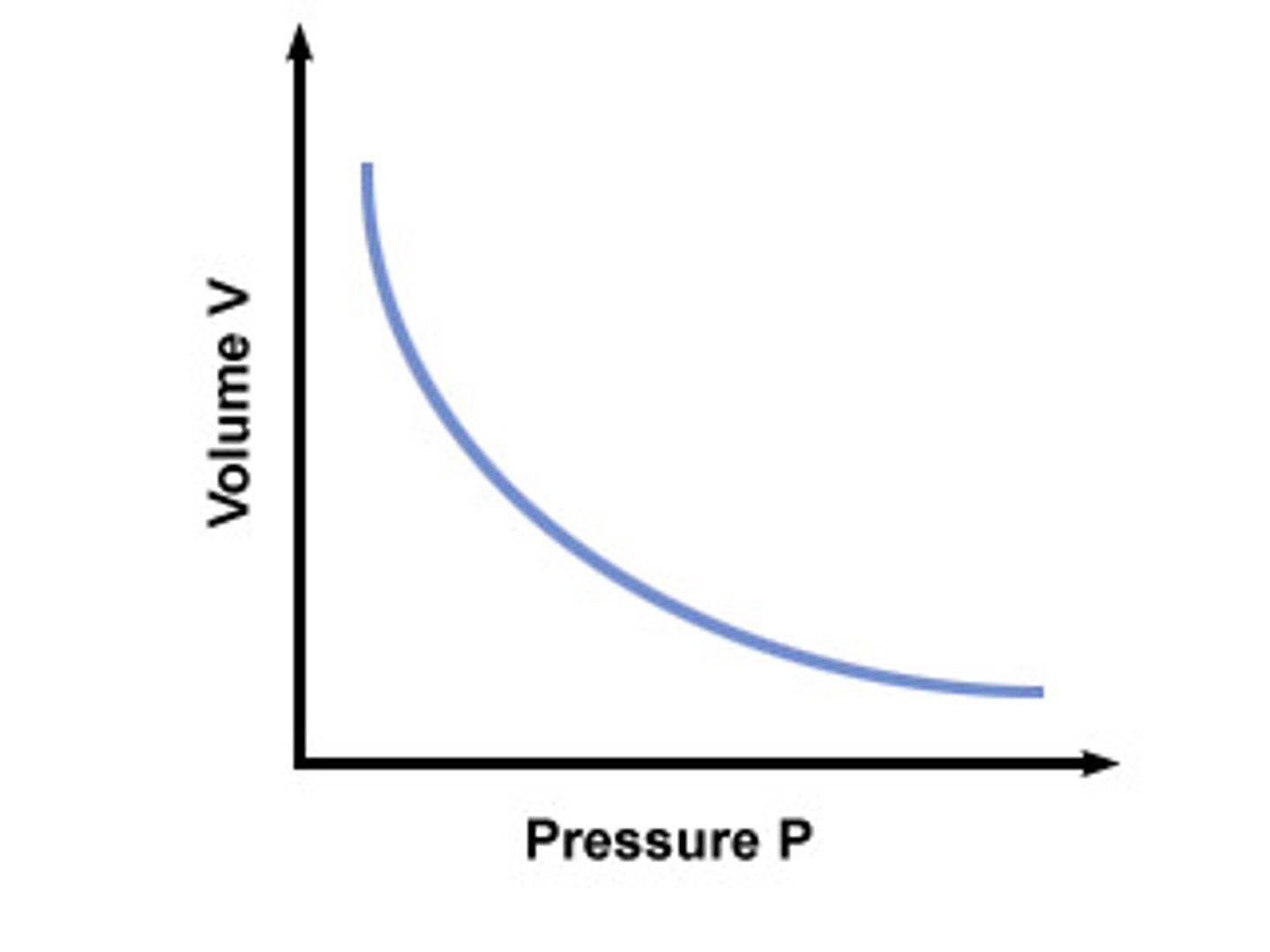
Pressure and volume in a gas are inversely proportional at a constant temperature
Model Answer: Work done on a gas TEMPERATURE CHANGES
Work is done on the gas when decreasing its volume.
This increases the internal energy of a gas
And so the temperature increases.
(the opposite is true if the volume increases)