Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
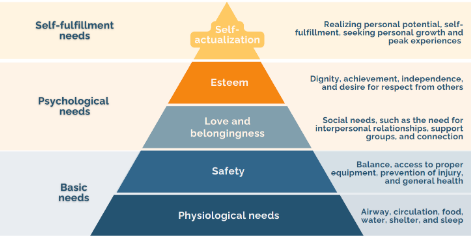
Maslow’s Hierarchy
Needs theory of motivation — dictates an individual’s behaviour (prioritize patient care)
Physiological Needs
Safety
Love and Belongingness
Esteem
Self- Actualization
Physiological Needs
Airway
Circulation
Food/Water
Shelter
Sleep
PT Management - Acute
Airway: Secretion Clearance, Difficulty Breathing
Circulation: Loss of Limb
Infection:
Non Acute:
Sleep: Chronic Tendoniitis (Recovery)
Food/Water/Shelter
Safety
Balance
Proper Equipment
Prevention of Injury
General Health
PT Management:
Balance/Fall Risk Assessment and Interventions — mobility impairments
Rehab after traumatic injuries — Fractures : restore physical function and prevent future injuries
Education/Training: Proper body mechanics and Ergonomics — workplace injuries or exacerbation of existing conditions
Love/Belongingess
Social Needs - Interpersonal Relationships. Support Groups and Connection
Friendship. Intimacy, Family, Sense of Connection
PT Management:
Group Therapy Sessions
Community Based Programs - Chronic Conditions
Family Education and Involvement in Rehab — recovery and wellbeing
Esteem
Dignity. Achievement, Independence — desire for respect from others (status, prestige)
PT Management:
Amputations/Disfigurement — body image and self confidence
Exercise Programmes and Goal Setting — physical strength, endurance and functional independence
Vocational rehab and Return to Work — injuries and disabilities, sense of achievement and self worth
Self- Actualization
Personal Potential
Self Fulfillment
Seeking Personal Growth
Peak Experiences
PT Management - Self Actualization
Maximizing Functional Abilities + Independence
Enable to pursue interests and passions
Adaptive equipment and Assistive technologies
Counselling and support
A physiotherapist is providing treatment fora patient following a motor vehicle collision that resulted in a fractured right distal tibia and fibula, as well as fractured left ribs 5-7, and post-concussive symptoms. The patient has been instructed topartiallyweight-bear on the affected leg. They are having a hard timelearning to use their crutches, as the right crutch hand bar is broken. The patient informsthe physiotherapist that they are unable to pay their rent and can’t afford to get new crutches. They are new to the area and coupled with their absence from work, they are feeling very isolated and lonely. Which of the following actions would be the greatest priority for the physiotherapist?
A.Educate the patient about pain management techniques
.B.Encourage the patient to reach out to their case manager and ask for information on financial assistance.
C.Teach the patient breathing exercises to help manage their frustrations.
D.Provide the patient with community resources that will provide replacement crutches at no cost.
Provide the patient with community resources that will provide replacement crutches at no cost
Patient’s psychological needs are met, but safety is not. The physiotherapist should prioritize the patient’s safety and find replacement crutches to ensure the patient can ambulate safely and avoid further injury
A 65-year-old patient underwent a total hip replacement yesterday. The physiotherapist arrives to mobilize the patient for the first-time post operatively. The patient has an intravenous line and catheter in situ and is on 2 litres of oxygen via nasal cannulas. Upon assessment, the physiotherapist notes that the patient appears to be in pain and their SpO2 level isat 91%. The patient has significant dyspnea. Which of the following should the physiotherapist prioritize during their physiotherapy assessment?
A.Assess the patient’s mobility.
B.Perform homan’s.
C.Auscultate the patient’s lungs.
D.Ask the patient about their pain level using the numerical pain rating scale (NPRS
Auscultate the patient’s lungs.
While all the options listed can be included in the assessment of this patient, the physiotherapist should prioritize the patient’s respiratory status. The information provided in the vignette indicates a lower-than-normal SpO2 level (normal is 95-100%) aswell as significant dyspnea. The patient’s physiological need of oxygen must be prioritized above all else. The physiotherapist should prioritize the assessment of the patient’s respiratory status and determine a plan of action to improve oxygenation and decrease dyspnea.
A 45-year-old male patient underwent a below the knee amputation 2.5 months ago and has been receiving regular physiotherapy. The patient’s lower leg was injured while at work when a wood structure collapsed onto his leg. The patient has a prosthesis and is learning how to ambulate with it. He can ambulate with the prosthesis and does not require any additional gait aids. The patient has two young children and a supportive spouse. He regularly expresses gratitude for having a strong social network, but he feels inadequate as he cannot fulfill the same fatherly role as he did before his injury. The patient currently cannot walk and carry his children or work to support his family financially. Which of the following should the physiotherapist prioritize to include in the patient’s treatment program?
Which of the following should the physiotherapist prioritize to include in the patient’s treatment program?
A.Recommend joining a community-based program for amputees to foster social support.
B.Create patient-centered goals to help align physiotherapy treatment with the patient’s goals.
C.Prescribe balance exercises to enhance stability while ambulating with the prosthesis.
D.Discuss adaptive equipment that can help the patient return to work quicker and maximize independence.
Create patient-centered goals to help align physiotherapy treatment with the patient’s goals: . The patient is struggling with his own self-esteem. He feels he cannot fulfill his role as a father due to his injury. Creating patient-centered goals will help the patient direct his attention and focus toward achieving those goals and improve his self-confidence. By creating patient-centered goals, the physiotherapist can ensure the physiotherapy program addresses the body function/structure impairments, the activity limitations and participation restrictions that matter most to this patient