RPI ASTRO 2050 EXAM 1
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
people not included
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Spring Tide
Occurs when the tidal bulges produced by the Sun and Moon are alligned
Neap Tide
Occurs when the tidal bulges are at right angles
Synodic Period
the time it takes a planet to return to the same position in the sky, relative to the Sun, as seen from the Earth
Conjunction
the planet is in the same direction as the Sun (as seen from Earth)
Opposition
the planet is in the opposite direction from the Sun, as seen from Earth
Inferior Planet
the distance from the Sun is smaller than the Earth-Sun distance
Aphelion
the point in a celestial body’s orbit where it is farthest from the sun
4 Terrestrial Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
4 Jovian Planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
more massive & larger radii, lower density
faster rotation periods, many moons, all have moons
Gas giants
hydrogen, helium
Ice giants
water, ammonia, methane
What are the five confirmed dwarf planets in our system?
Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Makemake, Haumea
Facts about Dwarf Planets
less dense than terrestrial planets, more dense than giant planets
Mostly in Kuiper Belt and Beyond (except Ceres)
Have not “cleared the neighborhood”
Planet
Celestial body in orbit around the Sun, has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes hydrostatic equilibrium (near-spherical shape), and is large enough to have cleared the neighborhood around its orbit of planetesimals
Dwarf Planet
like a planet except it has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit of planetesimals
Small solar system bodies
orbits the sun but not spherical
Moon
a natural celestial body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or minor planet
Rotation axis tilt
23.5o
Tropic of Cancer
largest latitude for the Sun to be overhead June solstice, Summer at the Northern Hemisphere
Tropic of Capricorn
lowest latitude for the Sun to be overhead during the year, December solstice
Lines of Longitude
lines that connect the north and south poles
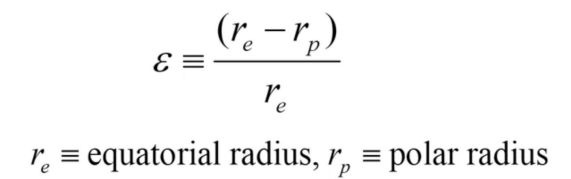
Oblateness
a measure of how squashed a planet is
Right ascension
measured in hours-minutes-seconds (24hrs/360o
Declination
Measured in degrees north or south of the celestial equation along hour circle
Sidereal Period
the time it takes a planet to complete one orbit of the sun, as seen from the stars
Sidereal day
the time it takes the Earth to spin once on its axis
Tropical Year
365.242 days
the time it takes from one winter solstice to the next
important to know for same weather patterns
Sidereal year
365.256
time it takes for Earth to go around the Sun once
important for astronomers to know when you are the same direction in the sky
Solar day
the time between consecutive times that the Sun is as high in the sky as it gets, is 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day
Direct orbit
same direction as the Earth’s orbit (counterclockwise)
Direct rotation
same direction as the orbit
Retrograde rotation
direction of orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum vectors are more than 90 degrees apart
Ecliptic plane
the plane of the Earth’s orbit (and all the other planets)
Superior Planet
the distance from the Sun is larger than the Earth-Sun distance
Perihelion
the point in a celestial body’s orbit where it is closest to the Sun
Quadrature
there is a 90 degree angle between the sun and the planet, as seen from the Earth
Elongation
the anger from the Sun to the planet (as seen from the Earth)
Comets
dirty snowballs of ice and dust
highly eccentric objects that come close to the Sun
short-period comets: P < 200 yrs
long-period comets: P up to > 10^6 yrs
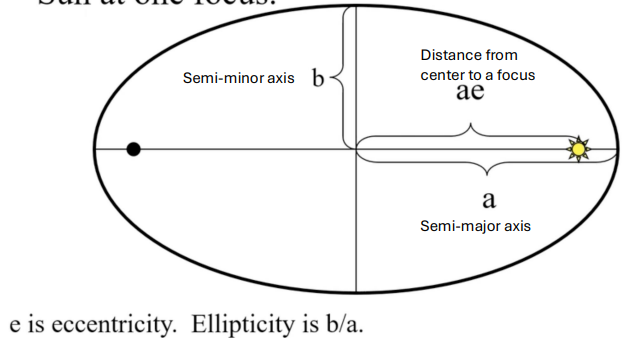
Kepler’s First Law
the orbit of each planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus
semi-minor axis depends on semi-major axis and eccentricity
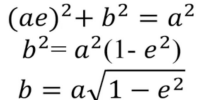
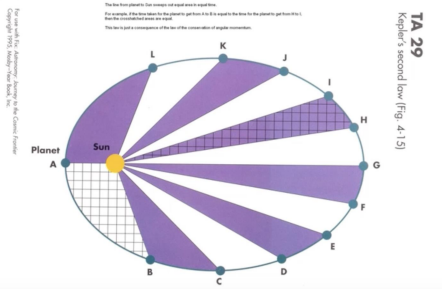
Kepler’s Second Law
The radial vector to a planet (from the Sun) sweeps out equal areas in equal areas of time
Kepler’s Third Law
The squares of orbital periods of the planets are proportional to the cubes of the semi-major axes of their orbits
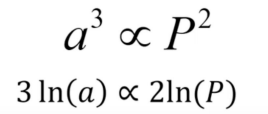
Virial Theorem
For a stable, self-gravitating, spherical distribution of equal mass objects, the time-averaged total kinetic energy of the objects is the negative of one half the time averaged total gravitational potential energy
2K + U = 0
Center of Mass
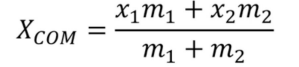
Blackbody
an optically dense object that is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation
do not have spectral lines in their spectra
Kirchhoff’s Rules
a hot an opaque solid, liquid, or highly compressed gas emits a continuum spectrum
a hot, transparent gas produces a spectrum of emission lines. the number and position of these lines in the spectrum depend on which elements are present in the gas
if light with a continuum spectrum passes through a transparent gas at a lower temperature the cooler gas causes the appearance of the absorption lines. Their position in the spectrum, their strength, and their number depends on the elements in the cooler gas
Planck’s Law
the energy radiated per second per unit wavelength per unit solid angle, in a given direction, from a surface which has a unit area perpendicular to the direction emission is called the monochromatic specific intensity
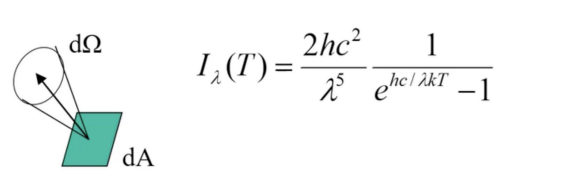
Wien distribution
approximation of Planck’s Law for low temperature, short wavelength
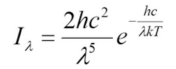
Rayleigh-Jeans
approximation of Planck’s Law for high temperature, long wavelength
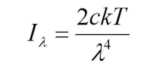
Wein’s Law
estimate of the peak of distribution
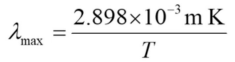
Blackbody Flux

Lunar Eclipse
when the Moon moves into the Earth’s shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened
Solar Eclipse
when the moon moves to be in between the Sun and Earth, aligned with the sun-earth plane
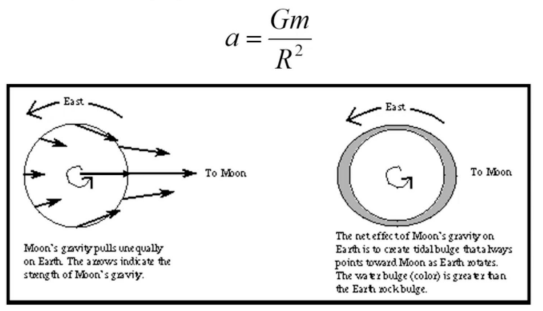
What causes tides?
The side of the Earth towards the Moon is closer than the side away from the Moon, and thus has a larger acceleration due to the Moon’s gravity
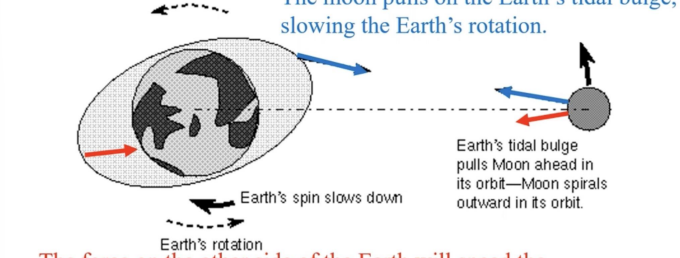
Why is the Earth slowing down?
the moon pulls on the Earth’s tidal bulge, slowing the Earth’s rotation. The angular momentum from the Earth’s spin is transferred to angular momentum of the Moon’s orbit (the moon is getting further away)
Tidal Locking
since there is friction on the earth, as the length of a day is shorter than the length of month, the tide is swept ahead of the orbit of the Moon. (THERE IS MORE I DIDNT FINISH THIS)
Roche Limit
a satellite cannot approach its primary planet too closely or stray too far without being ripped apart by tidal forces

Hill Radius
if a moon is orbiting a planet, and that planet is orbiting a star, there is a maximum distance the moon can be from the planet before the moon is ripped away from the planet and starts orbiting the star instead
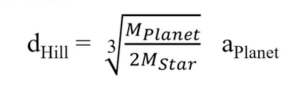
Stellar streams
tidal streams of stars that get pulled out of a gravitationally bound system as it approaches the Roche limit
Rayleigh Criterion
Two peaks can just barely be distinguished from each other when one of the peaks lies in the minimum of the second peak
Flux
the energy per time per unit area passing through a real or imaginary surface
Luminosity
the energy per time produced by an object. (This has the same units as power. Power is a more general term meaning energy per time. Luminosity is usually used for a source that is the source of electromagnetic radiation.)