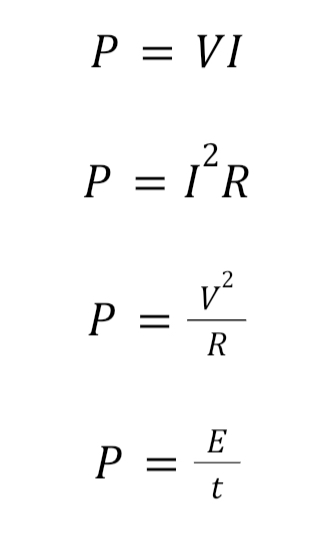Electricity (unfinished)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Conductors
Materials in which electric charges move relatively freely
Insulators
Materials in which electric charges do not move freely
Give examples of good conductors
Metals like Copper, Aluminum, Silver
Why are metals good conductors?
Because they have a large number of free moving electrons through them
What are some examples of insulators
PVC, polythene, nylon, glass, plastics, rubber, wax
Why can these materials not conduct electricity
They have no mobile charge carriers
Electric current
The flow of electric charge in a particular direction
What must occur in order to maintain an electric current?
The charge must have a continuous path to travel around. E.g. a closed circuit
Why do we say that current flows form positive to negative
Because Ben Franklin thought positive charges were the carriers of charge so we stuck with it, although it is actually the negative charges which are the carriers.
Electric current
The flow of electrons
Electron flow
Negative terminal to positive terminal
Conventional current
Flows from positive terminal to the negative one
Current
Charge on the move
What can be used to measure current
Ammeter
Equation for measuring current
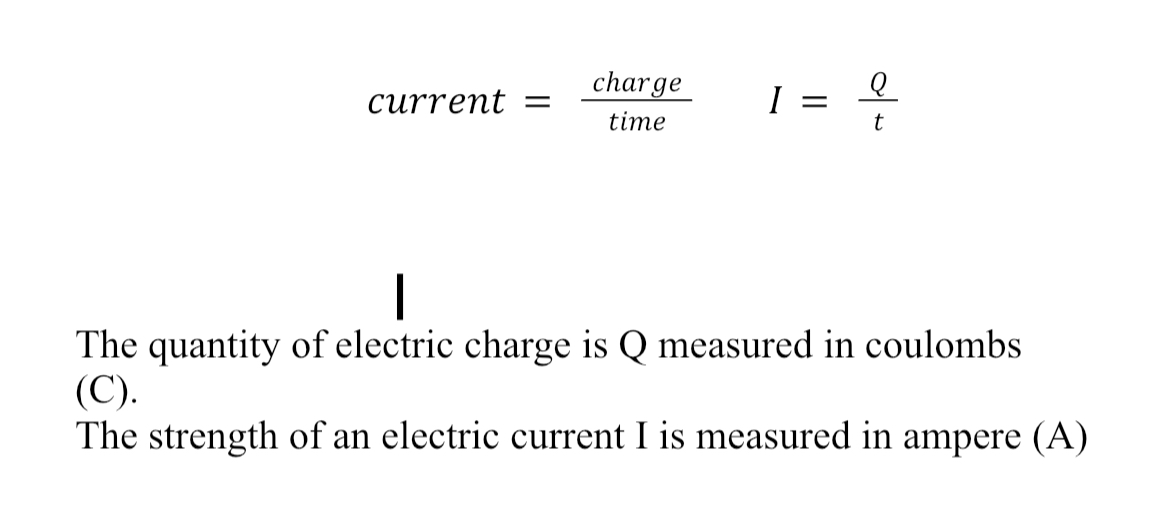
Unit for charge
C - Coulombs
Equation for charge
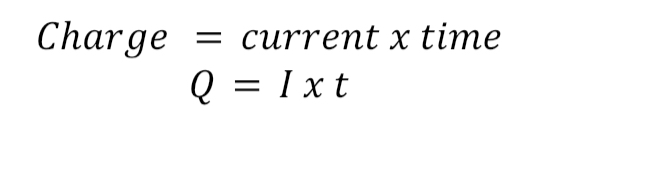
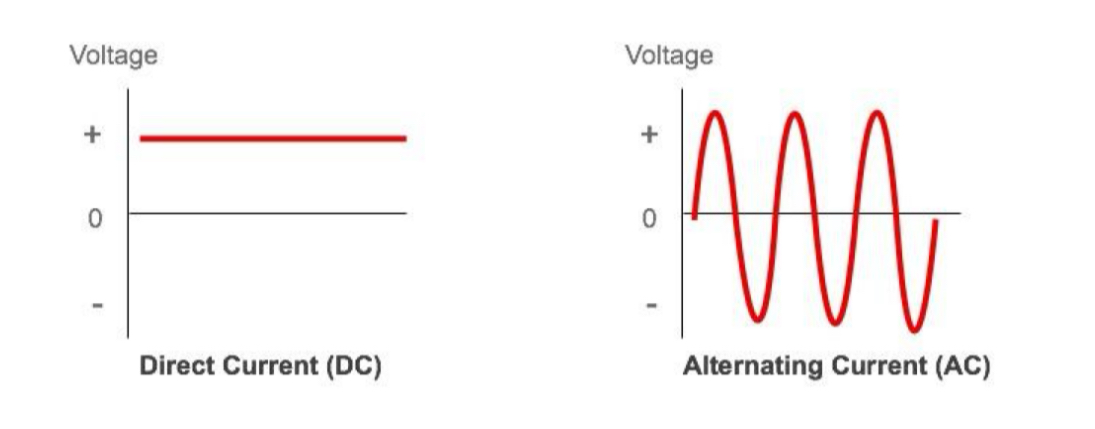
Alternating current
AC - electric current in which it’s direction and its magnitude change continuously with time and as a result, the voltage level also reverses along with the current
Direct current
Flows in one direction
What is A.C. Used for
Delivering power to houses, office buildings etc.
What is D.C. used for
Batteries, cells
Draw graphs of D.C and A.C.
Why is AC used over DC
AC voltage can be easily stepped up (increased) or stepped down (decreased) using transformers. This is crucial for long-distance transmission because
High voltage transmission reduces energy loss due to resistance in the wires.
Stepping up the voltage to very high levels allows for the transmission of large amounts of power with less current, minimizing energy loss.
Stepping down the voltage to lower levels before it reaches homes and businesses ensures safety.
Potential difference
Aka voltage
the work done, per coulomb, when electrical energy is converted to another form of energy when current flows through a circuit
Equation for voltage / potential difference
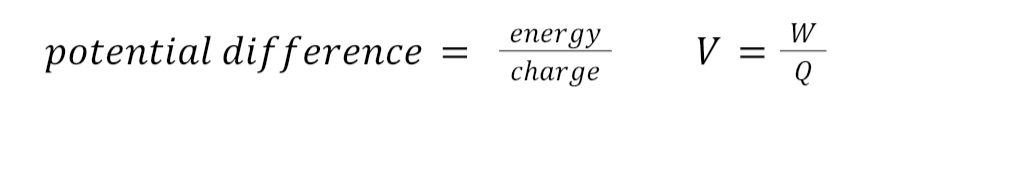
What is used to measure e.m.f or potential difference
Voltmeter
What is emf
Electromotive force
Unit: Volts (V)
the driving force behind the cell responsible for propelling the electrons or ions from a state of inertia to kinetic energy in order to move around the circuit.
Resistance
Symbol: R
Unit: Ohms
A measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit
Power
The rate of conversion when energy is changed from one form to another
Unit: watts
4 equations for power